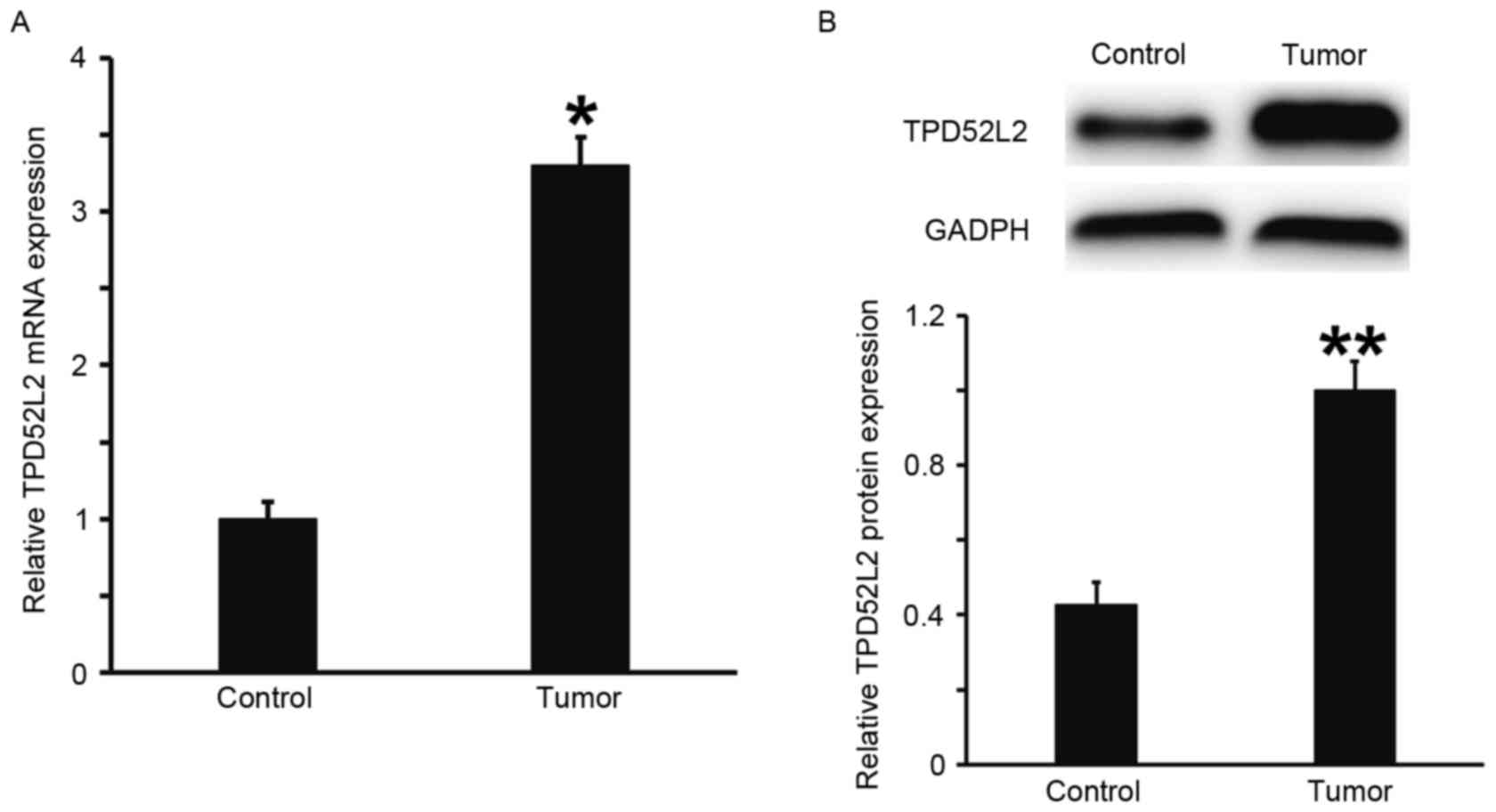
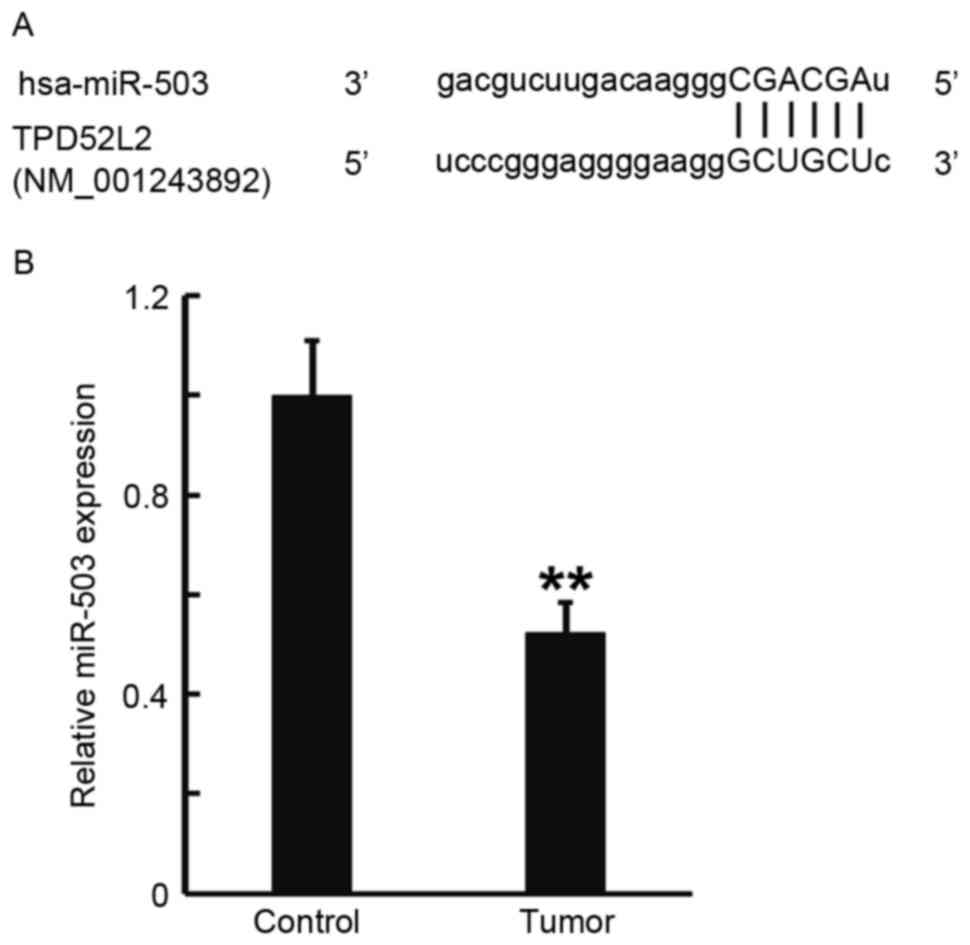
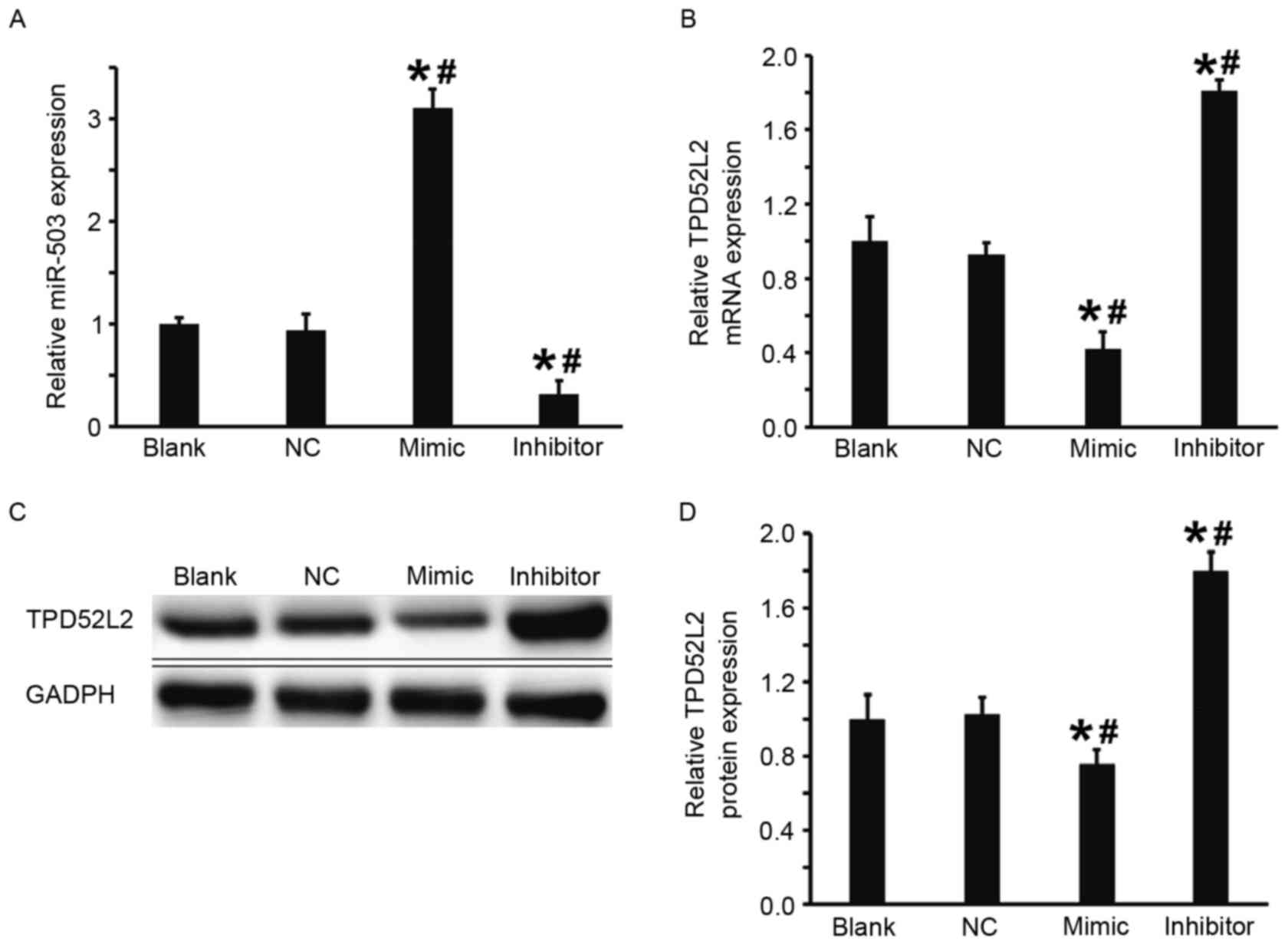
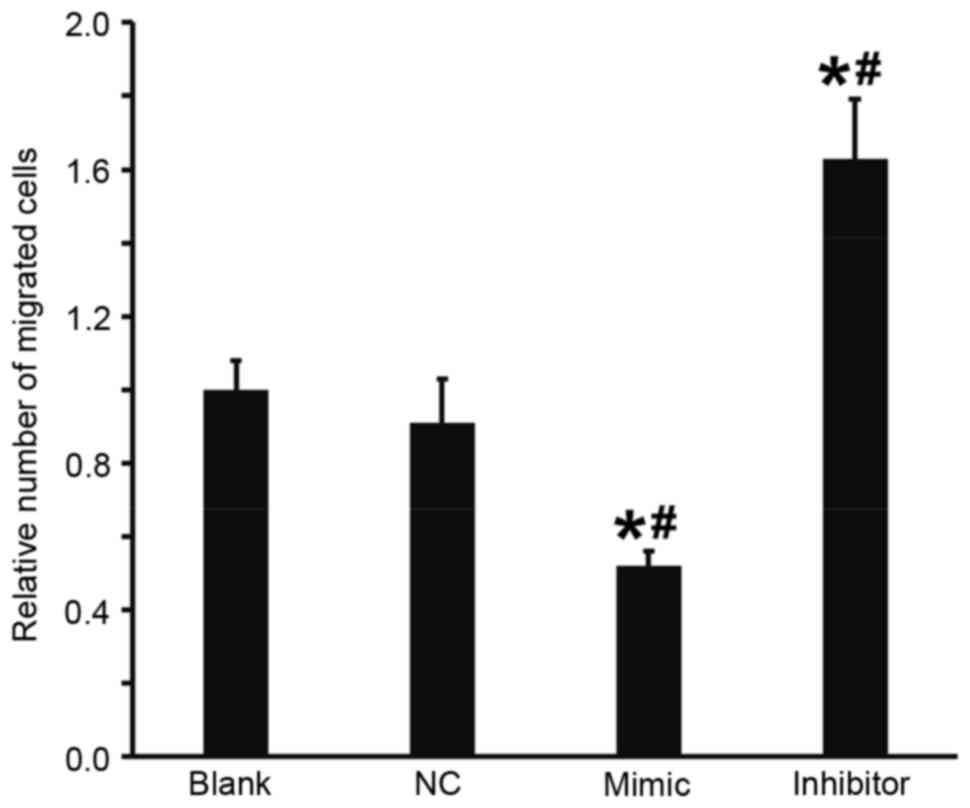
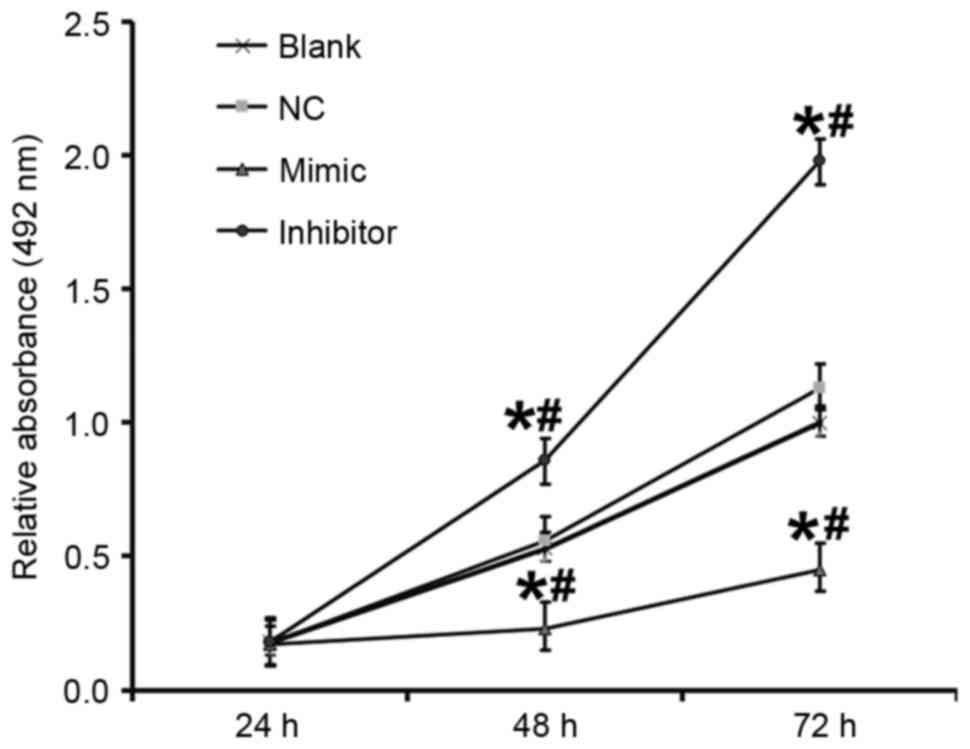
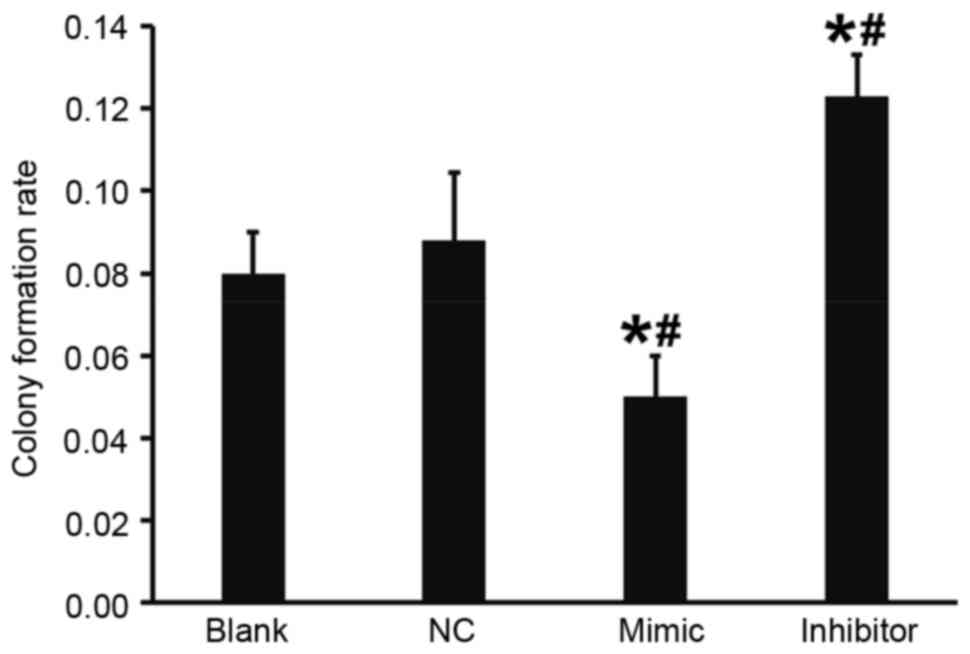
|
1
|
Grönberg H: Prostate cancer epidemiology.
Lancet. 361:859–864. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wong YC and Wang YZ: Growth factors and
epithelial-stromal interactions in prostate cancer development. Int
Rev Cytol. 199:65–116. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Taylor BS, Schultz N, Hieronymus H,
Gopalan A, Xiao Y, Carver BS, Arora VK, Kaushik P, Cerami E, Reva
B, et al: Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer.
Cancer Cell. 18:11–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Devaney JM, Wang S, Funda S, Long J,
