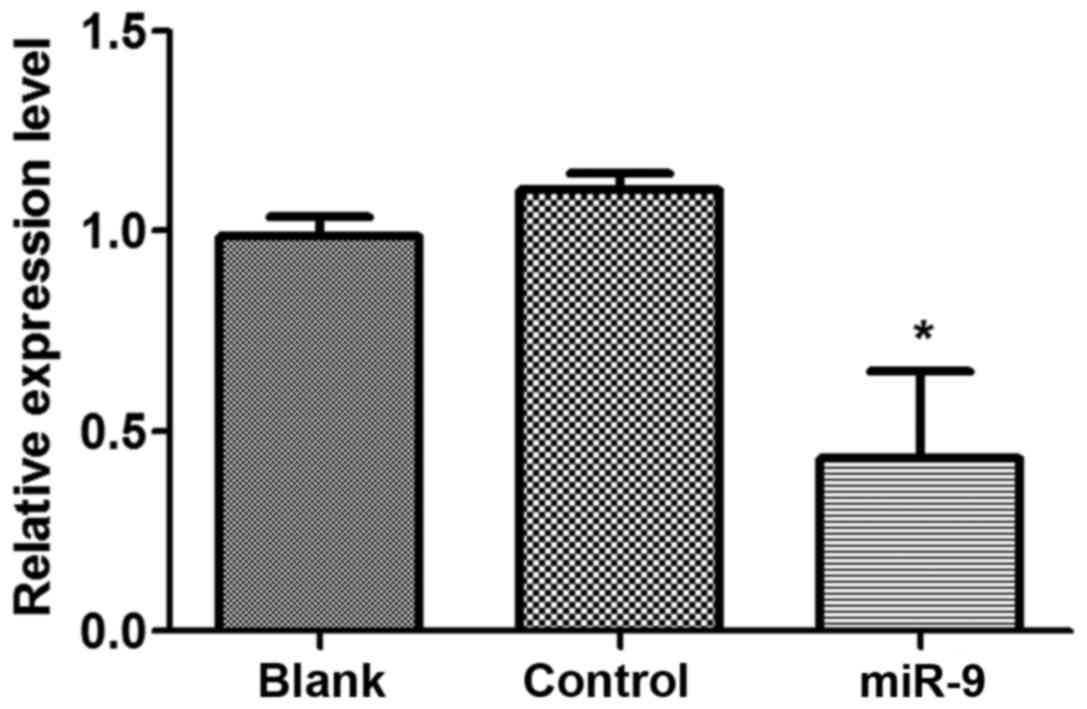
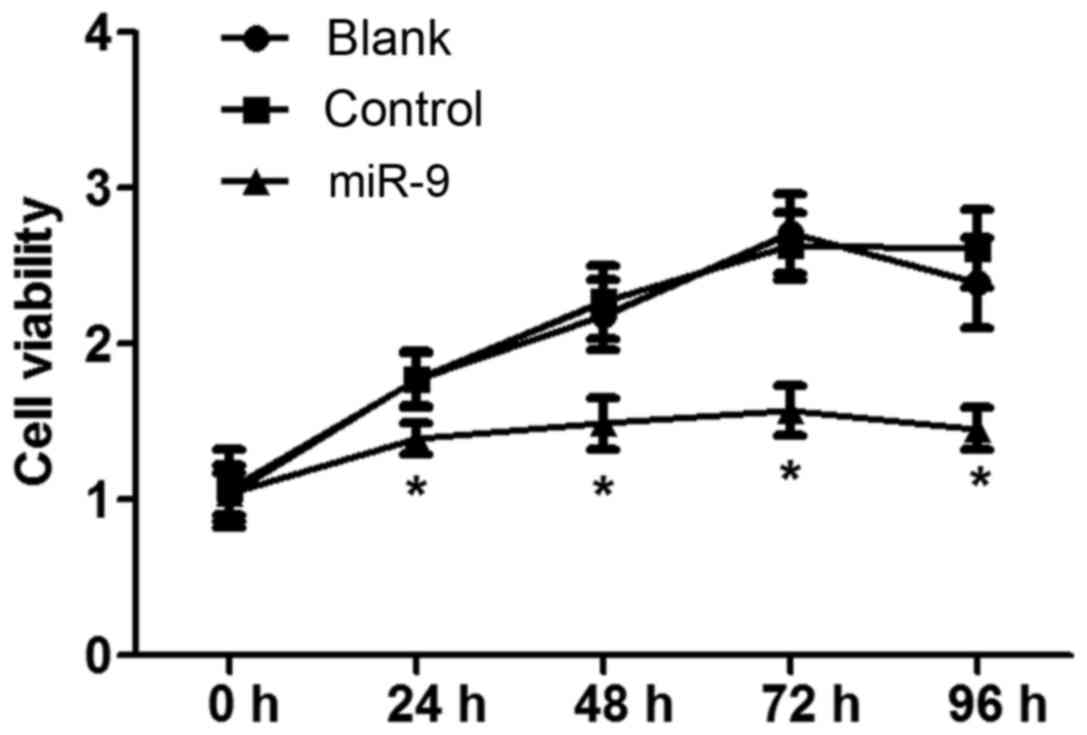
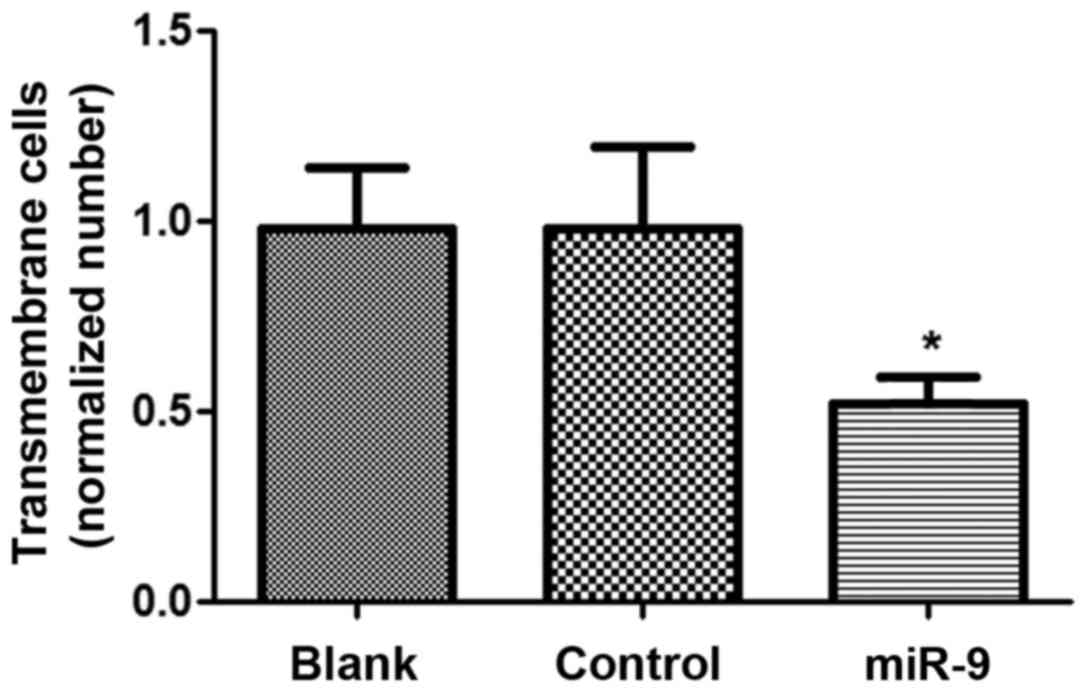
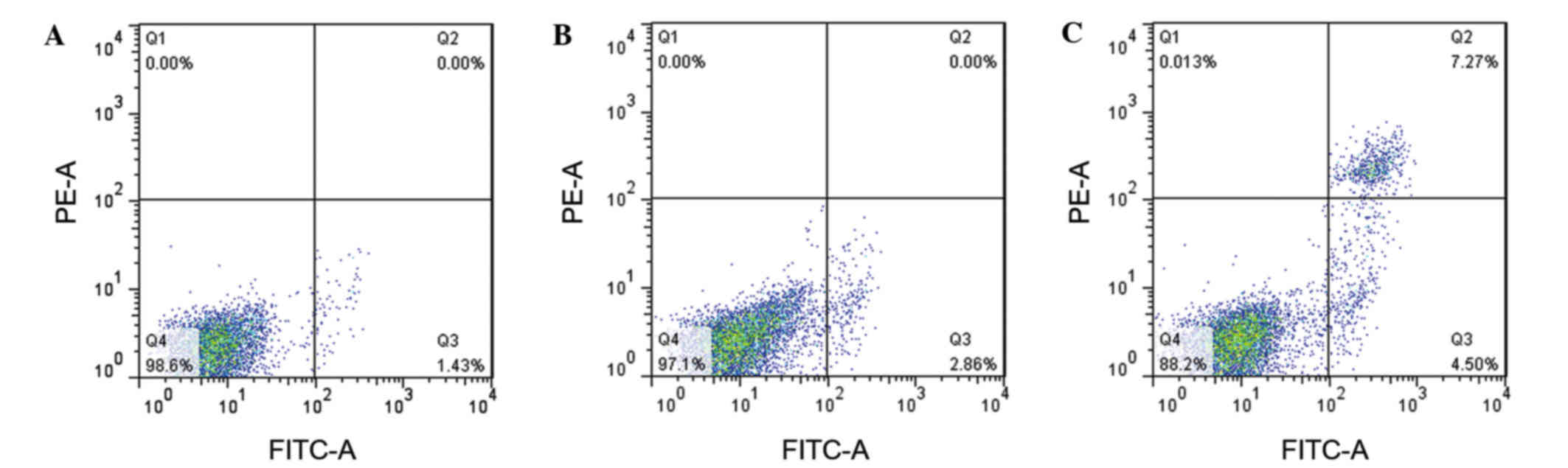
|
1
|
Miow QH, Tan TZ, Ye J, Lau JA, Yokomizo T,
Thiery JP and Mori S: Epithelial-mesenchymal status renders
differential responses to cisplatin in ovarian cancer. Oncogene.
34:1899–1907. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nik NN, Vang R, Shih IeM and Kurman RJ:
Origin and pathogenesis of pelvic (ovarian, tubal and primary
peritoneal) serous carcinoma. Ann Rev Pathol. 9:27–45. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Marcus CS, Maxwell GL, Darcy KM, Hamilton
CA and McGuire WP: Current approaches and challenges in managing
and monitoring treatment response in ovarian cancer. J Cancer.
