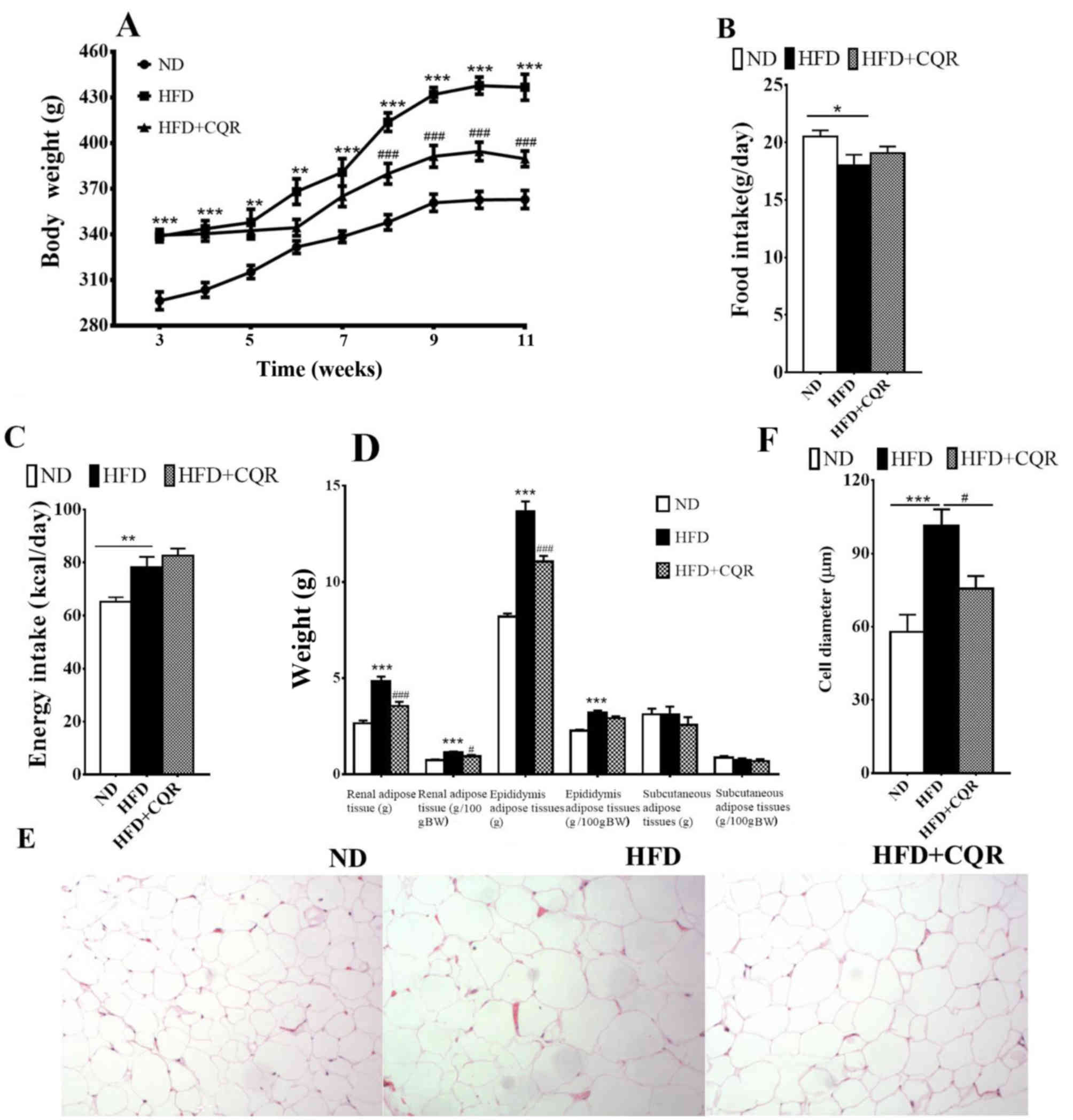
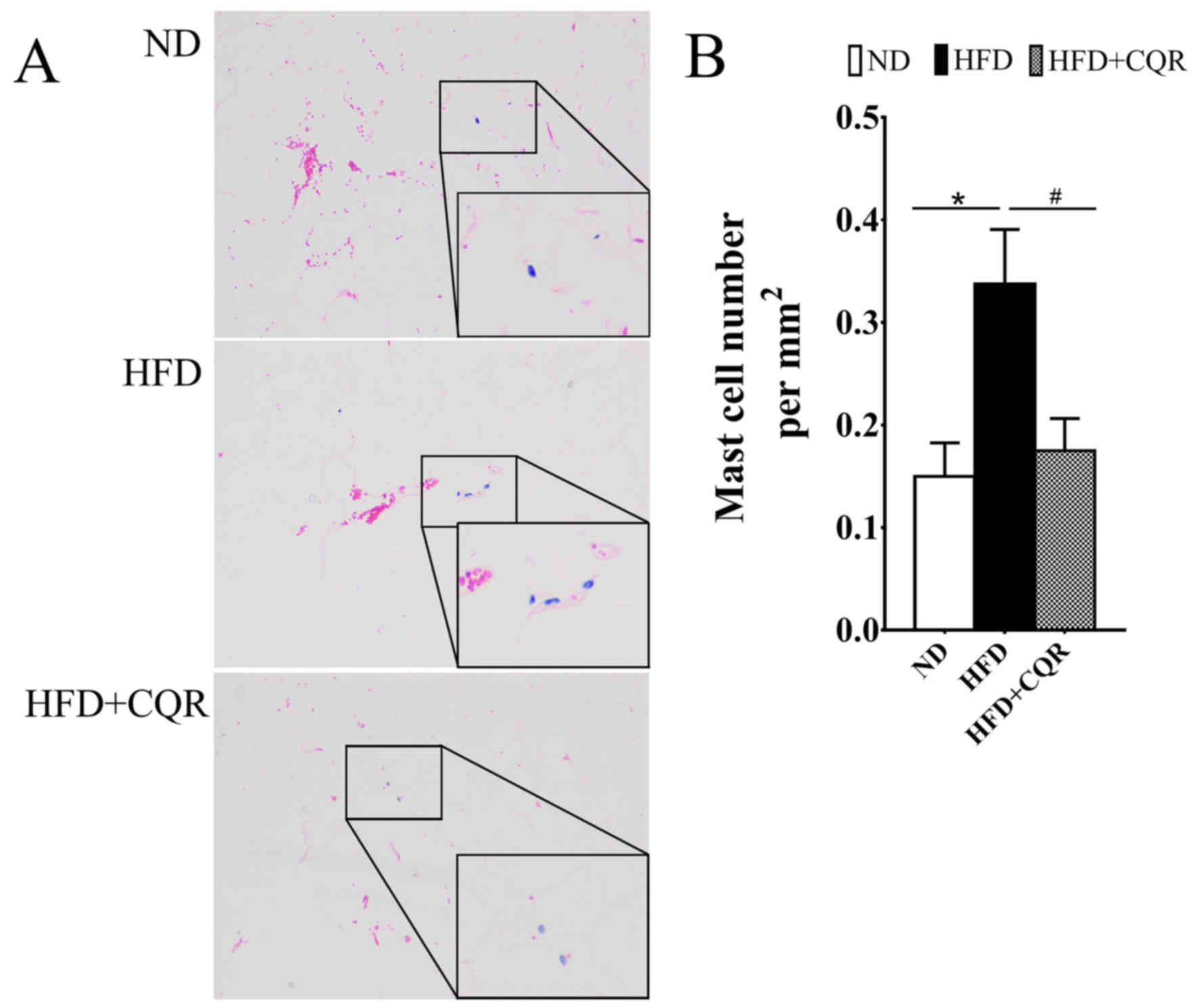
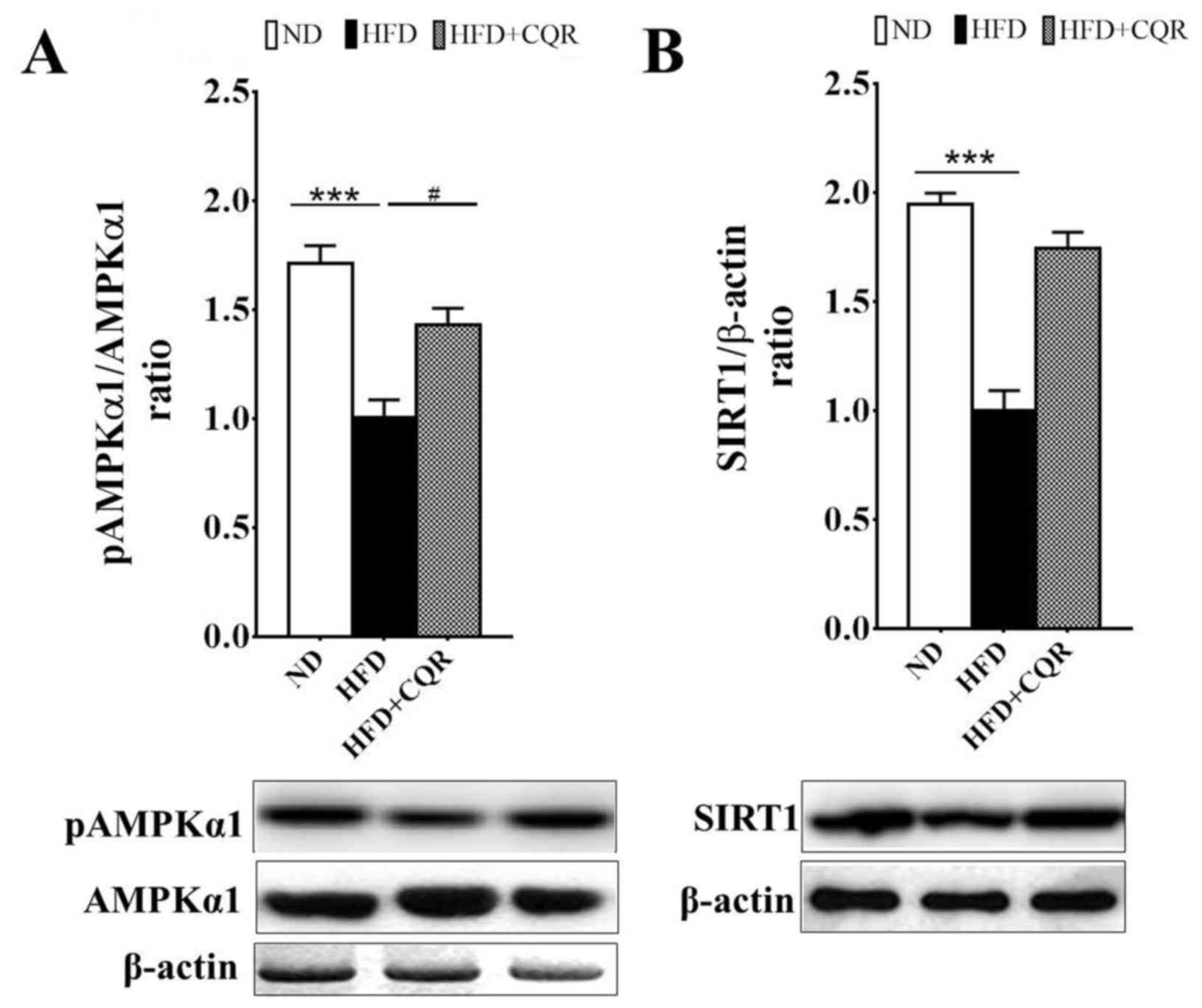
|
1
|
Wensveen FM, Valentić S, Šestan M, Turk
Wensveen T and Polić B: The ‘Big Bang’ in obese fat: Events
initiating obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation. Eur J
Immunol. 45:2446–2456. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van der Heijden RA, Sheedfar F, Morrison
MC, Hommelberg PP, Kor D, Kloosterhuis NJ, Gruben N, Youssef SA, de
Bruin A, Hofker MH, et al: High-fat diet induced obesity primes
inflammation in adipose tissue prior to liver in C57BL/6j mice.
