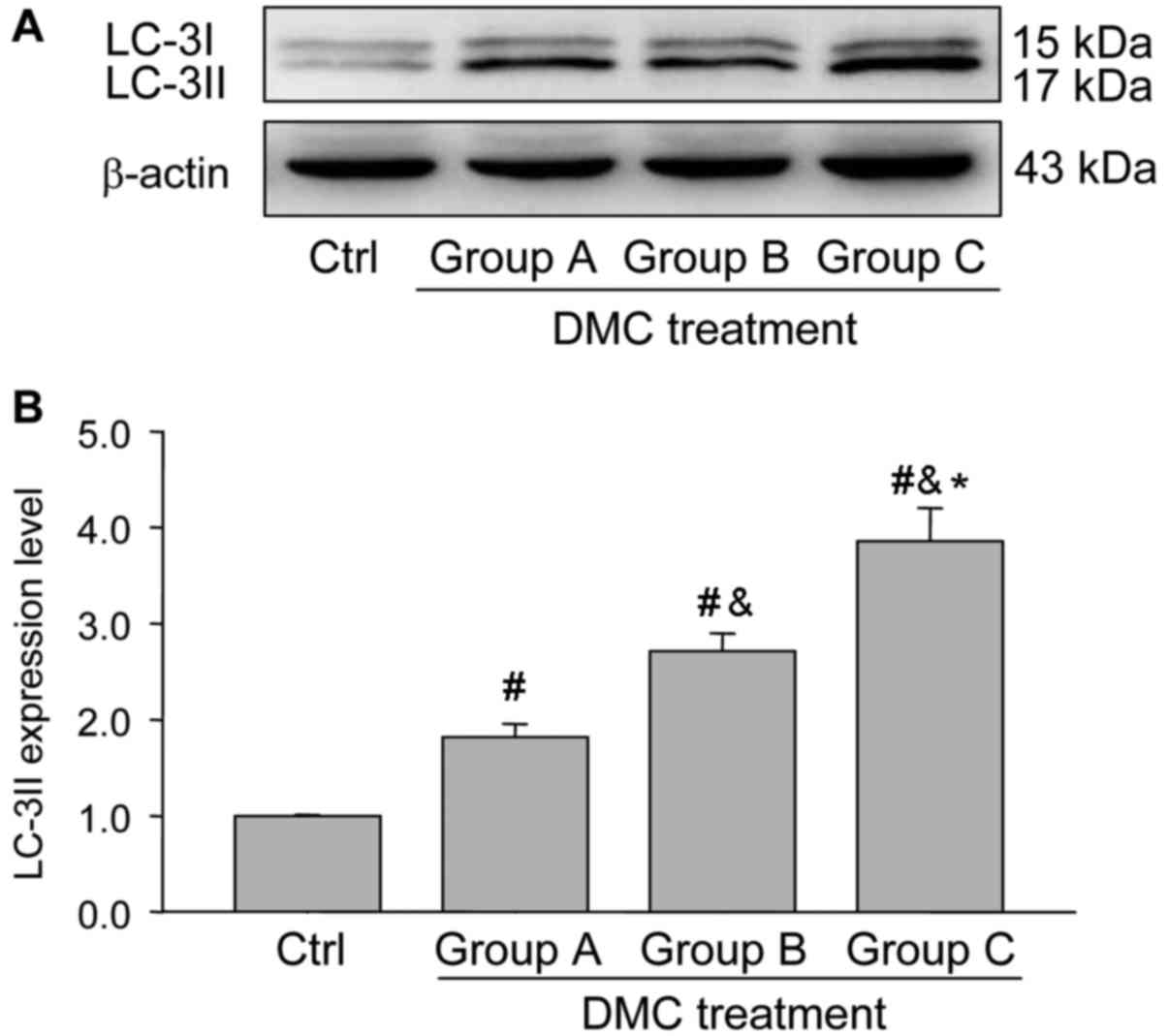
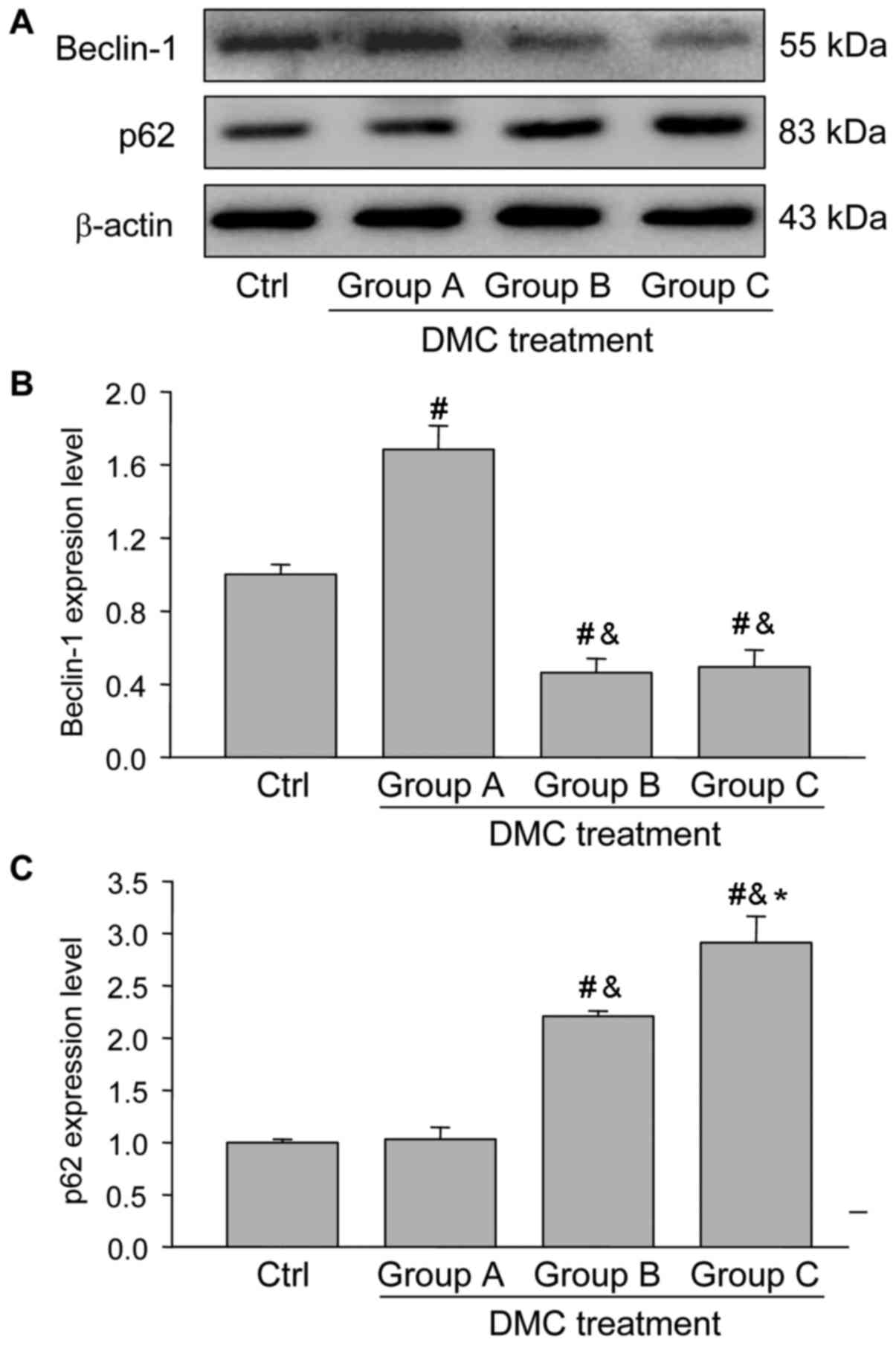
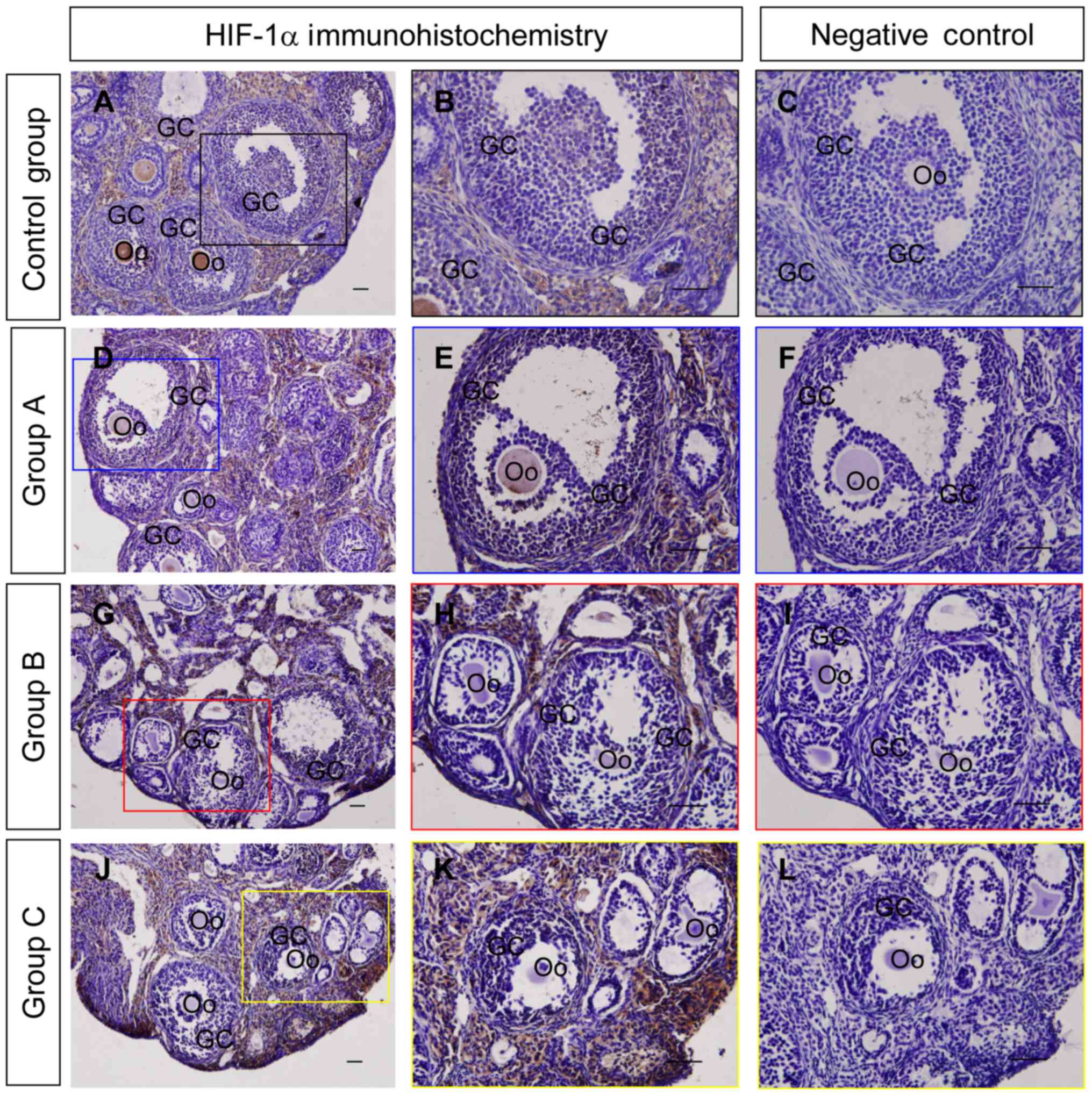
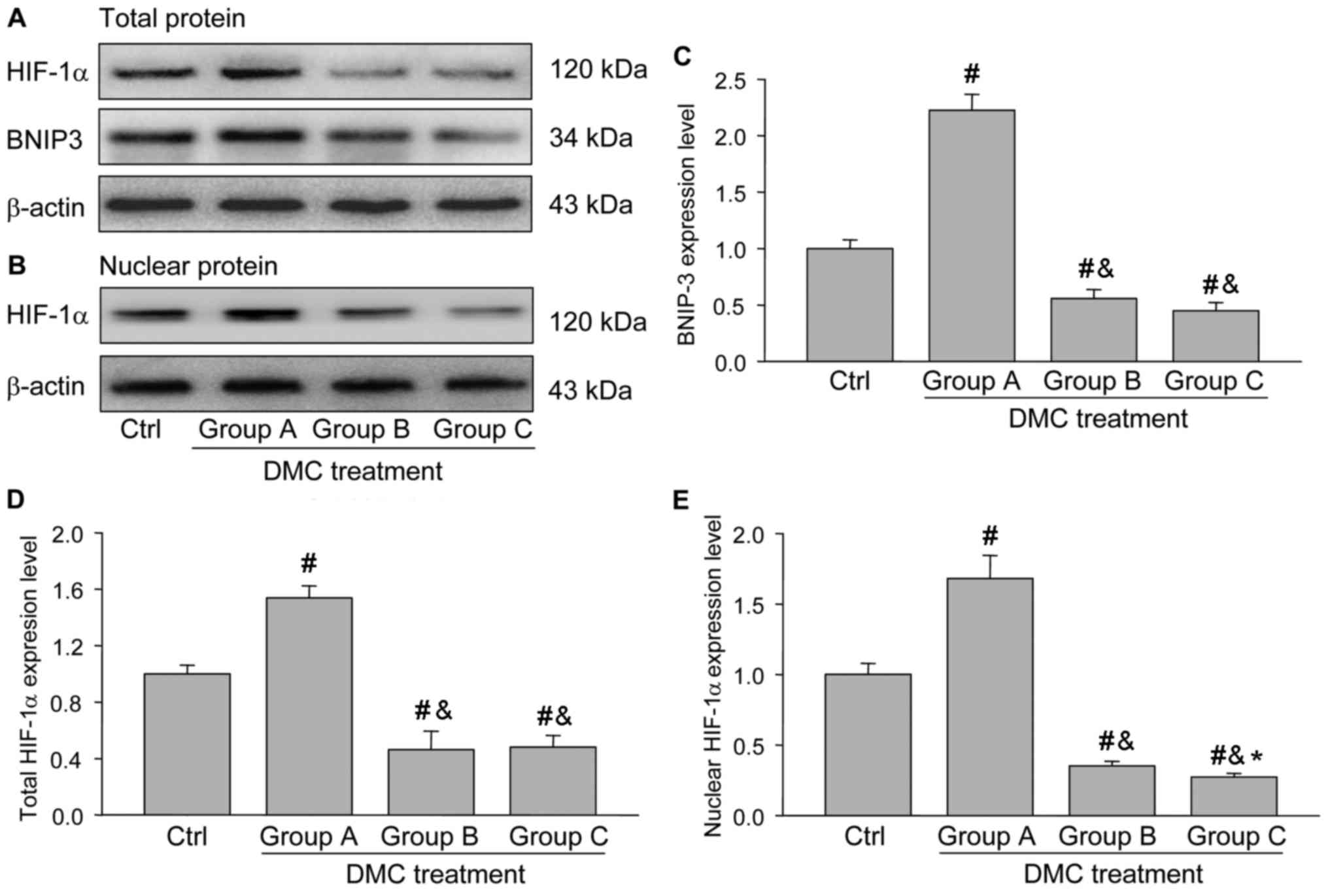
|
1
|
Zhang G, Liu K, Ling X, Wang Z, Zou P,
Wang X, Gao J, Yin L, Zhang X, Liu J, et al: DBP-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress in male germ cells causes autophagy,
which has a cytoprotective role against apoptosis in vitro and in
vivo. Toxicol Lett. 245:86–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang S, Niu Q, Gao H, Ma R, Lei R, Zhang
C, Xia T, Li P, Xu C, Wang C, et al: Excessive apoptosis and
defective autophagy contribute to developmental testicular toxicity
induced by fluoride. Environ Pollut. 212:97–104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lall R, Ganapathy S, Yang M, Xiao S, Xu T,
Su H, Shadfan M, Asara JM, Ha CS, Ben-Sahra I, et al: Low-dose
radiation exposure induces a HIF-1-mediated adaptive and protective
metabolic response. Cell Death Differ. 21:836–844. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P,
Chiche J, Roux D, Pouysségur J and Mazure NM: Hypoxia-induced
autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of
BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2570–2581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bevan C and Beyer B: Developmental
toxicity evaluation of dimethylcarbonate by inhalation in CD-1
mice. Int Toxicol. 7:721995.
