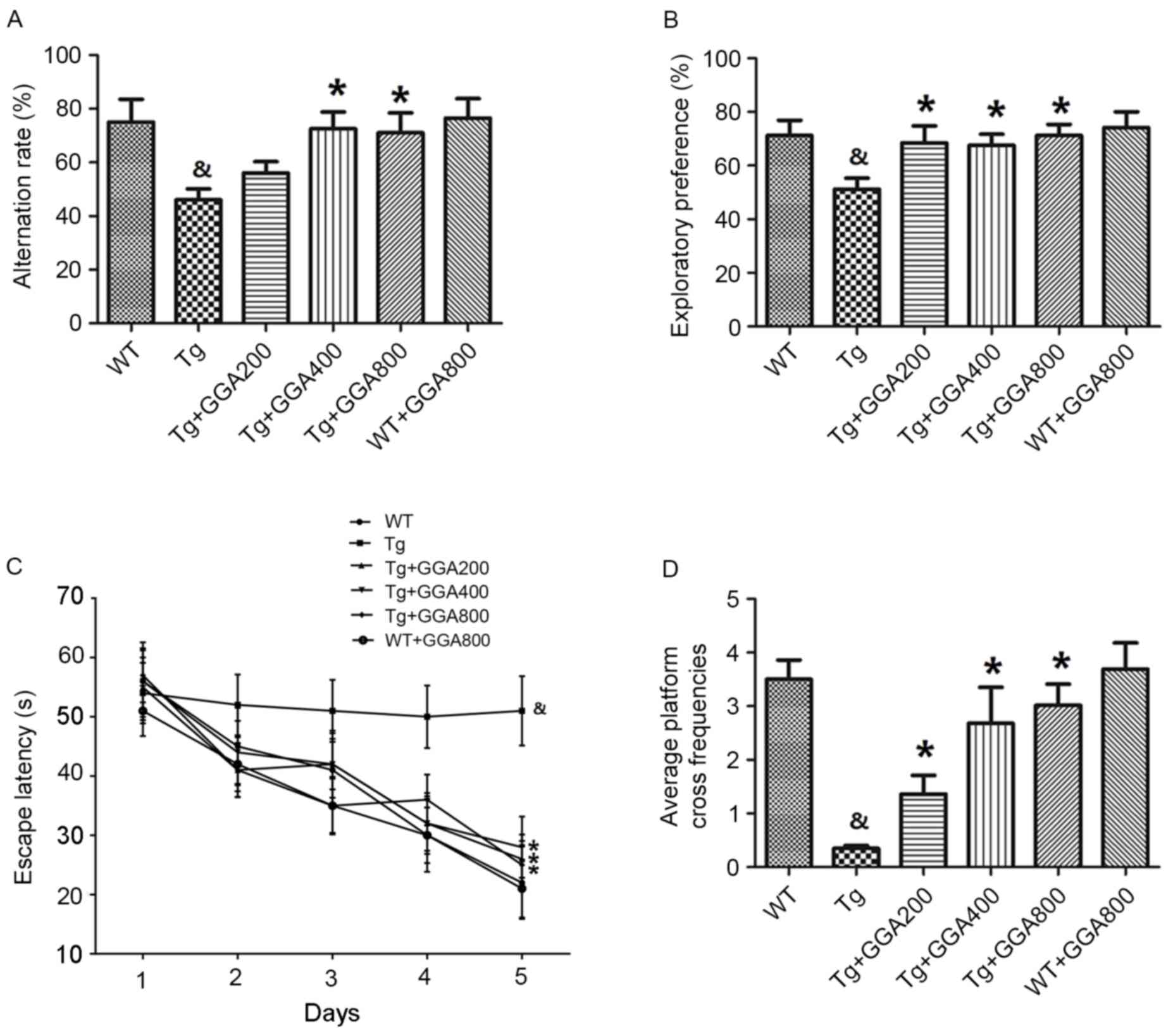
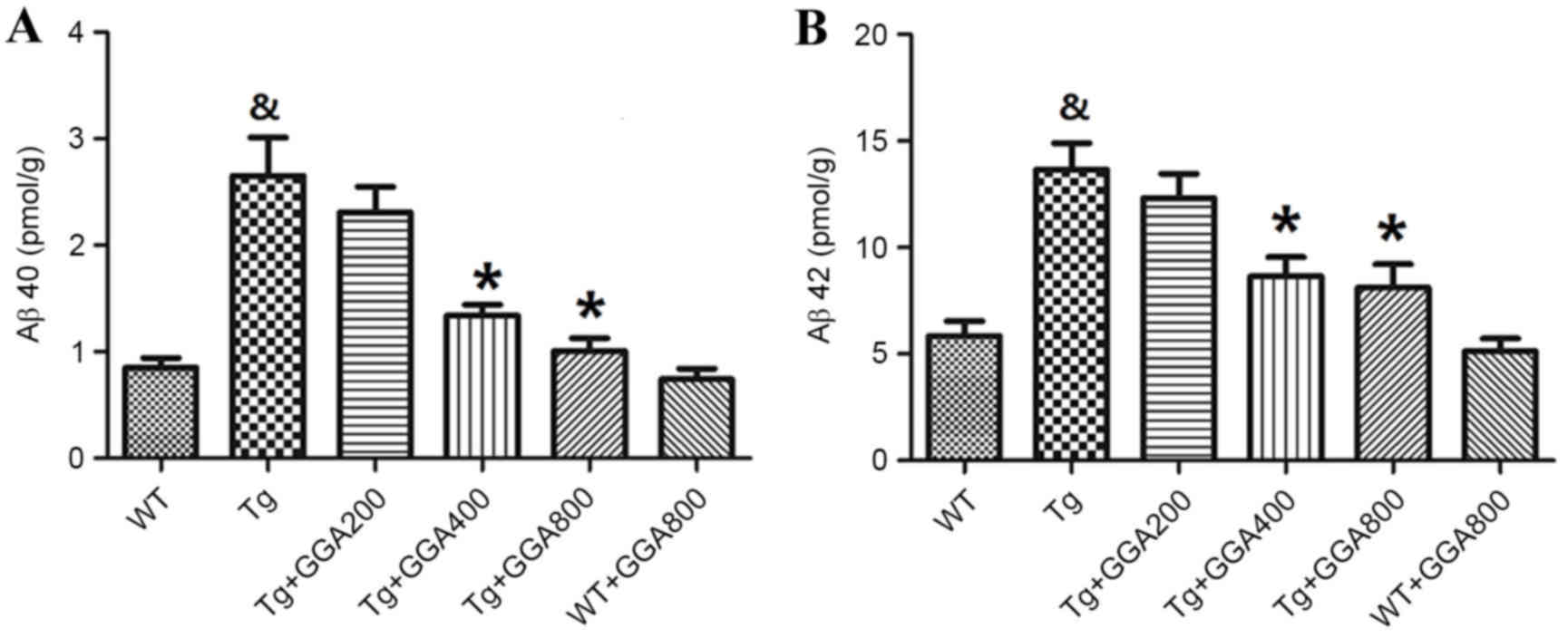
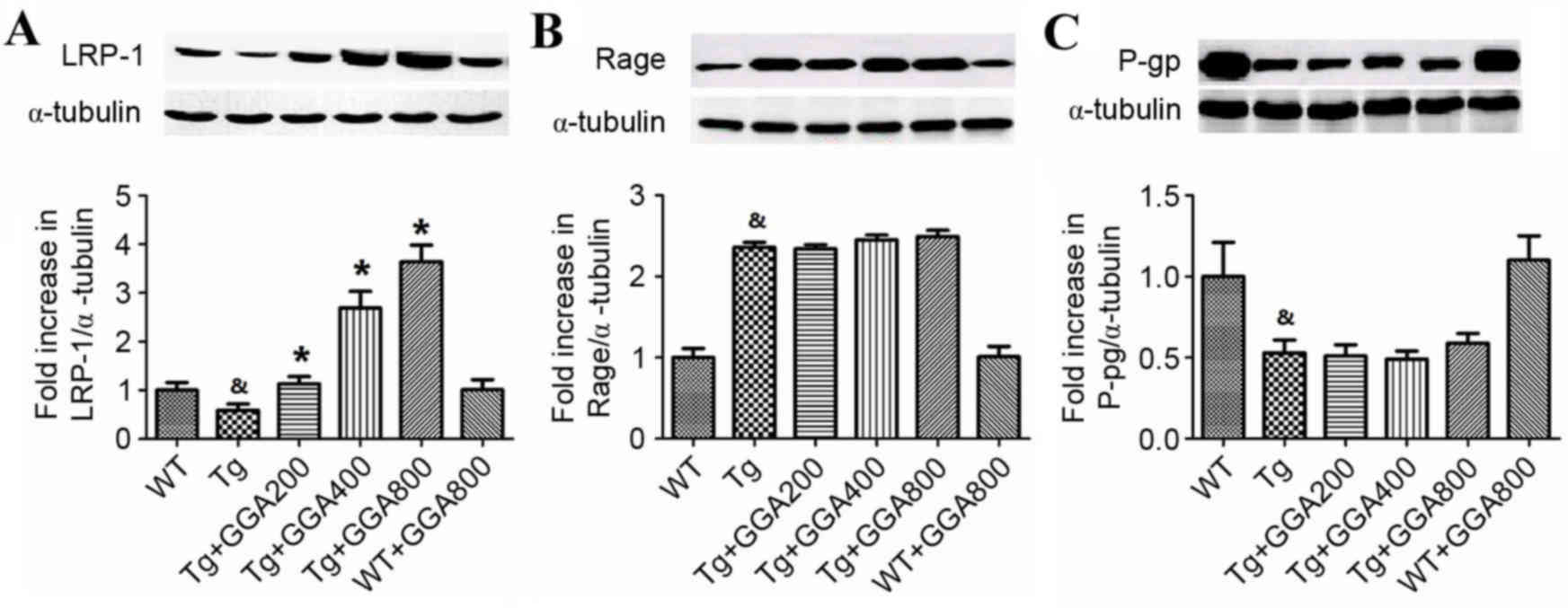
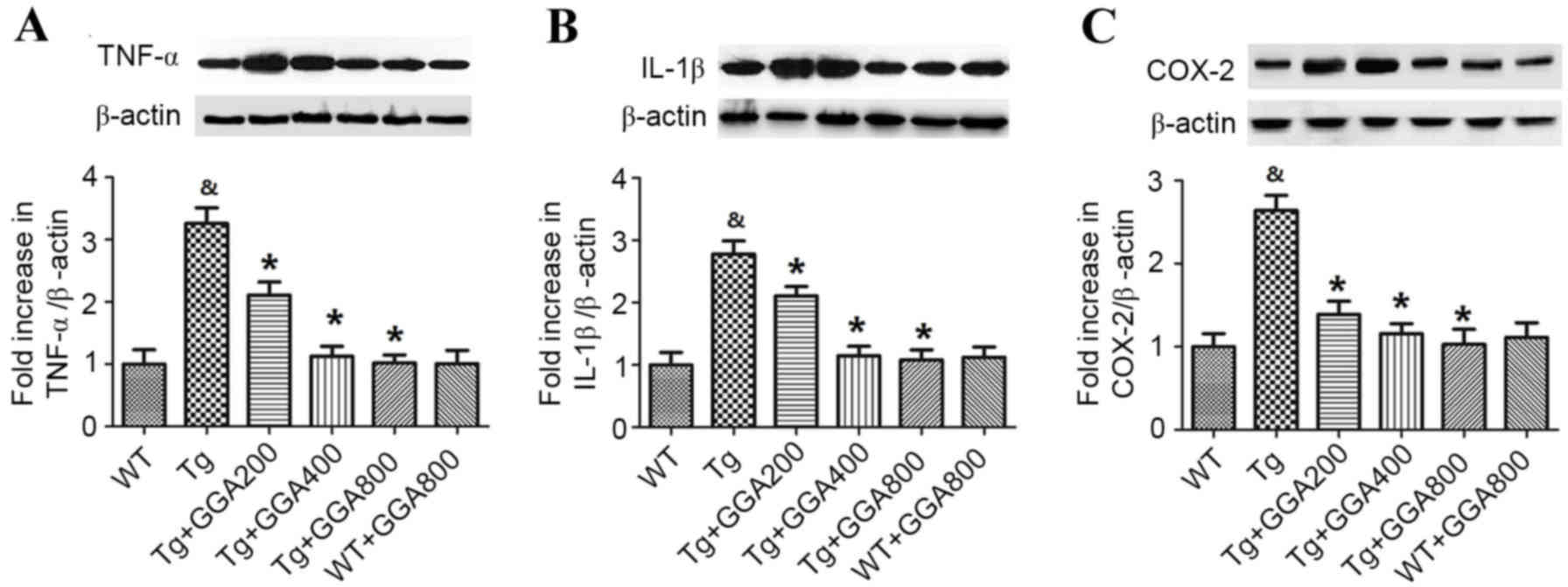
|
1
|
Katzman R: The prevalence and malignancy
of Alzheimer disease: A Major Killer. Arch Neurol. 33:217–218.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K
and Arrighi HM: Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer's
disease. Alzheimers Dement. 3:186–191. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman
R, Price D and Stadlan EM: Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's
disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices
of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on
Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 34:939–944. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hardy J and Selkoe DJ: The amyloid
hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: Progress and problems on the
road to therapeutics. Science. 297:353–356. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Whitwell JL, Dickson DW, Murray ME,
Weigand SD, Tosakulwong N, Senjem ML, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Parisi
JE, Petersen RC, et al: Neuroimaging correlates of pathologically
defined subtypes of Alzheimer's disease: A case-control study.
