Introduction
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) serves a
fundamental role in regulating blood pressure and maintaining fluid
homeostasis, and also processes nociceptive information (1,2). There
is substantial evidence that angiotensin II (Ang II), the active
principle of RAS, interacts with the autonomic system and
participates in the central and peripheral regulation of sensory
information (1,2). Ang II mediates its function primarily
through angiotensin II receptor types 1 (AT1) and 2 (AT2) (3). While the majority of physiological
effects caused by Ang II are mediated through AT1, the role of AT2
receptors remains controversial (4).
It has been indicated in an animal study and a phase II clinical
trial that a selective AT2 antagonist may successfully alleviate
neuropathic pain, suggesting that targeting AT2 may be developed as
a novel method of treating chronic inflammatory pain conditions and
peripheral neuropathy (5,6).
Propofol (2,6-diisopropylphenol) is a widely used
sedative-hypnotic agent that induces and maintains sedation and
anesthesia in critically ill patients (7). Advantages of propofol over the
application of similar agents include rapid recovery, a lower
incidence of side effects and an improved quality of anesthesia
(8). A previous study demonstrated
that topical propofol had antihyperalgesic and antinociceptive
effects on dorsal horn neurons, indicating that propofol exerts
peripheral antinociceptive action (9). A potential link has also been suggested
between propofol and the RAS in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons,
which are responsible for conducting information from the periphery
to the central nervous system (CNS) (8). Thus, understanding the connection
between propofol and the RAS will provide insights into potential
new mechanisms of regulating RAS signaling and nociception in the
peripheral nervous system. Previous studies have demonstrated that
AT1 and AT2 are expressed in DRGs (3,4);
therefore, in the present study the effect of propofol on the
expression of AT2 and AT1 in cultured DRG neurons was assessed.
Materials and methods
Reagents
Propofol, Ang II, transcription inhibitor
actinomycin D, the selective AT2 antagonist PD123319 and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002 were all
purchased from Sigma-Aldrich; Merck Millipore (Darmstadt, Germany).
Carrier free 125I-Sodium iodide (100 µl/ml) was
purchased from GE Healthcare Biosciences (Pittsburgh, PA, USA). Rat
AT2 gene promoter-luciferase reporter was generated as
described previously (10). The
dual-luciferase reporter assay system was purchased from Promega
Corporation (Madison, WI, USA). SuperScript™ II reverse
transcriptase, TRIzol® reagent and
Lipofectamine® 2000 transfection reagent were all
purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. (Waltham, MA, USA).
The SYBR®-Green Real-Time PCR Master Mix was purchased
from Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. The PI3K
Activity ELISA kit (K-1000s) was purchased from Echelon
Biosciences, Inc. (Salt Lake City, UT, USA). Rabbit anti-human AT1
polyclonal antibody (sc-579), rabbit anti-human AT2 polyclonal
antibody (sc-1173) and rabbit anti-human GAPDH polyclonal antibody
(sc-25778) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas,
TX, USA).
Cell culture and treatment
Primary neuron medium (CC-3256) and rat DRG neurons
(R-DRG-505) were purchased from Lonza Group (Basel, Switzerland).
The cells were treated with different concentrations of propofol
(0.5, 1, 5 or 10 µM) for different lengths of time (1, 2, 4 or 6
h). For LY29004 treatment, rat DRG neurons were pre-treated with
LY294002 for 30 min and incubated at 37°C with LY294002 and 10 µM
propofol for 4 h. For actinomycin D treatment, cells were
pre-treated with 1 mg/ml actinomycin D for 30 min and then cultured
for 1, 2 or 4 h in primary neuron medium (Lonza Group) containing 1
mg/ml actinomycin D with or without 10 µM propofol.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
RNAwas extracted from rat DRG neurons using TRIzol
reagent followed by purification with TURBO DNA-free system
(Ambion; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) for two independent times.
A SuperScript II reverse transcriptase kit (Applied Biosystems;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) was used to synthesize the cDNA.
RT-qPCR was performed on an ABI-PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection
System (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) with
the SYBR-Green Real-Time PCR Master Mix, following the
manufacturer's protocol. PCR amplification conditions were: 20 sec
at 95°C, followed by 40 cycles of 5 sec at 95°C and 30 sec at 60°C.
The results were normalized against that of GAPDH in the
same sample. The primers used were as follows: AT2, forward,
5′-CTTCAGTTTTGCTGCCACCA-3′ and reverse,
5′-TGTGTGAGCAATTAAAGGCGG-3′; GAPDH, forward,
5′-TGCAGTGGCAAAGTGGAGATT-3′ and reverse,
5′-TTGAATTTGCCGTGAGTGGA-3′. Relative quantification of the AT2 mRNA
level was determined using the 2−ΔΔCq method (11) and normalized against that of GAPDH in
the same sample.
