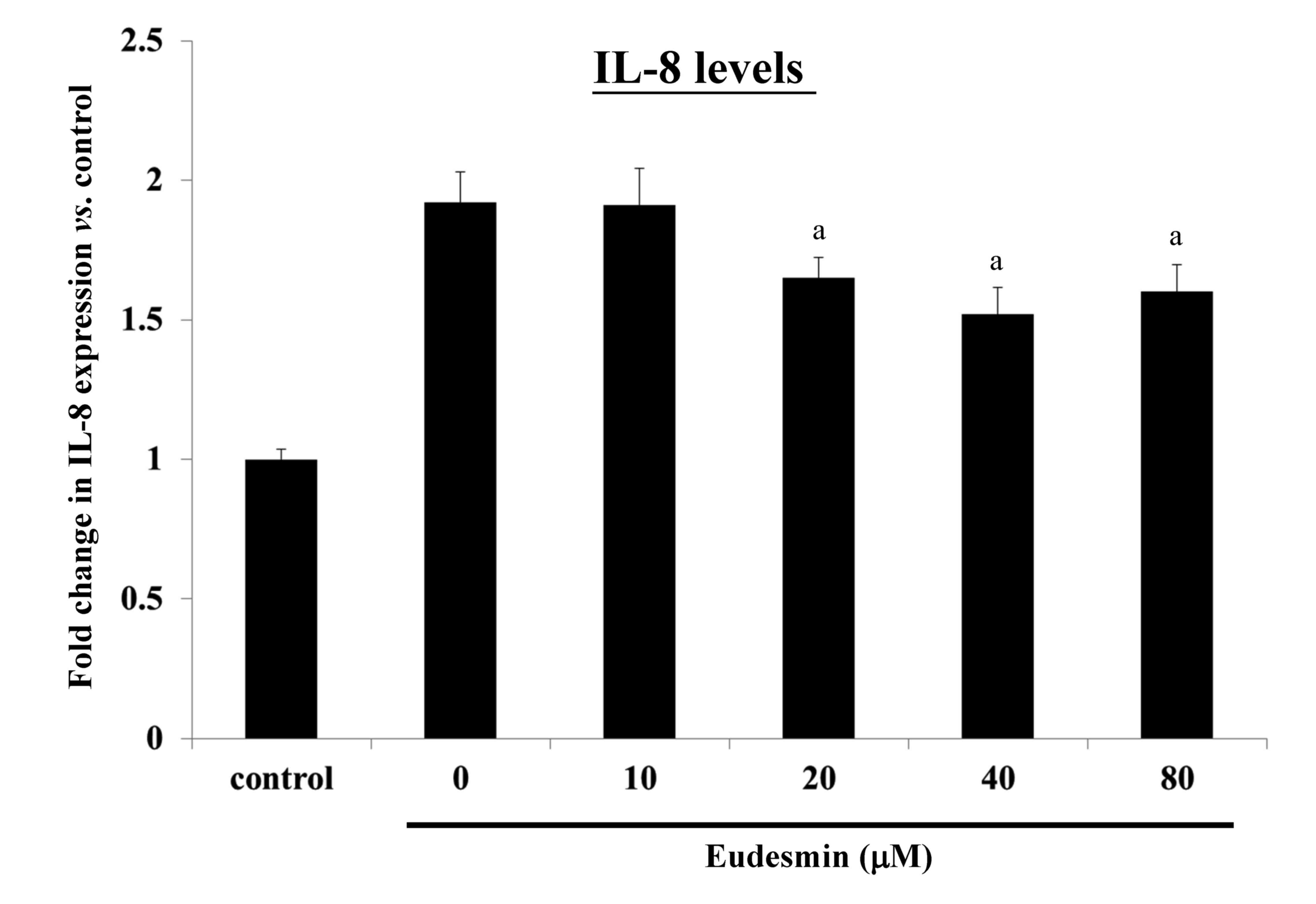
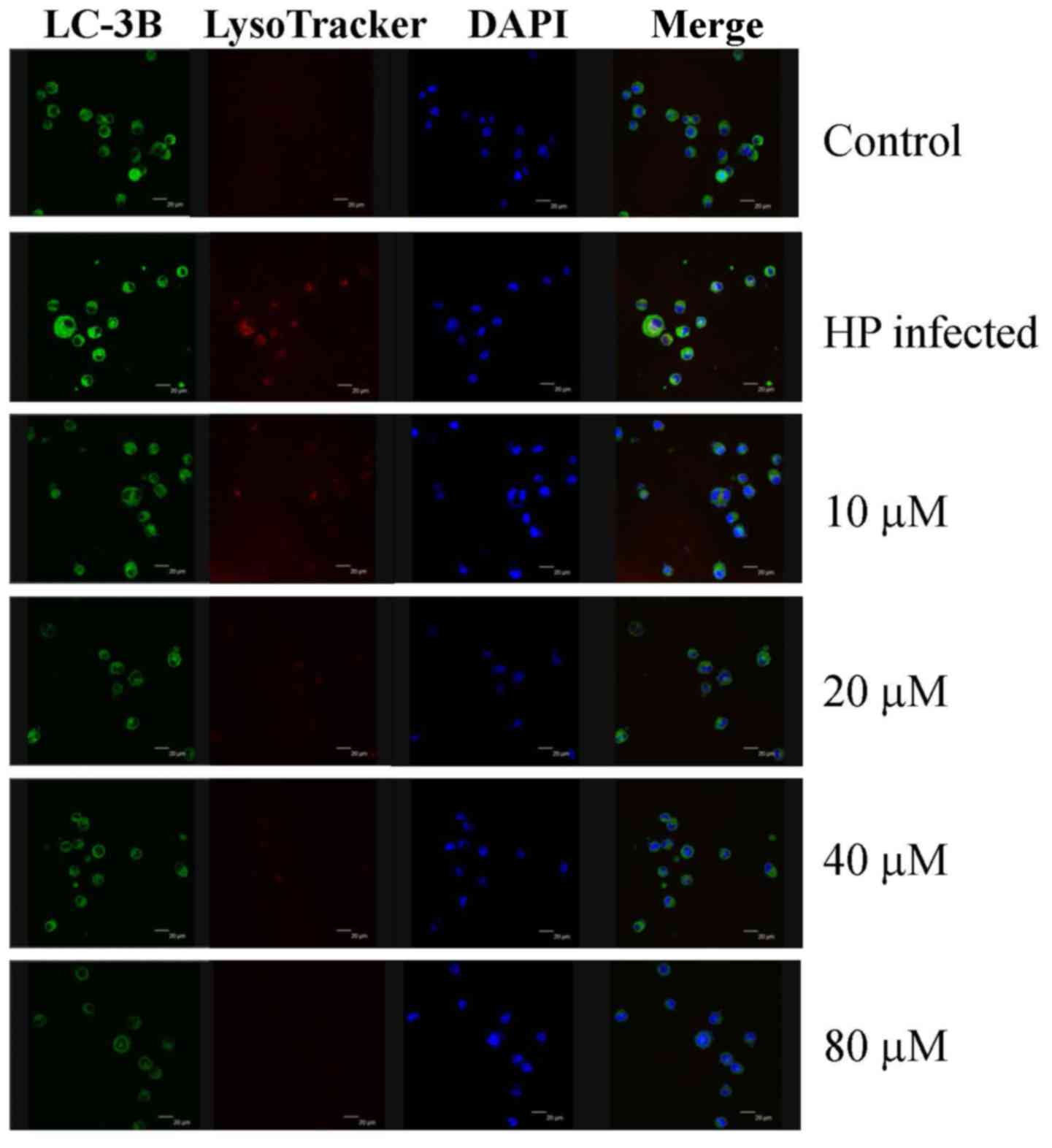
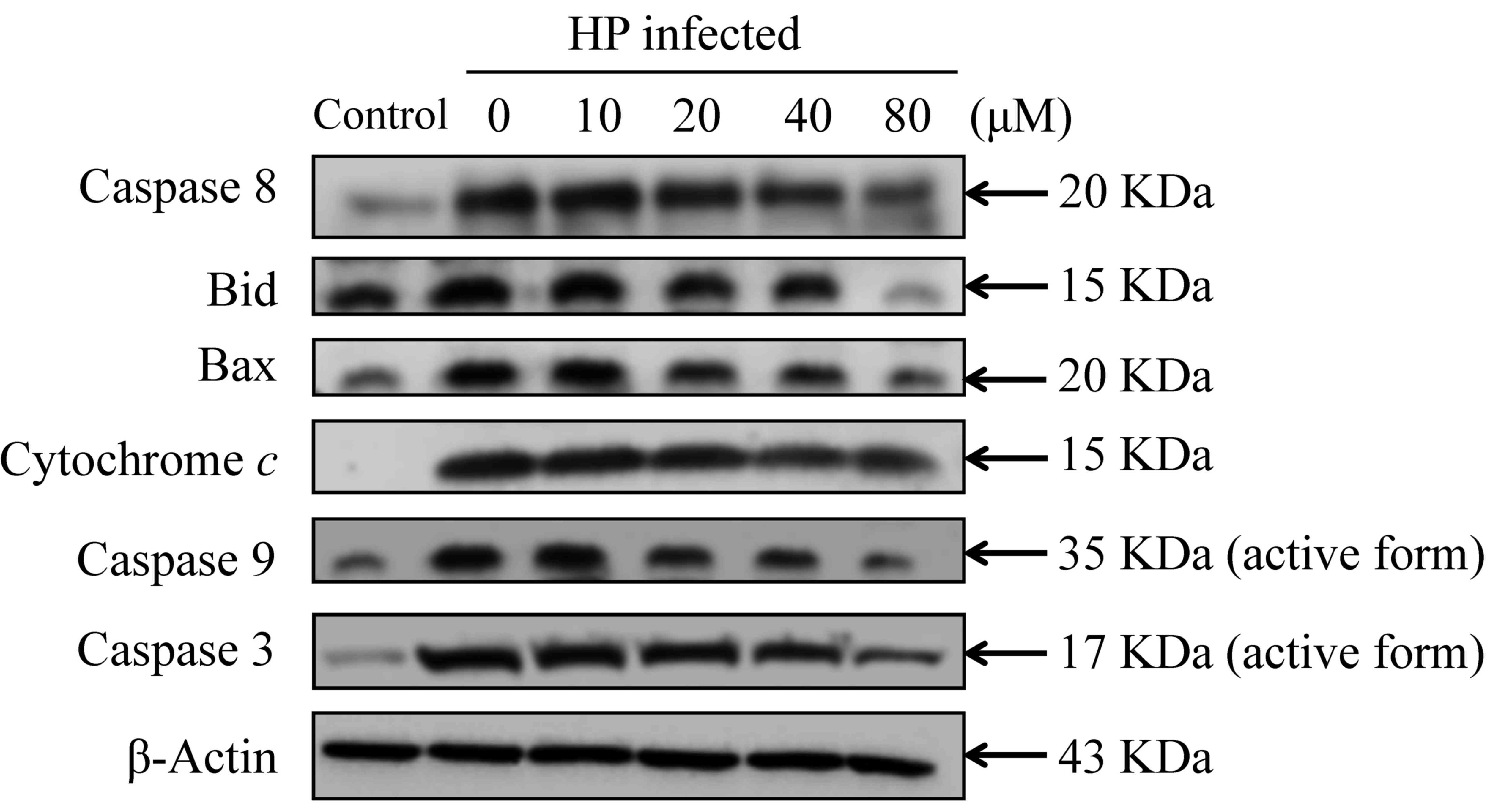
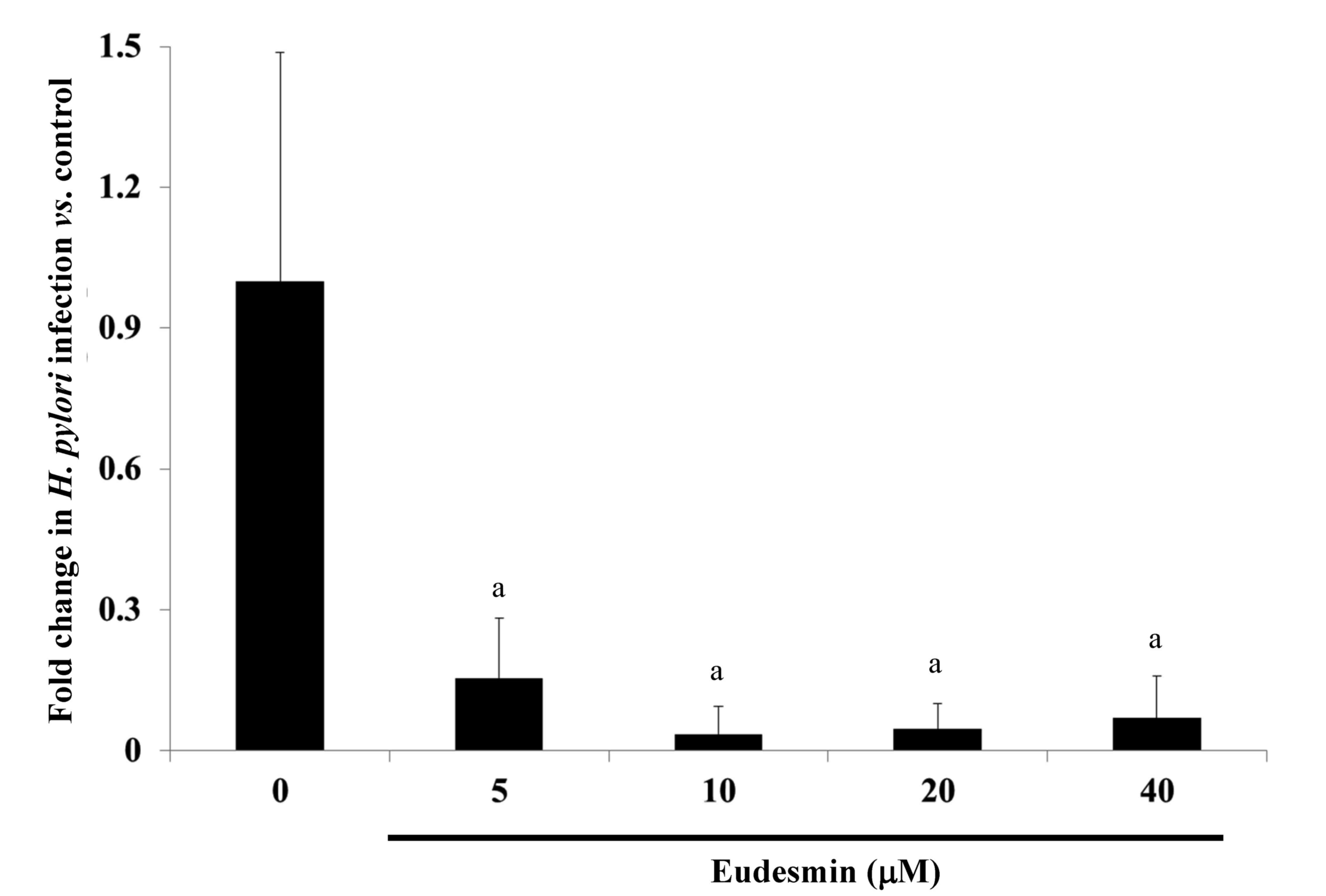
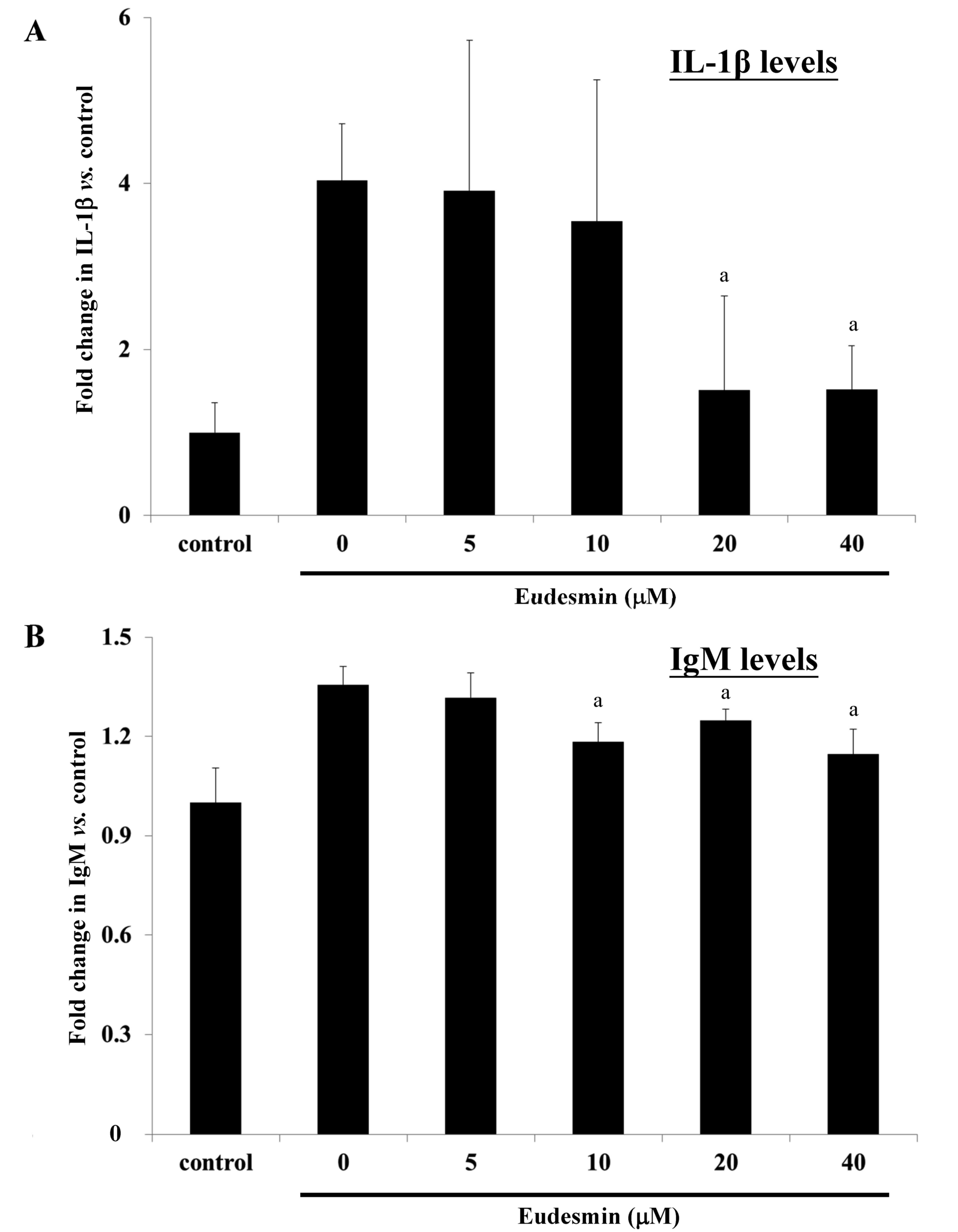
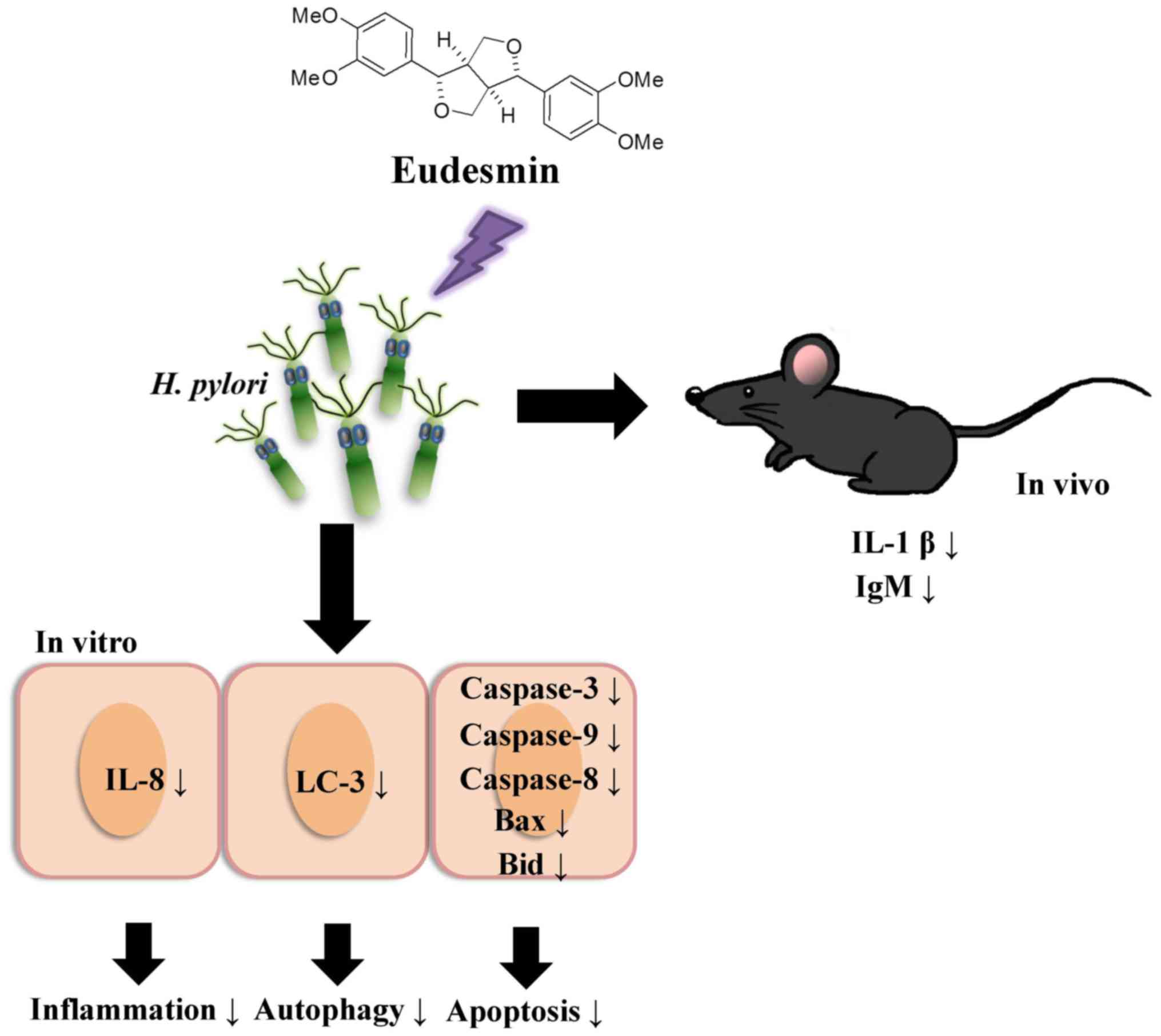
|
1
|
de Bernard M and Josenhans C: Pathogenesis
of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 19 Suppl 1:S11–S18.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kountouras J, Zavos C, Gavalas E and
