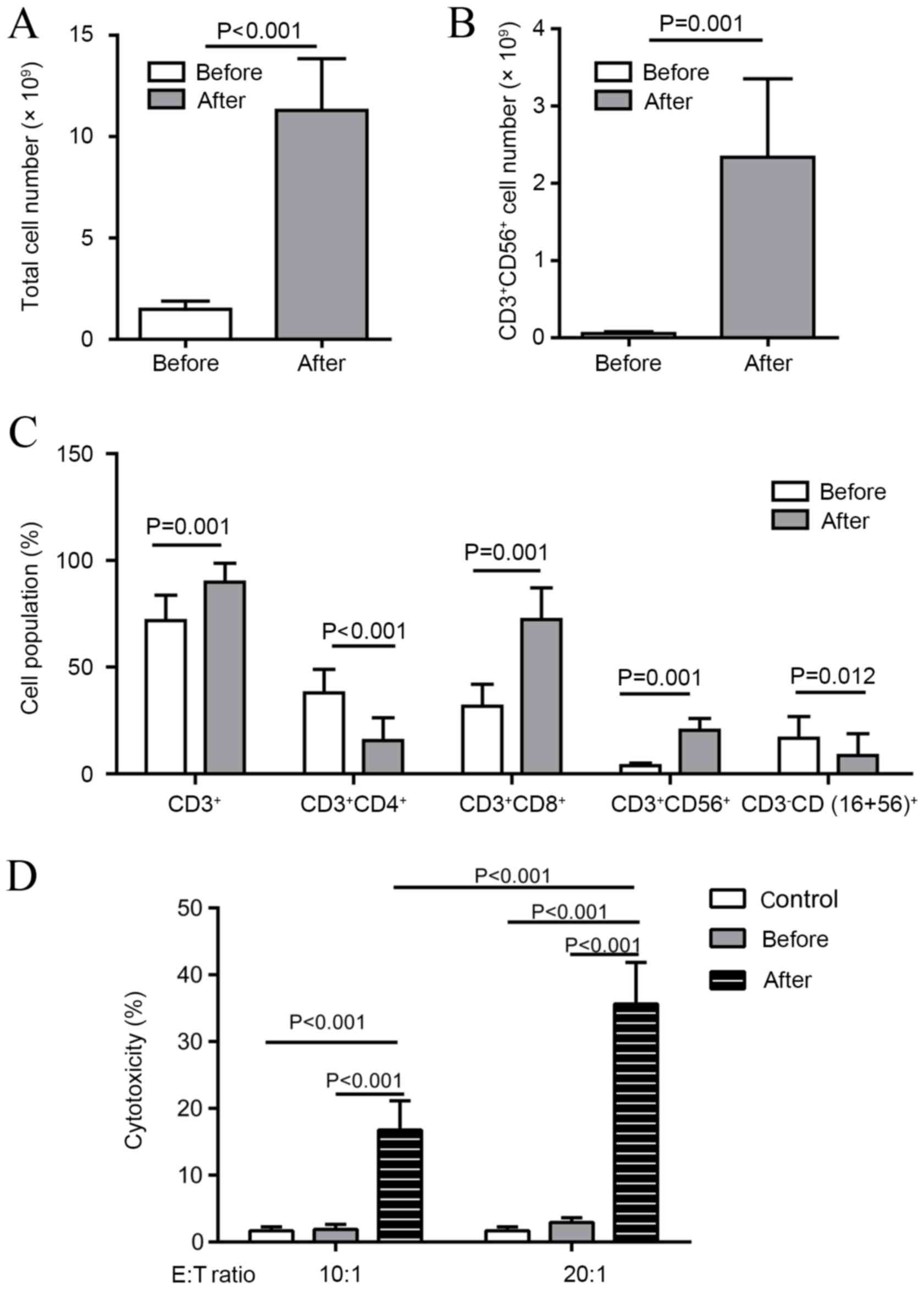
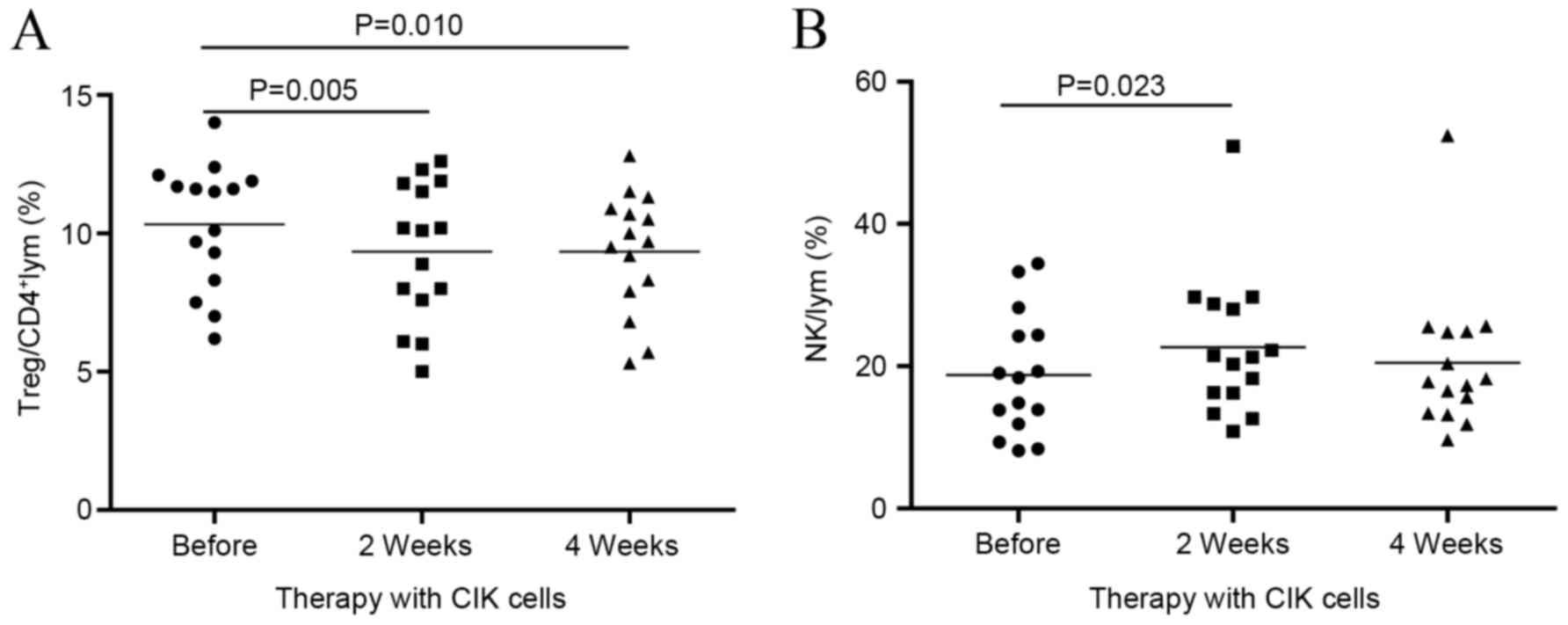