Aging (Albany NY). 7:256–268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ronti T, Lupattelli G and Mannarino E: The
endocrine function of adipose tissue: An update. Clin Endocrinol
(Oxf). 64:355–365. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ and Walsh K:
Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:85–97. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brito AF, Ribeiro M, Abrantes AM, Pires
AS, Teixo RJ, Tralhão JG and Botelho MF: Quercetin in cancer
treatment, alone or in combination with conventional therapeutics?
Curr Med Chem. 22:3025–3039. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chiow KH, Phoon MC, Putti T, Tan BK and
Chow VT: Evaluation of antiviral activities of Houttuynia cordata
Thunb. Extract, quercetin, quercetrin and cinanserin on murine
coronavirus and dengue virus infection. Asian Pac J Trop Med.
9:1–7. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boots AW, Haenen GR and Bast A: Health
effects of quercetin: From antioxidant to nutraceutical. Eur J
Pharmacol. 585:325–327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eid HM and Haddad PS: The antidiabetic
potential of quercetin: Underlying mechanisms. Curr Med Chem.
24:355–364. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Yao J, Han C, Yang J, Chaudhry MT,
Wang S, Liu H and Yin Y: Quercetin, inflammation and immunity.
Nutrients. 8:1672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Corrêa RCG, Peralta RM, Haminiuk CWI,
Maciel GM, Bracht A and Ferreira ICFR: New phytochemicals as
potential human anti-aging compounds: Reality, promise, and
challenges. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 13:1–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pashevin DA, Tumanovska LV, Dosenko VE,
Nagibin VS, Gurianova VL and Moibenko AA: Antiatherogenic effect of
quercetin is mediated by proteasome inhibition in the aorta and
circulating leukocytes. Pharmacol Rep. 63:1009–1018. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nabavi SF, Russo GL, Daglia M and Nabavi
SM: Role of quercetin as an alternative for obesity treatment: You
are what you eat! Food Chem. 179:305–310. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aguirre L, Fernández-Quintela A, Arias N
and Portillo M: Resveratrol: Anti-obesity mechanisms of action.
Molecules. 19:18632–18655. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
15
|
Altintas MM, Azad A, Nayer B, Contreras G,
Zaias J, Faul C, Reiser J and Nayer A: Mast cells, macrophages, and
crown-like structures distinguish subcutaneous from visceral fat in
mice. J Lipid Res. 52:480–488. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong J, Zhang X, Zhang L, Bian HX, Xu N,
Bao B and Liu J: Quercetin reduces obesity-associated ATM
infiltration and inflammation in mice: A mechanism including
AMPKα1/SIRT1. J Lipid Res. 55:363–374. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun S, Ji Y, Kersten S and Qi L:
Mechanisms of inflamatory responses in obese adipose tissue. Annu
Rev Nutr. 32:261–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu J, Divoux A, Sun J, Zhang J, Clément
K, Glickman JN, Sukhova GK, Wolters PJ, Du J, Gorgun CZ, et al:
Genetic deficiency and pharmacological stabilization of mast cells
reduce diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Nat Med.
15:940–945. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park HH, Lee S, Son HY, Park SB, Kim MS,
Choi EJ, Singh TS, Ha JH, Lee MG, Kim JE, et al: Flavonoids inhibit
histamine release and expression of proinfl ammatory cytokines in
mast cells. Arch Pharm Res. 31:1303–1311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee WH, Lin RJ, Lin SY, Chen YC, Lin HM
and Liang YC: Osthole enhances glucose uptake through activation of
AMP-activated protein kinase in skeletal muscle cells. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:12874–12881. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sag D, Carling D, Stout RD and Suttles J:
Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase promotes
macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory functional
phenotype. J Immunol. 181:8633–8641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoshizaki T, Milne JC, Imamura T, Schenk
S, Sonoda N, Babendure JL, Lu JC, Smith JJ, Jirousek MR and Olefsky
JM: SIRT1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects and improves insulin
sensitivity in adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 29:1363–1374. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Z, Kahn BB, Shi H and Xue BZ:
Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK)
antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1. J Biol
Chem. 285:19051–19059. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
De Ligt M, Timmers S and Schrauwen P:
Resveratrol and obesity: Can resveratrol relieve metabolic
disturbances? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1137–1144. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arias N, Macarulla MT, Aguirre L, Milton I
and Portillo MP: The combination of resveratrol and quercetin
enhances the individual effects of these molecules on
triacylglycerol metabolism in white adipose tissue. Eur J Nutr.