Taghipour DJ, Tbaishat R, Furbert-Harris P, Ittmann M and
Kwabi-Addo B: Identification of novel DNA-methylated genes that
correlate with human prostate cancer and high-grade prostatic
intraepithelial neoplasia. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
16:292–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marcelli M, Ittmann M, Mariani S,
Sutherland R, Nigam R, Murthy L, Zhao Y, DiConcini D, Puxeddu E,
Esen A, et al: Androgen receptor mutations in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 60:944–949. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Boutros R, Fanayan S, Shehata M and Byrne
JA: The tumor protein D52 family: Many pieces, many puzzles.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 325:1115–1121. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thomas DD, Martin CL, Weng N, Byrne JA and
Groblewski GE: Tumor protein D52 expression and Ca2+-dependent
phosphorylation modulates lysosomal membrane protein trafficking to
the plasma membrane. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 298:C725–C739.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Balleine RL, Fejzo MS, Sathasivam P,
Basset P, Clarke CL and Byrne JA: The hD52 (TPD52) gene is a
candidate target gene for events resulting in increased 8q21 copy
number in human breast carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
29:48–57. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Chen CL, Pan QZ, Wu YY, Zhao JJ,
Jiang SS, Chao J, Zhang XF, Zhang HX, Zhou ZQ, et al: Decreased
TPD52 expression is associated with poor prognosis in primary
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:6323–6334. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Z, Sun J, Zhao Y, Guo W, Lv K and
Zhang Q: Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of tumor protein D52-like 2
inhibits glioma cell proliferation. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
60:39–44. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pan ZY, Yang Y, Pan H, Zhang J, Liu H,
Yang Y, Huang G, Yin L, Huang J and Zhou WP: Lentivirus-mediated
TPD52L2 depletion inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells
in vitro. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:2334–2341. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Almeida MI, Reis RM and Calin GA: MicroRNA
history: Discovery, recent applications, and next frontiers. Mutat
Res. 717:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK,
Vessella RL, Tammela TL and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA expression
profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6130–6135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A,
Giuffrida R, Memeo L, D'Urso L, Pagliuca A, Biffoni M, Labbaye C,
et al: The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by
targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 14:1271–1277.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao P, Tchernyshyov I, Chang TC, Lee YS,
Kita K, Ochi T, Zeller KI, De Marzo AM, Van Eyk JE, Mendell JT and
Dang CV: c-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial
glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature.
