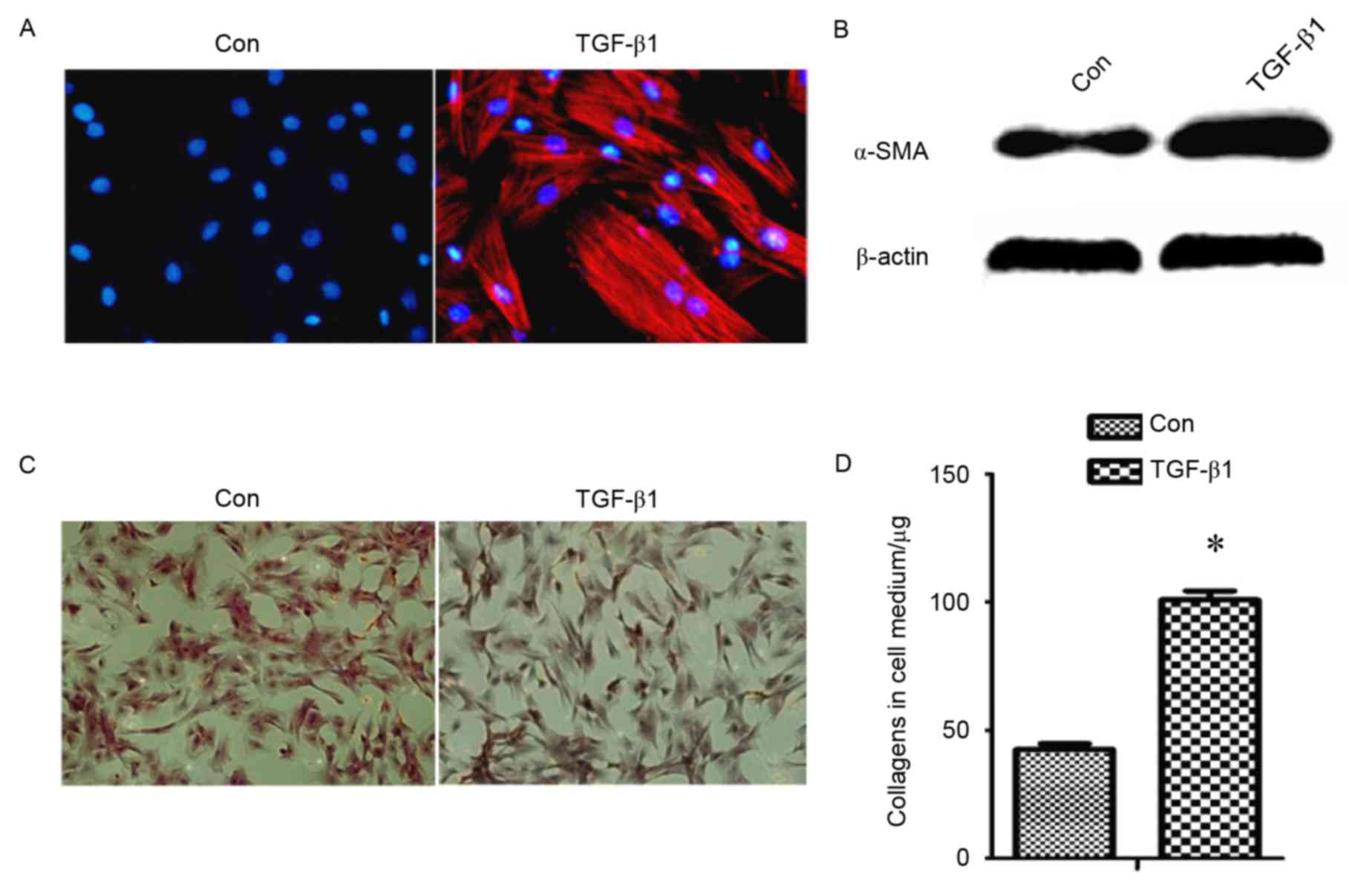
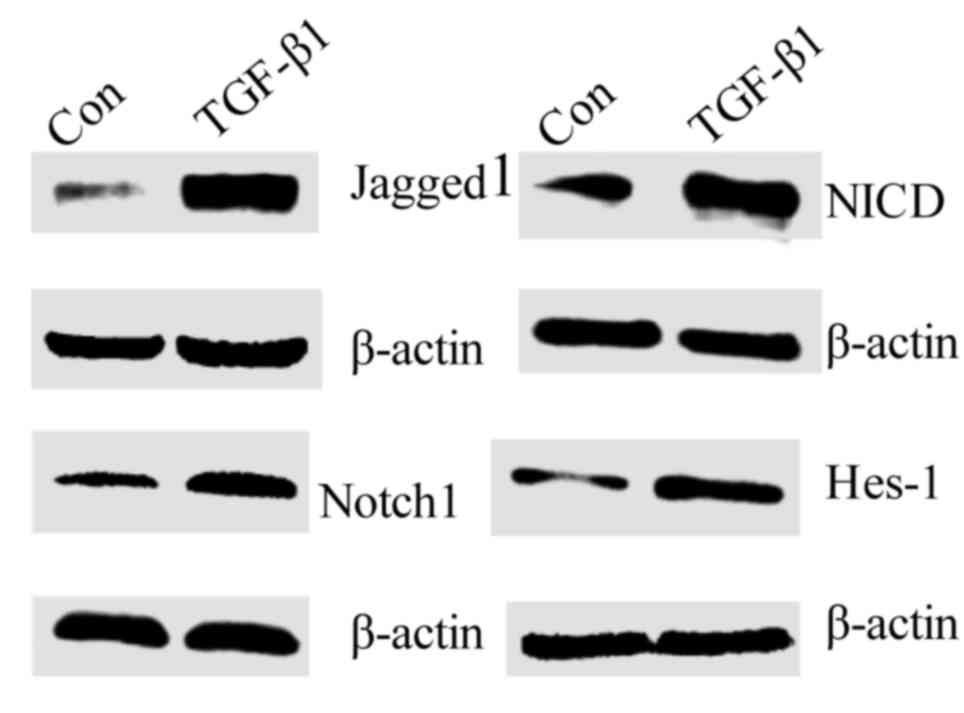
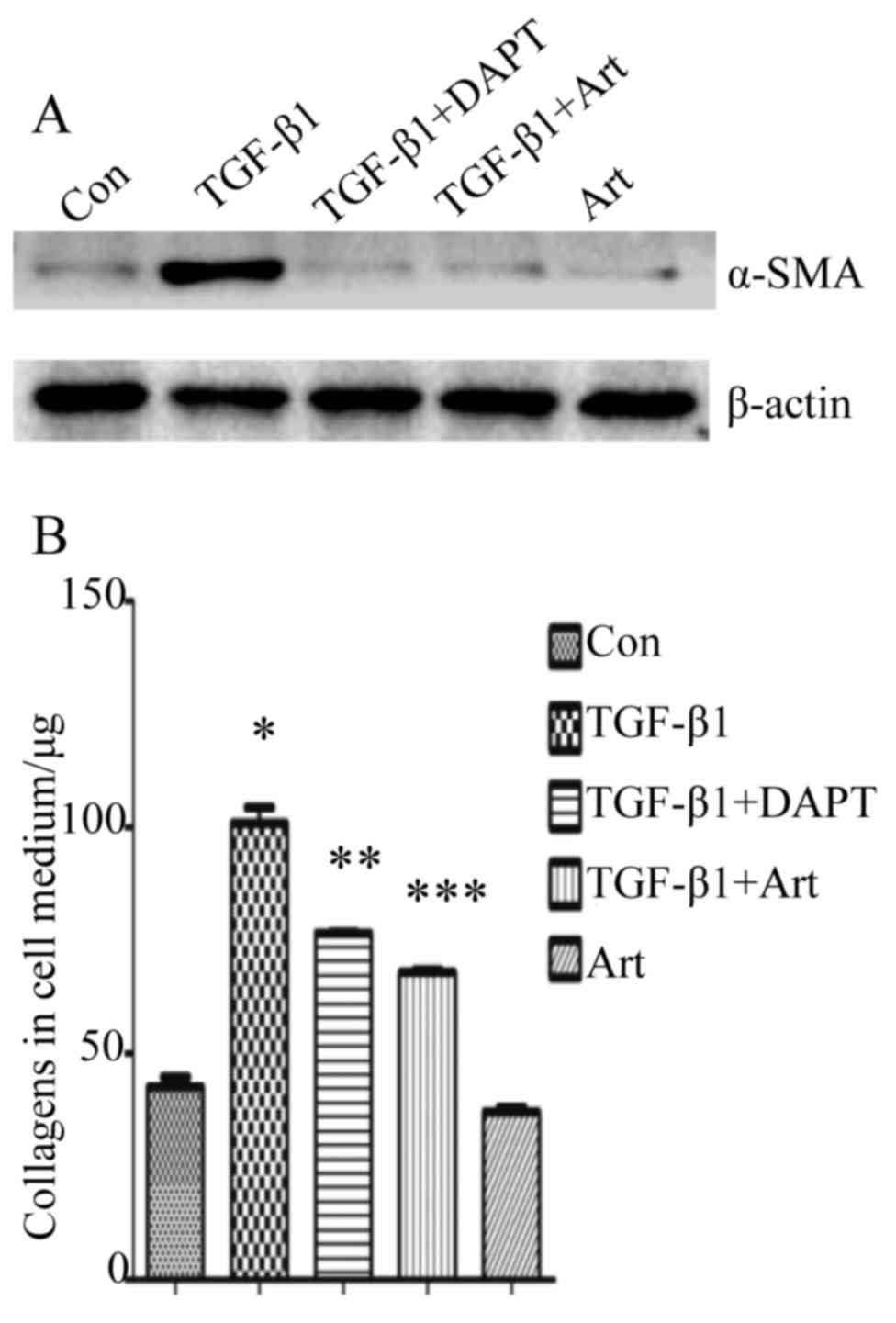
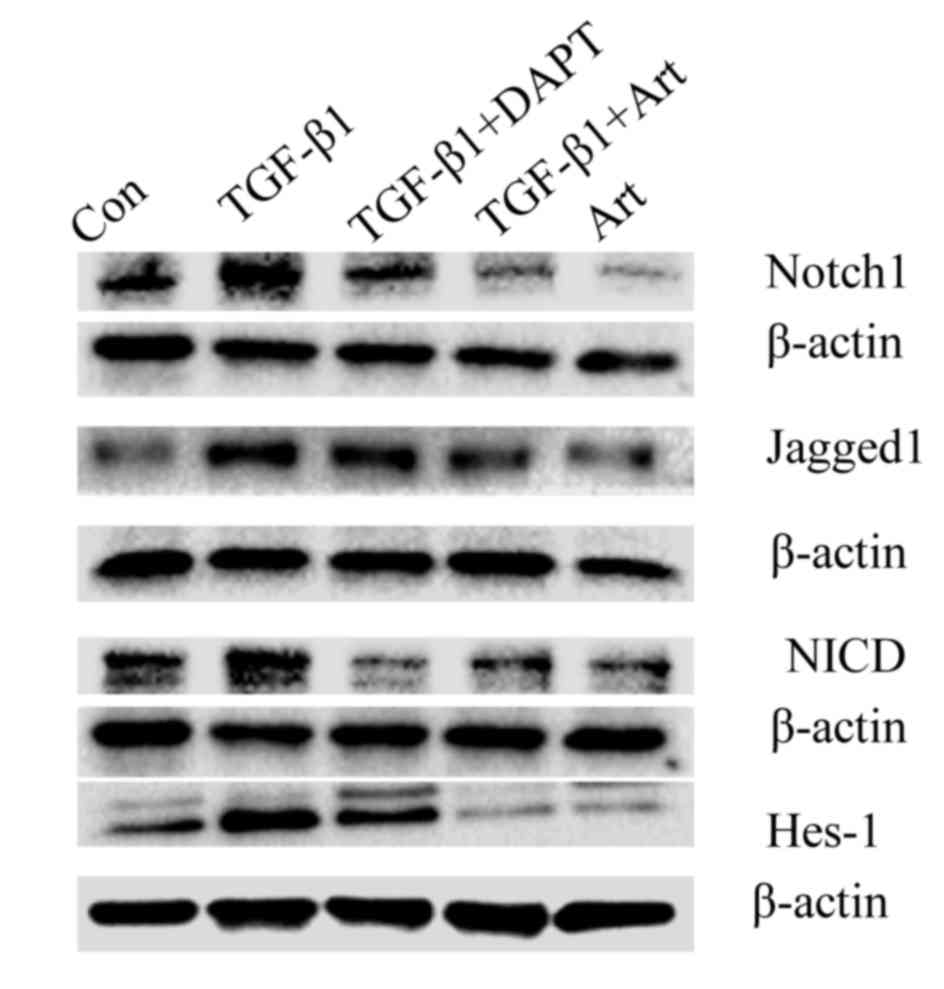
|
1
|
Puglisi S, Torrisi SE, Giuliano R,
Vindigni V and Vancheri C: What we know about the pathogenesis of
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med.
37:358–367. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim HJ, Perlman D and Tomic R: Natural
history of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Med. 109:661–670.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ,
Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, et
al: An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 183:788–824. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
King TE Jr, Pardo A and Selman M:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 378:1949–1961. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parker MW, Rossi D, Peterson M, Smith K,