Western blot analysis
Rat DRG neurons were lysed with a hypotonic buffer
containing 2% Nonidet-P and a protease inhibitor cocktail
(Sigma-Aldrich; Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) by sonication
three times, for 3 sec on ice. The supernatant obtained following
centrifugation at 2,000 × g at 4°C for 15 min was used for protein
concentration determination by the Pierce Coomassie Protein Assay
kit (23200; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the
manufacturer's protocol. Equal quantities of protein (2 µg) from
each sample were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and blotted onto a
polyvinylidene difluoride microporous membrane (EMD Millipore,
Billerica, MA, USA). Membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk
powder in Tris-buffered saline-Tween 20 (0.1%; TBST) at room
temperature for 2 h and incubated at room temperature for 1 h with
a 1:1,000 dilution of rabbit anti-human AT1 polyclonal antibody
(sc-579), rabbit anti-human AT2 polyclonal antibody (sc-1173), or
rabbit anti-human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)
polyclonal antibody (sc-25778). This was washed with TBST and
incubated at room temperature for 1 h with bovine anti-rabbit
(sc-2370) secondary antibody (1:5,000; Santa Cruz Biotechnology,
Inc.). Peroxidase was revealed using an Amersham ECL Western
Blotting Detection kit (GE Healthcare Life Shanghai, China)
according to the manufacturer's protocol. A total of three
independent experiments were performed.
AT2 receptor-binding assay
DRG neurons were lysed with CHAPS buffer containing
150 mmol/l sodium chloride, 10 mmol/l sodium pyrophosphate, 1%
Triton X-100, 0.1% CHAPS, 40 mmol/l Tris pH 7.5, 2 mmol/l EDTA, 10%
glycerol, 1 mmol/l sodium orthovanadate, 0.5 mmol/l
4-benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride, 10 mmol/l sodium
fluoride, 0.5 µg/ml aprotinin and 0.5 µg/ml leupeptin. The cell
lysates were incubated with 0.1 nmol/l
[125I]-Sar1-Ile8-Ang II in 50
mmol/l Tris (pH 7.5) buffer containing 200 mmol/l sodium chloride,
1 mmol/l EDTA, 10 mmol/l magnesium chloride, 0.1% bovine serum
albumin and 0.01% trypsin inhibitor at room temperature for 60 min
in the presence of guanosine 5′-O-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. Bound
radio-ligand was separated from free ligand and the radioactivity
was counted using a 1205 betaplate liquid scintillation counter
(Wallac; PerkinElmer, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) according to the
manufacturer's protocol. Specific AT2-receptor binding was
determined by the addition of 10 µM PD123319. The disintegrations
per minute data was normalized against cell number (per 20,000
cells) and presented as a percentage of untreated control cells
(designated as 100%).
Luciferase reporter assay
Rat AT2 gene promoter-luciferase reporter was
generated by inserting a PCR-amplified 1.3-kb rat AT2 gene
promoter fragment into the SacI and NcoI sites of a
promoterless basic luciferase vector pGL3-basic (Promega
Corporation). Rat DRG neurons were transfected with the rat
AT2 promoter-luciferase reporter plasmids followed by
treatment with 1 or 10 µM propofol with or without 50 µM LY294002,
for 4 h. Co-transfection of the plasmid PRL-CMV (E2261; Promega
Corporation) encoding Renilla reniformis luciferase (at one
fifth molar ratio to test plasmids) was performed, with test
plasmids in each transfection acting as an internal control to
allow data normalization. Luciferase assays were performed 24 h
following propofol treatment with the dual-luciferase reporter
assay system according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Measurement of mRNA stability
Rat DRG neurons were pre-treated with 1 mg/ml
actinomycin D for 30 min and cultured for 1, 2 or 4 h in primary
neuron medium (Lonza Group) containing 1 mg/ml actinomycin D with
or without 10 µM propofol. mRNA expression of AT2 was
determined with RT-qPCR following 1, 2 and 4 h propofol treatment
and expressed as fold changes relative to that of control cells
immediately prior to propofol treatment (designated as 1).
PI3K activity assay
A PI3K Activity ELISA kit was used to assess PI3K
activity, according to the manufacturer's protocol (12,13).