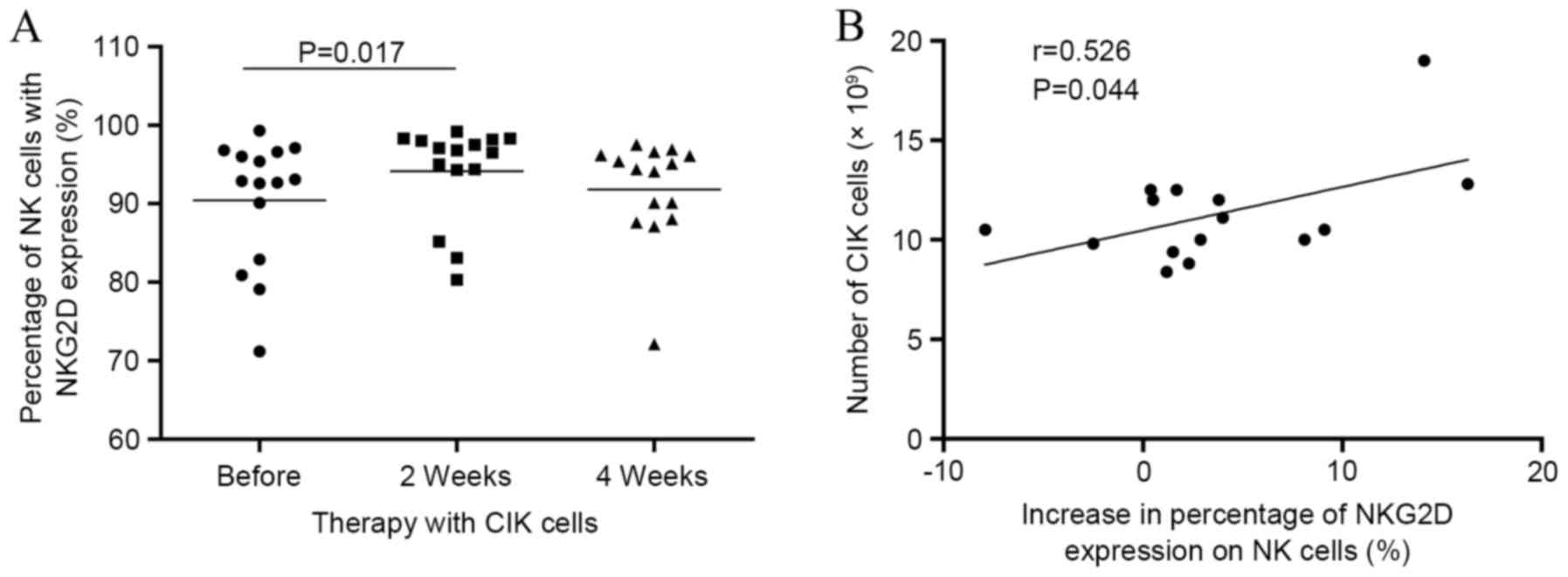
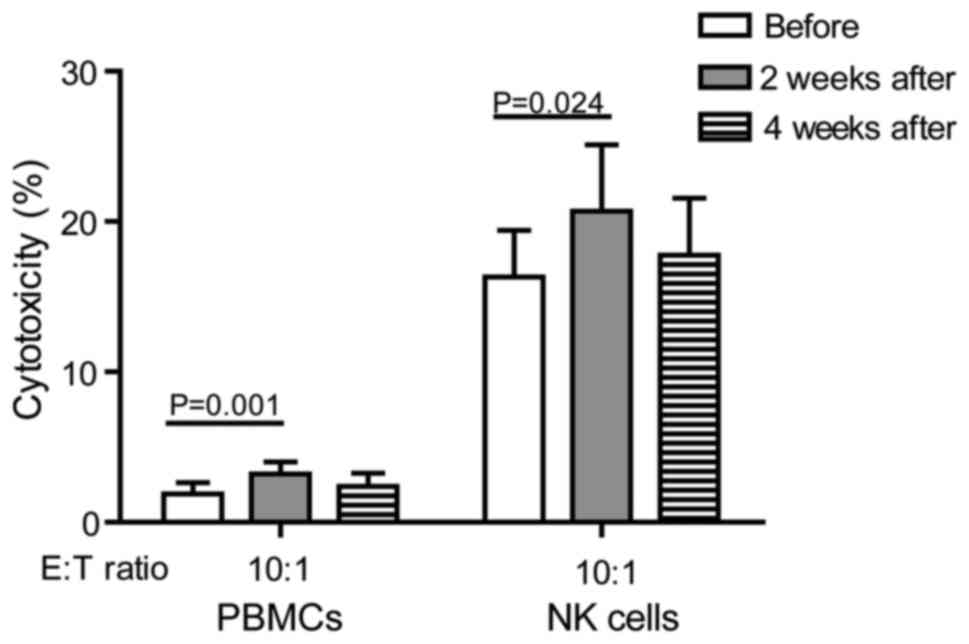
|
1
|
Finotello F and Trajanoski Z: New
strategies for cancer immunotherapy: Targeting regulatory T cells.