|
|
6
|
Anderson SE, Franko J, Anderson KL, Munson
AE, Lukomska E and Meade BJ: Immunotoxicity and allergic potential
induced by topical application of dimethyl carbonate (DMC) in a
murine model. J Immunotoxicol. 10:59–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Quan C, Wang C, Duan P, Huang W, Chen W,
Tang S and Yang K: Bisphenol a induces autophagy and apoptosis
concurrently involving the Akt/mTOR pathway in testes of pubertal
SD rats. Environ Toxicol. 32:1977–1989. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu ML, Wang JL, Wei J, Xu LL, Yu M, Liu
XM, Ruan WL and Chen JX: Tri-ortho-cresyl phosphate induces
autophagy of rat spermatogonial stem cells. Reproduction.
149:163–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Duan P, Hu C, Quan C, Yu T, Zhou W, Yuan
M, Shi Y and Yang K: 4-Nonylphenol induces apoptosis, autophagy and
necrosis in Sertoli cells: Involvement of ROS-mediated
AMPK/AKT-mTOR and JNK pathways. Toxicology. 341–343:28–40. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Wang Y, Kim E, Beemiller P, Wang CY,
Swanson J, You M and Guan KL: Bnip3 mediates the hypoxia-induced
inhibition on mammalian target of rapamycin by interacting with
Rheb. J Biol Chem. 282:35803–35813. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang M, Jiang M, Bi Y, Zhu H, Zhou Z and
Sha J: Autophagy and apoptosis act as partners to induce germ cell
death after heat stress in mice. PLoS One. 7:e414122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang SH, Shih YL, Ko WC, Wei YH and Shih
CM: Cadmium-induced autophagy and apoptosis are mediated by a
calcium signaling pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3640–3652. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu LL, Liu ML, Wang JL, Yu M and Chen JX:
Saligenin cyclic-o-tolyl phosphate (SCOTP) induces autophagy of rat
spermatogonial stem cells. Reprod Toxicol. 60:62–68. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang G, Liu K, Ling X, Wang Z, Zou P,
Wang X, Gao J, Yin L, Zhang X, Liu J, et al: DBP-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress in male germ cells causes autophagy,
which has a cytoprotective role against apoptosis in vitro and in
vivo. Toxicol Lett. 245:86–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Y, Zhou Y, Wang X, Qian W and Han X:
Microcystin-LR induces autophagy and apoptosis in rat Sertoli cells
in vitro. Toxicon. 76:84–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gannon AM, Stämpfli MR and Foster WG:
Cigarette smoke exposure elicits increased autophagy and
dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics in murine granulosa cells.
Biol Reprod. 88:632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Obert LA, Sobocinski GP, Bobrowski WF,
Metz AL, Rolsma MD, Altrogge DM and Dunstan RW: An
immunohistochemical approach to differentiate hepatic lipidosis
from hepatic phospholipidosis in rats. Toxicol Pathol. 35:728–734.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nahdi A, Hammami I, Kouidhi W, Chargui A,
Ben Ammar A, Hamdaoui MH, El May A and El May M: Protective effects
of crude garlic by reducing iron-mediated oxidative stress,
proliferation and autophagy in rats. J Mol Histol. 41:233–245.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin XM, Oltvai ZN and Korsmeyer SJ: BH1
and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis
and heterodimerization with Bax. Nature. 369:321–323. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Booth LA, Tavallai S, Hamed HA,
Cruickshanks N and Dent P: The role of cell signalling in the
crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Signal. 26:549–555.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Canipari R: Oocyte-granulosa cell
interactions. Hum Reprod Update. 6:279–289. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang C and Klionsky DJ: The molecular
mechanism of autophagy. Mol Med. 9:65–76. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nazarko VY and Zhong Q: ULK1 targets
Beclin-1 in autophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 15:727–728. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A,
Bruun JA, Outzen H, Øvervatn A, Bjørkøy G and Johansen T:
p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of
ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem.
