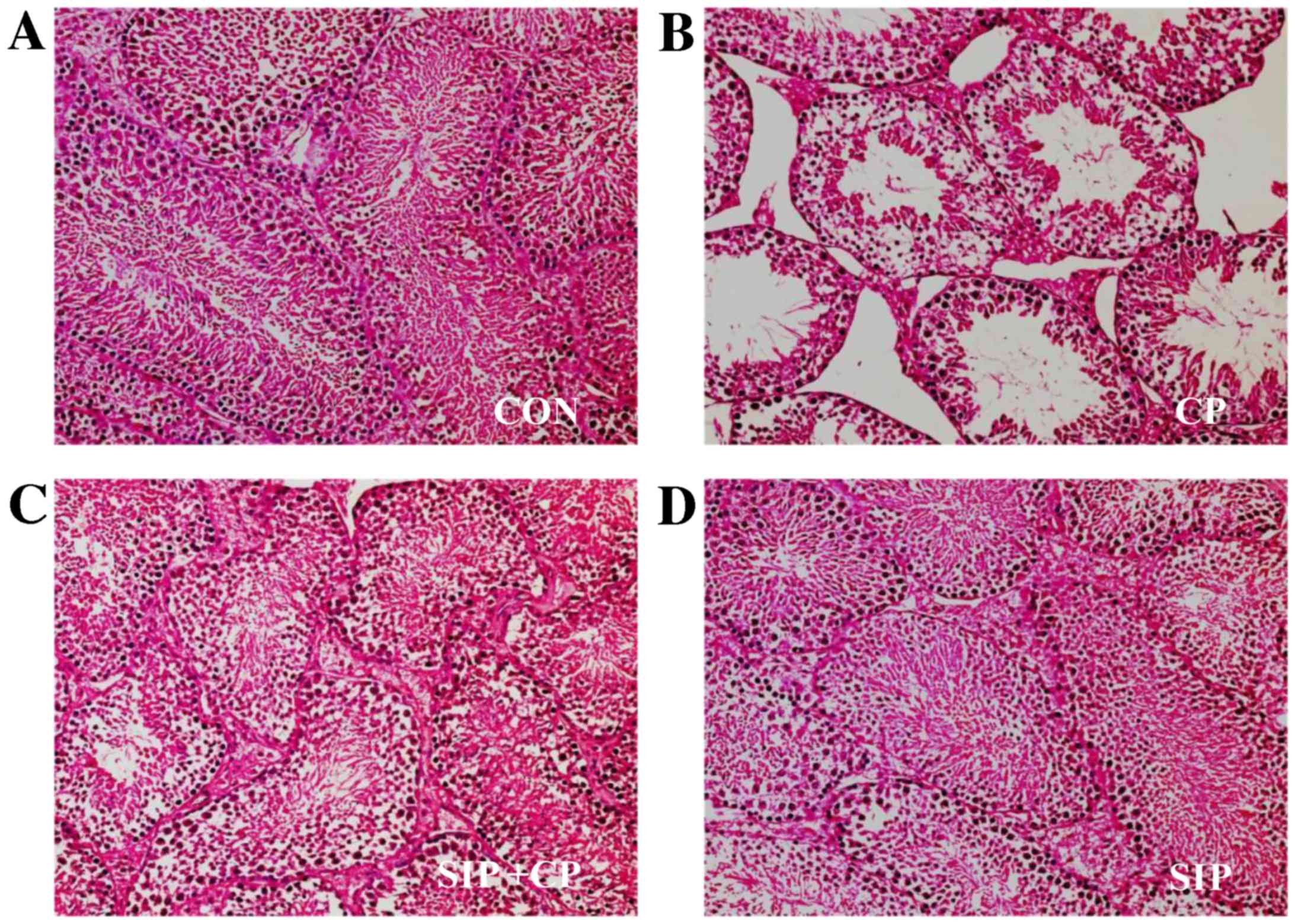
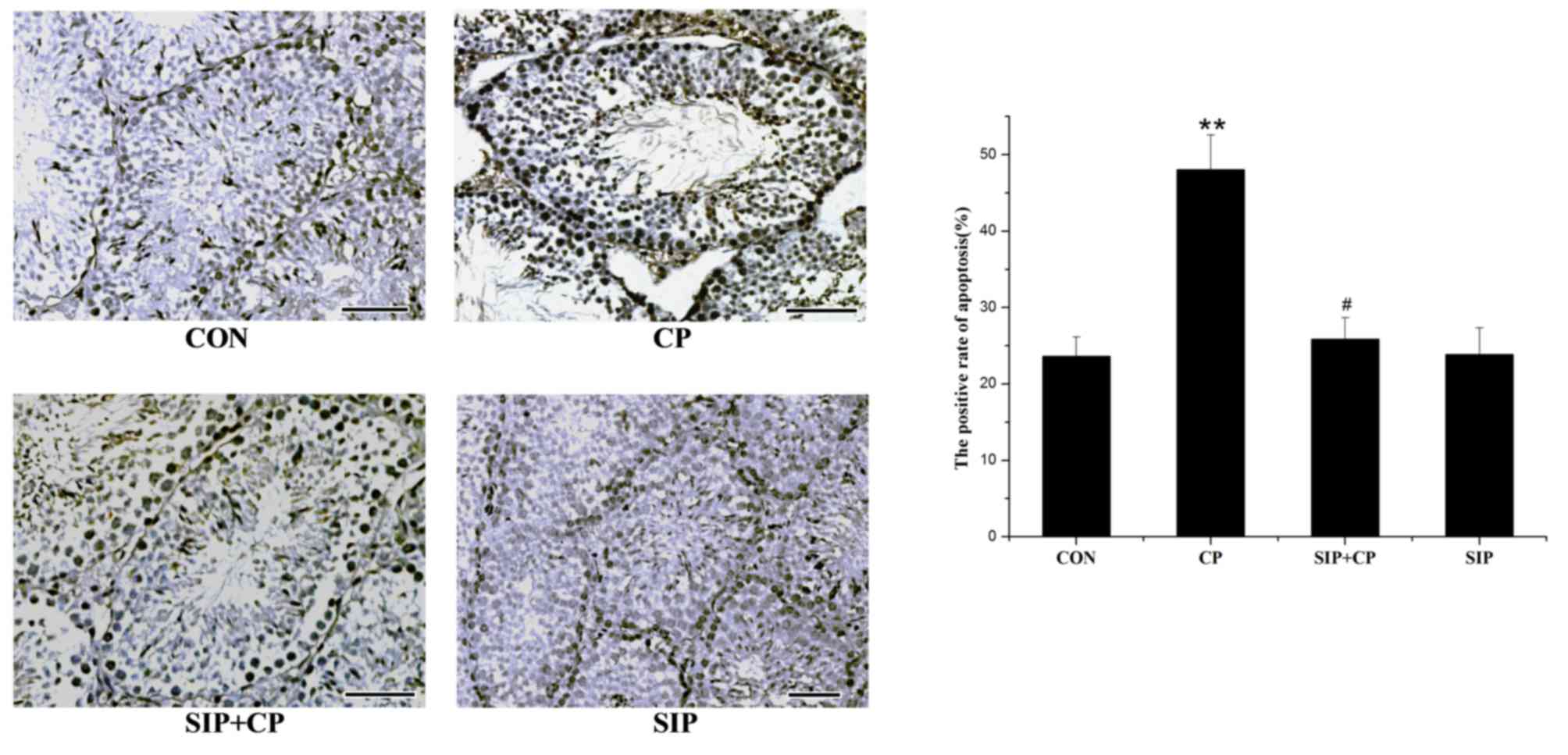
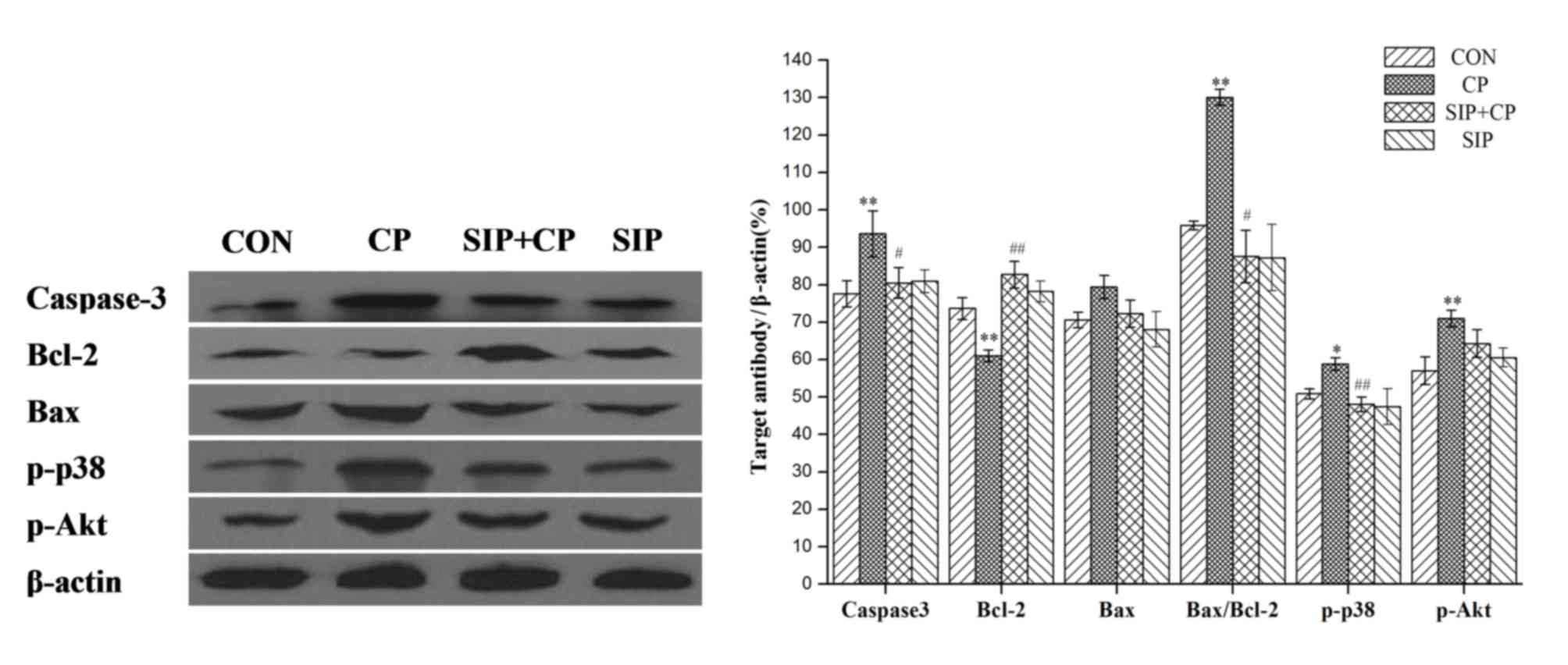
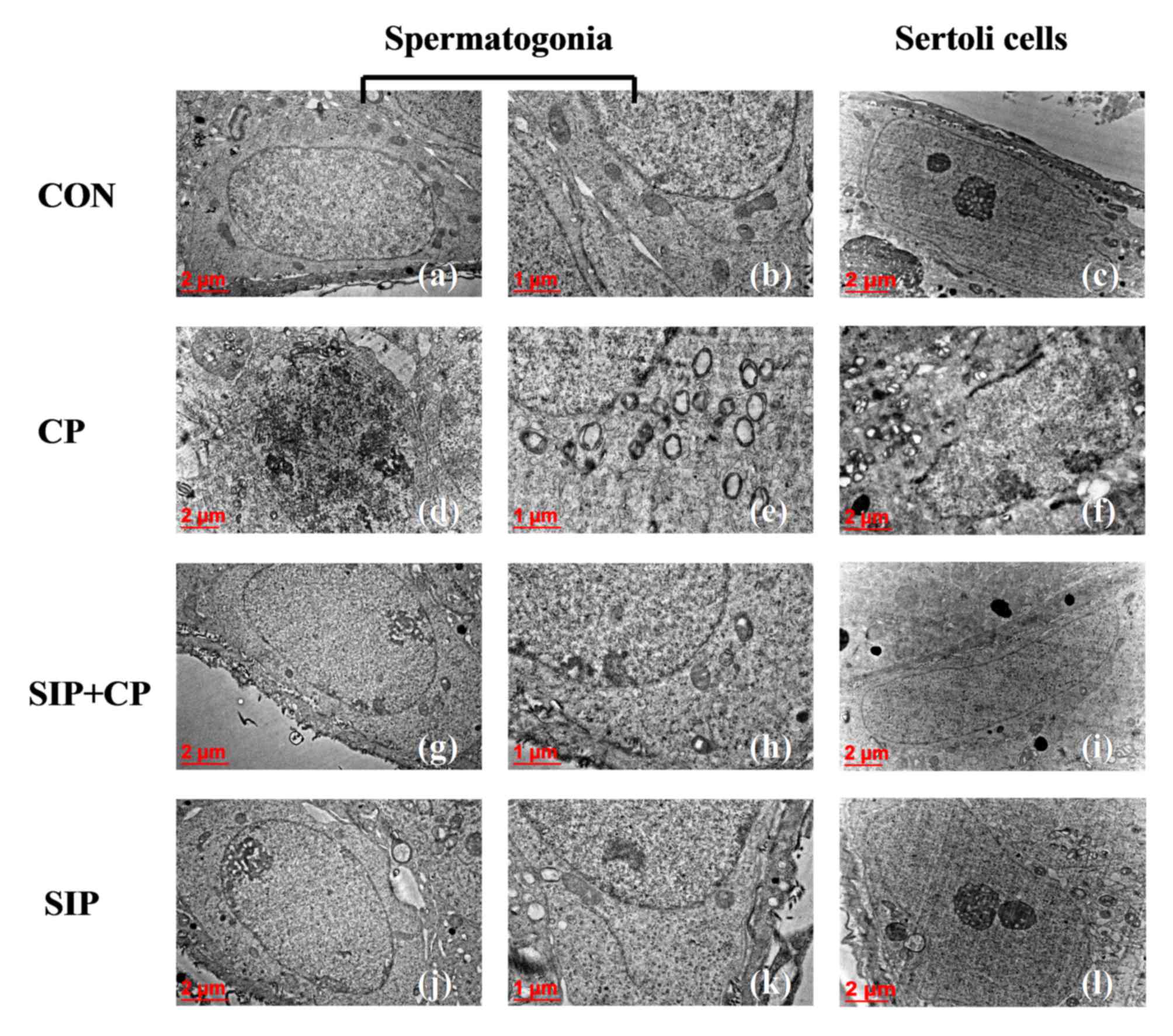
|
1
|
Le XY, Luo P, Gu YP, Tao YX and Liu HZ:
Interventional effects of squid ink polysaccharides on
cyclophosphamide-associated testicular damage in mice. Bratisl Lek
Listy. 116:334–339. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mythili Y, Sudharsan PT, Selvakumar E and
Varalakshmi P: Protective effect of DL-alpha-lipoic acid on
cyclophosphamide induced oxidative cardiac injury. Chem Biol
Interact. 151:13–19. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aguilar-Mahecha A, Hales B and Robaire B:
Effects of acute and chronic cyclophosphamide treatment on meiotic
progression and the induction of DNA double-strand breaks in rat
spermatocytes. Biol Reprod. 72:1297–1304. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang J, Ma K and Wang H: Cyclophosphamide
suppresses thioredoxin reductase in bladder tissue and its adaptive
response via inductions of thioredoxin reductase and gluththione
peroxidase. Chem Biol Interact. 162:24–30. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Faleiro L and Lazebnik Y: Caspases disrupt
the nuclear-cytoplasmic barrier. J Cell Biol. 151:951–959. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu Z, Wu L, Li L, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: p53-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by
shikonin via a caspase-9-dependent mechanism in human malignant
melanoma A375-S2 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 94:166–176. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maiuri MC, Tasdemir E, Criollo A, Morselli
E, Vicencio JM, Carnuccio R and Kroemer G: Control of autophagy by
oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Cell Death Differ. 16:87–93.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A and Levi-Schaffer F:
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction.
