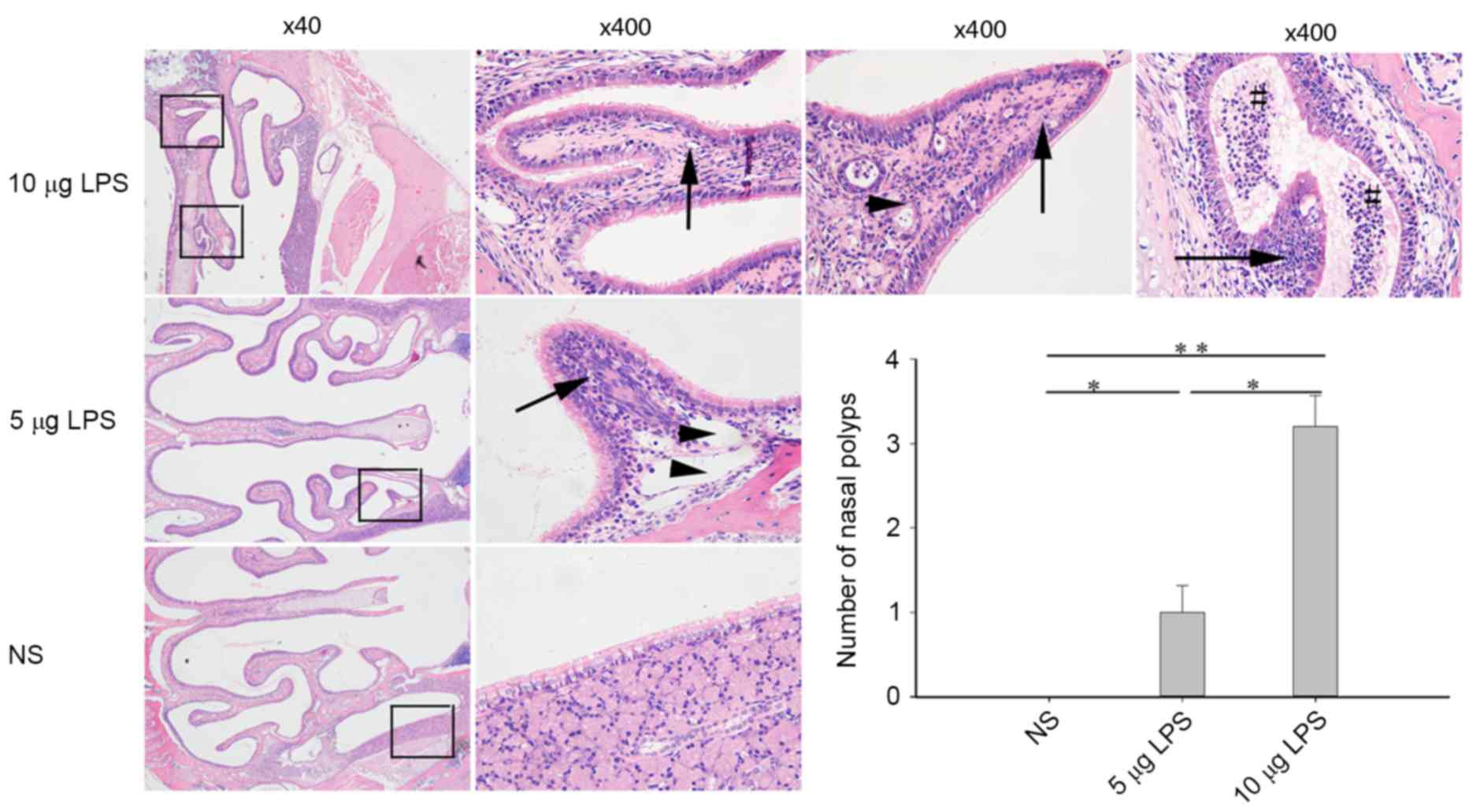
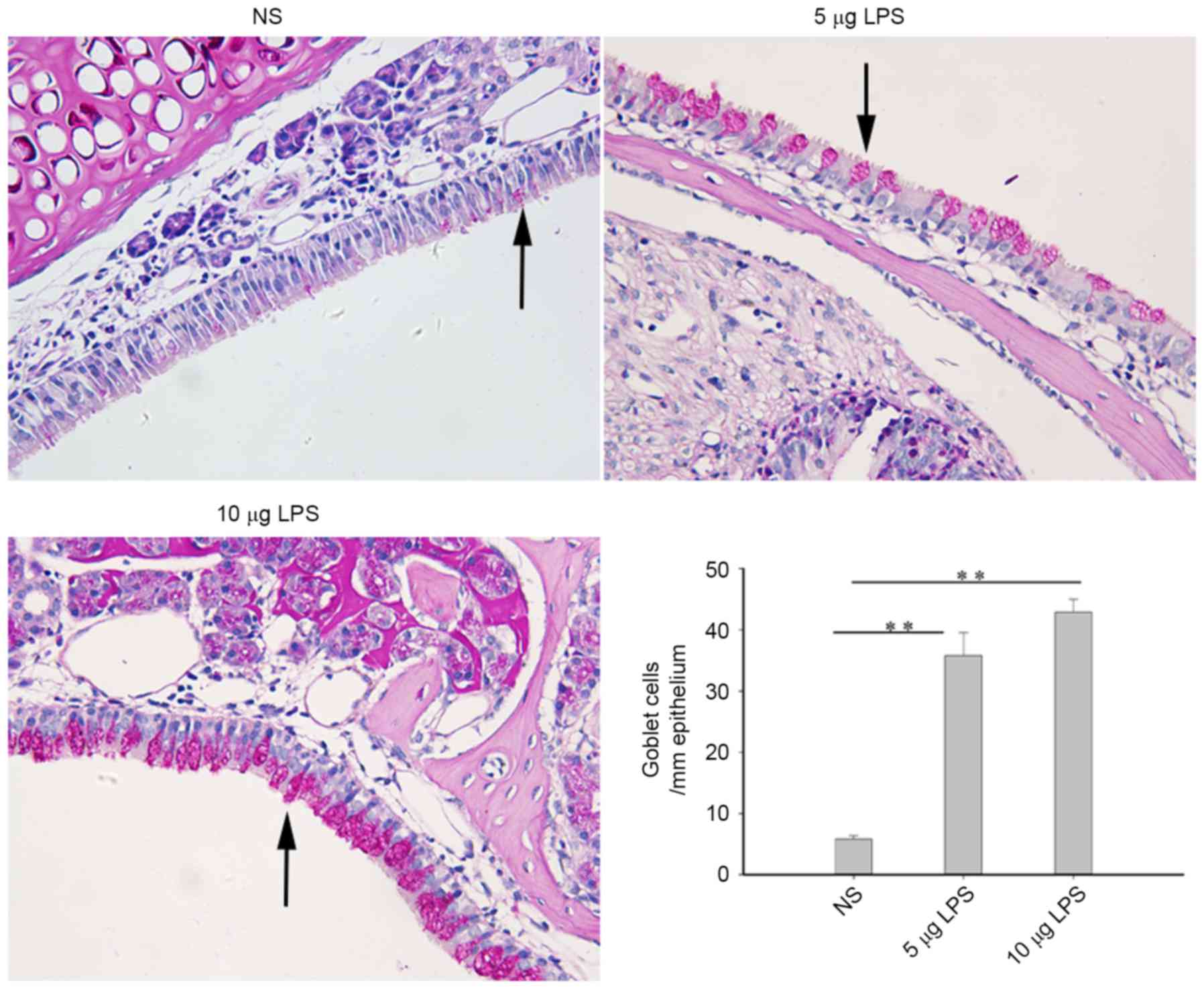
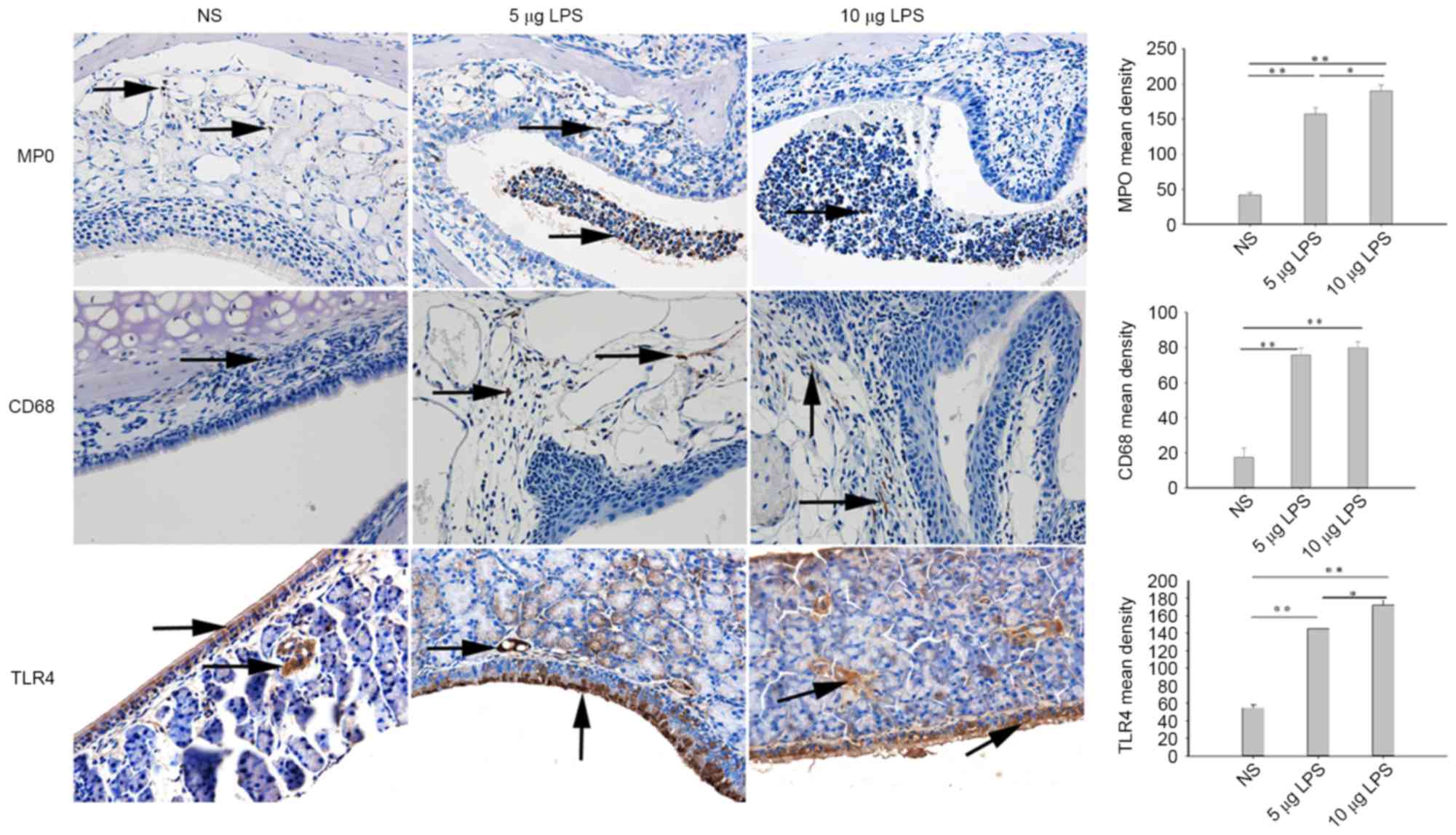