458:762–765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao JJ, Yang J, Lin J, Yao N, Zhu Y,
Zheng J, Xu J, Cheng JQ, Lin JY and Ma X: Identification of miRNAs
associated with tumorigenesis of retinoblastoma by miRNA microarray
analysis. Childs Nerv Syst. 25:13–20. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Watahiki A and Wang Y, Morris J, Dennis K,
O'Dwyer HM, Gleave M, Gout PW and Wang Y: MicroRNAs associated with
metastatic prostate cancer. PLoS One. 6:e249502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiu T, Zhou L, Wang T, Xu J, Wang J, Chen
W, Zhou X, Huang Z, Zhu W, Shu Y and Liu P: miR-503 regulates the
resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin by
targeting Bcl-2. Int J Mol Med. 32:593–598. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Epstein JI, Allsbrook WC Jr, Amin MB and
Egevad LL: ISUP Grading Committee: The 2005 International Society
of Urological Pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on Gleason
grading of prostatic carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 29:1228–1242.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N.: Single-step
method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium
thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem.
162:156–159. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li W, Ma H and Sun J: microRNA-34a/c
function as tumor suppressors in Hep-2 laryngeal carcinoma cells
and may reduce GALNT7 expression. Mol Med Rep. 9:1293–1298. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou B, Ma R, Si W, Li S, Xu Y, Tu X and
Wang Q: MicroRNA-503 targets FGF2 and VEGFA and inhibits tumor
angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Lett. 333:159–169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ummanni R, Teller S, Junker H, Zimmermann
U, Venz S, Scharf C, Giebel J and Walther R: Altered expression of
tumor protein D52 regulates apoptosis and migration of prostate
cancer cells. FEBS J. 275:5703–5713. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou J, Tao Y, Peng C, Gu P and Wang W:
miR-503 regulates metastatic function through Rho guanine
nucleotide exchanger factor 19 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg
Res. 188:129–136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Y, Liu L, Zhang Y, Guan H, Wu J, Zhu
X, Yuan J and Li M: MiR-503 targets PI3K p85 and IKK-β and
suppresses progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
135:1531–1542. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang T, Ge G, Ding Y, Zhou X, Huang Z, Zhu
W, Shu Y and Liu P: MiR-503 regulates cisplatin resistance of human
gastric cancer cell lines by targeting IGF1R and BCL2. Chin Med J
(Engl). 127:2357–2362. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li L, Sarver AL, Khatri R, Hajeri PB,
Kamenev I, French AJ, Thibodeau SN, Steer CJ and Subramanian S:
Sequential expression of miR-182 and miR-503 cooperatively targets
FBXW7, contributing to the malignant transformation of colon
adenoma to adenocarcinoma. J Pathol. 234:488–501. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu Y, Guo L, Liu J, Liu R, Liu M and Chen
J: The reversing and molecular mechanisms of miR-503 on the
drug-resistance to cisplatin in A549/DDP cells. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za
Zhi. 17:1–7. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Polioudakis D, Abell NS and Iyer VR:
miR-503 represses human cell proliferation and directly targets the
oncogene DDHD2 by non-canonical target pairing. BMC Genomics.
16:402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|