Tzilves D: Challenge in the pathogenesis of autoimmune
pancreatitis: Potential role of Helicobacter pylori infection via
molecular mimicry. Gastroenterology. 133:368–369. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ding SZ, Minohara Y, Fan XJ, Wang J, Reyes
VE, Patel J, Dirden-Kramer B, Boldogh I, Ernst PB and Crowe SE:
Helicobacter pylori infection induces oxidative stress and
programmed cell death in human gastric epithelial cells. Infect
Immun. 75:4030–4039. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clevers HC and Bevins CL: Paneth cells:
Maestros of the small intestinal crypts. Annu Rev Physiol.
75:289–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peek RM Jr, Fiske C and Wilson KT: Role of
innate immunity in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric malignancy.
Physiol Rev. 90:831–858. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Federico A, Gravina AG, Miranda A,
Loguercio C and Romano M: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
infection: Which regimen first? World J Gastroenterol. 20:665–672.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nam SY, Park BJ, Ryu KH and Nam JH: Effect
of Helicobacter pylori infection and its eradication on the fate of
gastric polyps. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:449–454.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang JC, Yang HC, Shun CT, Wang TH, Chien
CT and Kao JY: Catechins and sialic acid attenuate Helicobacter
pylori-triggered epithelial caspase-1 activity and eradicate
Helicobacter pylori infection. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:2485852013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Castano-Rodriguez N, Kaakoush NO, Goh KL,
Fock KM and Mitchell HM: Autophagy in Helicobacter pylori infection
and related gastric cancer. Helicobacter. 20:353–369. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Labbé K and Saleh M: Cell death in the
host response to infection. Cell Death Differ. 15:1339–1349. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu WH, Liu TC and Mong MC: Antibacterial
effects and action modes of asiatic acid. Biomedicine (Taipei).