Sikström K, White ES, Connett JE, Henke CA, Larsson O and Bitterman
PB: Fibrotic extracellular matrix activates a profibrotic positive
feedback loop. J Clin Invest. 124:1622–1635. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weiskirchen R and Tacke F: Liver fibrosis:
From pathogenesis to novel therapies. Dig Dis. 34:410–422. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pardo A, Cabrera S, Maldonado M and Selman
M: Role of matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. 17:232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou Y, Liao S, Zhang Z, Wang B and Wan L:
Astragalus injection attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis via down-regulating Jagged1/Notch1 in lungs. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 68:389–396. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu T, Hu B, Choi YY, Chung M, Ullenbruch
M, Yu H, Lowe JB and Phan SH: Notch1 signaling in FIZZ1 induction
of myofibroblast differentiation. Am J Pathol. 174:1745–1755. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reyburn H: New WHO guidelines for the
treatment of malaria. BMJ. 340:c26372010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang C, Xuan X, Yao W, Huang G and Jin J:
Anti-profibrotic effects of artesunate on bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in Sprague Dawley rats. Mol Med Rep.
12:1291–1297. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Huang G, Mo B and Wang C:
Artesunate modulates expression of matrix metalloproteinases and
their inhibitors as well as collagen-IV to attenuate pulmonary
fibrosis in rats. Genet Mol Res. 15:2016.
|
|
14
|
Hardie WD, Glasser SW and Hagood JS:
Emerging concepts in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Am J
Pathol. 175:3–16. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang K, Zhang YQ, Ai WB, Hu QT, Zhang QJ,
Wan LY, Wang XL, Liu CB and Wu JF: Hes1, an important gene for
activation of hepatic stellate cells, is regulated by Notch1 and
TGF-β/BMP signaling. World J Gastroenterol. 21:878–887. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu B, Wu Z, Bai D, Liu T, Ullenbruch MR
and Phan SH: Mesenchymal deficiency of Notch1 attenuates
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 185:3066–3075.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu Y, Liu W, Fang B, Gao S and Yan J:
Artesunate ameliorates hepatic fibrosis induced by bovine serum
albumin in rats through regulating matrix metalloproteinases. Eur J
Pharmacol. 744:1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang CM, Chen J, Jiang M, Xuan XP and Li
HX: Relationship between artesunate influence on the process of
TGF-beta1 induced alveolar epithelial cells transform into
mesenchymal cells and on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Yao Xue Xue
Bao. 49:142–147. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|