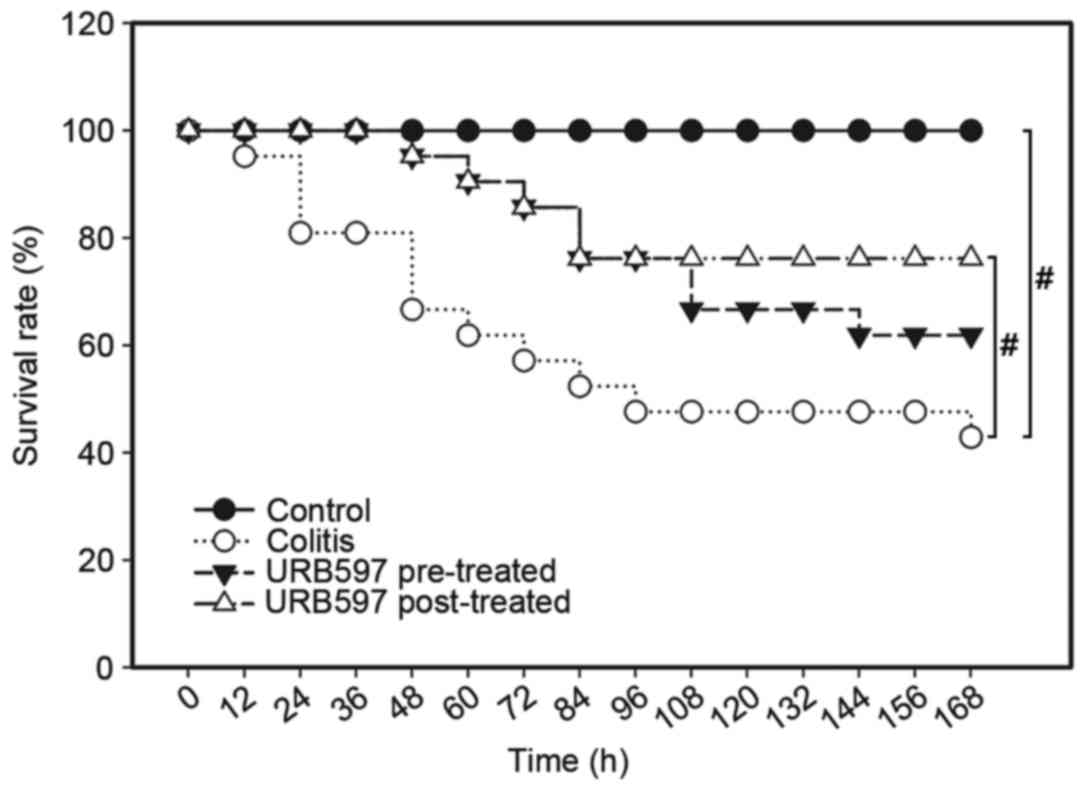
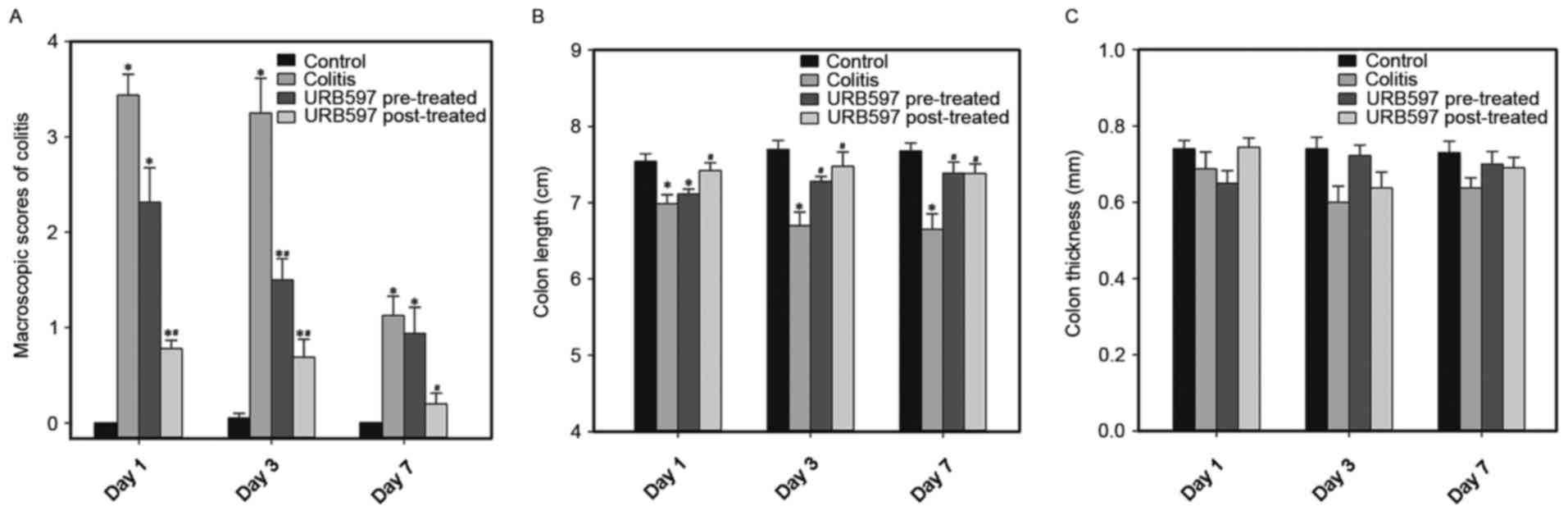
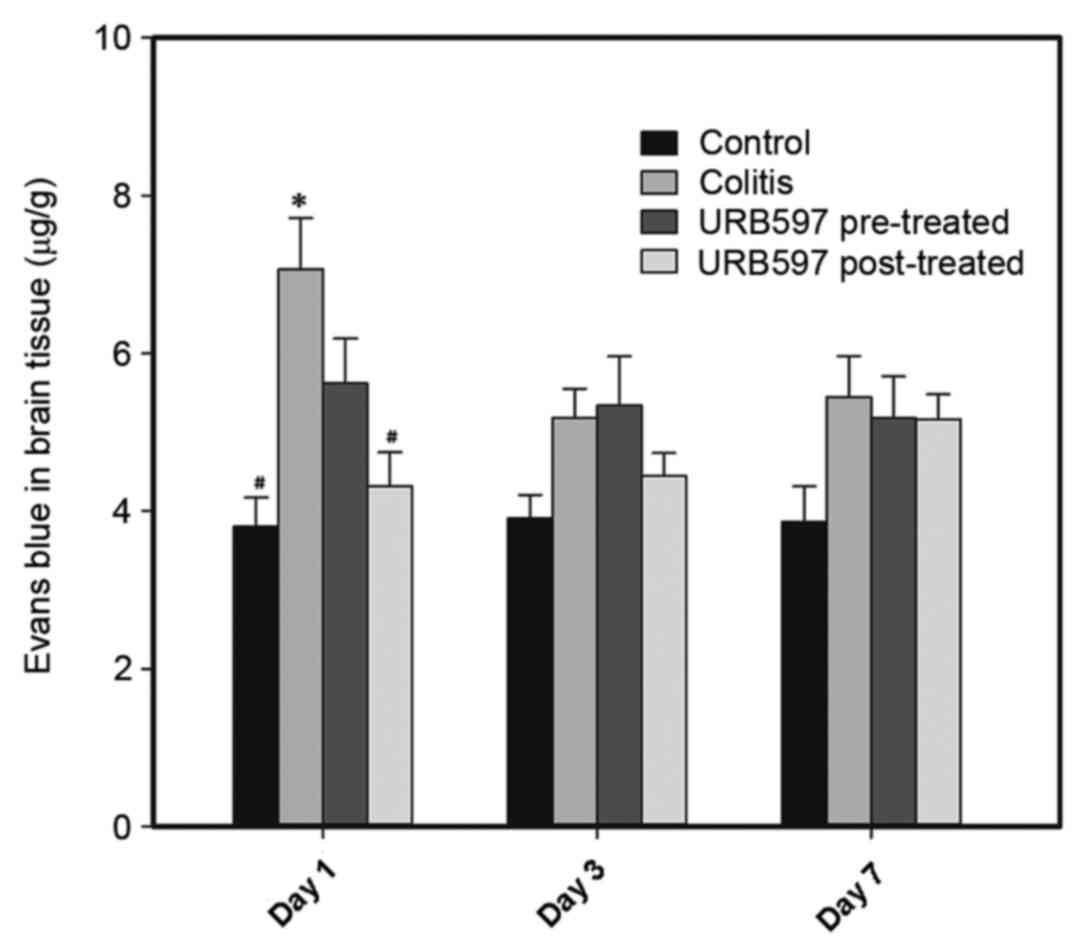
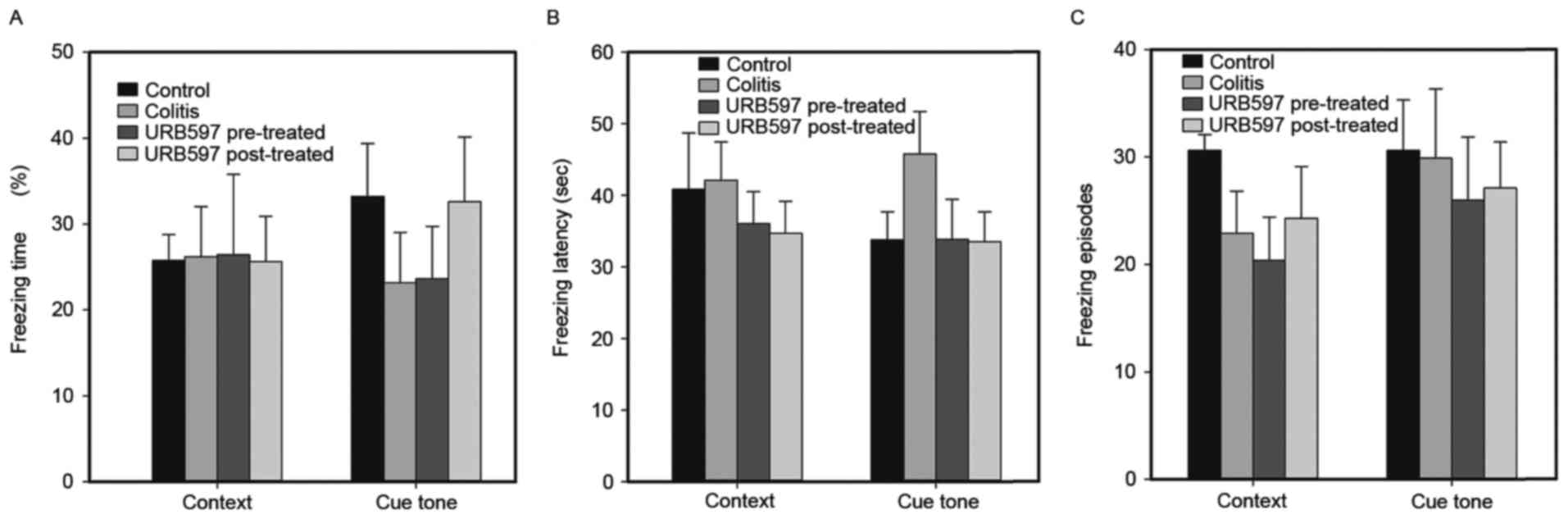
|
1
|
Di Marzo V, Bifulco M and de Petrocellis:
The endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic exploitation. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 3:771–784. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Piomelli D, Giuffrida A, Calignano A and
de Fonseca Rodríguez F: The endocannabinoid system as a target for
therapeutic drugs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 21:218–224. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pertwee RG: Targeting the endocannabinoid
system with cannabinoid receptor agonists: Pharmacological
strategies and therapeutic possibilities. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B
Biol Sci. 367:3353–3363. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Di Marzo V: The endocannabinoid system:
Its general strategy of action, tools for its pharmacological
manipulation and potential therapeutic exploitation. Pharmacol Res.
60:77–84. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maccarrone M, Bari M, Battista N and
Finazzi-Agrò A: Endocannabinoid degradation, endotoxic shock and
inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 1:53–63. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Marzo V and Piscitelli F: Gut feelings
about the endocannabinoid system. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
23:391–398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alhouayek M and Muccioli GG: The
endocannabinoid system in inflammatory bowel diseases: From
pathophysiology to therapeutic opportunity. Trends Mol Med.
