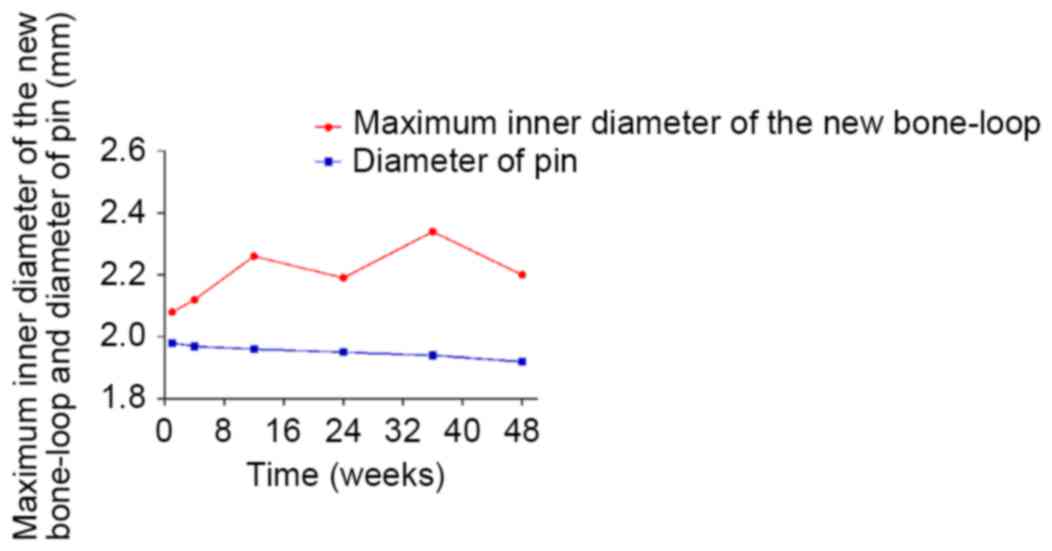
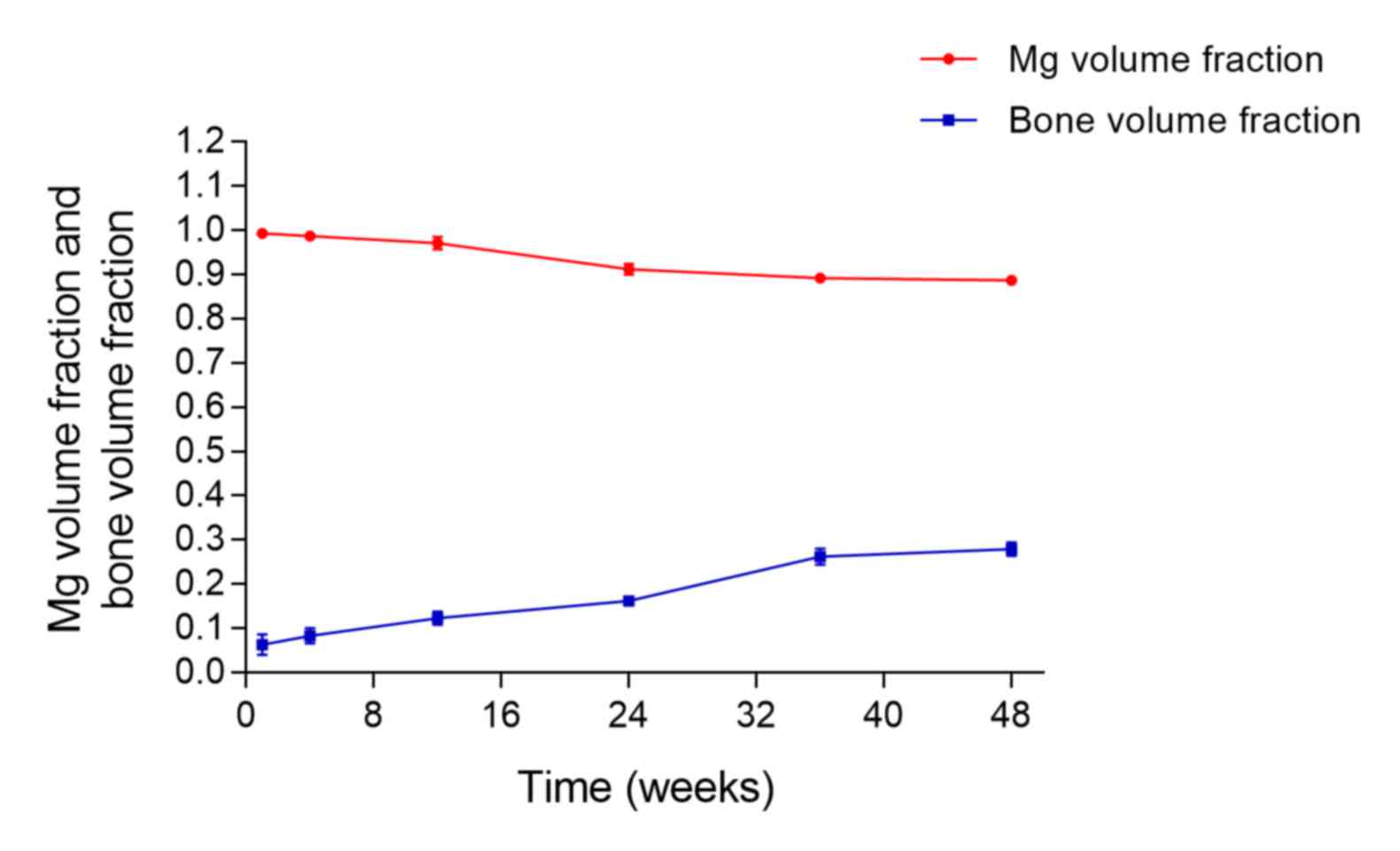
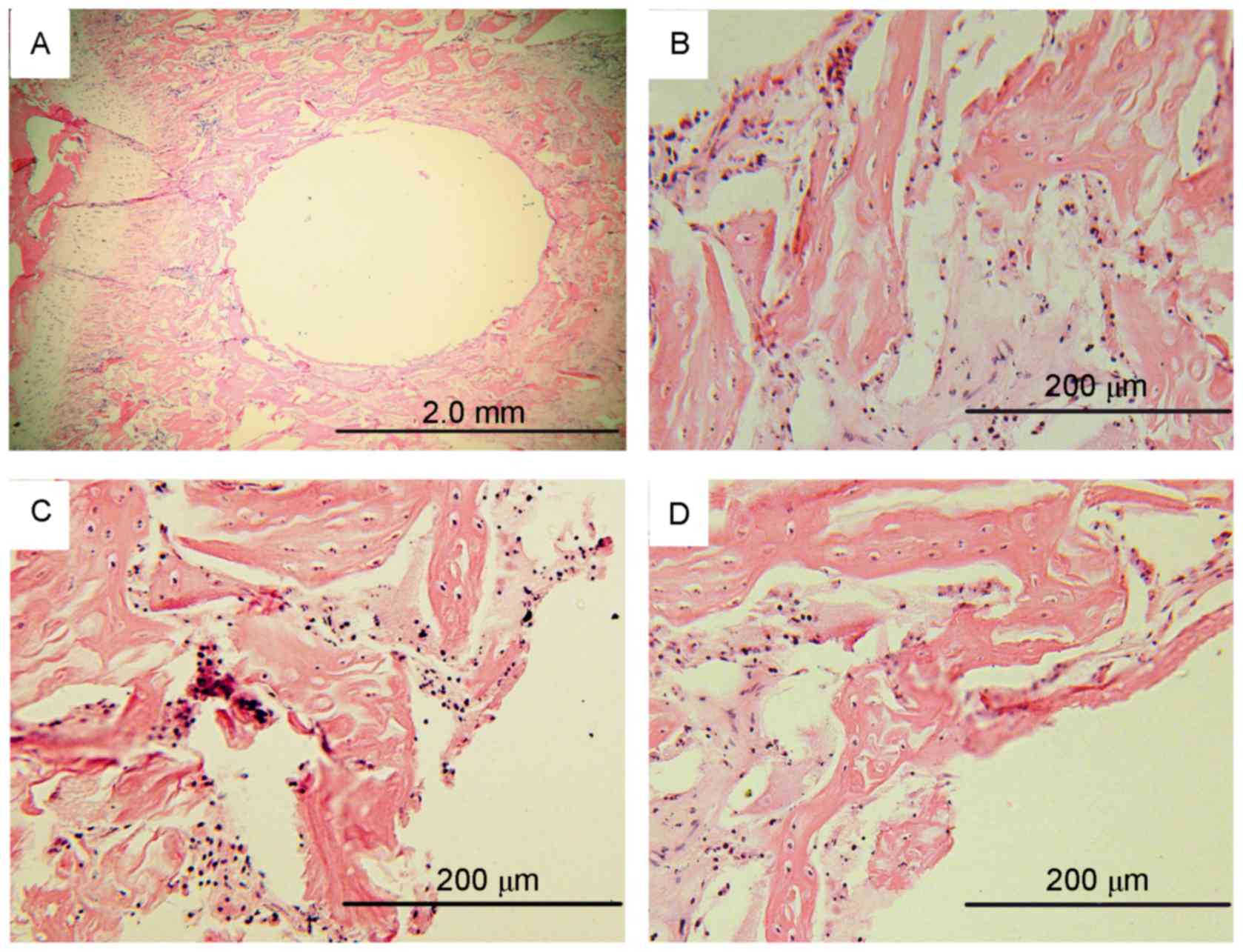
|
1
|
Staiger M, Pietak AM, Huadmai J and Dias
G: Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: A review.
Biomaterials. 27:1728–1734. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mantovani D and Witte F: The attraction of
a lightweight metal with mechanical properties suitable for many
applications brought a renewed focus on magnesium alloys in the
automotive and aerospace industries. Acta Biomater. 6:16792010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gordon LM and Joester D: Mapping residual
organics and carbonate at grain boundaries and the amorphous
interphase in mouse incisor enamel. Front Physiol. 6:572015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vladimirov BV, Krit BL, Lyudin VB,
Morozova NV, Rossiiskaya AD, Suminov IV and Epel'feld AV: Microarc
oxidation of magnesium alloys: A review. Surface Eng Applied