5:162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raju D, Hussey S, Ang M, Terebiznik MR,
Sibony M, Galindo-Mata E, Gupta V, Blanke SR, Delgado A,
Romero-Gallo J, et al: Vacuolating cytotoxin and variants in
Atg16L1 that disrupt autophagy promote Helicobacter pylori
infection in humans. Gastroenterology. 142:1160–1171. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
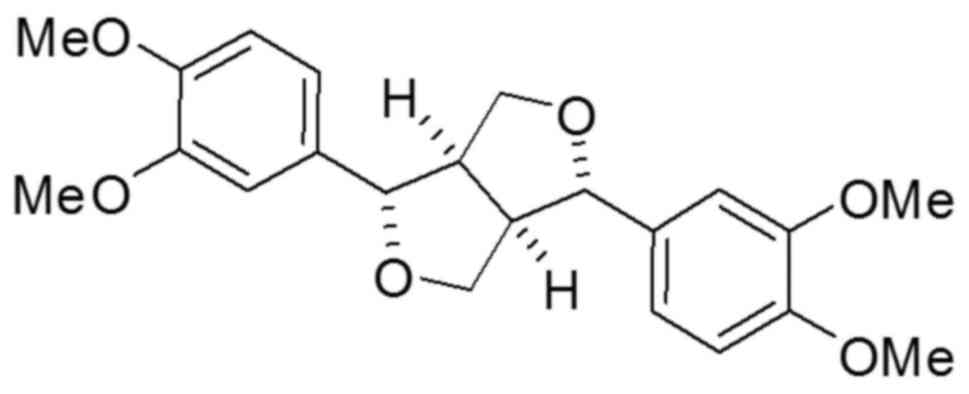
Liu H, Song Z, Liao DG, Zhang TY, Liu F,
Zhuang K, Luo K, Yang L, He J and Lei JP: Anticonvulsant and
sedative effects of eudesmin isolated from Acorus tatarinowii on
mice and rats. Phytother Res. 29:996–1003. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cho JY, Yoo ES, Baik KU and Park MH:
Eudesmin inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha production and T cell
proliferation. Arch Pharm Res. 22:348–353. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Raimundo JM, Trindade AP, Velozo LS,
Kaplan MA, Sudo RT and Zapata-Sudo G: The lignan eudesmin extracted
from Piper truncatum induced vascular relaxation via activation of
endothelial histamine H1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 606:150–154.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang YJ, Park JI, Lee HJ, Seo SM, Lee OK,
Choi DH, Paik KH and Lee MK: Effects of (+)-eudesmin from the stem
bark of magnolia kobus DC. var. borealis Sarg. on neurite outgrowth
in PC12 cells. Arch Pharm Res. 29:1114–1118. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang CM, Chen HT, Li TC, Weng JH, Jhan YL,
Lin SX and Chou CH: The role of pentacyclic triterpenoids in the
allelopathic effects of Alstonia scholaris. J Chem Ecol. 40:90–98.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Batista AND, Batista JM, Lopez SN, Furlan
M, Cavalheiro AJ, Silva DHS, Bolzani VDS, Nunomura M and Yoshida M:
Aromatic compounds from three Brazilian Lauraceae species. Quim
Nova. 33:321–323. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Poon SK, Chang CS, Su J, Lai CH, Yang CC,
Chen GH and Wang WC: Primary resistance to antibiotics and its
clinical impact on the efficacy of Helicobacter pylori
lansoprazole-based triple therapies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
16:291–296. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lai CH, Kuo CH, Chen PY, Poon SK, Chang CS
and Wang WC: Association of antibiotic resistance and higher
internalization activity in resistant Helicobacter pylori isolates.
J Antimicrob Chemother. 57:466–471. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li L, Kelly LK, Ayub K, Graham DY and Go
MF: Genotypes of Helicobacter pylori obtained from gastric ulcer
patients taking or not taking NSAIDs. Am J Gastroenterol.
94:1502–1507. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
da Costa DM, Pereira Edos S and Rabenhorst
SH: What exists beyond cagA and vacA? Helicobacter pylori genes in
gastric diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 21:10563–10572. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Torres J and Backert S: Pathogenesis of
Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 13 Suppl 1:S13–S17.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Alzahrani S, Lina TT, Gonzalez J, Pinchuk
IV, Beswick EJ and Reyes VE: Effect of Helicobacter pylori on
gastric epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol. 20:12767–12780.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Deen NS, Huang SJ, Gong L, Kwok T and
Devenish RJ: The impact of autophagic processes on the
intracellular fate of Helicobacter pylori: More tricks from an
enigmatic pathogen? Autophagy. 9:639–652. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
El-Omar EM, Carrington M, Chow WH, McColl
KE, Bream JH, Young HA, Herrera J, Lissowska J, Yuan CC, Rothman N,
et al: Interleukin-1 polymorphisms associated with increased risk
of gastric cancer. Nature. 404:398–402. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|