Apoptosis. 5:415–418. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Rabbani ZN, Jackson IL
and Vujaskovic Z: Oxidative stress mediates radiation lung injury
by inducing apoptosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 83:740–748.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cai L, Hales BF and Robaire B: Induction
of apoptosis in the germ cells of adult male rats after exposure to
cyclophosphamide. Biol Reprod. 56:1490–1497. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zong A, Zhao T, Zhang Y, Song X, Shi Y,
Cao H, Liu C, Cheng Y, Qu X, Cao J and Wang F: Anti-metastatic and
anti-angiogenic activities of sulfated polysaccharide of Sepiella
maindroni ink. Carbohyd Polym. 91:403–409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zuo T, He X, Cao L, Xue C and Tang QJ: The
dietary polysaccharide from Ommastrephes bartrami prevents
chemotherapeutic mucositis by promoting the gene expression of
antimicrobial peptides in Paneth cells. J Funct Foods. 12:530–539.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zuo T, Cao L, Xue C and Tang QJ: Dietary
squid ink polysaccharide induced goblet cells to protect small
intestine from chemotherapy induced injury. Food Funct. 6:981–986.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang Q, Zuo T, Lu S, Wu J, Wang J, Zheng
R, Chen S and Xue C: Dietary squid ink polysaccharides ameliorated
the intestinal microflora dysfunction in mice undergoing
chemotherapy. Food Funct. 5:2529–2535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zuo T, Cao L, Li X, Zhang Q, Xue C and
Tang QJ: The squid ink polysaccharides protect tight junctions and
adherens junctions from chemotherapeutic injury in the small
intestinal epithelium of mice. Nutr Cancer. 67:364–371. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zuo T, Cao L, Sun X, Li X, Wu J, Lu S, Xue
C and Tang Q: Dietary squid ink polysaccharide could enhance SIgA
secretion in chemotherapeutic mice. Food Funct. 5:3189–3196. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen S, Xu J, Xue C, Dong P, Sheng W, Yu G
and Chai W: Sequence determination of a non-sulfated
glycosaminoglycan-like polysaccharide from melanin-free ink of the
squid Ommastrephes bartrami by negative-ion electrospray tandem
mass spectrometry and NMR spectroscopy. Glycoconj J. 25:481–492.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu HZ, Wang G, Wu JL, Shi LS, Zhong JP
and Pan JQ: Amelioratory effects of squid ink polysaccharides on
partial internal organs injuried by cyclophosphamide. Chinese J Mod
Appl Pharm. 2:89–93. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Staub AM: Removal of protein-Sevag method.
