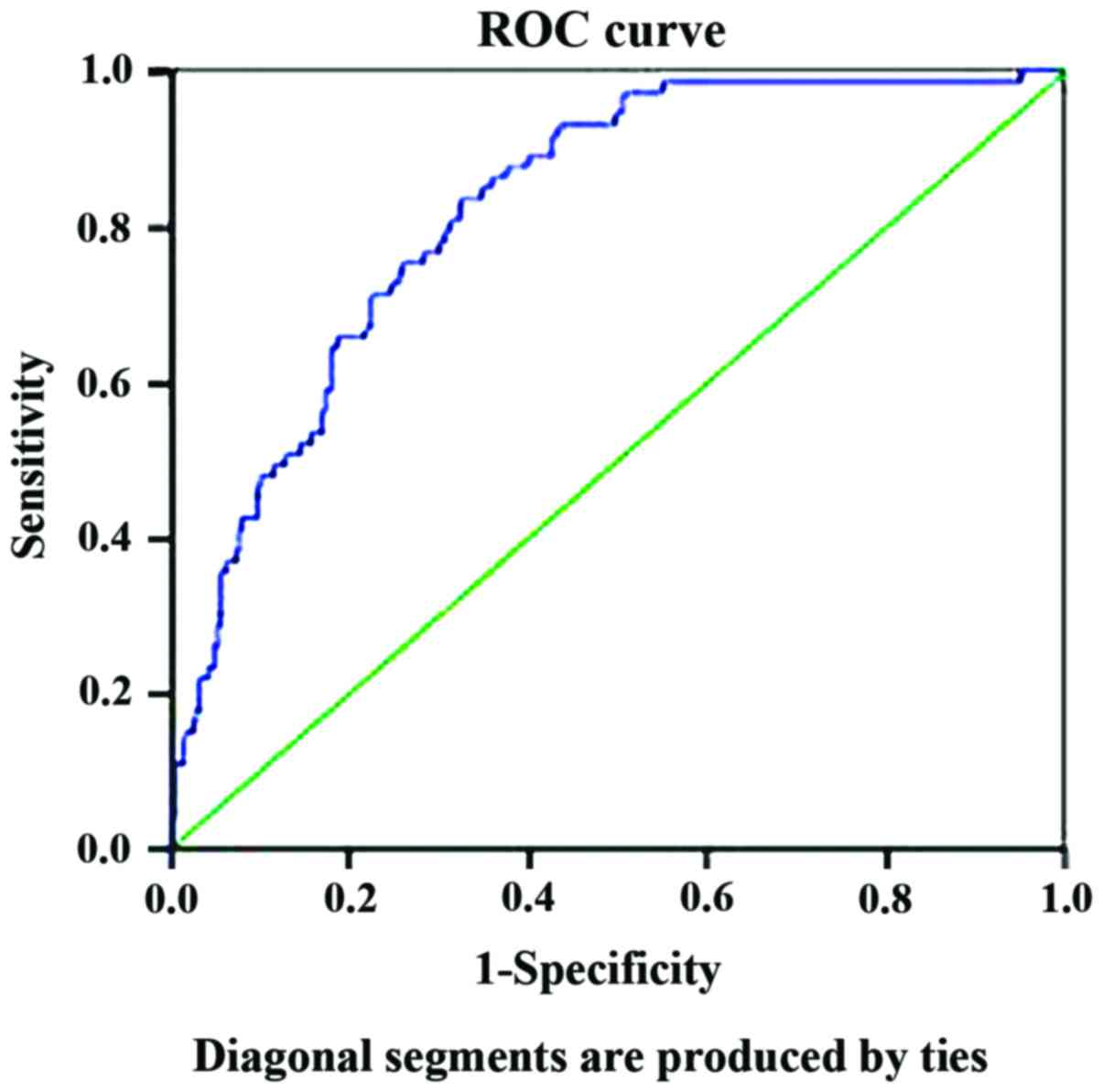
|
1
|
Hamilton CA: Low-density lipoprotein and
oxidised low-density lipoprotein: their role in the development of
atherosclerosis. Pharmacol Ther. 74:55–72. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barter PJ and Rye KA: The rationale for
using apoA-I as a clinical marker of cardiovascular risk. J Intern
Med. 259:447–454. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Faraj M, Messier L, Bastard JP, Tardif A,
Godbout A, Prud'homme D and Rabasa-Lhoret R: Apolipoprotein B: a
predictor of inflammatory status in postmenopausal overweight and
obese women. Diabetologia. 49:1637–1646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Franks S: Polycystic ovary syndrome. N
Engl J Med. 333:853–861. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maitra A, Pingle RR, Menon PS, Naik V,
Gokral JS and Meherji PK: Dyslipidemia with particular regard to
apolipoprotein profile in association with polycystic ovary
syndrome: a study among Indian women. Int J Fertil Womens Med.
46:271–277. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sniderman AD, Blank D, Zakarian R,
Bergeron J and Frohlich J: Triglycerides and small dense LDL: The
twin Achilles heels of the Friedewald formula. Clin Biochem.