Genome Med. 9:102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Farashi-Bonab S and Khansari N: Regulatory
T cells in cancer patients and their roles in cancer
development/progression. MOJ Immunol. 1:00024. 2014.
|
|
3
|
Chen C, Chen Z, Chen D, Zhang B, Wang Z
and Le H: Suppressive effects of gemcitabine plus cisplatin
chemotherapy on regulatory T cells in nonsmall-cell lung cancer. J
Int Med Res. 43:180–187. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM and
Hafler DA: FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system.
Nat Rev Immunol. 10:490–500. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Q, Yang L, Xu F, Wang J, An G and Ma
Y: Changes of lymphocyte subgroups in non-small cell lung cancer
patients before and during chemotherapy. Clin Lab. 61:1343–1351.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pan K, Guan XX, Li YQ, Zhao JJ, Li JJ, Qiu
HJ, Weng DS, Wang QJ, Liu Q, Huang LX, et al: Clinical activity of
adjuvant cytokine-induced killer cell immunotherapy in patients
with post-mastectomy triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 20:3003–3011. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang M, Shi SB, Qi JL, Tang XY and Tian J:
S-1 plus CIK as second-line treatment for advanced pancreatic
cancer. Med Oncol. 30:7472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen JL, Lao XM, Lin XJ, Xu L, Cui BK,
Wang J, Lin GH, Shuang ZY, Mao YZ, Huang X, et al: Adjuvant
cytokine-induced killer cell therapy improves disease-free and
overall survival in solitary and nonmicrovascular invasive
hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Medicine
(Baltimore). 95:e26652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Razzaghi H, Quesnel-Crooks S, Sherman R,
Joseph R, Kohler B, Andall-Brereton G, Ivey MA, Edwards BK, Mery L,
Gawryszewski V and Saraiya M: Leading causes of cancer
mortality-Caribbean region, 2003–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.
65:1395–1400. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tian J and Han S: Role of RRM1 in the
treatment and prognosis of advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 18:381–386. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Daga A, Ansari A, Patel S, Mirza S, Rawal
R and Umrania V: Current drugs and drug targets in non-small cell
lung cancer: Limitations and opportunities. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 16:4147–4156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vigneron N: Human tumor antigens and
cancer immunotherapy. Biomed Res Int. 2015:9485012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu K, Liu X, Peng Z, Sun H, Zhang M,
Zhang J, Liu S, Hao L, Lu G, Zheng K, et al: Retargeted human
avidin-CAR T cells for adoptive immunotherapy of EGFRvIII
expressing gliomas and their evaluation via optical imaging.
Oncotarget. 6:23735–23747. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bigley AB and Simpson RJ: NK cells and
exercise: Implications for cancer immunotherapy and survivorship.
Discov Med. 19:433–445. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ascierto ML, Melero I and Ascierto PA:
Melanoma: From incurable beast to a curable bet. The success of
immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 5:1522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang M, Cao JX, Pan JH, Liu YS, Xu BL, Li
D, Zhang XY, Li JL, Liu JL, Wang HB and Wang ZX: Adoptive
immunotherapy of cytokine-induced killer cell therapy in the
treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1126622014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Zhu L, Du H, He X, Yin Y, Gu Y,
Liu L, Lu K, Guo R, Liu P and Shu Y: Autologous cytokine-induced
killer cell therapy in lung cancer patients: A retrospective study.
Biomed Pharmacother. 70:248–252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang B, Lu XC, Zhu HL, Han WD, Wang Y, Fan
H, Li SX, Liu Y, Dai HR and Yao SQ: Clinical study of autologous
cytokine induced killer cells combined with IL-2 for therapy of
elderly patients with B-cell malignant lymphoma. Zhongguo Shi Yan
Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 18:1244–1249. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang S, He X, Li X and Ren Y: Clinical
study on cytokine induced killer cells therapy to laryngeal cancer
after radiotherapy. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi.