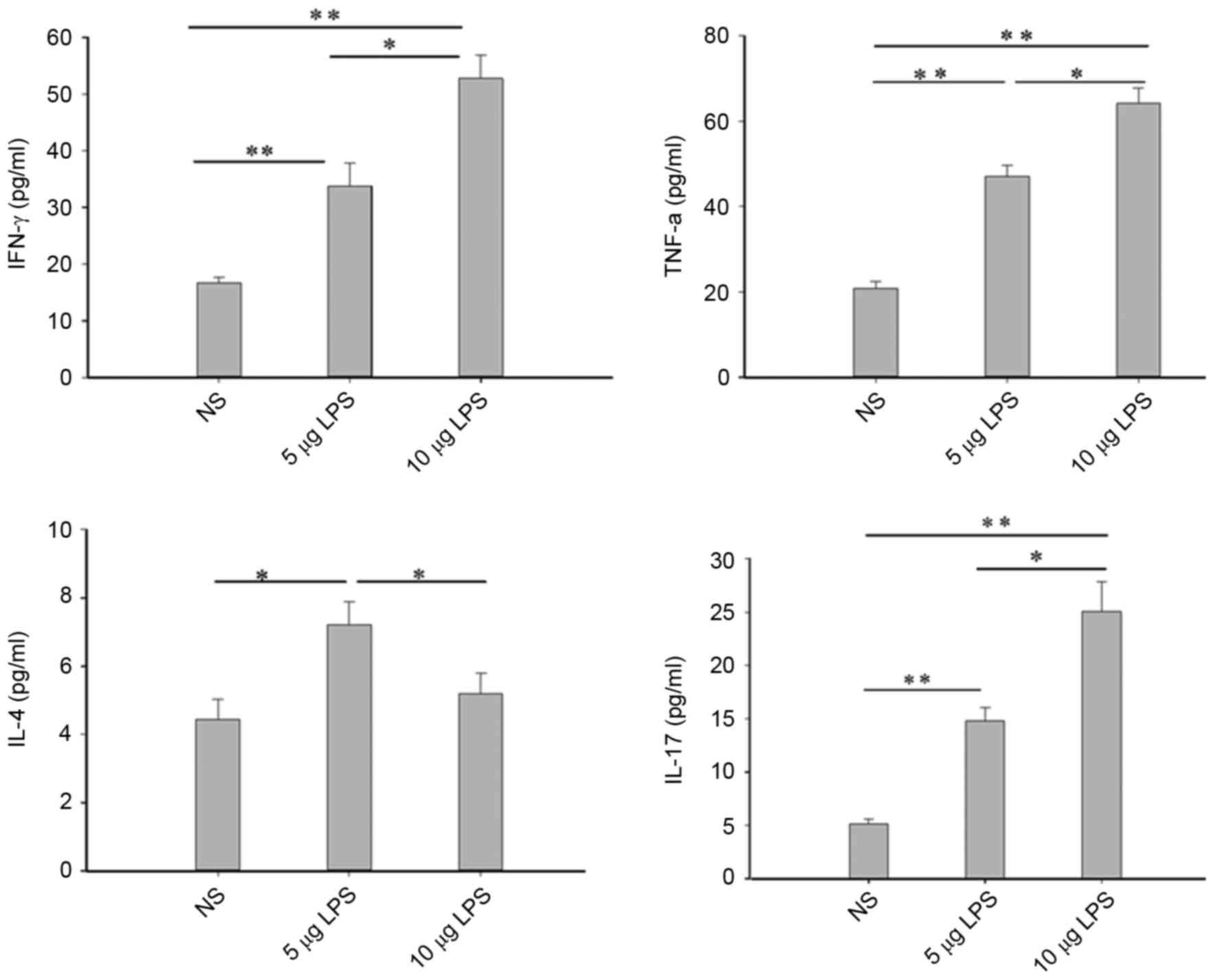
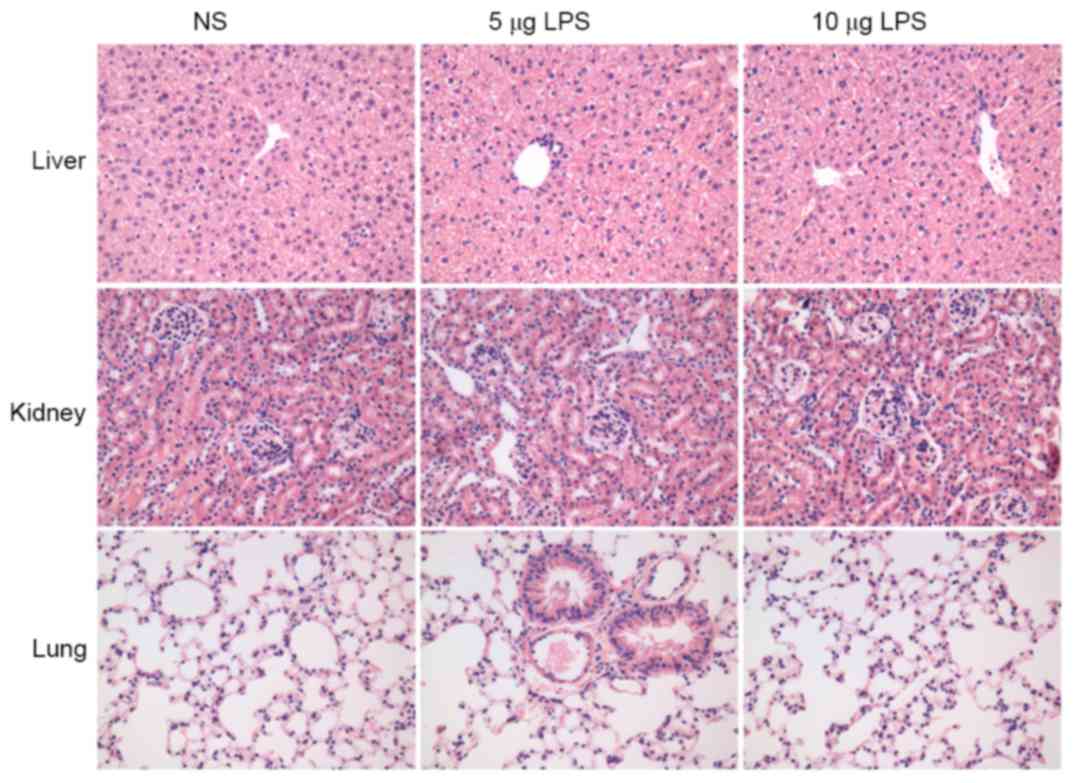
|
1
|
Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, Wang SB, You XJ,
Cui YH, Wang DY, Desrosiers M and Liu Z: Distinct immunopathologic
characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult
Chinese. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 124(478–484): 484.e1–e2. 2009.