Methods Carbohydrate Chem. 5:5–6. 1965.
|
|
20
|
Le X, Luo P, Gu Y, Tao Y and Liu H: Squid
ink polysaccharides reduces cyclophosphamide-induced testicular
damage via Nrf2/ARE activation pathway in mice. Iran J Basic Med
Sci. 18:827–831. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Elangovan N, Chiou TJ, Tzeng WF and Chu
ST: Cyclophosphamide treatment causes impairment of sperm and its
fertilizing ability in mice. Toxicology. 222:60–70. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brodsky RA: High-dose cyclophosphamide for
autoimmunity and alloimmunity. Immunol Res. 47:179–184. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Motoyoshi Y, Kaminoda K, Saitoh O,
Hamasaki K, Nakao K, Ishii N, Nagayama Y and Eguchi K: Different
mechanisms for anti-tumor effects of low- and high-dose
cyclophosphamide. Oncol Rep. 16:141–146. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guittin P, Labbe V, Cavalier JC, Delongeas
JL and Hodge T: Effects of cyclophosphamide administration on
different fertility evaluation tests in male rats. Teratology.
53:30A1996.
|
|
25
|
Luboshitzky R, Shen-Orr Z and Herer P:
Seminal plasma melatonin and gonadal steroids concentrations in
normal men. Arch Androl. 48:225–232. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Martin CW, Riley SC, Everington D, Groome
NP, Riemersma RA, Baird DT and Anderson RA: Dose-finding study of
oral desogestrel with testosterone pellets for suppression of the
pituitary-testicular axis in normal men. Hum Reprod. 15:1515–1524.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iuchi Y, Kaneko T, Matsuki S, Ishii T,
Ikeda Y, Uchida K and Fujii J: Carbonyl stress and detoxification
ability in the male genital tract and testis of rats. Histochem
Cell Biol. 121:123–130. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Selvakumar E, Prahalathan C, Sudharsan PT
and Varalakshmi P: Protective effect of lipoic acid on
cyclophosphamide-induced testicular toxicity. Clin Chim Acta.
367:114–119. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Motawi TM, Sadik NA and Refaat A:
Cytoprotective effects of DL-alpha-lipoic acid or squalene on
cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative injury: An experimental study on
rat myocardium, testicles and urinary bladder. Food Chem Toxicol.
48:2326–2336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tinari A, Garofalo T, Sorice M, Esposti MD
and Malorni W: Mitoptosis: Different pathways for mitochondrial
execution. Autophagy. 3:282–284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lindsay J, Esposti MD and Gilmore AP:
Bcl-2 proteins and mitochondria-specificity in membrane targeting
for death. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:532–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xie N, Li H, Wei D, LeSaga G, Chen L, Wang
S, Zhang Y, Chi L, Ferslew K, He L, et al: Glycogen synthase
kinase-3 and p38 MAPK are required for opioid-induced microglia
apoptosis. Neuropharmacology. 59:444–451. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen
GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S and Reed JC: Regulation of
cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science.
282:1318–1321. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Niquet J and Wasterlain CG: Bim, Bad, and
Bax: A deadly combination in epileptic seizures. J Clin Invest.
113:960–962. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jeong SJ, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF,
Park HU and Brady JN: Activated AKT regulates NF-kappaB activation,
p53 inhibition and cell survival in HTLV-1-transformed cells.
Oncogene. 24:6719–6728. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Goswami A, Burikhanov R, de Thonel A,
Fujita N, Goswami M, Zhao Y, Eriksson JE, Tsuruo T and Rangnekar
VM: Binding and phosphorylation of par-4 by akt is essential for
cancer cell survival. Mol Cell. 20:33–44. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dan HC, Sun M, Kaneko S, Feldman RI,
Nicosia SV, Wang HG, Tsang BK and Cheng JQ: Akt phosphorylation and
stabilization of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP). J
Biol Chem. 291:228462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PN, Steelman
LS, Shelton JG, Blalock WL, Franklin RA and McCubrey JA:
Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression,
apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: A target for cancer
chemotherapy. Leukemia. 17:590–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|