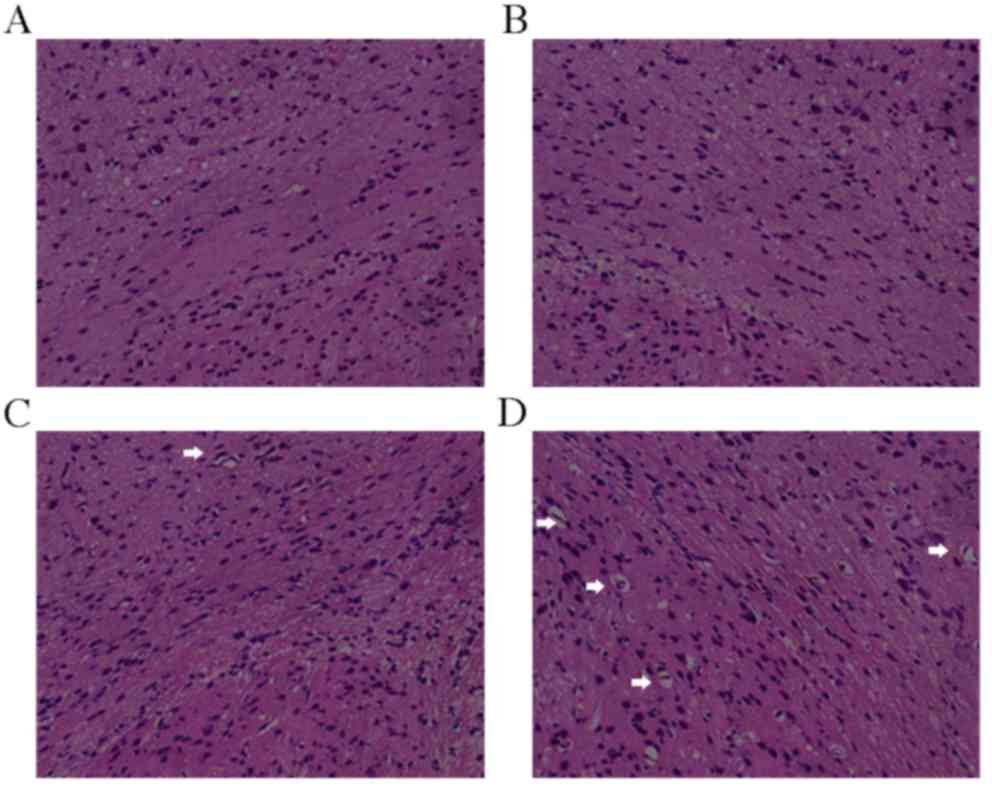
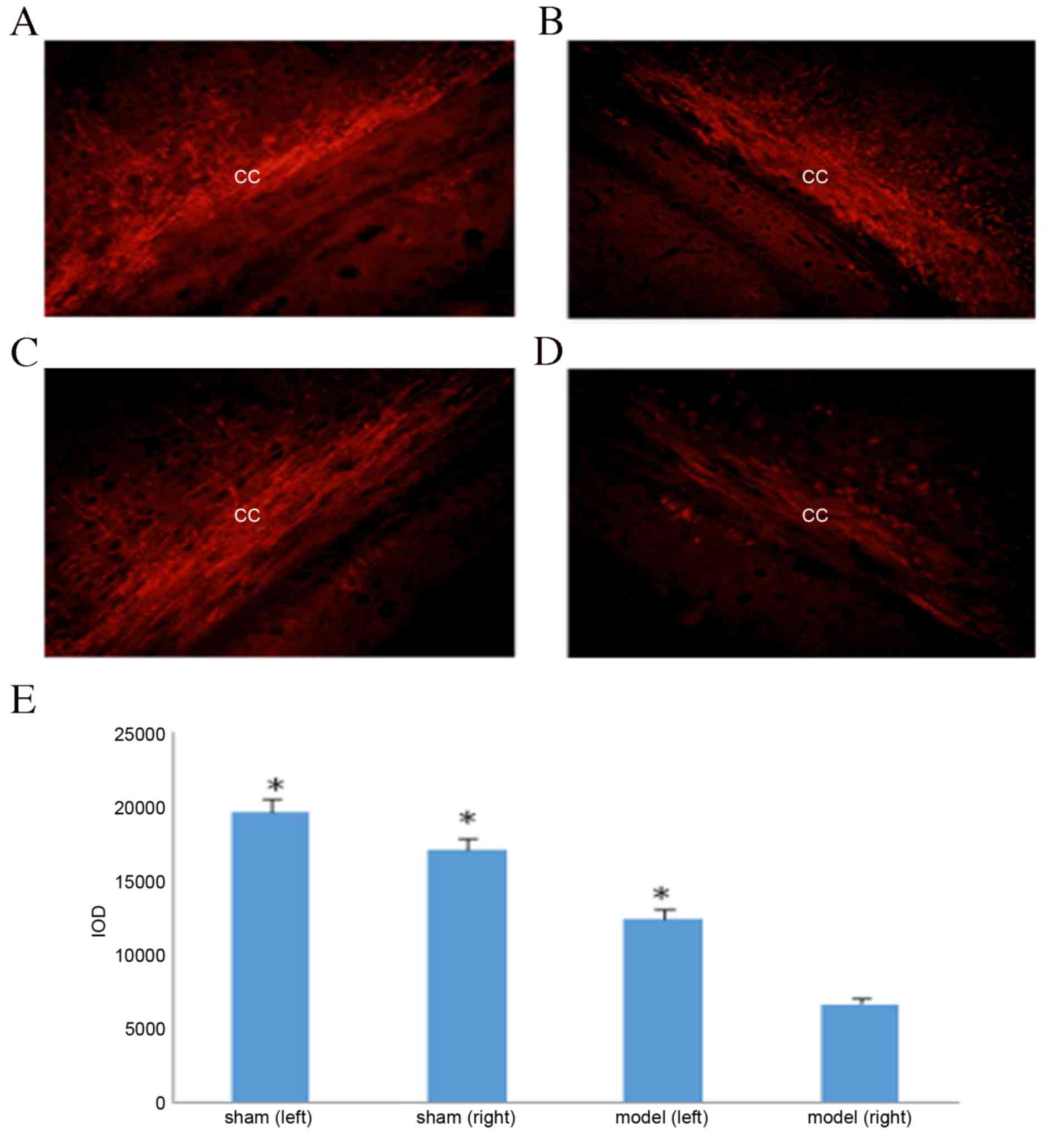
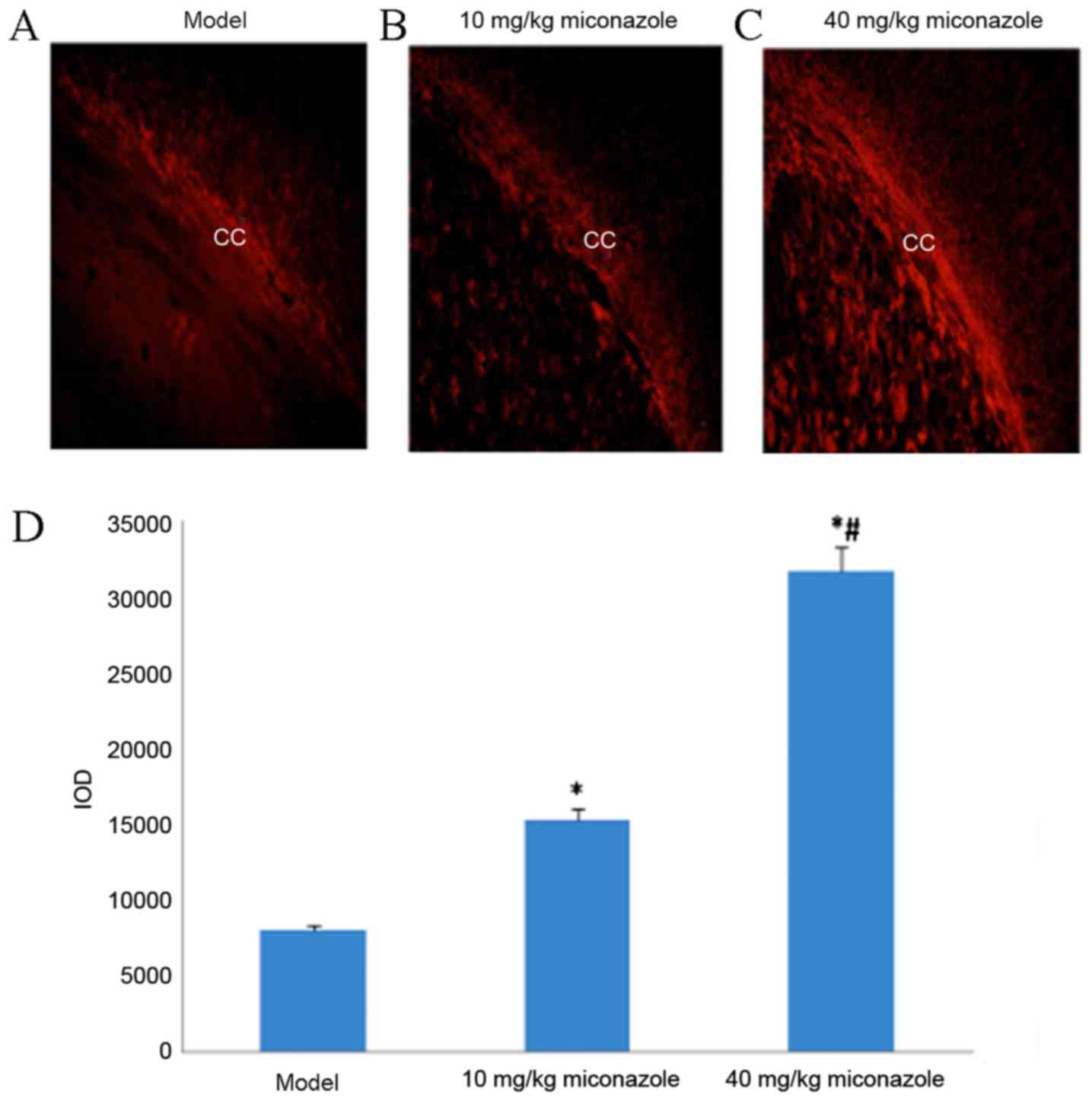
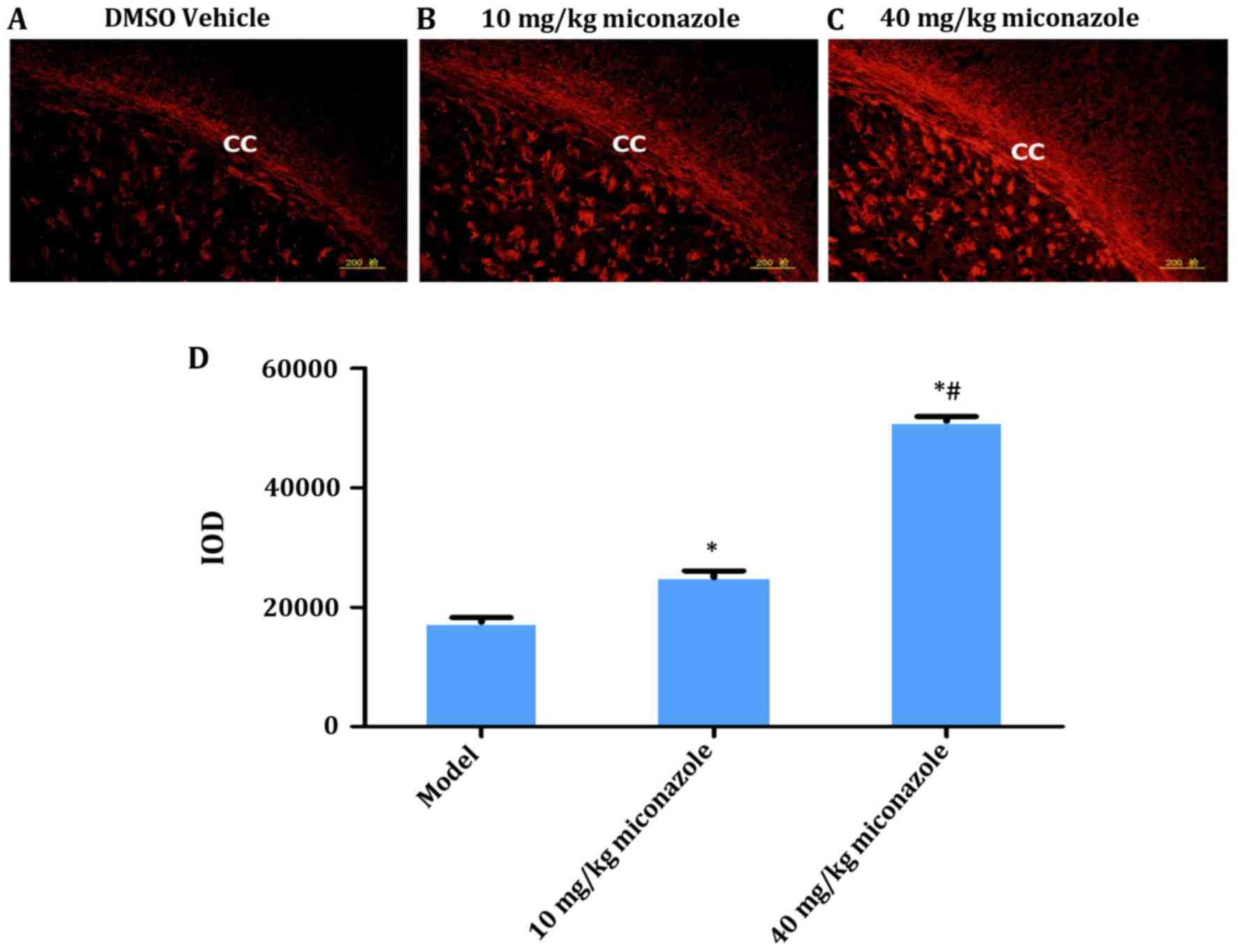
|
1
|
Lopez Juarez A, He D and Richard Lu Q:
Oligodendrocyte progenitor programming and reprogramming: Toward
myelin regeneration. Brain Res. 1638:209–220. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chew LJ and DeBoy CA: Pharmacological
approaches to intervention in hypomyelinating and demyelinating
white matter pathology. Neuropharmacology. 110:605–625. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ryan M, Ibrahim M and Parmar HA: Secondary
demyelination disorders and destruction of white matter. Radiol
Clin North Am. 52:337–354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bando Y, Nomura T, Bochimoto H, Murakami
K, Tanaka T, Watanabe T and Yoshida S: Abnormal morphology of
myelin and axon pathology in murine models of multiple sclerosis.