PI3K was isolated by immunoprecipitation using a rabbit anti-human
PI3K polyclonal antibody (1:500; 06–195; Merck Millipore,
Darmstadt, Germany) to the p85 adapter subunit to directly assess
PI3K activity. The ability of the co-precipitated catalytic p110
catalytic subunit to convert a standard phosphatidylinositol
(4,5)-bisphosphate to phosphatidylinositol
(3,4,5)-triphosphate (PIP3) in a kinase reaction
was assessed by measuring the PIP3 generated using the ELISA
kit.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS for
Windows 19.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). All continuous variable values
were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Comparisons of the
mean among multiple groups were performed with one-way analysis of
variance followed by post hoc pairwise comparisons using Tukey
tests. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
Propofol inhibits AT2 expression and
ligand-binding on DRG neurons
To examine the potential effect of propofol on the
expression of AT2 in DRG, DRG neurons were treated with different
concentrations of propofol (0.5, 1, 5 or 10 µM) for different
lengths of time (1, 2, 4 or 6 h). A concentration range of 0.5–5 µM
propofol decreased the AT2 mRNA level in DRG neurons in a
statistically significant concentration-dependent manner
(P<0.05) until reaching a plateau at 5–10 µM. The effect of
propofol on AT2 mRNA expression was eliminated by the PI3K
inhibitor LY294002 (Table I).
Propofol with the concentration 0.5 µM had no significant effect on
the AT2 mRNA level over time. However, propofol with a
concentration of 1–10 µM decreased the AT2 mRNA level in a
