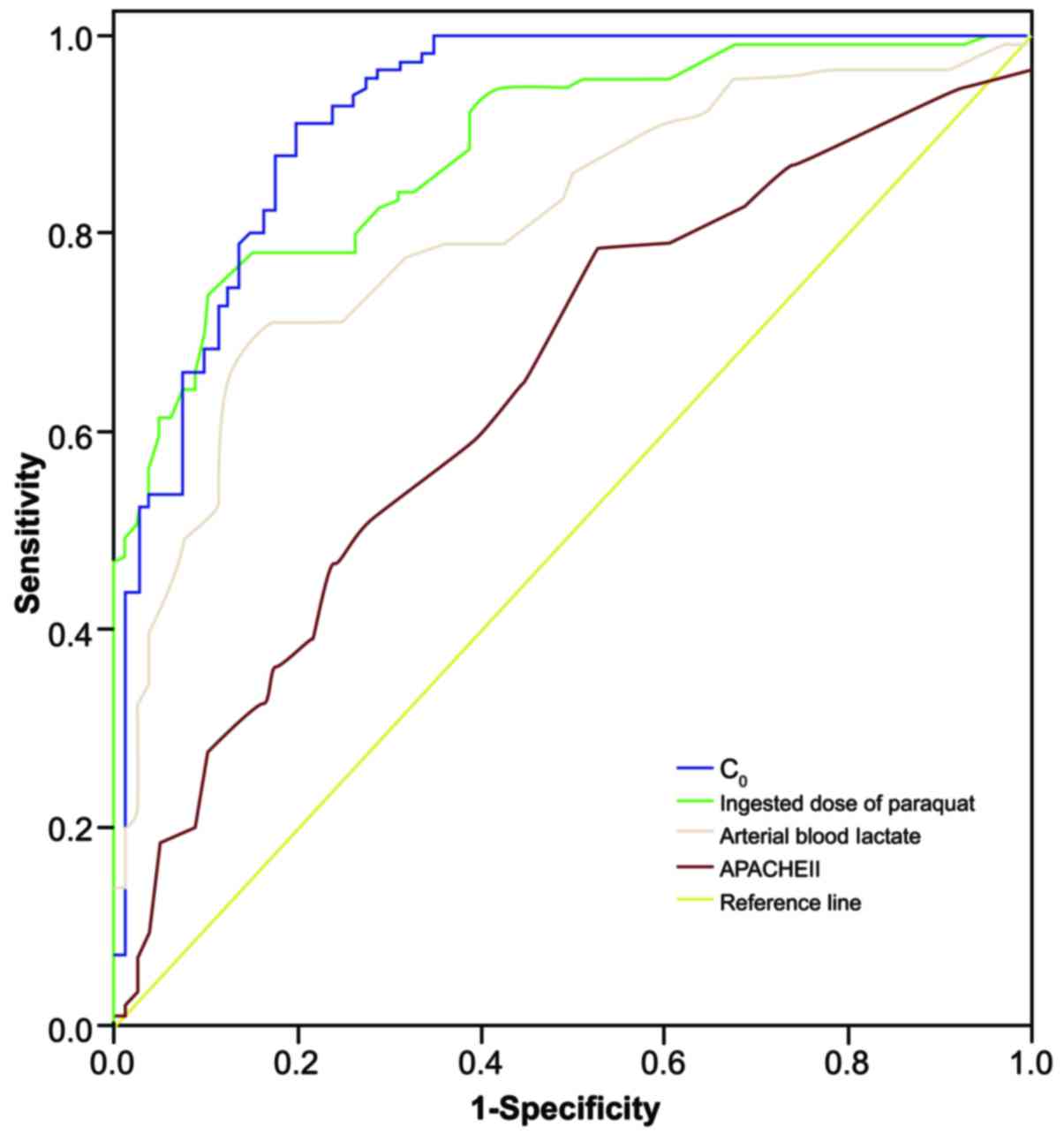
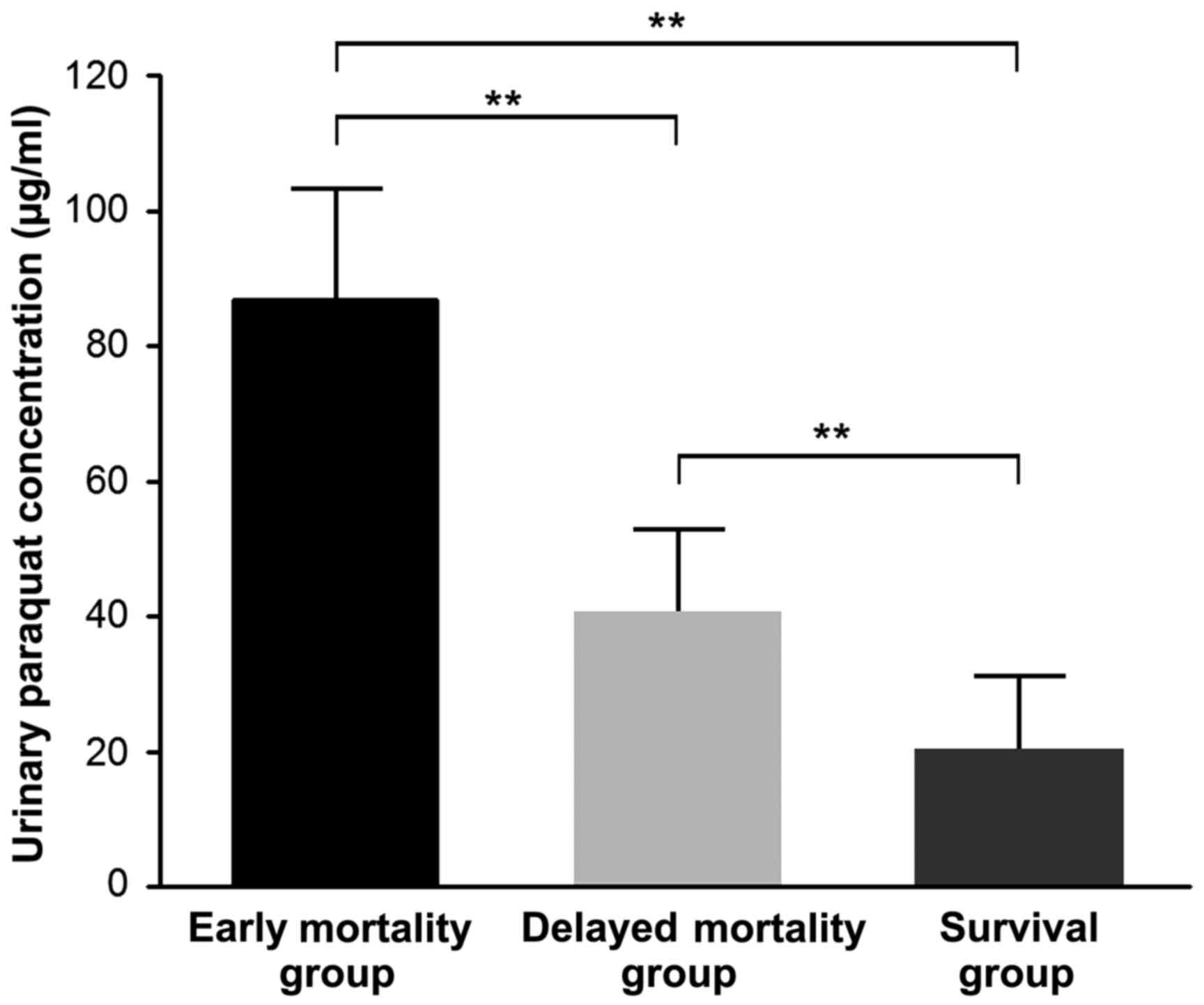
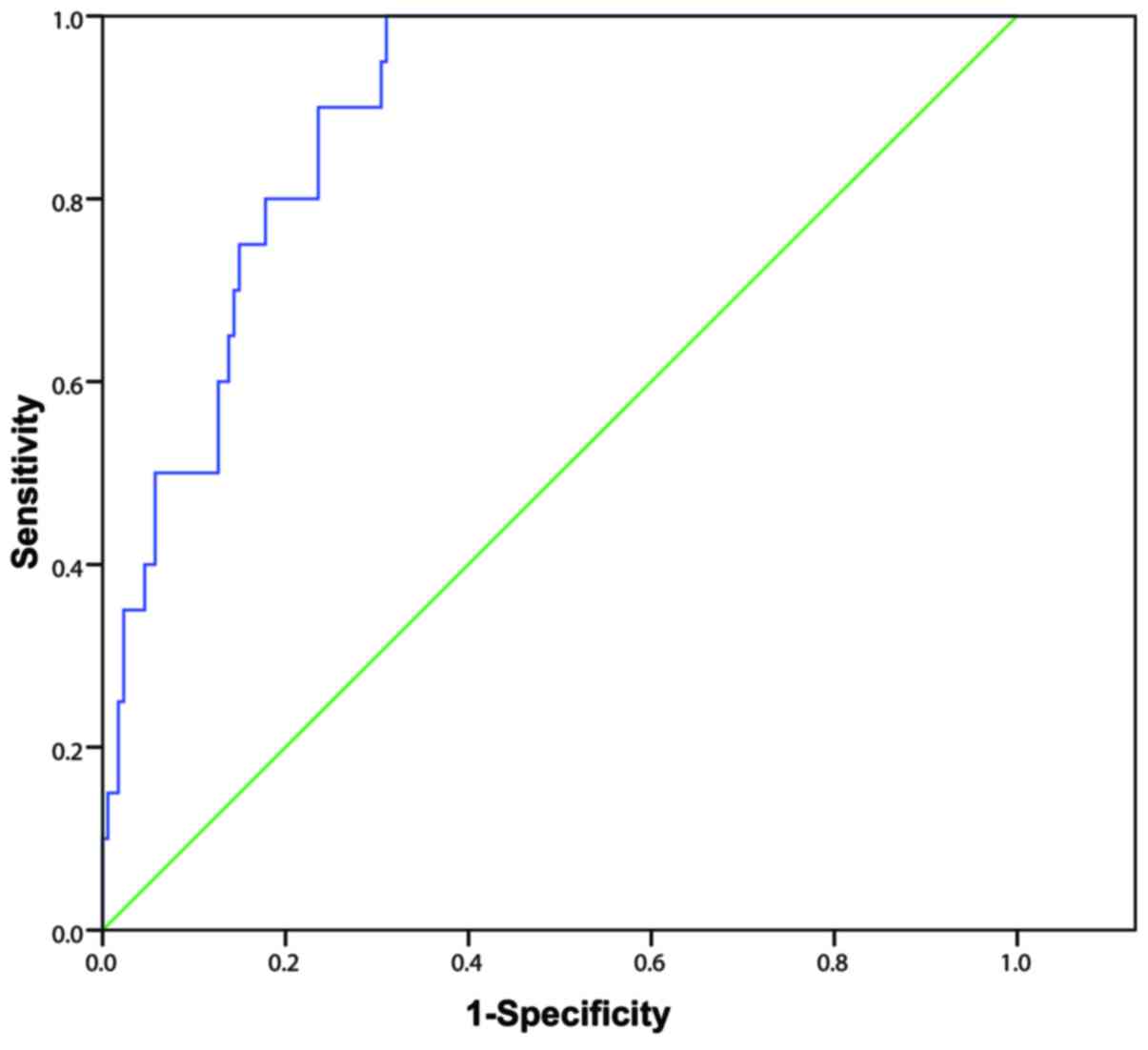
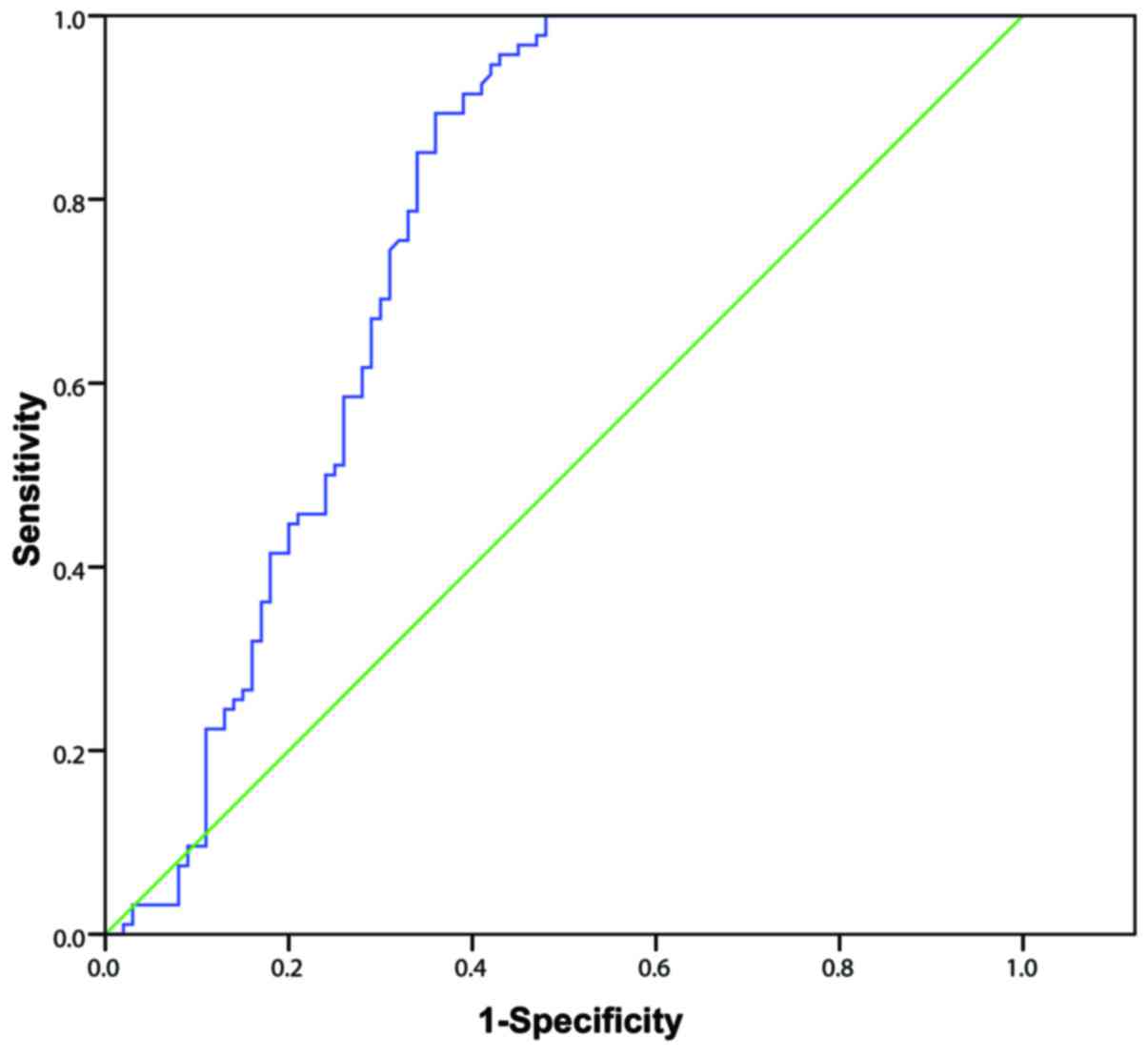
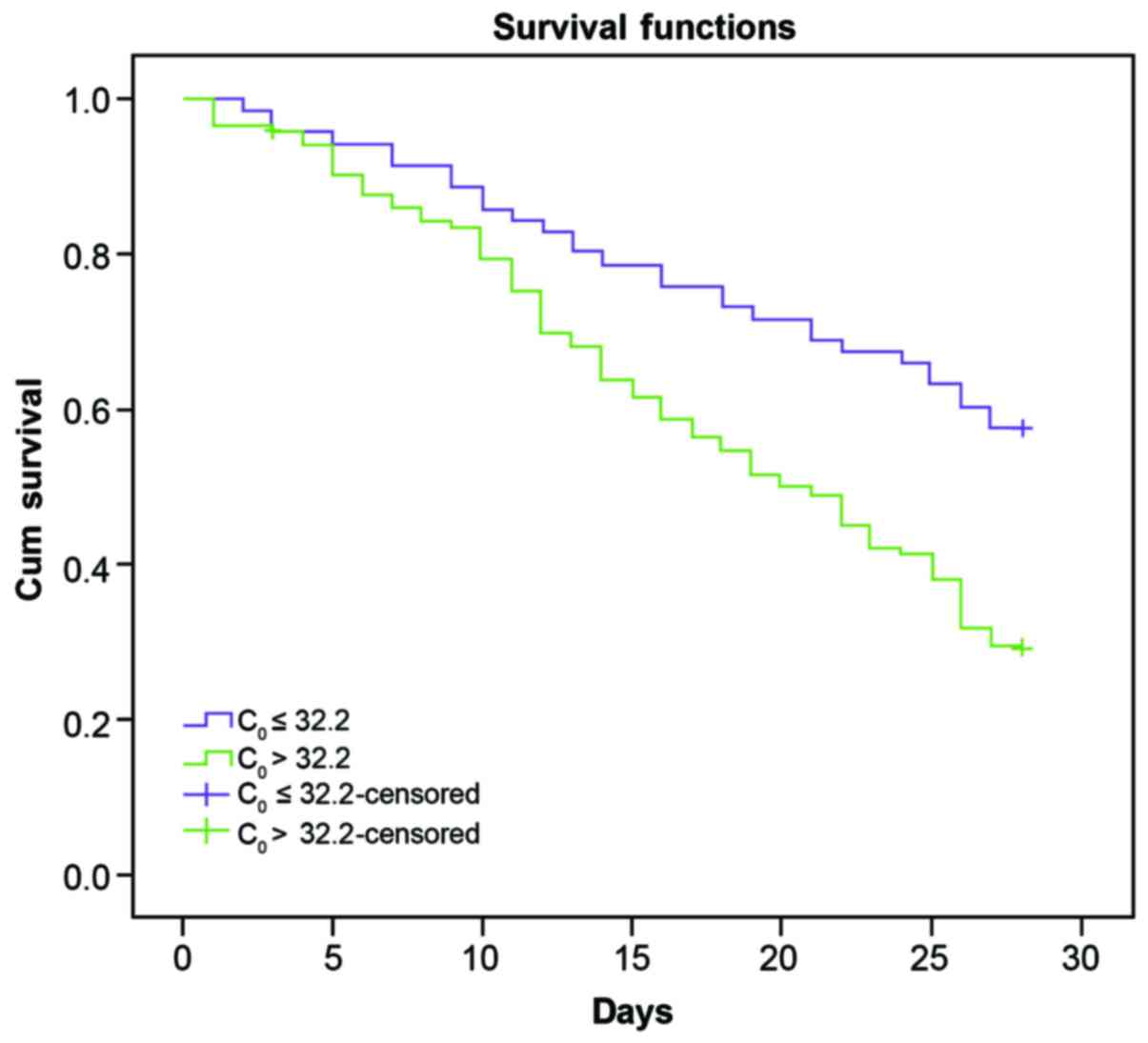
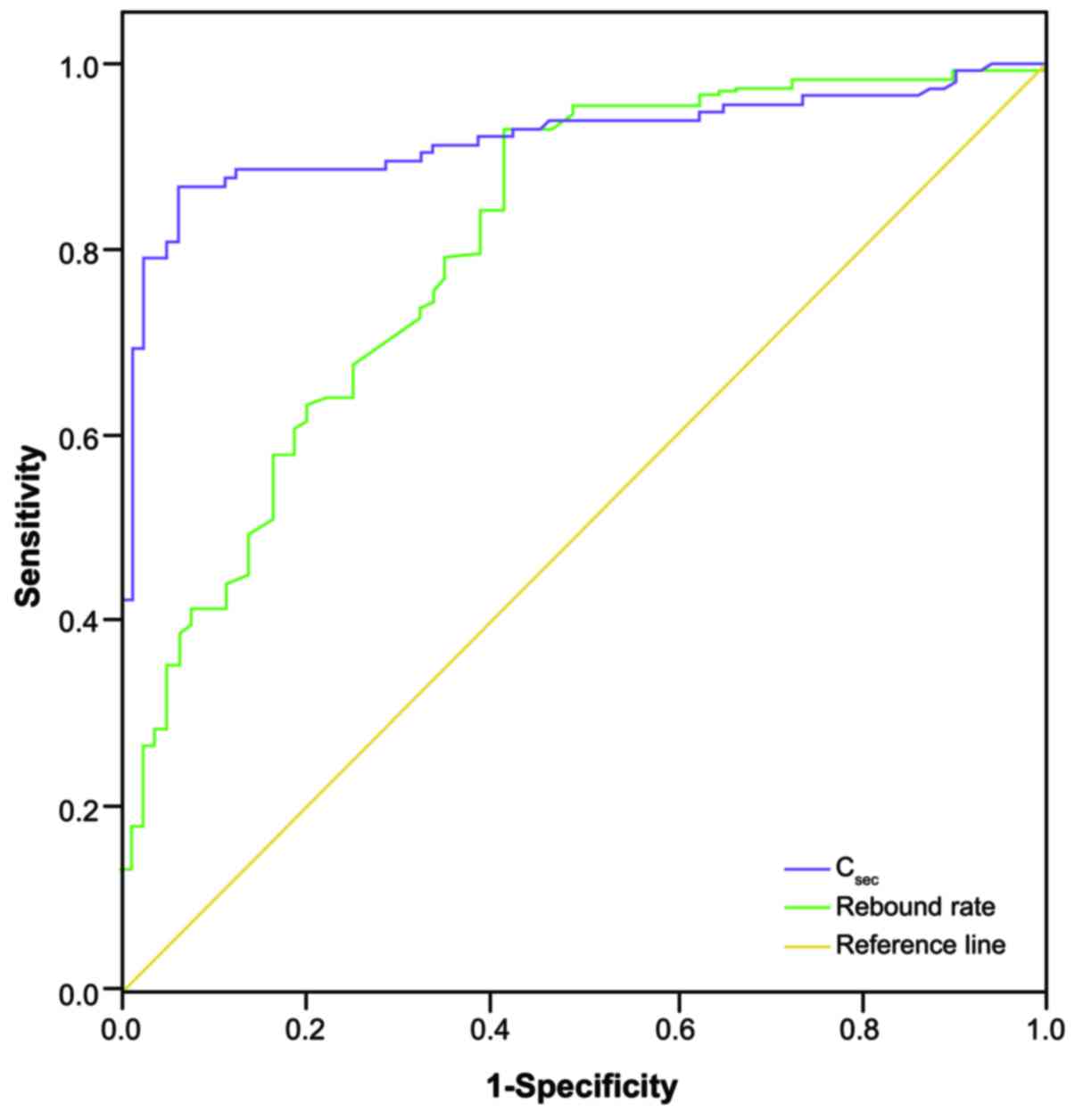
|
1
|
Sun IO and Lee KY: Cyclophosphamide dose:
How much is needed to win the war against paraquat poisoning?
Korean J Intern Med. 28:410–412. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu XW, Ma T, Qu B, Ji Y and Liu Z:
Prognostic value of initial arterial lactate level and lactate
metabolic clearance rate in patients with acute paraquat poisoning.
Am J Emerg Med. 31:1230–1235. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wunnapuk K, Mohammed F, Gawarammana I, Liu
X, Verbeeck RK, Buckley NA, Roberts MS and Musuamba FT: Prediction
of paraquat exposure and toxicity in clinically ill poisoned
patients: A model based approach. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 78:855–866.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Duarte JA,
Sánchez-Navarro A, Remião F, Bastos ML and Carvalho F: Paraquat
poisonings: Mechanisms of lung toxicity, clinical features, and
treatment. Crit Rev Toxicol. 38:13–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu B, Song B, Yang H, Huang B, Chi B, Guo
Y and Liu H: Central nervous system damage due to acute paraquat
poisoning: An experimental study with rat model. Neurotoxicology.