25:61–63. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li XD, Ji M, Zheng X, Ning ZH, Wu J, Lu B,
Wu CP and Jiang JT: Evaluation of tumor response to
cytokine-induced killer cells therapy in malignant solid tumors. J
Transl Med. 12:2152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Walasek T, Sas-Korczyńska B, Dąbrowski T,
Reinfuss M, Jakubowicz J, Blecharz P, Łuczyńska E, Darasz Z and
Skotnicki P: Palliative thoracic radiotherapy for patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer and poor performance status.
Lung Cancer. 87:130–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kverneland AH, Streitz M, Geissler E,
Hutchinson J, Vogt K, Boës D, Niemann N, Pedersen AE, Schlickeiser
S and Sawitzki B: Age and gender leucocytes variances and
references values generated using the standardized ONE-Study
protocol. Cytometry A. 89:543–564. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arias DA Alvarez, Kim HJ, Zhou P,
Holderried TA, Wang X, Dranoff G and Cantor H: Disruption of CD8+
Treg activity results in expansion of T follicular helper cells and
enhanced antitumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Res. 2:207–216. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bauer CA, Kim EY, Marangoni F, Carrizosa
E, Claudio NM and Mempel TR: Dynamic Treg interactions with
intratumoral APCs promote local CTL dysfunction. J Clin Invest.
124:2425–2440. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guzmán-Flores JM and Portales-Pérez DP:
Mechanisms of suppression of regulatory T-cells (Treg). Gac Med
Mex. 149:630–638. 2013.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Duan MC, Zhong XN, Liu GN and Wei JR: The
Treg/Th17 paradigm in lung cancer. J Immunol Res. 2014:7303802014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Perrone G, Ruffini PA, Catalano V, Spino
C, Santini D, Muretto P, Spoto C, Zingaretti C, Sisti V,
Alessandroni P, et al: Intratumoural FOXP3-positive regulatory T
cells are associated with adverse prognosis in radically resected
gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer. 44:1875–1882. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C, Leek RD, Garcia
JF, Harris AL and Banham AH: Quantification of regulatory T cells
enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and
those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol. 24:5373–5380. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mougiakakos D, Choudhury A, Lladser A,
Kiessling R and Johansson CC: Regulatory T cells in cancer. Adv
Cancer Res. 107:57–117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nishikawa H and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T
cells in tumor immunity. Int J Cancer. 127:759–767. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X,
Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L,
Burow M, et al: Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in
ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced
survival. Nat Med. 10:942–949. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bergmann C, Strauss L, Wang Y, Szczepanski
MJ, Lang S, Johnson JT and Whiteside TL: T regulatory type 1 cells
in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Mechanisms of
suppression and expansion in advanced disease. Clin Cancer Res.
14:3706–3715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alizadeh D and Larmonier N:
Chemotherapeutic targeting of cancer-induced immunosuppressive
cells. Cancer Res. 74:2663–2668. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou S, Chen L, Qin J, Li R, Tao H, Zhen
Z, Chen H, Chen G, Yang Y, Liu B, et al: Depletion of CD4+ CD25+
regulatory T cells promotes CCL21-mediated antitumor immunity. PLoS
One. 8:e739522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bulliard Y, Jolicoeur R, Zhang J, Dranoff
G, Wilson NS and Brogdon JL: OX40 engagement depletes intratumoral
Tregs via activating FcgRs, leading to antitumor efficacy. Immunol
Cell Biol. 92:475–480. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mattarollo SR, Steegh K, Li M, Duret H,
Ngiow S Foong and Smyth MJ: Transient Foxp3(+) regulatory T-cell
depletion enhances therapeutic anticancer vaccination targeting the
immune-stimulatory properties of NKT cells. Immunol Cell Biol.