statistically significant time-dependent manner (P<0.05) until
reaching a plateau at 4–6 h. This decrease was reversed by the
addition of LY294002 (Table I). By
contrast, treatment for 6 h with 10 µM propofol exerted no
significant effect on the AT1 mRNA level (data not
shown).
 | Table I.Relative angiotensin II type 2
receptor mRNA levels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons following
propofol treatment. |
Table I.
Relative angiotensin II type 2
receptor mRNA levels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons following
propofol treatment.
|
| Time (h) | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
|---|
| Propofol (mM) | 0.5 | 1.03±0.02 | 1.01±0.03 | 0.98±0.06 | 1.02±0.04 |
|
| 1 |
0.90±0.03a |
0.81±0.05a,c |
0.69±0.06a,c,d, |
0.66±0.06a,c,d, |
|
| 5 |
0.75±0.07a,b |
0.57±0.08a–c |
0.41±0.07a–d |
0.34±0.08a–d |
|
| 10 |
0.66±0.05a,b |
0.50±0.07a–c |
0.33±0.06a–d |
0.29±0.06a–d |
|
| 10+LY294002 (50
µM) | 1.02±0.04 | 0.98±0.03 | 1.01±0.02 | 1.03±0.03 |
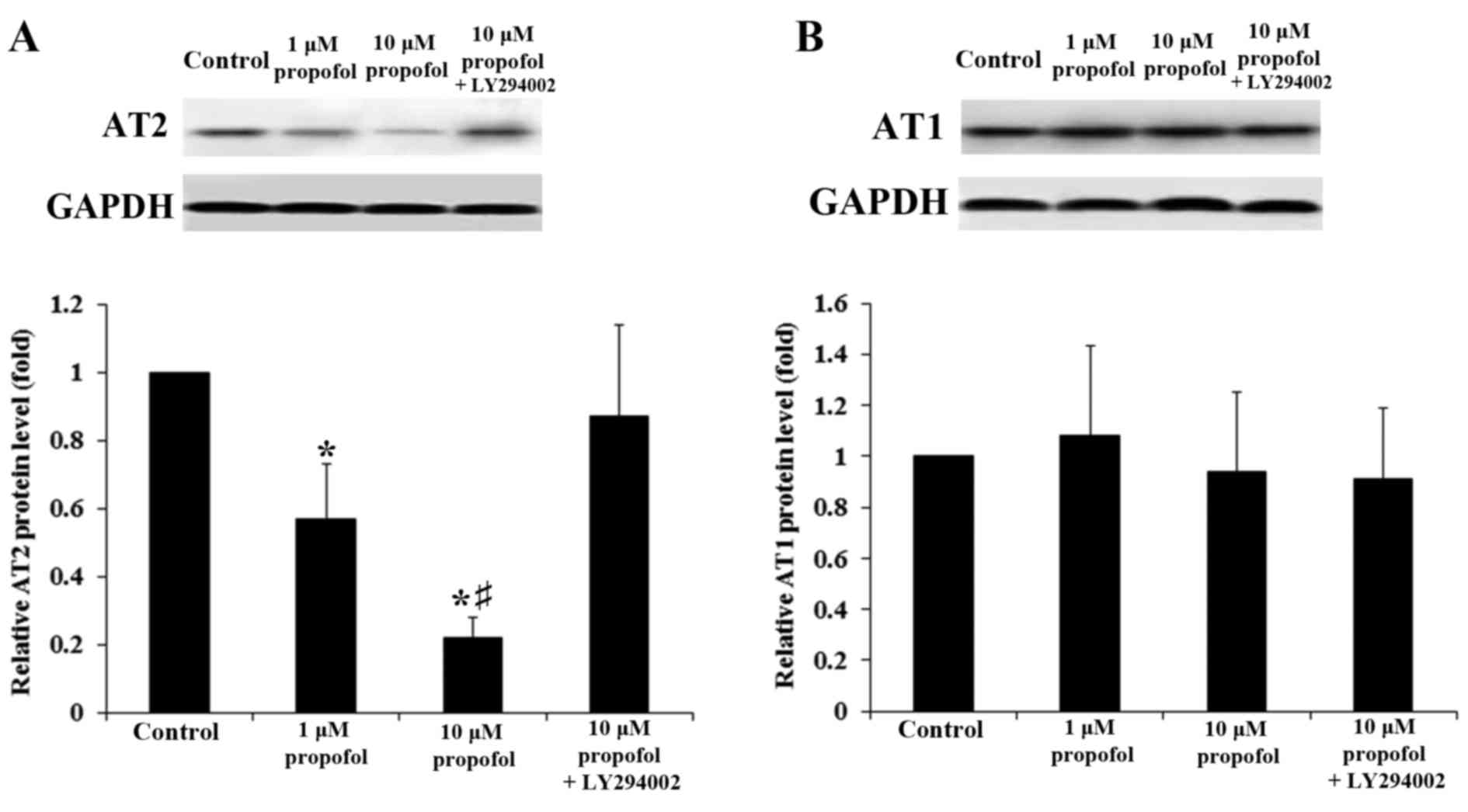
Western blot analysis confirmed that propofol
decreased levels of AT2 protein in DRG neurons within 4 h treatment
in a concentration-dependent manner (P<0.05). This decrease was
reversed with the addition of LY294002 (Fig. 1A); by contrast, propofol exerted no
significant effect on the levels of AT1 proteins in DRG neurons
(P>0.05; Fig. 1B). In line with
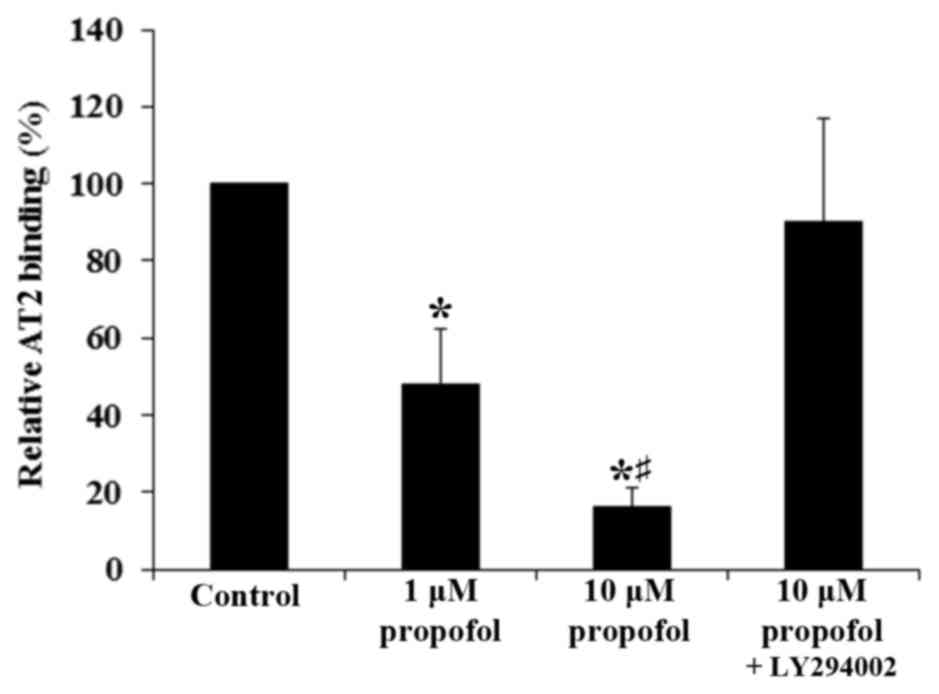
the aforementioned findings, propofol significantly decreased the
AT2-specific binding of Ang II to the cell membrane of DRG neurons
in a concentration-dependent manner (P<0.05). This was reversed
with the addition of LY294002 (Fig.
