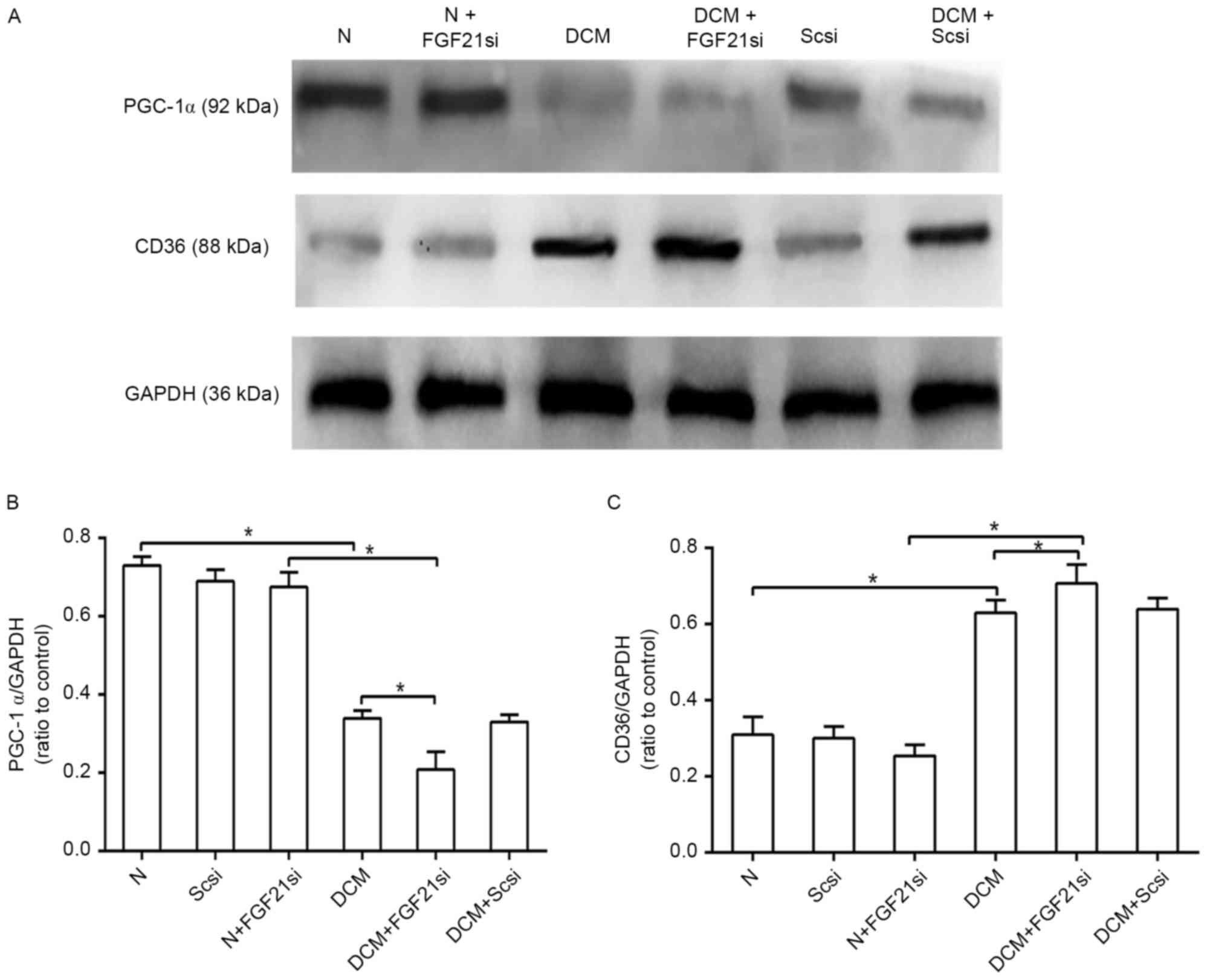
|
1
|
Lorenzo-Almorós A, Tuñón J, Orejas M,
Cortés M, Egido J and Lorenzo Ó: Diagnostic approaches for diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 16:282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang J, Song Y, Wang Q, Kralik PM and
Epstein PN: Causes and characteristics of diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Rev Diabet Stud. 3:108–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos
G, Flier JS and Maratos-Flier E: Hepatic fibroblast growth factor
21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid
metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 5:426–437. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Galman C, Lundåsen T, Kharitonenkov A,
Bina HA, Eriksson M, Hafström I, Dahlin M, Amark P, Angelin B and
Rudling M: The circulating metabolic regulator FGF21 is induced by
prolonged fasting and PPARalpha activation in man. Cell Metab.
8:169–174. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng P, Zhang F, Yu L, Lin X, He L, Li X,
Lu X, Yan X, Tan Y and Zhang C: Physiological and pharmacological
roles of FGF21 in cardiovascular diseases. J Diabetes Res.
2016:15402672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Planavila A, Redondo I, Hondares E,
Vinciguerra M, Munts C, Iglesias R, Gabrielli LA, Sitges M, Giralt
M, van Bilsen M and Villarroya F: Fibroblast growth factor 21
protects against cardiac hypertrophy in mice. Nat Commun.