91:105–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu N and Li X, Song W, Li D, Yu D, Zeng X,
Li M, Leng X and Li X: CD4(+)CD25 (+)CD127 (low/−) T cells: A more
specific Treg population in human peripheral blood. Inflammation.
35:1773–1780. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dasgupta A, Mahapatra M and Saxena R: Flow
cytometric immunophenotyping of regulatory T cells in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia: Comparative assessment of various markers and
use of novel antibody panel with CD127 as alternative to
transcription factor FoxP3. Leuk Lymphoma. 54:778–789. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Su H, Longhi MS, Wang P, Vergani D and Ma
Y: Human CD4+CD25(high)CD127 (low/neg) regulatory T cells. Methods
Mol Biol. 806:287–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Drennan S, Stafford ND, Greenman J and
Green VL: Increased frequency and suppressive activity of
CD127(low/−) regulatory T cells in the peripheral circulation of
patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma are associated
with advanced stage and nodal involvement. Immunology. 140:335–343.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jun C, Ke W, Qingshu L, Ping L, Jun D, Jie
L, Bo C and Su M: Protective effect of CD4(+)CD25(high)CD127(low)
regulatory T cells in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell
Immunol. 289:106–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Marek-Trzonkowska N, Myśliwiec M, Dobyszuk
A, Grabowska M, Derkowska I, Juścińska J, Owczuk R, Szadkowska A,
Witkowski P, Młynarski W, et al: Therapy of type 1 diabetes with
CD4(+)CD25(high)CD127-regulatory T cells prolongs survival of
pancreatic islets - results of one year follow-up. Clin Immunol.
153:23–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sugiyama D, Nishikawa H, Maeda Y, Nishioka
M, Tanemura A, Katayama I, Ezoe S, Kanakura Y, Sato E, Fukumori Y,
et al: Anti-CCR4 mAb selectively depletes effector-type FoxP3+CD4+
regulatory T cells, evoking antitumor immune responses in humans.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:pp. 17945–17950. 2013; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liakou CI, Kamat A, Tang DN, Chen H, Sun
J, Troncoso P, Logothetis C and Sharma P: CTLA-4 blockade increases
IFNgamma-producing CD4+ICOShi cells to shift the ratio of effector
to regulatory T cells in cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:pp. 14987–14992. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hodi FS, Butler M, Oble DA, Seiden MV,
Haluska FG, Kruse A, Macrae S, Nelson M, Canning C, Lowy I, et al:
Immunologic and clinical effects of antibody blockade of cytotoxic
T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 in previously vaccinated cancer
patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp. 3005–3010. 2008;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shimizu J, Yamazaki S and Sakaguchi S:
Induction of tumor immunity by removing CD25+CD4+ T cells: A common
basis between tumor immunity and autoimmunity. J Immunol.
163:5211–5218. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ko K, Yamazaki S, Nakamura K, Nishioka T,
Hirota K, Yamaguchi T, Shimizu J, Nomura T, Chiba T and Sakaguchi
S: Treatment of advanced tumors with agonistic anti-GITR mAb and
its effects on tumor-infiltrating Foxp3+CD25+CD4+ regulatory T
cells. J Exp Med. 202:885–891. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Onizuka S, Tawara I, Shimizu J, Sakaguchi
S, Fujita T and Nakayama E: Tumor rejection by in vivo
administration of anti-CD25 (interleukin-2 receptor alpha)
monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 59:3128–3133. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mitsui J, Nishikawa H, Muraoka D, Wang L,
Noguchi T, Sato E, Kondo S, Allison JP, Sakaguchi S, Old LJ, et al:
Two distinct mechanisms of augmented antitumor activity by
modulation of immunostimulatory/inhibitory signals. Clin Cancer
Res. 16:2781–2791. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Dannull J, Su Z, Rizzieri D, Yang BK,
Coleman D, Yancey D, Zhang A, Dahm P, Chao N, Gilboa E and Vieweg
J: Enhancement of vaccine-mediated antitumor immunity in cancer
patients after depletion of regulatory T cells. J Clin Invest.