2). These results suggest that propofol inhibited the
expression of AT2 but not AT1 in DRG neurons at the mRNA and
protein levels by a PI3K-depedent mechanism, leading to a
significant decrease in the density of Ang II-binding AT2 on the
cell membrane (P<0.05).
Propofol decreases AT2 mRNA stability
in DRG neurons by a PI3K-depedent mechanism
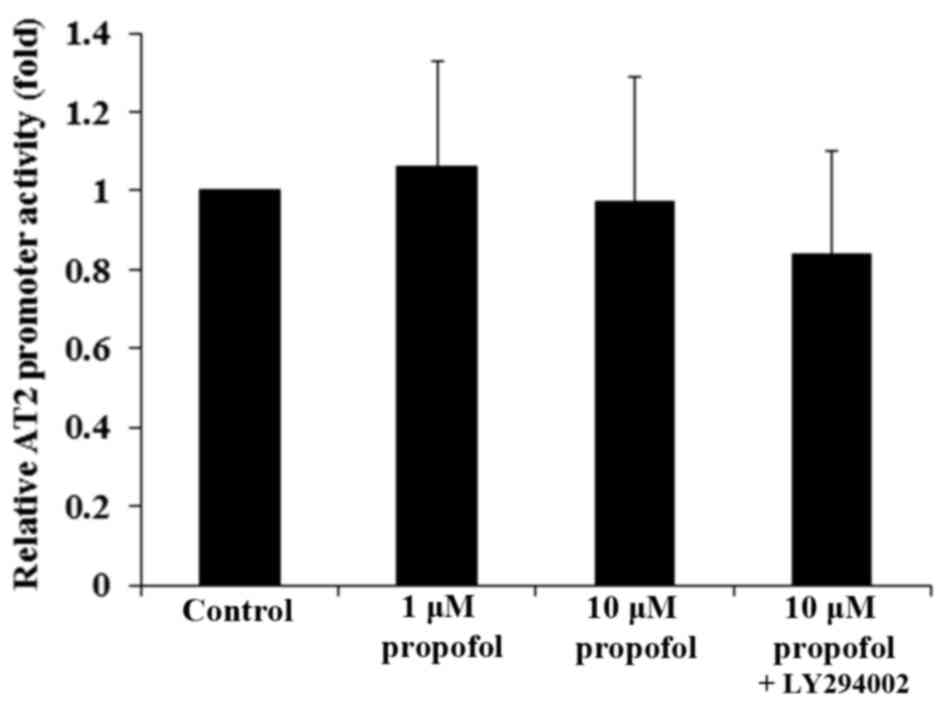
To examine whether propofol decreased AT2
mRNA expression in DRG neurons by transcriptionally inhibiting the
AT2 gene promoter, DRG neurons were transfected with an
AT2 gene promoter/luciferase reporter. Luciferase reporter
assays demonstrated that propofol had no significant effect on
AT2 gene promoter activity (Fig.
3; P>0.05), suggesting that propofol may not decrease the
AT2 mRNA level in DRG neurons by inhibiting the gene
promoter or transcription. The effect of propofol on AT2
mRNA stability was subsequently assessed using DRG neurons
pre-treated with the transcription inhibitor actinomycin D for 30
min, and then cultured for 1, 2 or 4 h in medium containing
actinomycin D with or without propofol. AT2 mRNA expression
was determined using RT-qPCR following 1, 2 and 4 h propofol
treatment and expressed as fold changes relative to mRNA expression
in control cells prior to propofol treatment.
