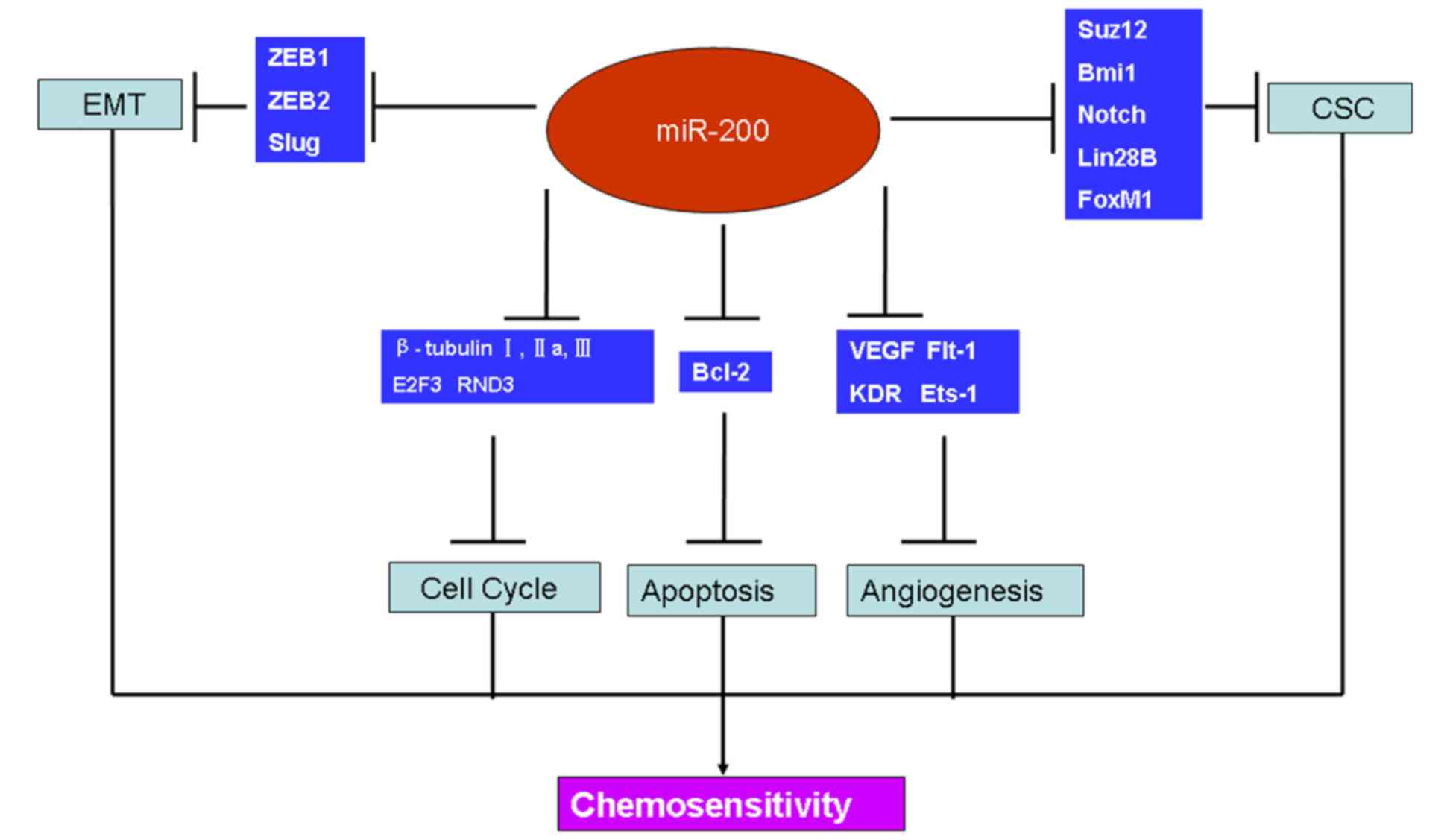
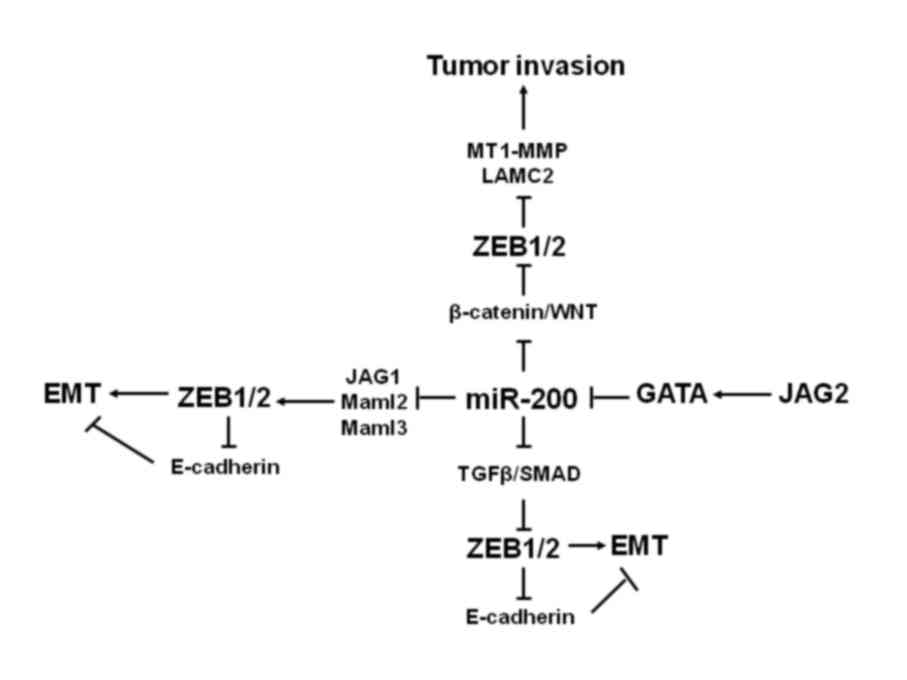
|
1
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sorek R and Cossart P: Prokaryotic
transcriptomics: A new view on regulation, physiology and
pathogenicity. Nat Rev Genet. 11:9–16. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tomasetti M, Lee W, Santarelli L and
Neuzil J: Exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer metabolism: Possible
implications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Exp Mol Med.
49:e2852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paul P, Chakraborty A, Sarkar D, Langthasa
M, Rahman M, Bari M, Singha RS, Malakar AK and Chakraborty S:
Interplay between miRNAs and human diseases: A review. J Cell
Physiol. Feb 9–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Meltzer PS: Cancer genomics: Small RNAs
with big impacts. Nature. 435:745–746. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang CJ, Chao CH, Xia W, Yang JY, Xiong
Y, Li CW, Yu WH, Rehman SK, Hsu JL, Lee HH, et al: p53 regulates
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties through
modulating miRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 13:317–323. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim T, Veronese A, Pichiorri F, Lee TJ,
Jeon YJ, Volinia S, Pineau P, Marchio A, Palatini J, Suh SS, et al:
p53 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through microRNAs
targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Exp Med. 208:875–883. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Humphries B and Yang C: The microRNA-200
family: Small molecules with novel roles in cancer development,
progression and therapy. Oncotarget. 6:6472–6498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zidar N, Boštjančič E, Gale N, Kojc N,
Poljak M, Glavač D and Cardesa A: Down-regulation of microRNAs of
the miR-200 family and miR-205, and an altered expression of
classic and desmosomal cadherins in spindle cell carcinoma of the
head and neck-hallmark of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hum
Pathol. 42:482–488. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Braun J, Hoang-Vu C, Dralle H and
Hüttelmaier S: Downregulation of microRNAs directs the EMT and
invasive potential of anaplastic thyroid carcinomas. Oncogene.
29:4237–4244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjøt
L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, Villadsen SB, Gao S, Ostenfeld MS,
Borre M, et al: Coordinated epigenetic repression of the miR-200
family and miR-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer.