Lancet Neurol. 11:868–877. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kurz A and Perneczky R: Amyloid clearance
as a treatment target against Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers
Dis. 24 Suppl 2:S61–S73. 2011.
|
|
7
|
Haass C and Selkoe DJ: Soluble protein
oligomers in neurodegeneration: Lessons from the Alzheimer's
amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:101–112. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tanzi RE, Moir RD and Wagner SL: Clearance
of Alzheimer's Aβ Peptide: The Many Roads to Perdition. Neuron.
43:605–608. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoon SS and Jo SA: Mechanisms of amyloid-β
peptide clearance: Potential therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's
disease. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 20:245–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zlokovic BV: Clearing amyloid through the
blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem. 89:807–811. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tuppo EE and Arias HR: The role of
inflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
37:289–305. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Selkoe DJ: Cell biology of protein
misfolding: The examples of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
Nat Cell Biol. 6:1054–1061. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Forloni G, Terreni L, Fogliarino S,
Invernizzi R, Assini A, Ribizzi G, Negro A, Calabrese E, Volonté
MA, Mariani C, et al: Protein misfolding in Alzheimer's and
Parkinson's disease: Genetics and molecular mechanisms. Neurobiol
Aging. 23:957–976. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liberek K, Lewandowska A and Zietkiewicz
S: Chaperones in control of protein disaggregation. EMBO J.
27:328–335. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meriin AB and Sherman MY: Role of
molecular chaperones in neurodegenerative disorders. Int J
Hyperthermia. 21:403–419. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wyttenbach A and Arrigo AP: The role of
heat shock proteins during neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's,
Parkinson's and Huntington's Disease. Heat Shock Proteins in Neural
Cells. 81–99. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bobkova NV, Garbuz DG, Nesterova I,
Medvinskaya N, Samokhin A, Alexandrova I, Yashin V, Karpov V,
Kukharsky MS, Ninkina NN, et al: Therapeutic effect of exogenous
hsp70 in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis.
38:425–435. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sinadinos C, Quraishe S, Sealey M, Samson
PB, Mudher A and Wyttenbach A: Low endogenous and chemical induced
heat shock protein induction in a 0N3Rtau-expressing drosophila
larval model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis.
33:1117–1133. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hoshino T, Murao N, Namba T, Takehara M,
Adachi H, Katsuno M, Sobue G, Matsushima T, Suzuki T and Mizushima
T: Suppression of Alzheimer's disease-related phenotypes by
expression of heat shock protein 70 in mice. J Neurosci.
31:5225–5234. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mikuriya T, Sugahara K, Takemoto T, Tanaka
K, Takeno K, Shimogori H, Nakai A and Yamashita H:
Geranylgeranylacetone, a heat shock protein inducer, prevents
acoustic injury in the guinea pig. Brain Res. 1065:107–114. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jankowsky JL, Fadale DJ, Anderson J, Xu
GM, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Lee MK, Younkin LH, Wagner
SL, et al: Mutant presenilins specifically elevate the levels of
the 42 residue beta-amyloid peptide in vivo: Evidence for
augmentation of a 42-specific gamma secretase. Hum Mol Genet.
13:159–170. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Katsuno M, Sang CH, Adachi H, Minamiyama
M, Waza M, Tanaka F, Doyu M and Sobue G: Pharmacological induction
of heat-shock proteins alleviates polyglutamine-mediated motor
neuron disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:pp. 16801–16806. 2005,
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bromley-Brits K, Deng Y and Song W: Morris
water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer's
disease model mice. J Vis Exp: pii. e29202011.
|
|
24
|
Hughes RN: The value of spontaneous
alternation behavior (SAB) as a test of retention in
pharmacological investigations of memory. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
28:497–505. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Broadbent NJ, Gaskin S, Squire LR and
Clark RE: Object recognition memory and the rodent hippocampus.