Electrochemistry. 50:195–232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Windhagen H, Radtke K, Weizbauer A,
Diekmann J, Noll Y, Kreimeyer U, Schavan R, Stukenborg-Colsman C
and Waizy H: Biodegradable magnesium-based screw clinically
equivalent to titanium screw in hallux valgus surgery: Short term
results of the first prospective, randomized, controlled clinical
pilot study. Biomed Eng Online. 12:622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamako G, Chosa E, Totoribe K, Watanabe S
and Sakamoto T: Trade-off between stress shielding and initial
stability on an anatomical cementless stem shortening: In-vitro
biomechanical study. Med Eng Phys. 37:820–825. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zielinski SM, Heetveld MJ, Bhandari M,
Patka P and Van Lieshout EM: FAITH Trial Investigators: Implant
removal after internal fixation of a femoral neck fracture: Effects
on physical functioning. J Orthop Trauma. 29:e285–e292. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wong K, Yeung K, Lam J, Chu P, Luk K and
Cheung K: Reduction of corrosion behavior of magnesium alloy by PCL
surface treatment. Ors Ann Meeting. 2009;
|
|
9
|
Liu GY, Hu J, Ding ZK and Wang C:
Bioactive calcium phosphate coating formed on micro-arc oxidized
magnesium by chemical deposition. App Surface Sci. 257:2051–2057.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kraus T, Fischerauer SF, Hänzi AC,
Uggowitzer PJ, Löffler JF and Weinberg AM: Magnesium alloys for
temporary implants in osteosynthesis: In vivo studies of their
degradation and interaction with bone. Acta Biomater. 8:1230–1238.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang E: Phosphate treatment of magnesium
alloy implants forbiomedical applicationsSurface Modification of
Magnesium and its Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Narayanan
TSNS, Park IS and Lee MH: Woodhead Publishing; Waltham, MA: pp.