282:24131–24145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA and Semenza GL:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS
heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 92:pp. 5510–5514. 1995, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Z, Tang L, Zhu Q, Yi F, Zhang F, Li
PL and Li N: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α contributes to the
profibrotic action of angiotensin II in renal medullary
interstitial cells. Kidney Int. 79:300–310. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Z, Zhu Q, Li PL, Dhaduk R, Zhang F,
Gehr TW and Li N: Silencing of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α gene
attenuates chronic ischemic renal injury in two-kidney, one-clip
rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 306:F1236–F1242. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Z, Zhu Q, Xia M, Li PL, Hinton SJ and
Li N: Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylase 2 senses
high-salt intake to increase hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha levels
in the renal medulla. Hypertension. 55:1129–1136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yaba A, Bianchi V, Borini A and Johnson J:
A putative mitotic checkpoint dependent on mTOR function controls
cell proliferation and survival in ovarian granulosa cells. Reprod
Sci. 15:128–138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, Laughner E,
Hanrahan C, Georgescu MM, Simons JW and Semenza GL: Modulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth
factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human
prostate cancer cells: Implications for tumor angiogenesis and
therapeutics. Cancer Res. 60:1541–1545. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wulff C, Dickson SE, Duncan WC and Fraser
HM: Angiogenesis in the human corpus luteum: Simulated early
pregnancy by HCG treatment is associated with both angiogenesis and
vessel stabilization. Hum Reprod. 16:2515–2524. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nishimura R and Okuda K: Hypoxia is
important for establishing vascularization during corpus luteum
formation in cattle. J Reprod Dev. 56:110–116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miyazawa M, Yasuda M, Fujita M,
Hirabayashi K, Hirasawa T, Kajiwara H, Muramatsu T, Miyazaki S,
Harasawa M, Matsui N, et al: Granulosa cell tumor with activated
mTOR-HIF-1alpha-VEGF pathway. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 36:448–453.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jewell UR, Kvietikova I, Scheid A, Bauer
C, Wenger RH and Gassmann M: Induction of HIF-1alpha in response to
hypoxia is instantaneous. FASEB J. 15:1312–1314. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Ma J, Yi X, Zhu Y, Xi X,
Feng Y and Jin Z: Reactive oxygen species regulate FSH-induced
expression of vascular endothelial growth factor via Nrf2 and HIF1α
signaling in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep.
29:1429–1434. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ietta F, Wu Y, Winter J, Xu J, Wang J,
Post M and Caniggia I: Dynamic HIF1A regulation during human
placental development. Biol Reprod. 75:112–121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen J, Bai M, Ning C, Xie B, Zhang J,
Liao H, Xiong J, Tao X, Yan D, Xi X, et al: Gankyrin facilitates
follicle-stimulating hormone-driven ovarian cancer cell
proliferation through the PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α/cyclin D1 pathway.
Oncogene. 35:2506–2517. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P,
Chiche J, Roux D, Pouysségur J and Mazure NM: Hypoxia-induced
autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of
BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2570–2581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao Y, Chen G, Zhang W, Xu N, Zhu JY, Jia
J, Sun ZJ, Wang YN and Zhao YF: Autophagy regulates hypoxia-induced
osteoclastogenesis through the HIF-1α/BNIP3 signaling pathway. J
Cell Physiol. 227:639–648. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu X, Xu L, Shen J, Wang J, Ruan W, Yu M
and Chen J: Involvement of oxidative stress in tri-ortho-cresyl
phosphate-induced autophagy of mouse Leydig TM3 cells in vitro.
Reprod Biol Endocrin. 14:302016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sun L, Li T, Wei Q, Zhang Y, Jia X, Wan Z
and Han L: Upregulation of BNIP3 mediated by ERK/HIF-1α pathway
induces autophagy and contributes to anoikis resistance of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Future Oncol. 10:1387–1398. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mathew R, Karp CM, Beaudoin B, Vuong N,
Chen G, Chen HY, Bray K, Reddy A, Bhanot G, Gelinas C, et al:
Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis through elimination of p62.
Cell. 137:1062–1075. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen G, Zhang W, Li YP, Ren JG, Xu N, Liu
H, Wang FQ, Sun ZJ, Jia J and Zhao YF: Hypoxia-induced autophagy in
endothelial cells: A double-edged sword in the progression of
infantile haemangioma? Cardiovasc Res. 98:437–448. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|