128:1327–1334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aydoğdu E, Katchy A, Tsouko E, Lin CY,
Haldosén LA, Helguero L and Williams C: MicroRNA-regulated gene
networks during mammary cell differentiation are associated with
breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:1502–1511. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee JW, Park YA, Choi JJ, Lee YY, Kim CJ,
Choi C, Kim TJ, Lee NW, Kim BG and Bae DS: The expression of the
miRNA-200 family in endometrial endometrioid carcinoma. Gynecol
Oncol. 120:56–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Du Y, Xu Y, Ding L, Yao H, Yu H, Zhou T
and Si J: Down-regulation of miR-141 in gastric cancer and its
involvement in cell growth. J Gastroenterol. 44:556–561. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ladeiro Y, Couchy G, Balabaud C,
Bioulac-Sage P, Pelletier L, Rebouissou S and Zucman-Rossi J:
MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with
clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations.
Hepatology. 47:1955–1963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pacurari M, Addison JB, Bondalapati N, Wan
YW, Luo D, Qian Y, Castranova V, Ivanov AV and Guo NL: The
microRNA-200 family targets multiple non-small cell lung cancer
prognostic markers in H1299 cells and BEAS-2B cells. Int J Oncol.
43:548–560. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wiklund ED, Gao S, Hulf T, Sibbritt T,
Nair S, Costea DE, Villadsen SB, Bakholdt V, Bramsen JB, Sørensen
JA, et al: MicroRNA alterations and associated aberrant DNA
methylation patterns across multiple sample types in oral squamous
cell carcinoma. PloS One. 6:e278402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, Kim H, Kim YT, Kim
JH, Kim JW and Kim S: MicroRNA expression profiles in serous
ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2690–2695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gee GV, Koestler DC, Christensen BC,
Sugarbaker DJ, Ugolini D, Ivaldi GP, Resnick MB, Houseman EA,
Kelsey KT and Marsit CJ: Downregulated microRNAs in the
differential diagnosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Int J
Cancer. 127:2859–2869. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Barron N, Keenan J, Gammell P, Martinez
VG, Freeman A, Masters JR and Clynes M: Biochemical relapse
following radical prostatectomy and miR-200a levels in prostate
cancer. Prostate. 72:1193–1199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Castro-Vega LJ, Jouravleva K, Liu WY,
Martinez C, Gestraud P, Hupé P, Servant N, Albaud B, Gentien D, Gad
S, et al: Telomere crisis in kidney epithelial cells promotes the
acquisition of a microRNA signature retrieved in aggressive renal
cell carcinomas. Carcinogenesis. 34:1173–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Balaguer F,
Nagasaka T, Koike J, Hemmi H, Koi M, Boland CR and Goel A:
MicroRNA-200c modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)
in human colorectal cancer metastasis. Gut. 62:1315–1326. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
van Kempen LC, van den Hurk K, Lazar V,
Michiels S, Winnepenninckx V, Stas M, Spatz A and van den Oord JJ:
Loss of microRNA-200a and c, and microRNA-203 expression at the
invasive front of primary cutaneous melanoma is associated with
increased thickness and disease progression. Virchows Arch.
461:441–448. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu J, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Sato N,
Kayashima T, Fujita H, Nakata K and Tanaka M: MicroRNA,
hsa-miR-200c, is an independent prognostic factor in pancreatic
cancer and its upregulation inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion but
increases cell proliferation. Mol Cancer. 9:1692010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xia H, Ng SS, Jiang S, Cheung WK, Sze J,
Bian XW, Kung HF and Lin MC: miR-200a-mediated downregulation of
ZEB2 and CTNNB1 differentially inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cell growth, migration and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
391:535–541. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baer C, Claus R and Plass C: Genome-wide
epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:473–477.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pal MK, Jaiswar SP, Dwivedi VN, Tripathi
AK, Dwivedi A and Sankhwar P: MicroRNA: A new and promising
potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian cancer.