23–57. 2015, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Feng H, Wang G, Jin W, Zhang X, Huang Y,
Gao A, Wu H, Wu G and Chu PK: Systematic study of inherent
anti-bacterial properties of magnesium-based biomaterials. Acs App
Mater Interfaces. 8:9662–9673. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Warwick ME and Binions R: Advances in
thermochromic vanadium dioxide films. J Mat Chem A. 2:3275–3292.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ko YM, Lee K and Kim BH: Effect of
functional groups on biodegradation and pre-osteoblastic cell
response on the plasma-polymerized magnesium surface. Jap J App
Phy. 52:20–21. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Sealy MP, Guo YB, Caslaru RC, Sharkins J
and Feldman D: Fatigue performance of biodegradable
magnesium-calcium alloy processed by laser shock peening for
orthopedic implants. Int J Fatigue. 82:428–436. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sandip S, Asha K, Paulin G, Hiren S,
Gagandeep S and Amit V: A comparative study of serum uric acid,
calcium and magnesium in preeclampsia and normal pregnancy. J Adv
Res Biol Sci. 5:55–58. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Yoshizawa S, Brown A, Barchowsky A and
Sfeir C: Magnesium ion stimulation of bone marrow stromal cells
enhances osteogenic activity, simulating the effect of magnesium
alloy degradation. Acta Biomater. 10:2834–2842. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoshizawa S, Brown A, Barchowsky A and
Sfeir C: Role of magnesium ions on osteogenic response in bone
marrow stromal cells. Connect Tissue Res. 55 Suppl 1:S155–S159.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Castellani C, Lindtner RA, Hausbrandt P,
Tschegg E, Stanzl-Tschegg SE, Zanoni G, Beck S and Weinberg AM:
Bone-implant interface strength and osseointegration: Biodegradable
magnesium alloy versus standard titanium control. Acta Biomater.
7:432–440. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Johnson I, Akari K and Liu H:
Nanostructured hydroxyapatite/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)
composite coating for controlling magnesium degradation in
simulated body fluid. Nanotechnology. 24:3751032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barfield WR, Colbath G, Desjardins JD, An
Yuehuei H, Hartsock and Langdon A: The potential of magnesium alloy
use in orthopaedic surgery. Curr Orthopaedic Practice. 23:146–150.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Seyedraoufi ZS and Sh M: Synthesis,
microstructure and mechanical properties of porous Mg-Zn scaffolds.
J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 21:1–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fischerauer SF, Kraus T, Wu X, Tangl S,
Sorantin E, Hänzi AC, Löffler JF, Uggowitzer PJ and Weinberg AM: In
vivo degradation performance of micro-arc-oxidized magnesium
implants: A micro-CT study in rats. Acta Biomater. 9:5411–5420.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Song G: Control of biodegradation of
biocompatable magnesium alloys. Corrosion Sci. 49:1696–1701. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chaya A, Yoshizawa S, Verdelis K, Myers N,
Costello BJ, Chou DT, Pal S, Maiti S, Kumta PN and Sfeir C: In vivo
study of magnesium plate and screw degradation and bone fracture
healing. Acta Biomater. 18:262–269. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li H, Pan H, Ning C, Tan G, Liao J and Ni
G: Magnesium with micro-arc oxidation coating and polymeric
membrane: An in vitro study on microenvironment. J Mater Sci Mater
Med. 26:1472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang YS and Liu HW: TEM Analysis on
Micro-Arc Oxide Coating on the Surface of Magnesium Alloy. J Mat
Eng Perf. 20:463–467. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ma WH, Liu YJ, Wang W and Zhang YZ:
Improved biological performance of magnesium by micro-arc
oxidation. Braz J Med Biol Res. 48:214–225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pan YK, Chen CZ, Wang DG and Yu X:
Microstructure and biological properties of micro-arc oxidation
coatings on ZK60 magnesium alloy. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl
Biomater. 100:1574–1586. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han P, Tan M, Zhang S, Ji W, Li J, Zhang
X, Zhao C, Zheng Y and Chai Y: Shape and Site dependent in vivo
degradation of Mg-Zn pins in rabbit femoral condyle. Int J Mol Sci.