18:615–625. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nasser Y, Bashashati M and Andrews CN:
Toward modulation of the endocannabinoid system for treatment of
gastrointestinal disease: FAAHster but not ‘higher’.
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 26:447–454. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Izzo AA and Sharkey KA: Cannabinoids and
the gut: New developments and emerging concepts. Pharmacol Ther.
126:21–38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ravikoff Allegretti J, Courtwright A,
Lucci M, Korzenik JR and Levine J: Marijuana use patterns among
patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
19:2809–2814. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Engel MA, Kellermann CA, Burnat G, Hahn
EG, Rau T and Konturek PC: Mice lacking cannabinoid CB1-,
CB2-receptors or both receptors show increased susceptibility to
trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis. J Physiol
Pharmacol. 61:89–97. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alhouayek M, Lambert DM, Delzenne NM, Cani
PD and Muccioli GG: Increasing endogenous 2-arachidonoylglycerol
levels counteracts colitis and related systemic inflammation. FASEB
J. 25:2711–2721. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Storr MA, Keenan CM, Emmerdinger D, Zhang
H, Yüce B, Sibaev A, Massa F, Buckley NE, Lutz B, Göke B, et al:
Targeting endocannabinoid degradation protects against experimental
colitis in mice: Involvement of CB1 and CB2 receptors. J Mol Med
(Berl). 86:925–936. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Downer EJ: Cannabinoids and innate
immunity: Taking a toll on neuroinflammation.
ScientificWorldJournal. 11:855–865. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fishbein-Kaminietsky M, Gafni M and Sarne
Y: Ultralow doses of cannabinoid drugs protect the mouse brain from
inflammation-induced cognitive damage. J Neurosci Res.
92:1669–1677. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sardinha J, Kelly ME, Zhou J and Lehmann
C: Experimental cannabinoid 2 receptor-mediated immune modulation
in sepsis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:9786782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dowie MJ, Howard ML, Nicholson LF, Faull
RL, Hannan AJ and Glass M: Behavioural and molecular consequences
of chronic cannabinoid treatment in Huntington's disease transgenic
mice. Neuroscience. 170:324–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murphy N, Cowley TR, Blau CW, Dempsey CN,
Noonan J, Gowran A, Tanveer R, Olango WM, Finn DP, Campbell VA and
Lynch MA: The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 exerts
anti-inflammatory effects in hippocampus of aged rats and restores
an age-related deficit in long-term potentiation. J
Neuroinflammation. 9:792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Henry RJ, Kerr DM, Finn DP and Roche M:
FAAH-mediated modulation of TLR3-induced neuroinflammation in the
rat hippocampus. J Neuroimmunol. 276:126–134. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Katz PS, Sulzer JK, Impastato RA, Teng SX,
Rogers EK and Molina PE: Endocannabinoid degradation inhibition
improves neurobehavioral function, blood brain barrier integrity,
and neuroinflammation following mild traumatic brain injury. J
Neurotrauma. 32:297–306. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fichna J, Dicay M, Lewellyn K, Janecka A,
Zjawiony JK, MacNaughton WK and Storr MA: Salvinorin A has
antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects in experimental models
of colitis in mice mediated by KOR and CB1 receptors. Inflamm Bowel
Dis. 18:1137–1145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wirtz S and Neurath MF: Mouse models of
inflammatory bowel disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 59:1073–1083. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shoji H, Takao K, Hattori S and Miyakawa
T: Contextual and cued fear conditioning test using a video
analyzing system in mice. J Vis Exp. 85:e508712014.doi:
10.3791/50871.
|
|
24
|
Lomazzo E, Bindila L, Remmers F, Lerner R,
Schwitter C, Hoheisel U and Lutz B: Therapeutic potential of
inhibitors of endocannabinoid degradation for the treatment of
stress-related hyperalgesia in an animal model of chronic pain.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 40:488–501. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vendel E and de Lange EC: Functions of the
CB1 and CB 2 receptors in neuroprotection at the level of the
blood-brain barrier. Neuromolecular Med. 16:620–642. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|