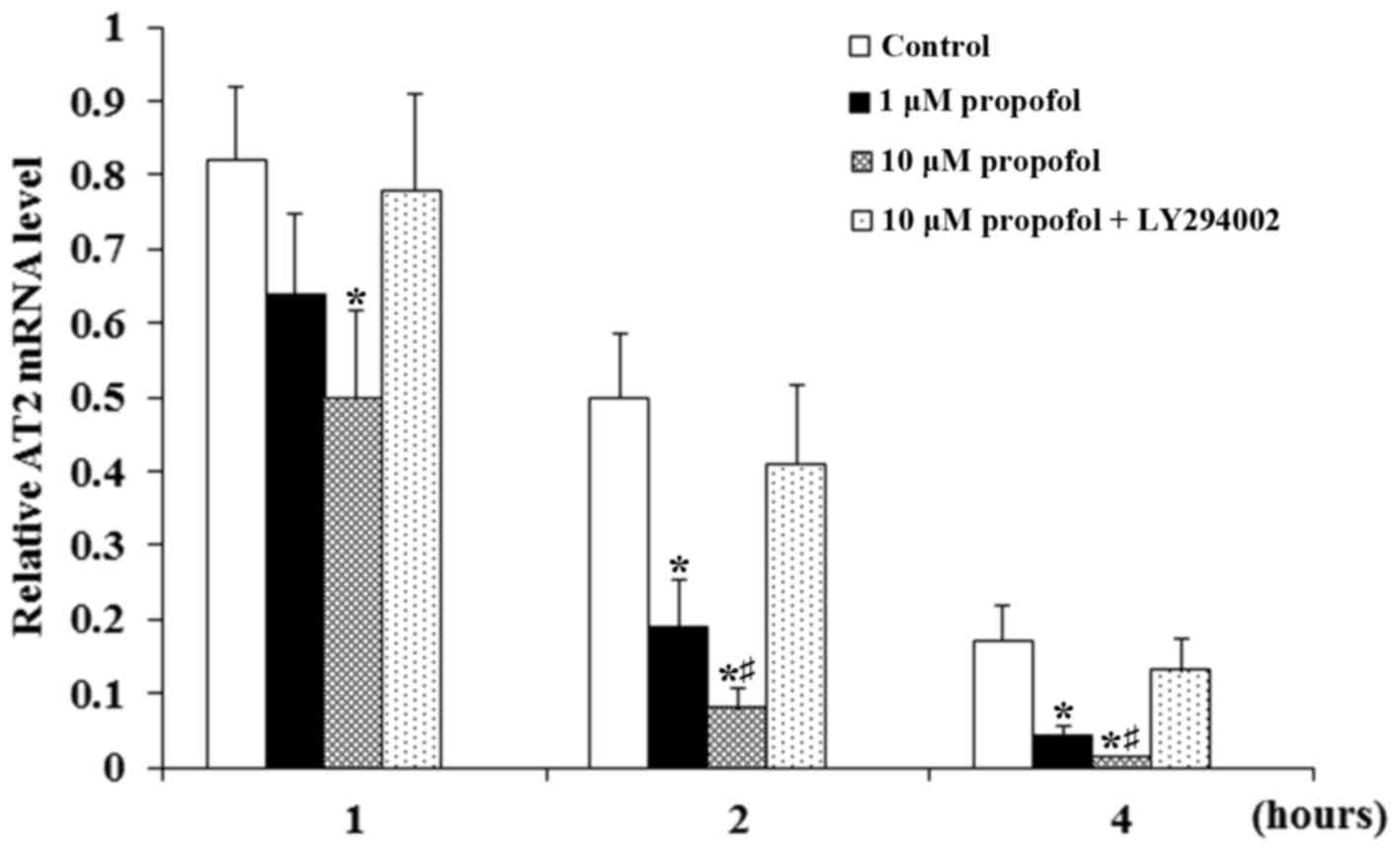
Propofol significantly enhanced the decrease in AT2
mRNA expression that occurred over time compared with the control
(P<0.05; Fig. 4). The decrease
was greatest in neurons treated with 10 µM propofol. Furthermore,
the effect became much more pronounced over time during actinomycin
treatment but was eliminated following the addition of LY294002 at
each time point (Fig. 4). The
results suggest that propofol decreased the stability of the
AT2 mRNA in DRG neurons through a PI3K-depedent mechanism.