15:2959–2970. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marukawa E, Tamai M, Takahashi Y,
Hatakeyama I, Sato M, Higuchi Y, Kakidachi H, Taniguchi H, Sakamoto
T, Honda J, et al: Comparison of magnesium alloys and
poly-l-lactide screws as degradable implants in a canine fracture
model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 104:1282–1289. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Victor SP and Muthu J: Bioactive,
mechanically favorable, and biodegradable copolymer nanocomposites
for orthopedic applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
39:150–160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Walker J, Shadanbaz S, Woodfield TB,
Staiger MP and Dias GJ: Magnesium biomaterials for orthopedic
application: A review from a biological perspective. J Biomed Mater
Res B Appl Biomater. 102:1316–1331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yeung KW and Wong KH: Biodegradable
metallic materials for orthopaedic implantations: A review. Technol
Health Care. Sep 6–2012.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Niu Y, Dong W, Guo H, Deng Y, Guo L, An X,
He D, Wei J and Li M: Mesoporous magnesium silicate-incorporated
poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone)
bioactive composite beneficial to osteoblast behaviors. Int J
Nanomedicine. 9:2665–2675. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hofstetter J, Martinelli E, Weinberg AM,
Becker M, Mingler B, Peter J, Uggowitzera J and Löffler JF:
Assessing the degradation performance of ultrahigh-purity magnesium
in vitro, and in vivo. Corrosion Sci. 91:29–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Witkowski M, Hubert J and Mazur A: Methods
of assessment of magnesium status in humans: A systematic review.
Magnes Res. 24:1632011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schambach SJ, Bag S, Schilling L, Groden C
and Brockmann MA: Application of micro-CT in small animal imaging.
Methods. 50:2–13. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vanderoost J and van Lenthe GH: From
histology to micro-CT: Measuring and modeling resorption cavities
and their relation to bone competence. World J Radiol. 6:643–656.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Karl-Göran Thorngren: Proceedings of the
Swedish Orthopedic Society Helsingborg, June 1–2, 1987. Acta Orth.
59:77–100. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang ZL, Yu S, Sether LA and Haughton VM:
Incidence of unfused ossicles in the lumbar facet joints: CT, MR,
and cryomicrotomy study. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 13:594–597. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kapadia RD, Stroup GB, Badger AM, Koller
B, Levin JM, Coatney RW, Dodds RA, Liang X, Lark MW and Gowen M:
Applications of micro-CT and MR microscopy to study pre-clinical
models of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Technol Health Care.
6:361–372. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ding M, Odgaard A and Hvid I: Accuracy of
cancellous bone volume fraction measured by micro-CT scanning. J
Biomech. 32:323–326. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Salmon P: Micro-CT 3D Image Analysis
Techniques for Orthopedic Applications: Metal Implant-to-Bone
Contact Surface and Porosity of BiomaterialsA Practical Manual For
Musculoskeletal Research. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte.
Ltd.; Hackensack, NJ: pp. 583–603. 2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Rhee Y, Hur JH, Won YY, Lim SK, Beak MH,
Cui WQ, Kim KG and Kim YE: Assessment of bone quality using finite
element analysis based upon micro-CT images. Clin Orthop Surg.
1:40–47. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Agholme F, Li X, Isaksson H, Ke HZ and
Aspenberg P: Sclerostin antibody treatment enhances metaphyseal
bone healing in rats. J Bone Miner Res. 25:2412–2418. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang J, Bi L, Bai JP, et al: Comparative
study of micro-CT and histological section in bone morphometry.