115:3623–3633. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Tao Q, Chen T, Tao L, Wang H, Pan Y, Xiong
S and Zhai Z: IL-15 improves the cytotoxicity of cytokine-induced
killer cells against leukemia cells by upregulating CD3+CD56+ cells
and downregulating regulatory T cells as well as IL-35. J
Immunother. 36:462–467. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ganesan AP, Johansson M, Ruffell B,
Yagui-Beltrán A, Lau J, Jablons DM and Coussens LM:
Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells inhibit endogenous cytotoxic
T cell responses to lung adenocarcinoma. J Immunol. 191:2009–2017.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Walter S, Weinschenk T, Stenzl A, Zdrojowy
R, Pluzanska A, Szczylik C, Staehler M, Brugger W, Dietrich PY,
Mendrzyk R, et al: Multipeptide immune response to cancer vaccine
IMA901 after single-dose cyclophosphamide associates with longer
patient survival. Nat Med. 18:1254–1261. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lanier LL: NK cell recognition. Annu Rev
Immunol. 23:225–274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
McDowell KA, Hank JA, DeSantes KB,
Capitini CM, Otto M and Sondel PM: NK cell-based immunotherapies in
pediatric oncology. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 37:79–93. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Crouse J, Xu HC, Lang PA and Oxenius A: NK
cells regulating T cell responses: Mechanisms and outcome. Trends
Immunol. 36:49–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sentman CL and Meehan KR: NKG2D CARs as
cell therapy for cancer. Cancer J. 20:156–159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sarkar S, Germeraad WT, Rouschop KM,
Steeghs EM, van Gelder M, Bos GM and Wieten L: Hypoxia induced
impairment of NK cell cytotoxicity against multiple myeloma can be
overcome by IL-2 activation of the NK cells. PLoS One.
8:e648352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hromadnikova I, Pirkova P and Sedlackova
L: Influence of in vitro IL-2 or IL-15 alone or in combination with
Hsp-70-derived 14-mer peptide (TKD) on the expression of NK cell
activatory and inhibitory receptors. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:4052952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Konjevic G, Jurisic V, Jovic V, Vuletic A,
Martinovic K Mirjacic, Radenkovic S and Spuzic I: Investigation of
NK cell function and their modulation in different malignancies.
Immunol Res. 52:139–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Luo Y, Henning J and O'Donnell MA: Th1
cytokine-secreting recombinant Mycobacterium bovis bacillus
Calmette-Guérin and prospective use in immunotherapy of bladder
cancer. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011:7289302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ito N, Nakamura H, Tanaka Y and Ohgi S:
Lung carcinoma: Analysis of T helper type 1 and 2 cells and T
cytotoxic type 1 and 2 cells by intracellular cytokine detection
with flow cytometry. Cancer. 85:2359–2367. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Romano S, D'Angelillo A, D'Arrigo P,
Staibano S, Greco A, Brunetti A, Scalvenzi M, Bisogni R, Scala I
and Romano MF: FKBP51 increases the tumour-promoter potential of
TGF-beta. Clin Transl Med. 3:12014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhuo C, Xu Y, Ying M, Li Q, Huang L, Li D,
Cai S and Li B: FOXP3+ Tregs: Heterogeneous phenotypes and
conflicting impacts on survival outcomes in patients with
colorectal cancer. Immunol Res. 61:338–347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wilson EB, El-Jawhari JJ, Neilson AL, Hall
GD, Melcher AA, Meade JL and Cook GP: Human tumour immune evasion
via TGF-β blocks NK cell activation but not survival allowing
therapeutic restoration of anti-tumour activity. PLoS One.
6:e228422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Itoh S and Itoh F: Implication of TGF-β as
a survival factor during tumour development. J Biochem.
151:559–562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Du Y, Chen X, Lin XQ, Wu W and Huang ZM:
Tumor-derived CD4+CD25+ Tregs inhibit the maturation and
antigen-presenting function of dendritic cells. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 16:2665–2669. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|