Cancer Biol Med. 12:328–341. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Azrak SS, Ginel-Picardo A, Drosten M,
Barbacid M and Santos E: Reversible, interrelated mRNA and miRNA
expression patterns in the transcriptome of Rasless fibroblasts:
Functional and mechanistic implications. BMC Genomics. 14:7312013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siomi H and Siomi MC: Posttranscriptional
regulation of microRNA biogenesis in animals. Mol Cell. 38:323–332.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Browne G, Sayan AE and Tulchinsky E: ZEB
proteins link cell motility with cell cycle control and cell
survival in cancer. Cell Cycle. 9:886–891. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gibbons DL, Lin W, Creighton CJ, Rizvi ZH,
Gregory PA, Goodall GJ, Thilaganathan N, Du L, Zhang Y,
Pertsemlidis A and Kurie JM: Contextual extracellular cues promote
tumor cell EMT and metastasis by regulating miR-200 family
expression. Genes Dev. 23:2140–2151. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pożarowska D and Pożarowski P: The era of
anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) drugs in
ophthalmology, VEGF and anti-VEGF therapy. Cent Eur J Immunol.
41:311–316. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Welti J, Loges S, Dimmeler S and Carmeliet
P: Recent molecular discoveries in angiogenesis and antiangiogenic
therapies in cancer. J Clin Invest. 123:3190–3200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang HF, Xu LY and Li EM: A family of
pleiotropically acting microRNAs in cancer progression, miR-200:
Potential cancer therapeutic targets. Curr Pharm Des. 20:1896–1903.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu H, Brannon AR, Reddy AR, Alexe G,
Seiler MW, Arreola A, Oza JH, Yao M, Juan D, Liou LS, et al:
Identifying mRNA targets of microRNA dysregulated in cancer: With
application to clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Syst Biol.
4:512010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Choi YC, Yoon S, Jeong Y, Yoon J and Baek
K: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling by
miR-200b. Mol Cells. 32:77–82. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Roybal JD, Zang Y, Ahn YH, Yang Y, Gibbons
DL, Baird BN, Alvarez C, Thilaganathan N, Liu DD, Saintigny P, et
al: miR-200 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion and
metastasis by targeting Flt1/VEGFR1. Mol Cancer Res. 9:25–35. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chan YC, Khanna S, Roy S and Sen CK:
miR-200b targets Ets-1 and is down-regulated by hypoxia to induce
angiogenic response of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem.
286:2047–20156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chan YC, Roy S, Khanna S and Sen CK:
Downregulation of endothelial microRNA-200b supports cutaneous
wound angiogenesis by desilencing GATA binding protein 2 and
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 32:1372–1382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pecot CV, Rupaimoole R, Yang D, Akbani R,
Ivan C, Lu C, Wu S, Han HD, Shah MY, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, et al:
Tumour angiogenesis regulation by the miR-200 family. Nat Commun.
4:24272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Knezevic J, Pfefferle AD, Petrovic I,
Greene SB, Perou CM and Rosen JM: Expression of miR-200c in
claudin-low breast cancer alters stem cell functionality, enhances
chemosensitivity and reduces metastatic potential. Oncogene.
34:5997–6006. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rossi L, Bonmassar E and Faraoni I:
Modification of miR gene expression pattern in human colon cancer
cells following exposure to 5-fluorouracil in vitro. Pharmacol Res.
56:248–253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pogribny IP, Filkowski JN, Tryndyak VP,
Golubov A, Shpyleva SI and Kovalchuk O: Alterations of microRNAs
and their targets are associated with acquired resistance of MCF-7
breast cancer cells to cisplatin. Int J Cancer. 127:1785–1794.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rui W, Bing F, Hai-Zhu S, Wei D and
Long-Bang C: Identification of microRNA profiles in
docetaxel-resistant human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells
(SPC-A1). J Cell Mol Med. 14:206–214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen DQ, Pan BZ, Huang JY, Zhang K, Cui
SY, De W, Wang R and Chen LB: HDAC 1/4-mediated silencing of
microRNA-200b promotes chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma
cells. Oncotarget. 5:3333–3349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kinose Y, Sawada K, Nakamura K and Kimura
T: The role of microRNAs in ovarian cancer. Biomed Res Int.
2014:2493932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G and Kang Y: The
miR-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin
transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem.
283:14910–14914. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT, Chae SS,
Booth MF, Garkavtsev I, Xu L, Hicklin DJ, Fukumura D, di Tomaso E,
et al: Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade
governs brain tumor response to radiation: Role of oxygenation,
angiopoietin-1, and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell.