36:499–504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Walldius G, Jungner I, Aastveit AH, Holme
I, Furberg CD and Sniderman AD: The apoB/apoA-I ratio is better
than the cholesterol ratios to estimate the balance between plasma
proatherogenic and antiatherogenic lipoproteins and to predict
coronary risk. Clin Chem Lab Med. 42:1355–1363. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McQueen MJ, Hawken S, Wang X, Ounpuu S,
Sniderman A, Probstfield J, Steyn K, Sanderson JE, Hasani M,
Volkova E, et al: INTERHEART study investigators: Lipids,
lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins as risk markers of myocardial
infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): a case-control
study. Lancet. 372:224–233. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yin Q, Chen X, Li L, Zhou R, Huang J and
Yang D: Apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A1 ratio is a good
predictive marker of metabolic syndrome and pre-metabolic syndrome
in Chinese adolescent women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J
Obstet Gynaecol Res. 39:203–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS
Consensus Workshop Group: Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic
criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary
syndrome. Fertil Steril. 81:19–25. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Azziz R, Woods KS, Reyna R, Key TJ,
Knochenhauer ES and Yildiz BO: The prevalence and features of the
polycystic ovary syndrome in an unselected population. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 89:2745–2749. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hatch R, Rosenfield RL, Kim MH and Tredway
D: Hirsutism: implications, etiology, and management. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 140:815–830. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
International Diabetes Federation, . The
IDF consensus worldwide definition of the metabolic syndrome.
http://www.idf.org/webdata/docs/Metabolic_syndrome_definition.pdfAccessed.
July 10–2008.
|
|
14
|
World Health Organization, . Measuring
obesity: classification and description of anthropometric data:
report on a WHO consultation on the epidemiology of obesity.
Warsaw, 21–23 October 1987. World Health Organization; Copenhagen:
1989
|
|
15
|
Chen X, Yang D, Li L, Feng S and Wang L:
Abnormal glucose tolerance in Chinese women with polycystic ovary
syndrome. Hum Reprod. 21:2027–2032. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sung KC and Hwang ST: Association between
insulin resistance and apolipoprotein B in normoglycemic Koreans.
Atherosclerosis. 180:161–169. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sierra-Johnson J, Romero-Corral A, Somers
VK, Lopez-Jimenez F, Walldius G, Hamsten A, Hellénius ML and Fisher
RM: ApoB/apoA-I ratio: αn independent predictor of insulin
resistance in US non-diabetic subjects. Eur Heart J. 28:2637–2643.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taghibiglou C, Carpentier A, Van Iderstine
SC, Chen B, Rudy D, Aiton A, Lewis GF and Adeli K: Mechanisms of
hepatic very low density lipoprotein overproduction in insulin
resistance. Evidence for enhanced lipoprotein assembly, reduced
intracellular ApoB degradation, and increased microsomal
triglyceride transfer protein in a fructose-fed hamster model. J
Biol Chem. 275:8416–8425. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taghibiglou C, Rashid-Kolvear F, Van
Iderstine SC, Le-Tien H, Fantus IG, Lewis GF and Adeli K: Hepatic
very low density lipoprotein-ApoB overproduction is associated with
attenuated hepatic insulin signaling and overexpression of
protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B in a fructose-fed hamster model of
insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 277:793–803. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jing F, Mao Y, Guo J, Zhang Z, Li Y, Ye Z,
Ding Y, Wang J, Jin M and Chen K: The value of Apolipoprotein
B/Apolipoprotein A1 ratio for metabolic syndrome diagnosis in a
Chinese population: a cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis.
13:812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Erdeve S Savas, Simsek E, Dallar Y and
Biyikli Z: Utility of ApoB/ApoA1 ratio for the prediction of
cardiovascular risk in children with metabolic syndrome. Indian J
Pediatr. 77:1261–1265. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wallenfeldt K, Bokemark L, Wikstrand J,
Hulthe J and Fagerberg B: Apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A-I in
relation to the metabolic syndrome and change in carotid artery
intima-media thickness during 3 years in middle-aged men. Stroke.
35:2248–2252. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sierra-Johnson J, Somers VK, Kuniyoshi FH,
Garza CA, Isley WL, Gami AS and Lopez-Jimenez F: Comparison of
apolipoprotein-B/apolipoprotein-AI in subjects with versus without
the metabolic syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 98:1369–1373. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhong L, Li Q, Jiang Y, Cheng D, Liu Z,
Wang B, Luo R, Cheng Q and Qing H: The ApoB/ApoA1 ratio is
associated with metabolic syndrome and its components in a Chinese
population. Inflammation. 33:353–358. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Haffner SM, Kushwaha RS, Foster DM,
Applebaum-Bowden D and Hazzard WR: Studies on the metabolic
mechanism of reduced high density lipoproteins during anabolic
steroid therapy. Metabolism. 32:413–420. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Elbers JM, Giltay EJ, Teerlink T, Scheffer
PG, Asscheman H, Seidell JC and Gooren LJ: Effects of sex steroids
on components of the insulin resistance syndrome in transsexual
subjects. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 58:562–571. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|