5:25–30. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tone AA, McConechy MK, Yang W, Ding J, Yip
S, Kong E, Wong KK, Gershenson DM, Mackay H, Shah S, et al:
Intratumoral heterogeneity in a minority of ovarian low-grade
serous carcinomas. BMC Cancer. 14:9822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dillman RO, DePriest C, Ellis R and de
Leon C: 5-year survival for patients with metastatic melanoma who
had no evidence of disease at time of treatment with patient
specific tumor stem cell vaccines. Cancer Res. 74 Suppl 19:1972014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O'Donnell
JD, Wang J, Wenham RM, Coppola D, Kruk PA, Nicosia SV and Cheng JQ:
MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214
induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN.
Cancer Res. 68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vecchione A, Belletti B, Lovat F, Volinia
S, Chiappetta G, Giglio S, Sonego M, Cirombella R, Onesti EC,
Pellegrini P, et al: A microRNA signature defines chemoresistance
in ovarian cancer through modulation of angiogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:9845–9850. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cekaite L, Rantala JK, Bruun J, Guriby M,
Agesen TH, Danielsen SA, Lind GE, Nesbakken A, Kallioniemi O, Lothe
RA and Skotheim RI: MiR-9, −31, and −182 deregulation promote
proliferation and tumor cell survival in colon cancer. Neoplasia.
14:868–879. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Laios A, O'Toole S, Flavin R, Martin C,
Kelly L, Ring M, Finn SP, Barrett C, Loda M, Gleeson N, et al:
Potential role of miR-9 and miR-223 in recurrent ovarian cancer.