Orth J Chin. 381–384. 009.(In Chinese).
|
|
48
|
Park CH, Abramson ZR, Taba M Jr, Jin Q,
Chang J, Kreider JM, Goldstein SA and Giannobile WV:
Three-dimensional micro-computed tomographic imaging of alveolar
bone in experimental bone loss or repair. J Periodontol.
78:273–281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Buie HR, Campbell GM, Klinck RJ, MacNeil
JA and Boyd SK: Automatic segmentation of cortical and trabecular
compartments based on a dual threshold technique for in vivo
micro-CT bone analysis. Bone. 41:505–515. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Clark DP and Badea CT: Micro-CT of
rodents: State-of-the-art and future perspectives. Phys Med.
30:619–634. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chang CY, Huang AJ and Palmer WE:
Radiographic evaluation of hip implants. Semin Musculoskeletal
Radiol. 19:12–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ding W: Opportunities and challenges for
the biodegradable magnesium alloys as next-generation biomaterials.
Regen Biomater. 3:79–86. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu YJ, Yang ZY, Tan LL, Li H and Zhang
YZ: An animal experimental study of porous magnesium scaffold
degradation andosteogenesis. Braz J Med Biol Res. 47:715–720. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
World Health Organization (WHO), .
Strategic Initiative for Developing Capacity in Ethical Review.
WHO; Geneva: 2005
|
|
55
|
Wong RW, Rabie B, Bendeus M and Hägg U:
The effects of Rhizoma Curculiginis and Rhizoma Drynariae, extracts
on bones. Chin Med. 2:132007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Feldkamp LA, Goldstein SA, Parfitt AM,
Jesion G and Kleerekoper M: The direct examination of
three-dimensional bone architecture in vitro by computed
tomography. J Bone Miner Res. 4:3–11. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang J, Witte F, Xi T, Zheng Y, Yang K,
Yang Y, Zhao D, Meng J, Li Y and Li W: Recommendation for modifying
current cytotoxicity testing standards for biodegradable
magnesium-based materials. Acta Biomater. 21:237–249. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen X, Geng Y and Pan F: Research
progress in magnesium alloys as functional materials. Rare Metal
Mat Eng. 45:2269–2274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Chen Y, Xu Z, Smith C and Sankar J: Recent
advances on the development of magnesium alloys for biodegradable
implants. Acta Biomater. 10:4561–4573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Weizbauer A, Kieke M, Rahim MI, Angrisani
GL, Willbold E, Diekmann J, Flörkemeier T, Windhagen H, Müller PP,
Behrens P and Budde S: Magnesium-containing layered double
hydroxides as orthopaedic implant coating materials An in vitro and
in vivo study. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 104:525–531.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Janning C, Willbold E, Vogt C, Nellesen J,
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Windhagen H, Thorey F and Witte F: Magnesium
hydroxide temporarily enhancing osteoblast activity and decreasing
the osteoclast number in peri-implant bone remodeling. Acta
Biomater. 6:1861–1868. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Salahshoor M and Guo Y: Biodegradable
orthopedic magnesium-calcium (MgCa) alloys, processing, and
corrosion performance. Materials (Basel). 5:135–155. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Weng L and Webster TJ: Nanostructured
magnesium has fewer detrimental effects on osteoblast function. Int
J Nanomedicine. 8:1773–1781. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hampp C, Ullmann B, Reifenrath J, Nina A,
Dina D, Dirk B, Jan-Marten S and Andrea ML: Research on the
biocompatibility of the new magnesium alloy LANd442-An in vivo
study in the Rabbit Tibia over 26 weeks. Advanced Engineering
Materials. 14:B28–B37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Kuhlmann J, Bartsch I, Willbold E,
Schuchardt S, Holz O, Hort N, Höche D, Heineman WR and Witte F:
Fast escape of hydrogen from gas cavities around corroding
magnesium implants. Acta Biomater. 9:8714–8721. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|