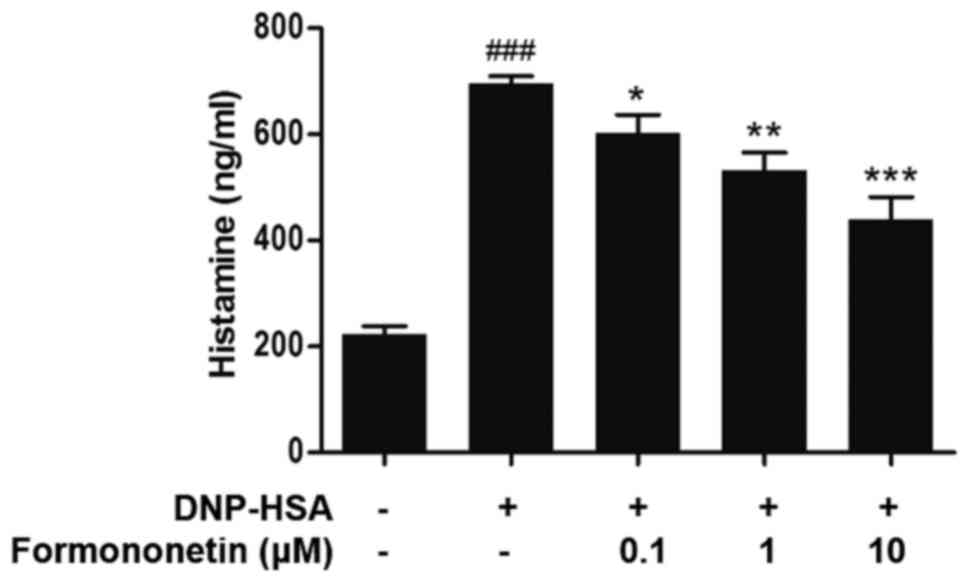
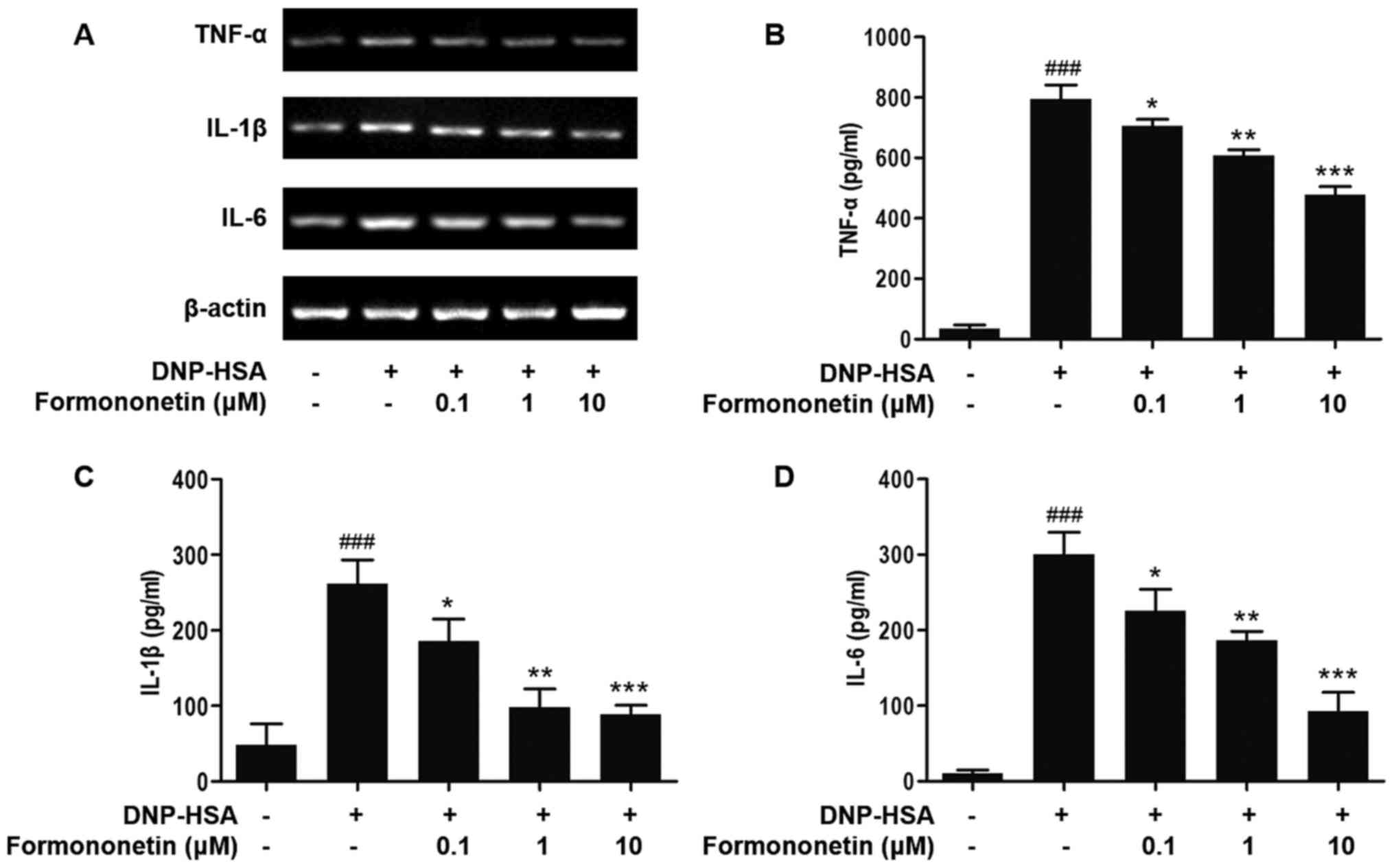
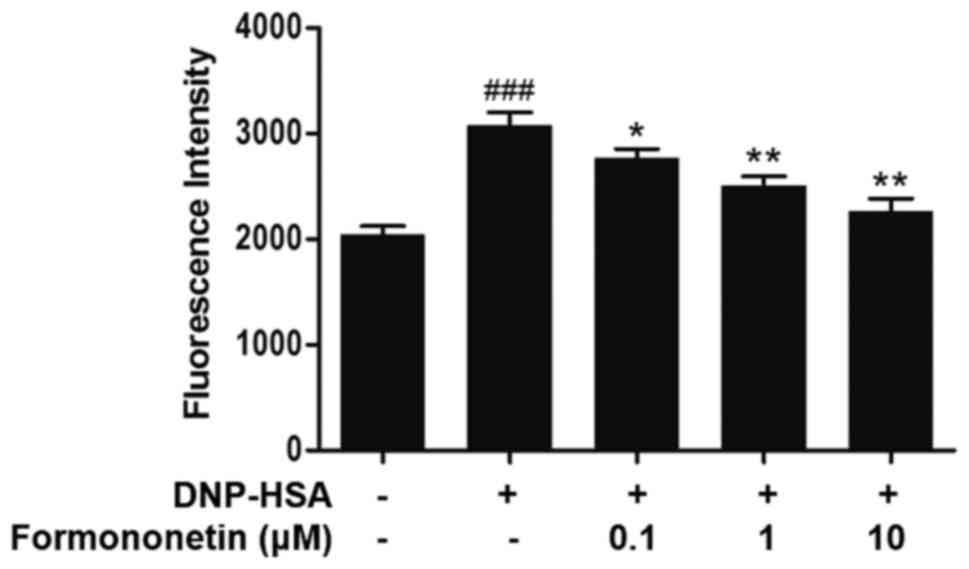
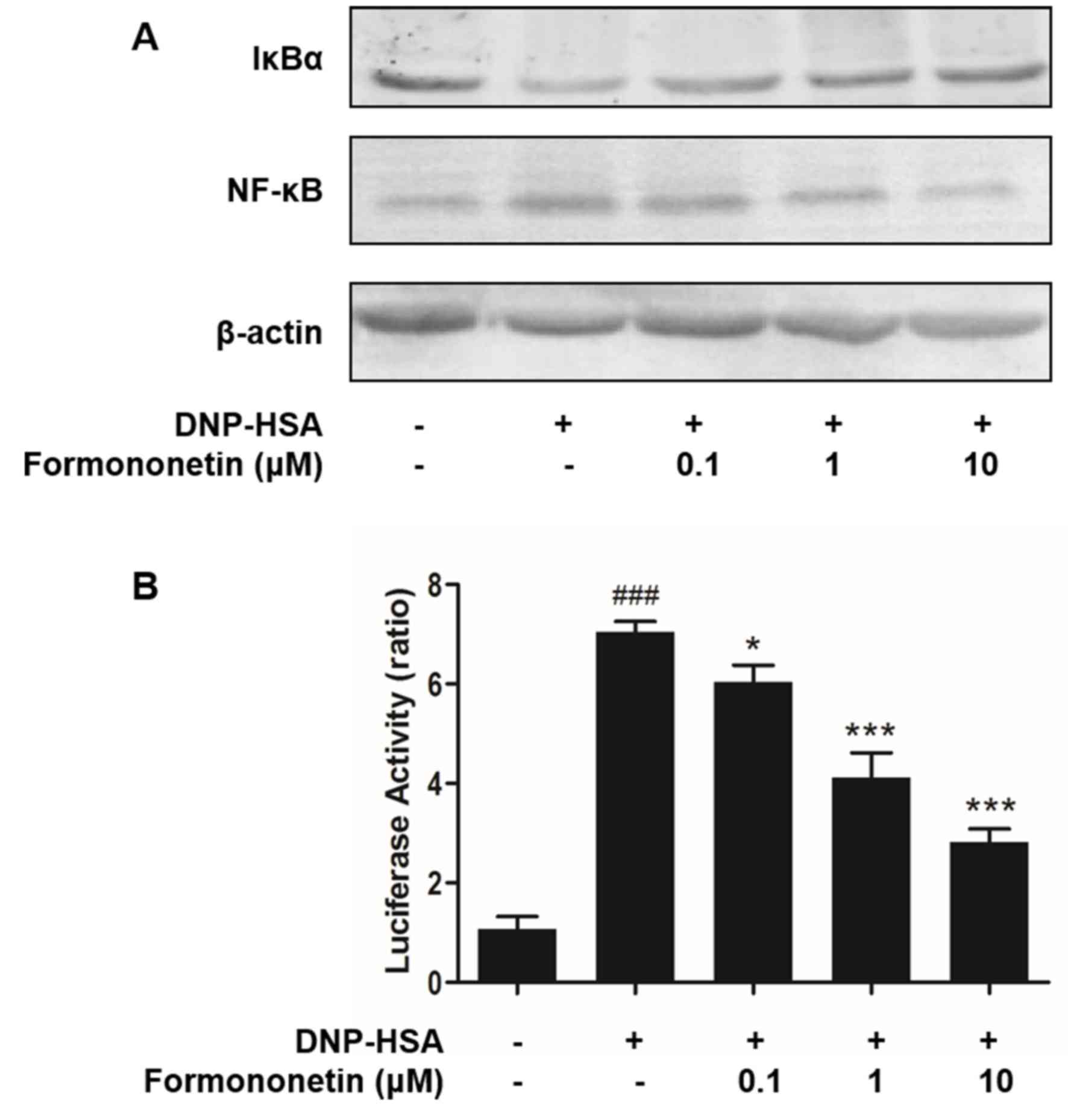
|
1
|
Beghdadi W, Madjene LC, Benhamou M,
Charles N, Gautier G, Launay P and Blank U: Mast cells as cellular
sensors in inflammation and immunity. Front Immunol. 2:372011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galli SJ and Tsai M: IgE and mast cells in
allergic disease. Nat Med. 18:693–704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim HH, Bae Y and Kim SH: Galangin
attenuates mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation. Food Chem
Toxicol. 57:209–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Galli SJ, Tsai M and Piliponsky AM: The
development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 454:445–454. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bansal G, Xie Z, Rao S, Nocka KH and Druey
KM: Suppression of immunoglobulin E-mediated allergic responses by
regulator of G protein signaling 13. Nat Immunol. 9:73–80. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Je IG, Kim DS, Kim SW, Lee S, Lee HS, Park
EK, Khang D and Kim SH: Tyrosol suppresses allergic inflammation by
inhibiting the activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in mast
cells. PLoS One. 10:e01298292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kalesnikoff J and Galli SJ: New
developments in mast cell biology. Nat Immunol. 9:1215–1223. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB in
immunobiology. Cell Res. 21:223–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lamkanfi M, Vande Walle L and Kanneganti
TD: Deregulated inflammasome signaling in disease. Immunol Rev.