Mol Cancer. 7:352008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tang H, Yao L, Tao X, Yu Y, Chen M, Zhang
R and Xu C: miR-9 functions as a tumor suppressor in ovarian serous
carcinoma by targeting TLN1. Int J Mol Med. 32:381–388.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Teicher BA and Fricker SP: CXCL12
(SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2927–2931.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Y, Shi X, Shu Z, Xie T, Huang K, Wei L,
Song H, Zhang W and Xue X: Stromal cell-derived factor-1
(SDF-1)/CXCR4 axis enhances cellular invasion in ovarian carcinoma
cells via integrin β1 and β3 expressions. Oncol Res. 21:217–225.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kinouchi M, Uchida D, Kuribayashi N,
Tamatani T, Nagai H and Miyamoto Y: Isolation of a novel
metastasis-related microRNA, miR-518c-5p, induced by the stromal
cell-derived factor (SDF)-1/CXCR4 system in oral cancer. Cancer
Res. 74 Suppl 19:14462014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hummon AB, Lim SR, Difilippantonio MJ and
Ried T: Isolation and solubilization of proteins after TRIzol
extraction of RNA and DNA from patient material following prolonged
storage. Biotechniques. 42:467–470. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Szotek PP, Pieretti-Vanmarcke R, Masiakos
PT, Dinulescu DM, Connolly D, Foster R, Dombkowski D, Preffer F,
Maclaughlin DT and Donahoe PK: Ovarian cancer side population
defines cells with stem cell-like characteristics and mullerian
inhibiting substance responsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:11154–11159. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shirali S, Aghaei M, Shabani M, Fathi M,
Sohrabi M and Moeinifard M: Adenosine induces cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis via cyclinD1/Cdk4 and Bcl-2/Bax pathways in human ovarian
cancer cell line OVCAR-3. Tumor Biol. 34:1085–1095. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zetter BR: Angiogenesis and tumor
metastasis. Ann Rev Med. 49:407–424. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Steeg PS: Tumor metastasis: Mechanistic
insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 12:895–904. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo LM, Pu Y, Han Z, Liu T, Li YX, Liu M,
Li X and Tang H: MicroRNA-9 inhibits ovarian cancer cell growth
through regulation of NF-kappaB1. FEBS J. 276:5537–5546. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tan HX, Wang Q, Chen LZ, Huang XH, Chen
JS, Fu XH, Cao LQ, Chen XL, Li W and Zhang LJ: MicroRNA-9 reduces
cell invasion and E-cadherin secretion in SK-Hep-1 cell. Med Oncol.
27:654–660. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero
S, Sánchez-Céspedes M, Blanco D, Montuenga LM, Rossi S, Nicoloso
MS, Faller WJ, et al: A microRNA DNA methylation signature for
human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:13556–13561.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Obermajer N, Muthuswamy R, Odunsi K,
Edwards RP and Kalinski P: PGE2-induced CXCL12 production and CXCR4
expression controls the accumulation of human MDSCs in ovarian
cancer environment. Cancer Res. 71:7463–7470. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hall JM and Korach KS: Endocrine
disrupting chemicals promote the growth of ovarian cancer cells via
the ER-CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling axis. Mol Carcinog. 52:715–725. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Popple A, Durrant L, Spendlove I, Rolland
P, Scott IV, Deen S and Ramage JM: The chemokine, CXCL12, is an
independent predictor of poor survival in ovarian cancer. Br J
Cancer. 106:1306–1313. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu J, Luo H, Liu X, Peng Y, Zhang B, Wang
L, Xu X, Peng X, Li G, Tian W, et al: miR-9 targets CXCR4 and
functions as a potential tumor suppressor in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 35:554–563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu T, Liu K, Wu Y, Fan J, Chen J, Li C,
Yang Q and Wang Z: MicroRNA-9 inhibits the proliferation of oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing expression of CXCR4
via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogene. 33:5017–5027.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hatano K, Yamaguchi S, Nimura K, Murakami
K, Nagahara A, Fujita K, Uemura M, Nakai Y, Tsuchiya M, Nakayama M,
et al: Residual prostate cancer cells after docetaxel therapy
increase the tumorigenic potential via constitutive signaling of
CXCR4, ERK1/2 and c-Myc. Mol Cancer Res. 11:1088–1100. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu T, Wu Y, Helman JI, Wen Y, Wang C and
Li L: CXCR4 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma migration and
invasion through inducing expression of MMP-9 and MMP-13 via the
ERK signaling pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 9:161–172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Roomi M, Monterrey J, Kalinovsky T, Rath M
and Niedzwiecki A: In vitro modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in human
cervical and ovarian cancer cell lines by cytokines, inducers and
inhibitors. Oncol Rep. 23:605–614. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu Y, Li H, Xue B, Jiang X, Huang K, Ge J,
Zhang H and Chen B: SDF-1/CXCR7 axis enhances ovarian cancer cell
invasion by MMP-9 expression through p38 MAPK pathway. DNA Cell
Biol. 33:543–549. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|