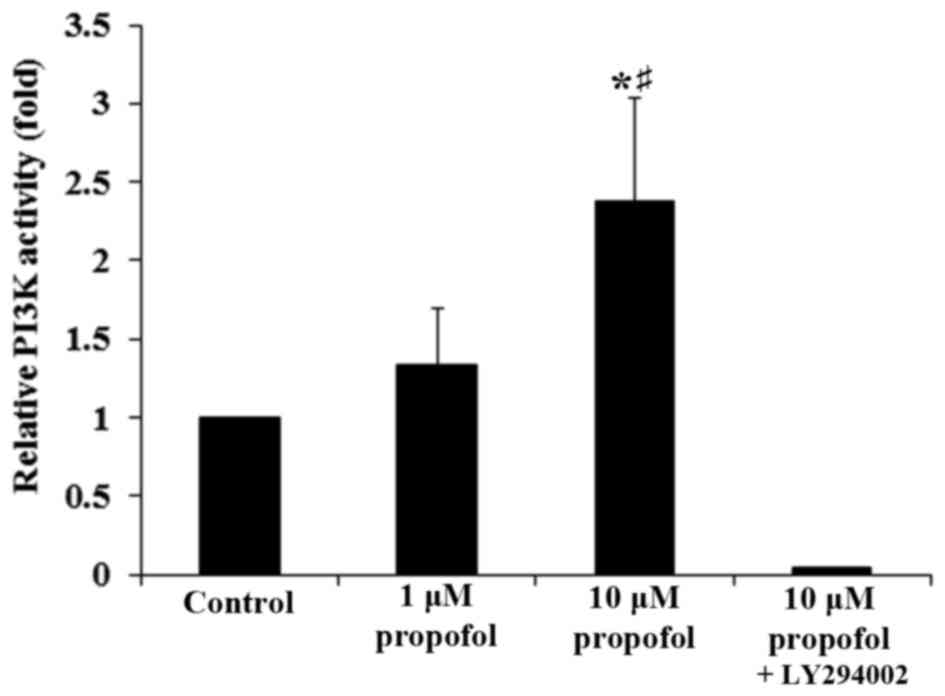
Furthermore, propofol significantly increased PI3K activity in DRG
neurons in a concentration-dependent manner, which was completely
reversed following the addition of LY294002 (P<0.05; Fig. 5). This demonstrates that a
PI3K-depedent mechanism may be involved in the effect of propofol
on the expression of AT2 in DRG neurons.
Discussion
The RAS is involved in nociception and affects the
cardiovascular system (1,2). The active principle of RAS is AT2,
which functions to mediate the effect of Ang II; due to this, AT2
has become a novel therapeutic target to treat peripheral
neuropathic pain (5,6). As a popular induction agent for general
anesthesia, propofol exerts peripheral antinociceptive effects
(9). To the best of our knowledge,
the present study provides the first evidence indicating that
propofol inhibits the expression of AT2 in DRG neurons, which
conduct information from the periphery to CNS and are therefore
linked to peripheral neuropathic pain (8).
It has been reported that Ang II interacts with the
autonomic system and participates in the central and peripheral
regulation of sensory information (14). Ang II exerts its physiological action
by acting as an agonist for AT1 and AT2 (15). Ang II/AT1 signaling has been well
characterized in the cardiovascular system, tumorigenesis, tissue
remodeling, the renal system, cognition, embryonic development,
reproduction and bone homeostasis (16). Additionally, it has been suggested
that Ang II/AT2 signaling serves a key role in the pathobiology of
peripheral neuropathic pain, since selective AT2 antagonists have
been demonstrated to produce dose-dependent analgesia in rat models
of peripheral neuropathic pain, as well as in a phase II clinical
trial (5,6). In the present study, propofol with a
concentration of 0.5–5 µM decreased expression of AT2 mRNA
in a statistically significant dose- and time-dependent manner
within 4 h of treatment, resulting in decreased density of Ang
II-binding AT2 on the cell membrane of DRG neurons. Notably, 10 µM
propofol decreased the expression of AT2 and its Ang II-binding
activity in DRG neurons by ~80% within 4 h, suggesting that
propofol is a strong inhibitor of Ang II/AT2 signaling in DRG
neurons and thus may be useful for the clinical treatment of
peripheral neuropathic pain. A PI3K inhibitor eliminated the effect
of propofol, suggesting that the inhibitory effect of propofol on
the expression of AT2 in DRG neurons occurs in a PI3K-depedent
manner. This was corroborated by the finding that propofol
increased PI3K activity in DRG neurons in a concentration-dependent
manner (Fig. 5). In addition, the
results of the current study suggest that propofol inhibits the
expression of AT2 in DRG neurons by decreasing the stability of
AT2 mRNA. Further studies are required to elucidate the
mechanisms by which propofol decreases the stability of the
AT2 mRNA via PI3K signaling.
The general anesthetic properties of propofol may be
due to its function of enhancing GABA and glycinergic
neurotransmission (17). Analgesic
effects of subhypnotic doses of propofol in humans have been
reported in several studies investigating experimental pain
(18,19). Due to the potentially important role
of Ang II/AT2 signaling in peripheral nociception (5,6), the
finding that propofol inhibits the expression of AT2 in DRG neurons
indicates a novel mechanism for the peripheral antinociceptive
action of propofol. A previous study has suggested a mechanism of
peripheral antinociceptive action of propofol by demonstrating that
propofol upregulates the expression of Mas, a receptor of
Ang-(1–7), in DRG neurons (8). Ang-(1–7)/Mas
signaling is a component of the RAS signaling system and is similar
to Ang II/AT2 signaling (8).