|
|
2
|
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C,
Alobid I, Baroody F, Cohen N, Cervin A, Douglas R, Gevaert P, et
al: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps
2012. Rhinol Suppl. 23(3): p preceding table of contents. 1–298.
2012.
|
|
3
|
Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, Bai J, Fan Y, Xia
W, Luo Q, Zheng J, Wang H, Li Z, et al: Increased neutrophilia in
nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 129:1522–1528.e5. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smith KA and Rudmik L: Impact of continued
medical therapy in patients with refractory chronic rhinosinusitis.
Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 4:34–38. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim DW, Khalmuratova R, Hur DG, Jeon SY,
Kim SW, Shin HW, Lee CH and Rhee CS: Staphylococcus aureus
enterotoxin B contributes to induction of nasal polypoid lesions in
an allergic rhinosinusitis murine model. Am J Rhinol Allergy.
25:e255–e261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim DH, Jeon EJ, Park SN, Park KH, Park YS
and Yeo SW: Effects of a tumor necrosis factor-a antagonist on
experimentally induced rhinosinusitis. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011:3604572011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang H, Lu X, Cao PP, Chu Y, Long XB,
Zhang XH, You XJ, Cui YH and Liu Z: Histological and immunological
observations of bacterial and allergic chronic rhinosinusitis in
the mouse. Am J Rhinol. 22:343–348. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jin M, Gu Z, Bian Z, Yang J, Cao Z, Yu X
and Guo G: Developing a mouse model of acute bacterial
rhinosinusitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 268:857–861. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim SW, Kim JH, Jung MH, Hur DG, Lee HK,
Jeon SY and Kim DW: Periostin may play a protective role in the
development of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal
polyps in a mouse model. Laryngoscope. 123:1075–1081. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rylander R: Endotoxin in the
environment-exposure and effects. J Endotoxin Res. 8:241–252. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grindler D, Thomas C, Hall GS and Batra
PS: The role of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in refractory chronic
rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 24:200–204. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rombaux P, Collet S, Hamoir M, Eloy P,
Bertrand B, Jamart F and Gigi J: The role of nasal cavity
disinfection in the bacteriology of chronic sinusitis. Rhinology.
43:125–129. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang SB, Deng YQ, Ren J, Xiao BK, Liu Z
and Tao ZZ: Exogenous interleukin-10 alleviates allergic
inflammation but inhibits local interleukin-10 expression in a
mouse allergic rhinitis model. BMC Immunol. 15:92014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peterson S, Poposki JA, Nagarkar DR,
Chustz RT, Peters AT, Suh LA, Carter R, Norton J, Harris KE,
Grammer LC, et al: Increased expression of CC chemokine ligand 18
in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 129(119–127): e1–e9. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Potter PC and Pawankar R: Indications,
efficacy, and safety of intranasal corticosteriods in
rhinosinusitis. World Allergy Organ J. 5 Suppl 1:S14–S17. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mitroi M, Căpitănescu A, Georgescu CV,
Mogoantă CA, Popescu C, Georgescu M, Mitroi G and Ioniţă E:
Expression pattern of CK7 and CK20 in nasal polyps, at patients
with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Rom J Morphol
Embryol. 52 3 Suppl:S1051–S1057. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Dlugaszewska J, Leszczynska M, Lenkowski
M, Tatarska A, Pastusiak T and Szyfter W: The pathophysiological
role of bacterial biofilms in chronic sinusitis. Eur Arch
Otorhinolaryngol. 273:1989–1994. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rom D, Snidvongs K, Sacks PL, Dalgorf D,
Pratt E, Earls P, Sacks R and Harvey RJ: The impact of culturable
bacterial community on histopathology in chronic rhinosinusitis.
Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 4:29–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bhattacharyya N and Kepnes LJ: The
microbiology of recurrent rhinosinusitis after endoscopic sinus
surgery. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 125:1117–1120. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Curran CS, Demick KP and Mansfield JM:
Lactoferrin activates macrophages via TLR4-dependent and
-independent signaling pathways. Cell Immunol. 242:23–30. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Inubushi T, Kawazoe A, Miyauchi M, Kudo Y,
Ao M, Ishikado A, Makino T and Takata T: Molecular mechanisms of
the inhibitory effects of bovine lactoferrin on
lipopolysaccharide-mediated osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem.
287:23527–23536. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guha M and Mackman N: LPS induction of
gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal. 13:85–94. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsukamoto H, Fukudome K, Takao S,
Tsuneyoshi N and Kimoto M: Lipopolysaccharide-binding
protein-mediated Toll-like receptor 4 dimerization enables rapid
signal transduction against lipopolysaccharide stimulation on
membrane-associated CD14-expressing cells. Int Immunol. 22:271–280.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tanno D, Akahori Y, Toyama M, Sato K, Kudo
D, Abe Y, Miyasaka T, Yamamoto H, Ishii K, Kanno E, et al:
Involvement of Gr-1 dull+ cells in the production of TNF-α and
IL-17 and exacerbated systemic inflammatory response caused by
lipopolysaccharide. Inflammation. 37:186–195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cao AT, Yao S, Stefka AT, Liu Z, Qin H,
Liu H, Evans-Marin HL, Elson CO, Nagler CR and Cong Y: TLR4
regulates IFN-γ and IL-17 production by both thymic and induced
Foxp3+ Tregs during intestinal inflammation. J Leukoc Biol.
96:895–905. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Barboza R, Câmara NO, Gomes E, Sá-Nunes A,
Florsheim E, Mirotti L, Labrada A, Alcântara-Neves NM and Russo M:
Endotoxin exposure during sensitization to blomia tropicalis
allergens shifts TH2 immunity towards a TH17-mediated airway
neutrophilic inflammation: Role of TLR4 and TLR2. PLoS One.
8:e671152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elass-Rochard E, Legrand D, Salmon V,
Roseanu A, Trif M, Tobias PS, Mazurier J and Spik G: Lactoferrin
inhibits the endotoxin interaction with CD14 by competition with
the lipopolysaccharide-binding protein. Infect Immun. 66:486–491.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qin H, Holdbrooks AT, Liu Y, Reynolds SL,
Yanagisawa LL and Benveniste EN: SOCS3 deficiency promotes M1
macrophage polarization and inflammation. J Immunol. 189:3439–3448.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Al Faraj A, Sultana Shaik A, Pureza MA,
Alnafea M and Halwani R: Preferential macrophage recruitment and
polarization in LPS-induced animal model for COPD: Noninvasive
tracking using MRI. PLoS One. 9:e908292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dong L, Li H, Wang S and Li Y: Different
doses of lipopolysaccharides regulate the lung inflammation of
asthmatic mice via TLR4 pathway in alveolar macrophages. J Asthma.
46:229–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim YK, Oh SY, Jeon SG, Park HW, Lee SY,
Chun EY, Bang B, Lee HS, Oh MH, Kim YS, et al: Airway exposure
levels of lipopolysaccharide determine type 1 versus type 2
experimental asthma. J Immunol. 178:5375–5382. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee S, Hwang HJ and Kim Y: Modeling the
role of TGF-β in regulation of the Th17 phenotype in the LPS-driven
immune system. Bull Math Biol. 76:1045–1080. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Q, Wang CS, Han DM, Sy C, Huang Q,
Sun Y, Fan EZ, Li Y and Zhou B: Differential expression of
Toll-like receptor pathway genes in chronic rhinosinusitis with or
without nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol. 133:165–173. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tengroth L, Millrud CR, Kvarnhammar AM,
Kumlien Georén S, Latif L and Cardell LO: Functional effects of
Toll-like receptor (TLR)3, 7, 9, RIG-I and MDA-5 stimulation in
nasal epithelial cells. PLoS One. 9:e982392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|