243:163–173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Miao EA, Rajan JV and Aderem A:
Caspase-1-induced pyroptotic cell death. Immunol Rev. 243:206–214.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baba Y, Nishida K, Fujii Y, Hirano T,
Hikida M and Kurosaki T: Essential function for the calcium sensor
STIM1 in mast cell activation and anaphylactic responses. Nat
Immunol. 9:81–88. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li J, Jiang Z, Li X, Hou Y, Liu F, Li N,
Liu X and Yang L: Natural therapeutic agents for neurodegenerative
diseases from a traditional herbal medicine Pongamia pinnata
(L.) Pierre. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 25:53–58. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li W, Sun YN, Yan XT, Yang SY, Kim S, Lee
YM, Koh YS and Kim YH: Flavonoids from Astragalus
membranaceus and their inhibitory effects on LPS-stimulated
pro-inflammatory cytokine production in bone marrow-derived
dendritic cells. Arch Pharm Res. 37:186–192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ghribi L, Waffo-Téguo P, Cluzet S, Marchal
A, Marques J, Mérillon JM and Ben Jannet H: Isolation and structure
elucidation of bioactive compounds from the roots of the Tunisian
Ononis angustissima L. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 25:3825–3830.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tava A, Pecio Ł, Stochmal A and Pecetti L:
Clovamide and flavonoids from leaves of Trifolium pratense
and T. pratense subsp. nivale grown in Italy. Nat Prod Commun.
10:933–936. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun T, Cao L, Ping NN, Wu Y, Liu DZ and
Cao YX: Formononetin upregulates nitric oxide synthase in arterial
endothelium through estrogen receptors and MAPK pathways. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 68:342–351. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu XY, Xu H, Wu ZF, Chen C, Liu JY, Wu GN,
Yao XQ, Liu FK, Li G and Shen L: Formononetin, a novel FGFR2
inhibitor, potently inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in
preclinical models. Oncotarget. 6:44563–44578. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu W and Xiao Z: Formononetin induces
apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cell line U2OS by regulating the
expression of Bcl-2, Bax and MiR-375 in vitro and in vivo. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 37:933–939. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Je IG, Kim HH, Park PH, Kwon TK, Seo SY,
Shin TY and Kim SH: SG-HQ2 inhibits mast cell-mediated allergic
inflammation through suppression of histamine release and
pro-inflammatory cytokines. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:631–638.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bae Y, Lee S and Kim SH: Chrysin
suppresses mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation: Involvement of
calcium, caspase-1 and nuclear factor-κB. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
254:56–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim HH, Park SB, Lee S, Kwon TK, Shin TY,
Park PH, Lee SH and Kim SH: Inhibitory effect of putranjivain A on
allergic inflammation through suppression of mast cell activation.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 274:455–461. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tanaka S, Mikura S, Hashimoto E, Sugimoto
Y and Ichikawa A: Ca2+ influx-mediated histamine
synthesis and IL-6 release in mast cells activated by monomeric
IgE. Eur J Immunol. 35:460–468. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee NY, Chung KS, Jin JS, Bang KS, Eom YJ,
Hong CH, Nugroho A, Park HJ and An HJ: Effect of chicoric acid on
mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation in vitro and in vivo. J
Nat Prod. 78:2956–2962. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shen D, Xie X, Zhu Z, Yu X, Liu H, Wang H,
Fan H, Wang D, Jiang G and Hong M: Screening active components from
Yu-ping-feng-san for regulating initiative key factors in allergic
sensitization. PLoS One. 9:e1072792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Besnard AG, Togbe D, Couillin I, Tan Z,
Zheng SG, Erard F, Le Bert M, Quesniaux V and Ryffel B:
Inflammasome-IL-1-Th17 response in allergic lung inflammation. J
Mol Cell Biol. 4:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|