Therefore, future studies should assess how the propofol-regulated
expression of AT2 and Mas in DRG neurons relate to each other and
orchestrate antinociceptive action.
In conclusion, to the best of our knowledge, the
present study provides the first evidence indicating that propofol
inhibits the expression of AT2 in DRG neurons via decreasing
AT2 mRNA stability through a PI3K-dependent mechanism. The
results add novel insights into the mechanisms of the peripheral
antinociceptive action of propofol and suggest a potential novel
means of regulating Ang II/AT2 signaling in the peripheral nervous
system.
References
|
1
|
Pelegrini-da-Silva A, Martins AR and Prado
WA: A new role for the renin-angiotensin system in the rat
periaqueductal gray matter: Angiotensin receptor-mediated
modulation of nociception. Neuroscience. 132:453–463. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sakagawa T, Okuyama S, Kawashima N, Hozumi
S, Nakagawasai O, Tadano T, Kisara K, Ichiki T and Inagami T: Pain
threshold, learning and formation of brain edema in mice lacking
the angiotensin II type 2 receptor. Life Sci. 67:2577–2585. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pavel J, Tang H, Brimijoin S, Moughamian
A, Nishioku T, Benicky J and Saavedra JM: Expression and transport
of Angiotensin II AT1 receptors in spinal cord, dorsal root ganglia
and sciatic nerve of the rat. Brain Res. 1246:111–122. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anand U, Facer P, Yiangou Y, Sinisi M, Fox
M, McCarthy T, Bountra C, Korchev YE and Anand P: Angiotensin II
type 2 receptor (AT2R) localization and antagonist-mediated
inhibition of capsaicin responses and neurite outgrowth in human
and rat sensory neurons. Eur J Pain. 17:1012–1026. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Smith MT, Wyse BD and Edwards SR: Small
molecule angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R) antagonists as novel
analgesics for neuropathic pain: Comparative pharmacokinetics,
radioligand binding, and efficacy in rats. Pain Med. 14:692–705.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rice AS, Dworkin RH, McCarthy TD, Anand P,
Bountra C, McCloud PI, Hill J, Cutter G, Kitson G, Desem N, et al:
EMA401, an orally administered highly selective angiotensin II type
2 receptor antagonist, as a novel treatment for postherpetic
neuralgia: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2
clinical trial. Lancet. 383:1637–1647. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marik PE: Propofol: An immunomodulating
agent. Pharmacotherapy. 25:28S–33S. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cao L, Xun J, Jiang X and Tan R: Propofol
up-regulates Mas receptor expression in dorsal root ganglion
neurons. Pharmazie. 68:677–680. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takechi K, Carstens MI, Klein AH and
Carstens E: The antinociceptive and antihyperalgesic effects of
topical propofol on dorsal horn neurons in the rat. Anesth Analg.
116:932–938. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ichiki T, Kambayashi Y and Inagami T:
Transcription of the rat angiotensin II type 2-receptor gene.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 222:566–571. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cao CM, Zhang Y, Weisleder N, Ferrante C,
Wang X, Lv F, Zhang Y, Song R, Hwang M, Jin L, et al: MG53
constitutes a primary determinant of cardiac ischemic
preconditioning. Circulation. 121:2565–2574. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fos C, Salles A, Lang V, Carrette F,
Audebert S, Pastor S, Ghiotto M, Olive D, Bismuth G and Nunès JA:
ICOS ligation recruits the p50alpha PI3K regulatory subunit to the
immunological synapse. J Immunol. 181:1969–1977. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Y, Wu H, Yan JQ, Song ZB and Guo QL:
Tumor necrosis factor-α inhibits angiotensin II receptor type 1
expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons via β-catenin signaling.
Neuroscience. 248:383–391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Verdonk K, Danser AH and van Esch JH:
Angiotensin II type 2 receptor agonists: Where should they be
applied? Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 21:501–513. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Paul M, Mehr A Poyan and Kreutz R:
Physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol Rev.
86:747–803. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamakura T, Bertaccini E, Trudell JR and
Harris RA: Anesthetics and ion channels: Molecular models and sites
of action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 41:23–51. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bandschapp O, Filitz J, Ihmsen H, Berset
A, Urwyler A, Koppert W and Ruppen W: Analgesic and
antihyperalgesic properties of propofol in a human pain model.
Anesthesiology. 113:421–428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hand R Jr, Riley GP, Nick ML, Shott S and
Faut-Callahan M: The analgesic effects of subhypnotic doses of
propofol in human volunteers with experimentally induced tourniquet
pain. AANA J. 69:466–470. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|