55:341–348. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gómez-Zorita S, Fernández-Quintela A,
Macarulla MT, Aguirre L, Hijona E, Bujanda L, Milagro F, Martínez
JA and Portillo MP: Resveratrol attenuates steatosis in obese
Zucker rats by decreasing fatty acid availability and reducing
oxidative stress. Br J Nutr. 107:202–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rivera L, Morón R, Sánchez M, Zarzuelo A
and Galisteo M: Quercetin ameliorates metabolic syndrome and
improves the inflammatory status in obese Zucker rats. Obesity
Silver (Spring). 16:2081–2087. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jung CH, Cho I, Ahn J, Jeon TI and Ha TY:
Quercetin reduces high-fat diet-induced fat accumulation in the
liver by regulating lipid metabolism genes. Phytother Res.
27:139–143. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kobori M, Masumoto S, Akimoto Y and Oike
H: Chronic dietary intake of quercetin alleviates hepatic fat
accumulation associated with consumption of a Western-style diet in
C57/BL6J mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:530–540. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alberdi G, Rodríguez VM, Miranda J,
Macarulla MT, Arias N, Andrés-Lacueva C and Portillo MP: Changes in
white adipose tissue metabolism induced by resveratrol in rats.
Nutr Metab (Lond). 8:292011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z,
Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P,
Elliott P, et al: Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and
protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and
PGC-1alpha. Cell. 127:1109–1122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou M, Wang S, Zhao A, Wang K, Fan Z,
Yang H, Liao W, Bao S, Zhao L, Zhang Y, et al: Transcriptomic and
metabonomic profiling reveal synergistic effects of quercetin and
resveratrol supplementation in high fat diet fed mice. J Proteome
Res. 11:4961–4971. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amiot MJ, Riva C and Vinet A: Effects of
dietary polyphenols on metabolic syndrome features in humans: A
systematic review. Obes Rev. 17:573–586. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Andrade JM, Frade AC, Guimarães JB,
Freitas KM, Lopes MT, Guimarães AL, de Paula AM, Coimbra CC and
Santos SH: Resveratrol increases brown adipose tissue thermogenesis
markers by increasing SIRT1 and energy expenditure and decreasing
fat accumulation in adipose tissue of mice fed a standard diet. Eur
J Nutr. 53:1503–1510. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu Z, Zhao J, Xu H, Lyv Y, Feng X, Fang Y
and Xu Y: Maternal quercetin administration during gestation and
lactation decrease endoplasmic reticulum stress and related
inflammation in the adult offspring of obese female rats. Eur J
Nutr. 53:1669–1683. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu H, Guo X, Chu Y and Lu S: Heart
protective effects and mechanism of quercetin preconditioning on
anti-myocardial ischemia reperfusion (IR) injuries in rats. Gene.
545:149–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJ, Duarte FV,
Martin-Montalvo A, North BJ, Agarwal B, Ye L, Ramadori G, Teodoro
JS, et al: SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial
effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab.
15:675–690. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Arias N, Macarulla MT, Aguirre L, Miranda
J and Portillo MP: Liver delipidating effect of a combination of
resveratrol and quercetin in rats fed an obesogenic diet. J Physiol
Biochem. 71:569–576. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Harwood M, Danielewska-Nikiel B,
Borzelleca JF, Flamm GW, Williams GM and Lines TC: A critical
review of the data related to the safety of quercetin and lack of
evidence of in vivo toxicity, including lack of
genotoxic/carcinogenic properties. Food Chem Toxicol. 45:2179–2205.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Panchal SK, Poudyal H and Brown L:
Quercetin ameliorates cardiovascular, hepatic, and metabolic
changes in diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. J Nutr.