6:553–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Thomas S, Quinn BA, Das SK, Dash R, Emdad
L, Dasgupta S, Wang XY, Dent P, Reed JC, Pellecchia M, et al:
Targeting the Bcl-2 family for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:61–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kurashige J, Kamohara H, Watanabe M,
Hiyoshi Y, Iwatsuki M, Tanaka Y, Kinoshita K, Saito S, Baba Y and
Baba H: MicroRNA-200b regulates cell proliferation, invasion, and
migration by directly targeting ZEB2 in gastric carcinoma. Ann Surg
Oncol. 19 Suppl 3:S656–S664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Leskelä S, Leandro-García LJ, Mendiola M,
Barriuso J, Inglada-Pérez L, Muñoz I, Martínez-Delgado B, Redondo
A, De Santiago J, Robledo M, et al: The miR-200 family controls
beta-tubulin III expression and is associated with paclitaxel-based
treatment response and progression-free survival in ovarian cancer
patients. Endocr Relat Cancer. 18:85–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xia W, Li J, Chen L, Huang B, Li S, Yang
G, Ding H, Wang F, Liu N, Zhao Q, et al: MicroRNA-200b regulates
cyclin D1 expression and promotes S-phase entry by targeting RND3
in HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 344:261–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Koutsaki M, Spandidos DA and Zaravinos A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated miRNAs in ovarian
carcinoma, with highlight on the miR-200 family: Prognostic value
and prospective role in ovarian cancer therapeutics. Cancer Lett.
351:173–181. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Feng X, Wang Z, Fillmore R and Xi Y:
MiR-200, a new star miRNA in human cancer. Cancer Lett.
344:166–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hill L, Browne G and Tulchinsky E:
ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop: At the crossroads of signal transduction
in cancer. Int J Cancer. 132:745–754. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yang Y, Ahn YH, Gibbons DL, Zang Y, Lin W,
Thilaganathan N, Alvarez CA, Moreira DC, Creighton CJ, Gregory PA,
et al: The Notch ligand Jagged2 promotes lung adenocarcinoma
metastasis through a miR-200-dependent pathway in mice. J Clin
Invest. 121:1373–1385. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ahn SM, Cha JY, Kim J, Kim D, Trang HT,
Kim YM, Cho YH, Park D and Hong S: Smad3 regulates E-cadherin via
miRNA-200 pathway. Oncogene. 31:3051–3059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhou X, Wang Y, Shan B, Han J, Zhu H, Lv
Y, Fan X, Sang M, Liu XD and Liu W: The downregulation of
miR-200c/141 promotes ZEB1/2 expression and gastric cancer
progression. Med Oncol. 32:4282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Argast GM, Krueger JS, Thomson S,
Sujka-Kwok I, Carey K, Silva S, O'Connor M, Mercado P, Mulford IJ,
Young GD, et al: Inducible expression of TGFβ, snail and Zeb1
recapitulates EMT in vitro and in vivo in a NSCLC model. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 28:593–614. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Brabletz S, Bajdak K, Meidhof S, Burk U,
Niedermann G, Firat E, Wellner U, Dimmler A, Faller G, Schubert J
and Brabletz T: The ZEB1/miR-200 feedback loop controls Notch
signalling in cancer cells. EMBO J. 30:770–782. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sánchez-Tilló E, de Barrios O, Valls E,
Darling DS, Castells A and Postigo A: ZEB1 and TCF4 reciprocally
modulate their transcriptional activities to regulate Wnt target
gene expression. Oncogene. 34:5760–5770. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zaravinos A: The regulatory role of
microRNAs in EMT and cancer. J Oncol. 2015:8658162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Kahlert C, Lahes S, Radhakrishnan P, Dutta
S, Mogler C, Herpel E, Brand K, Steinert G, Schneider M,
Mollenhauer M, et al: Overexpression of ZEB2 at the invasion front
of colorectal cancer is an independent prognostic marker and
regulates tumor invasion in vitro. Clin Cancer Res. 17:7654–7663.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Saydam O, Shen Y, Würdinger T, Senol O,
Boke E, James MF, Tannous BA, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Yi M, Stephens
RM, et al: Downregulated microRNA-200a in meningiomas promotes
tumor growth by reducing E-cadherin and activating the
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 29:5923–5940.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|