35:62–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Z, Zhao H, Liu W, Li T, Wang Y and
Zhao M: NLRP3 inflammasome activation is essential for
paraquat-induced acute lung injury. Inflammation. 38:433–444. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ruan XL, Qiu JJ, Wu C, Huang T, Meng RB
and Lai YQ: Magnetic single-walled carbon nanotubes-dispersive
solid-phase extraction method combined with liquid
chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of
paraquat in urine. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
965:85–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yeo CD, Kim JW, Kim YO, Yoon SA, Kim KH
and Kim YS: The role of pentraxin-3 as a prognostic biomarker in
paraquat poisoning. Toxicol Lett. 212:157–160. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee Y, Lee JH, Seong AJ, Hong CK, Lee HJ,
Shin DH and Hwang SY: Arterial lactate as a predictor of mortality
in emergency department patients with paraquat intoxication. Clin
Toxicol (Phila). 50:52–56. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seok S, Kim YH, Gil HW, Song HY and Hong
SY: The time between paraquat ingestion and a negative dithionite
urine test in an independent risk factor for death and organ
failure in acute paraquat intoxication. J Korean Med Sci.
27:993–998. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gil HW, Kang MS, Yang JO, Lee EY and Hong
SY: Association between plasma paraquat level and outcome of
paraquat poisoning in 375 paraquat poisoning patients. Clin Toxicol
(Phila). 46:515–518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hassanian-Moghaddam H, Amiri H, Zamani N,
Rahimi M, Shadnia S and Taherkhani M: QT dispersion and
prognostication of the outcome in acute cardiotoxicities: A
comparison with SAPS II and APACHE II scoring systems. Cardiovasc
Toxicol. 14:129–133. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mikkelsen ME, Miltiades AN, Gaieski DF,
Goyal M, Fuchs BD, Shah CV, Bellamy SL and Christie JD: Serum
lactate is associated with mortality in severe sepsis independent
of organ failure and shock. Crit Care Med. 37:1670–1677. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Weil MH and Tang W: Clinical correlates of
arterial lactate levels in STEMI patients. Crit Care. 15:1132011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang CJ, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Weng CH, Hsu
CW, Lee SY, Lee SH, Chang CM, Lin WR and Yen TH: Spectrum of toxic
hepatitis following intentional paraquat ingestion: Analysis of 187
cases. Liver Int. 32:1400–1406. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
M PN: World Medical Association publishes
the Revised Declaration of Helsinki. Natl Med J India.
27:562014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Berry DJ and Grove J: The determination of
paraquat (I,I'-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridylium cation) in urine. Clin
Chim Acta. 34:5–11. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Z, Liu D, Zhang X, Wang H and Hao F:
Prognosis value of urine paraquat semi-quantitative in the patients
with acute paraquat poisoning. Chinese Journal of Industrial
Hygiene and Occupational Diseases. 32:378–380. 2014.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh AP, Junemann A, Muthuraman A, Jaggi
AS, Singh N, Grover K and Dhawan R: Animal models of acute renal
failure. Pharmacol Rep. 64:31–44. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Weng CH, Hu CC, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Huang
WH, Hsu CW and Yen TH: Sequential organ failure assessment score
can predict mortality in patients with paraquat intoxication. PLoS
One. 7:e517432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang NC, Hung YM, Lin SL, Wann SR, Hsu
CW, Ger LP, Hung SY, Chung HM and Yeh JH: Further evidence of the
usefulness of acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II
scoring system in acute paraquat poisoning. Clin Toxicol (Phila).
44:99–102. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang MW, Chang SS, Lee CC, Sheu BF and
Young YR: Hypokalemia and hypothermia are associated with 30-day
mortality in patients with acute paraquat poisoning. Am J Med Sci.
335:451–456. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Howell MD, Donnino M, Clardy P, Talmor D
and Shapiro NI: Occult hypoperfusion and mortality in patients with
suspected infection. Intensive Care Med. 33:1892–1899. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|