Neurochem Int. 81:16–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jeong IH, Choi JY, Kim SH, Hyun JW, Joung
A, Lee J and Kim HJ: Comparison of myelin water fraction values in
periventricular white matter lesions between multiple sclerosis and
neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Mult Scler. 22:1616–1620.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Counsell SJ, Rutherford MA, Cowan F and
Edwards AD: Magnetic resonance imaging of preterm brain injury.
Arch Dis Child FetalNeonatal Ed. 88:F269–F274. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Deverman BE and Patterson PH: Exogenous
leukemia inhibitory factor stimulates oligodendrocyte progenitor
cell proliferation and enhances hippocampal remyelination. J
Neurosci. 32:2100–2109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Grulova I, Slovinska L, Blaško J, Devaux
S, Wisztorski M, Salzet M, Fournier I, Kryukov O, Cohen S and
Cizkova D: Delivery of alginate scaffold releasing two trophic
factors for spinal cord injury repair. Sci Rep. 5:137022015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jiang S, Seng S, Avraham HK, Fu Y and
Avraham S: Process elongation of oligodendrocytes is promoted by
the Kelch-related protein MRP2/KLHL1. J Biol Chem. 282:12319–12329.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Najm FJ, Madhavan M, Zaremba A, Shick E,
Karl RT, Factor DC, Miller TE, Nevin ZS, Kantor C, Sargent A, et
al: Drug-based modulation of endogenous stem cells promotes
functional remyelination in vivo. Nature. 522:216–220. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Volpe JJ: Cerebral white matter injury of
the premature infant-more common than you think. Pediatrics.
112:176–180. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Erceg S, Ronaghi M, Oria M, Roselló MG,
Aragó MA, Lopez MG, Radojevic I, Moreno-Manzano V,
Rodríguez-Jiménez FJ, Bhattacharya SS, et al: Transplanted
oligodendrocytes and motoneuron progenitors generated from human
embryonic stem cells promote locomotor recovery after spinal cord
transection. Stem Cells. 28:1541–1549. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Welin AK, Sedin P, Lapatto R, Sultan B,
Hagberg H, Gressens P, Kjellmer I and Mallard C: Melatonin reduces
inflammation and cell death in white matter in the midgestation
fetal sheep following umbilical cord occlusion. Pediatr Res.
61:153–158. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yuan QC, Jiang L, Zhu LH and Yu DF:
Impacts of erythropoietin on vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 2 by the extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling
pathway in a neonatal rat model of periventricular white matter
damage. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 38: 217–221, 2016.
Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 38: 217–221, 2016. 38: 217–221,
2016:217–221, 2016–221, 2016. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Coetzee T, Fujita N, Dupree J, Shi R,
Blight A, Suzuki K, Suzuki K and Popko B: Myelination in the
absence of galactocerebroside and sulfatide: Normal structure with
abnormal function and regional instability. Cell. 86:209–219. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mineur YS, Belzung C and Crusio WE:
Effects of unpredictable chronic mild stress on anxiety and
depression-like behavior in mice. Behav Brain Res. 175:43–50. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Breu M, Zhang J, Porambo M, Pletnikov MV,
Goeral K, Kakara M, Johnston MV and Fatemi A: Diffusion tensor
imaging abnormalities in the cerebral white matter correlate with
sex-dependent neurobehavioral deficits in adult mice with neonatal
ischemia. Dev Neurosci. 38:83–95. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Anderson PJ: Neuropsychological outcomes
of children born very preterm. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 19:90–96.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Barateiro A and Fernandes A: Temporal
oligodendrocyte lineage progression: In vitro models of
proliferation, differentiation and myelination. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1843:1917–1929. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nistor GI, Totoiu MO, Haque N, Carpenter
MK and Keirstead HS: Human embryonic stem cells differentiate into
oligodendrocytes in high purity and myelinate after spinal cord
transplantation. Glia. 49:385–396. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Webber DJ, van Blitterswijk M and Chandran
S: Neuroprotective effect of oligodendrocyte precursor cell
transplantation in a long-term model of periventricular
leukomalacia. Am J Pathol. 175:2332–2342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chong SY and Chan JR: Tapping into the
glial reservoir: Cells committed to remaining uncommitted. J Cell
Biol. 188:305–312. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dooley D, Vidal P and Hendrix S:
Immunopharmacological intervention for successful neural stem cell
therapy: New perspectives in CNS neurogenesis and repair. Pharmacol
Ther. 141:21–31. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhao XH, Jin WL and Ju G: An in vitro
study on the involvement of LINGO-1 and Rho GTPases in Nogo-A
regulated differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Mol
Cell Neurosci. 36:260–269. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gard AL and Pfeiffer SE: Oligodendrocyte
progenitors isolated directly from developing telencephalon at a
specific phenotypic stage: Myelinogenic potential in a defined
environment. Development. 106:119–132. 1989.
|
|
26
|
Haynes RL, Folkerth RD, Keefe RJ, Sung I,
Swzeda LI, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ and Kinney HC: Nitrosative and
oxidative injury to premyelinating oligodendrocytes in
periventricular leukomalacia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 62:441–450.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jeffries MA, Urbanek K, Torres L, Wendell
SG, Rubio ME and Fyffe-Maricich SL: ERK1/2 activation in
preexisting oligodendrocytes of adult mice drives new myelin
synthesis and enhanced CNS function. J Neurosci. 36:9186–9200.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xiao J, Ferner AH, Wong AW, Denham M,
Kilpatrick TJ and Murray SS: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
1/2 signaling promotes oligodendrocyte myelination in vitro. J
Neurochem. 122:1167–1180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Guardiola-Diaz HM, Ishii A and Bansal R:
Erk1/2 MAPK and mTOR signaling sequentially regulates progression
through distinct stages of oligodendrocyte differentiation. Glia.
60:476–486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gaesser JM and Fyffe-Maricich SL:
Intracellular signaling pathway regulation of myelination and
remyelination in the CNS. Exp Neurol. 283:501–511. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ishii A, Furusho M, Dupree JL and Bansal
R: Role of ERK1/2 MAPK signaling in the maintenance of myelin and
axonal integrity in the adult CNS. J Neurosci. 34:16031–16045.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fyffe-Maricich SL, Schott A, Karl M,
Krasno J and Miller RH: Signaling through ERK1/2 controls myelin
thickness during myelin repair in the adult central nervous system.
J Neurosci. 33:18402–18408. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Xie D, Shen F, He S, Chen M, Han Q, Fang
M, Zeng H, Chen C and Deng Y: IL-1β induces hypomyelination in the
periventricular white matter through inhibition of oligodendrocyte
progenitor cell maturation via FYN/MEK/ERK signaling pathway in
septic neonatal rats. Glia. 64:583–602. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Suzuki T, Hori N, Miyake T, Hori Y and
Mochizuki K: Keratitis caused by a rare fungus, Malassezia
restricta. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 51:292–294. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|