Learn Mem. 17:5–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Iwata N, Mizukami H, Shirotani K, Takaki
Y, Muramatsu S, Lu B, Gerard NP, Gerard C, Ozawa K and Saido TC:
Presynaptic localization of neprilysin contributes to efficient
clearance of amyloid-beta peptide in mouse brain. J Neurosci.
24:991–998. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Munoz L and Ammit AJ: Targeting p38 MAPK
pathway for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Neuropharmacology. 58:561–568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Adachi H, Katsuno M, Waz M, Minamiyam M,
Tanak F and Sobue G: Heat shock proteins in neurodegenerative
diseases: Pathogenic roles and therapeutic implications. Int J
Hyperthermia. 25:647–654. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hoshino T, Suzuki K, Matsushima T,
Yamakawa N, Suzuki T and Mizushima T: Suppression of Alzheimer's
disease-related phenotypes by geranylgeranylacetone in mice. PLoS
One. 8:e763062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Seno K, Joh T, Yokoyama Y and Itoh M: Role
of mucus in gastric mucosal injury induced by local
ischemia/reperfusion. J Lab Clin Med. 126:287–293. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Murakami M, Oketani K, Fujisaki H,
Wakabayashi T and Ohgo T: Antiulcer effect of
geranylgeranylacetone, a new acyclic polyisoprenoid on
experimentally induced gastric and duodenal ulcers in rats.
Arzneimittelforschung. 31:799–804. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Donahue JE, Flaherty SL, Johanson CE,
Duncan JA III, Silverberg GD, Miller MC, Tavares R, Yang W, Wu Q,
Sabo E, et al: RAGE, LRP-1, and amyloid-beta protein in Alzheimer's
disease. Acta Neuropathol. 112:405–415. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Weller RO, Subash M, Preston SD, Mazanti I
and Carare RO: SYMPOSIUM: Clearance of Aβ from the brain in
Alzheimer's disease: Perivascular drainage of amyloid-β peptides
from the brain and its failure in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and
Alzheimer's disease. Brain Pathol. 18:253–266. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Finch CE and Morgan TE: Systemic
inflammation, infection, ApoE alleles, and Alzheimer disease: A
position paper. Curr Alzheimer Res. 4:185–189. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Griffin WS and Mrak RE: Interleukin-1 in
the genesis and progression of and risk for development of neuronal
degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. J Leukoc Biol. 72:233–238.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bona DD, Plaia A, Vasto S, Cavallone L,
Lescai F, Franceschi C, Licastro F, Colonna-Romano G, Lio D,
Candore G and Caruso C: Association between the interleukin-1beta
polymorphisms and Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Brain Res Rev. 59:155–163. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Deane R, Sagare A and Zlokovic BV: The
role of the cell Surface LRP and Soluble LRP in blood-brain barrier
abeta clearance in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Pharm Des.
14:1601–1605. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jacquier-Sarlin MR, Fuller K, Dinh-Xuan
AT, Richard MJ and Polla BS: Protective effects of the hsp70 in
inflammation. Experimentia. 50:1031–1038. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Colombo A, Bastone A, Ploia C, Sclip A,
Salmona M, Forloni G and Borsello T: JNK regulates APP cleavage and
degradation in a model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis.
33:518–525. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Webber KM, Smith MA, Lee HG, Harris PL,
Moreira P, Perry G and Zhu X: Mitogen- and stress-activated protein
kinase 1: Convergence of the ERK and p38 pathways in Alzheimer's
disease. J Neurosci Res. 79:554–560. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Roux PP and Blenis J: ERK and p38
MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with
diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 68:320–344.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sarina, Yagi Y, Nakano O, Hashimoto T,
Kimura K, Asakawa Y, Zhong M, Narimatsu S and Gohda E: Induction of
neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells by artemisinin through activation
of ERK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Brain Res. 1490:61–71.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lenka M and Alaina JA: Targeting p38 MAPK
pathway for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Neuropharmacology. 58:561–568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Khan TK and Alkon DL: Alzheimer's
disease-specific alterations of the Erk1/Erk2 phosphorylation
ratio. Journal. 2009.
|