142:1026–1032. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Boesch-Saadatmandi C, Wagner AE, Wolffram
S and Rimbach G: Effect of quercetin on inflammatory gene
expression in mice liver in vivo-role of redox factor 1, miRNA-122
and miRNA-125b. Pharmacol Res. 65:523–530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pan QR, Ren YL, Zhu JJ, Hu YJ, Zheng JS,
Fan H, Xu Y, Wang G and Liu WX: Resveratrol increases nephrin and
podocin expression and alleviates renal damage in rats fed a
high-fat diet. Nutrients. 6:2619–2631. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Peredo-Escárcega AE, Guarner-Lans V,
Pérez-Torres I, Ortega-Ocampo S, Carreón-Torres E, Castrejón-Tellez
V, Díaz-Díaz E and Rubio-Ruiz ME: The combination of resveratrol
and quercetin attenuates metabolic syndrome in rats by modifying
the serum fatty acid composition and by upregulating SIRT1 and
SIRT2 expression in white adipose tissue. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2015:4740322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bays HE: Adiposopathy is ‘sick fat’ a
cardiovascular disease? J Am Coll Cardiol. 57:2461–2473. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chaudhari HS, Bhandari U and Khanna G:
Preventive effect of embelin from embelia ribes on lipid metabolism
and oxidative stress in high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats.
Planta Med. 78:651–657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Franco JG, Lisboa PC, Lima NS, Amaral TA,
Peixoto-Silva N, Resende AC, Oliveira E, Passos MC and Moura EG:
Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress and prevents steatosis and
hypertension in obese rats programmed by early weaning. J Nutr
Biochem. 24:960–966. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Baek SH, Chung HJ, Lee HK, D'Souza R, Jeon
Y, Kim HJ, Kweon SJ and Hong ST: Treatment of obesity with the
resveratrol-enriched rice DJ-526. Sci Rep. 4:38792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
D'Andrea G: Quercetin: A flavonol with
multifaceted therapeutic applications? Fitoterapia. 106:256–271.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun S, Ji Y, Kersten S and Qi L:
Mechanisms of inflammatory responses in obese adipose tissue. Annu
Rev Nutr. 32:261–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Osborn O and Olefsky JM: The cellular and
signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in
disease. Nat Med. 18:363–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Berg AH and Scherer PE: Adipose tissue,
inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 13:939–949.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum
M, Leibel RL and Ferrante AW Jr: Obesity is associated with
macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Investig.
112:1796–1808. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fantuzzi G and Faggioni R: Leptin in the
regulation of immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. J Leukoc
Biol. 68:437–446. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Weng SY and Schuppan D: AMPK regulates
macrophage polarization in adipose tissue inflammation and NASH. J
Hepatol. 58:619–621. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Salminen A, Hyttinen JM and Kaarniranta K:
AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits NF-κB signaling and
inflammation: Impact on healthspan and lifespan. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:667–676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Eo H, Jeon YJ, Lee M and Lim Y: Brown Alga
Ecklonia cava polyphenol extract ameliorates hepatic lipogenesis,
oxidative stress, and inflammation by activation of AMPK and SIRT1
in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J Agric Food Chem. 63:349–359.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yang Z, Kahn BB, Shi H and Xue BZ:
Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK)
antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1. J Biol
Chem. 285:19051–19059. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Grisouard J, Dembinski K, Mayer D, Keller
U, Müller B and Christ-Crain M: Targeting AMP-activated protein
kinase in adipocytes to modulate obesity-related adipokine
production associated with insulin resistance and breast cancer
cell proliferation. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 3:162011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Łabuzek K, Liber S, Gabryel B and Okopień
B: AICAR (5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-4-ribofuranoside)
increases the production of toxic molecules and affects the profile
of cytokines release in LPS-stimulated rat primary microglial
cultures. Neurotoxicology. 31:134–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gillum MP, Kotas ME, Erion DM, Kursawe R,
Chatterjee P, Nead KT, Muise ES, Hsiao JJ, Frederick DW, Yonemitsu
S, et al: SirT1 regulates adipose tissue inflammation. Diabetes.
60:3235–3245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Bitterman JL and Chung JH: Metabolic
effects of resveratrol: Addressing the controversies. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 72:1473–1488. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|