4:20192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chow WS, Xu A, Woo YC, Tso AW, Cheung SC,
Fong CH, Tse HF, Chau MT, Cheung BM and Lam KS: Serum fibroblast
growth factor-21 levels are associated with carotid atherosclerosis
independent of established cardiovascular risk factors.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:2454–2459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Semba RD, Crasto C, Strait J, Sun K,
Schaumberg DA and Ferrucci L: Elevated serum fibroblast growth
factor 21 is associated with hypertension in community-dwelling
adults. J Hum Hypertens. 27:397–399. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin Z, Wu Z, Yin X, Liu Y, Yan X, Lin S,
Xiao J, Wang X, Feng W and Li X: Serum levels of FGF-21 are
increased in coronary heart disease patients and are independently
associated with adverse lipid profile. PLoS One. 5:e155342010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Planavila A, Redondo-Angulo I, Ribas F,
Garrabou G, Casademont J, Giralt M and Villarroya F: Fibroblast
growth factor 21 protects the heart from oxidative stress.
Cardiovasc Res. 106:19–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang R, Yi X, Li X and Jiang X: Fibroblast
growth factor-21 is positively associated with atrial fibrosis in
atrial fibrillation patients with rheumatic heart disease. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:14901–14908. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang W, Chu S, Ding W and Wang F: Serum
level of fibroblast growth factor 21 is independently associated
with acute myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 10:e01297912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koonen DP, Glatz JF, Bonen A and Luiken
JJ: Long-chain fatty acid uptake and FAT/CD36 translocation in
heart and skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1736:163–180.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Greenwalt DE, Scheck SH and
Rhinehart-Jones T: Heart CD36 expression is increased in murine
models of diabetes and in mice fed a high fat diet. J Clin Invest.
96:1382–1388. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral
T, Branwood AW and Grishman A: New type of cardiomyopathy
associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol.
30:595–602. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dandamudi S, Slusser J, Mahoney DW,
Redfield MM, Rodeheffer RJ and Chen HH: The prevalence of diabetic
cardiomyopathy: A population-based study in Olmsted County,
Minnesota. J Card Fail. 20:304–309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yilmaz S, Canpolat U, Aydogdu S and Abboud
HE: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; summary of 41 years. Korean Circ J.
45:266–272. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Boudina S and Abel ED: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation. 115:3213–3223. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Muise ES, Souza S, Chi A, Tan Y, Zhao X,
Liu F, Dallas-Yang Q, Wu M, Sarr T, Zhu L, et al: Downstream
signaling pathways in mouse adipose tissues following acute in vivo
administration of fibroblast growth factor 21. PLoS One.
8:e730112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang C, Shao M, Yang H, Chen L, Yu L,
Cong W, Tian H, Zhang F, Cheng P, Jin L, et al: Attenuation of
hyperlipidemia- and diabetes-induced early-stage apoptosis and
late-stage renal dysfunction via administration of fibroblast
growth factor-21 is associated with suppression of renal
inflammation. PLoS One. 8:e822752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Goldberg IJ, Trent CM and Schulze PC:
Lipid metabolism and toxicity in the heart. Cell Metab. 15:805–812.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Neely JR, Rovetto MJ and Oram JF:
Myocardial utilization of carbohydrate and lipids. Prog Cardiovasc
Dis. 15:289–329. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Herrero P, Peterson LR, McGill JB, Matthew
S, Lesniak D, Dence C and Gropler RJ: Increased myocardial fatty
acid metabolism in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 47:598–604. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Asch AS, Barnwell J, Silverstein RL and
Nachman RL: Isolation of the thrombospondin membrane receptor. J
Clin Invest. 79:1054–1061. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Silverstein RL, Asch AS and Nachman RL:
Glycoprotein IV mediates thrombospondin-dependent platelet-monocyte
and platelet-U937 cell adhesion. J Clin Invest. 84:546–552. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Endemann G, Stanton LW, Madden KS, Bryant
CM, White RT and Protter AA: CD36 is a receptor for oxidized low
density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 268:11811–11816. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Koonen DP, Febbraio M, Bonnet S, Nagendran
J, Young ME, Michelakis ED and Dyck JR: CD36 expression contributes
to age-induced cardiomyopathy in mice. Circulation. 116:2139–2147.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Puigserver P, Rhee J, Donovan J, Walkey
CJ, Yoon JC, Oriente F, Kitamura Y, Altomonte J, Dong H, Accili D
and Spiegelman BM: Insulin-regulated hepatic gluconeogenesis
through FOXO1-PGC-1alpha interaction. Nature. 423:550–555. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin J, Handschin C and Spiegelman BM:
Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription
coactivators. Cell Metab. 1:361–370. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Finck BN and Kelly DP: PGC-1 coactivators:
Inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J
Clin Invest. 116:615–622. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Handschin C and Spiegelman BM: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 coactivators,
energy homeostasis, and metabolism. Endocr Rev. 27:728–735. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Potthoff MJ, Inagaki T, Satapati S, Ding
X, He T, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Finck BN, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA
and Burgess SC: FGF21 induces PGC-1alpha and regulates carbohydrate
and fatty acid metabolism during the adaptive starvation response.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:pp. 10853–10858. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|