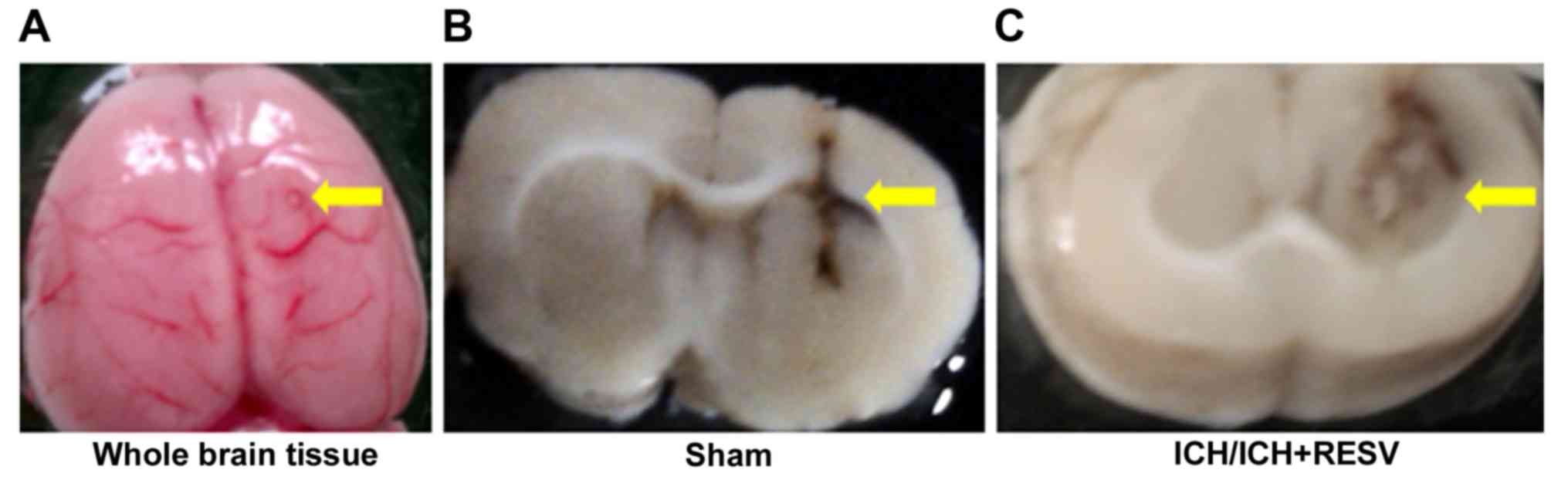
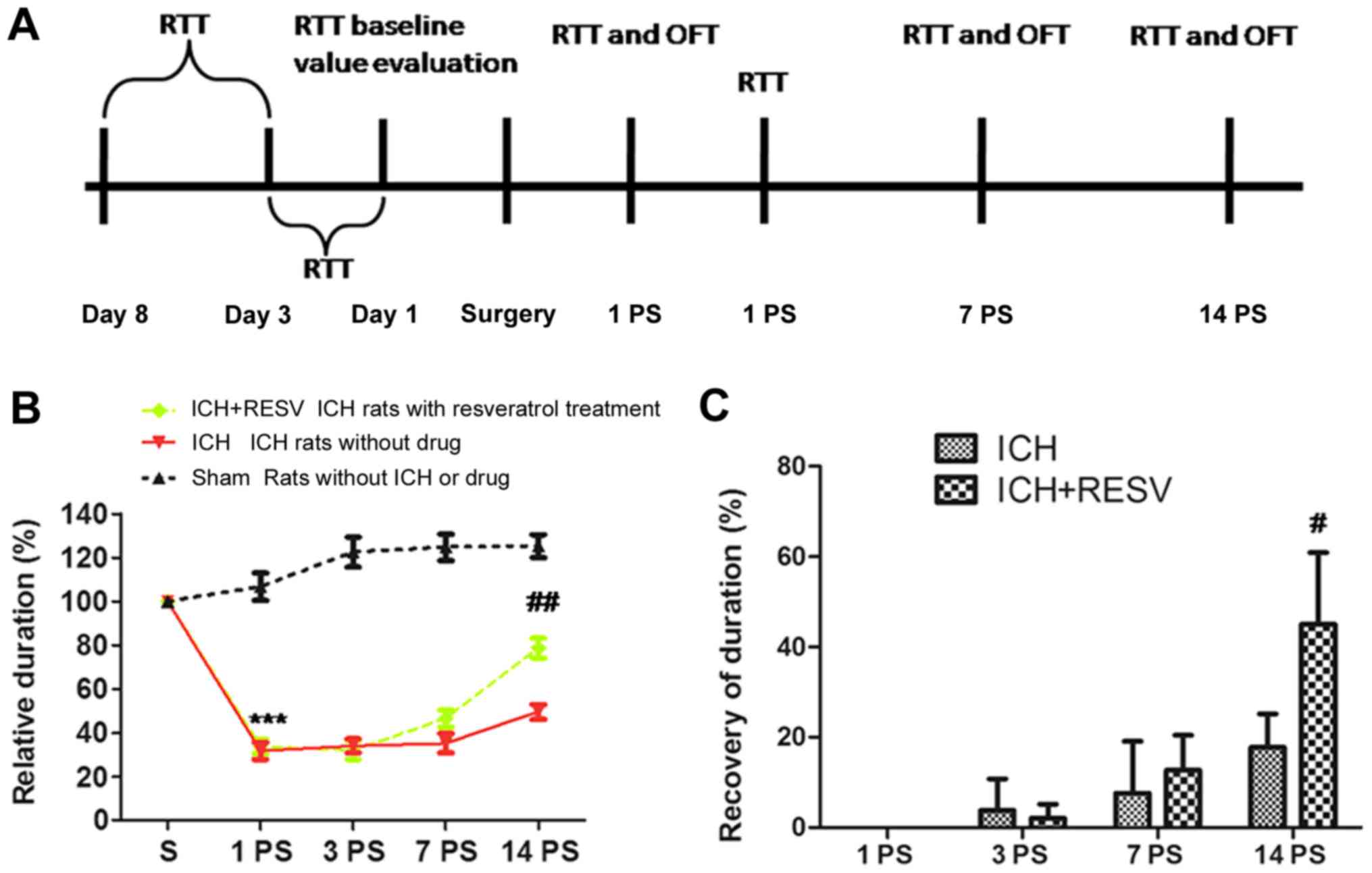
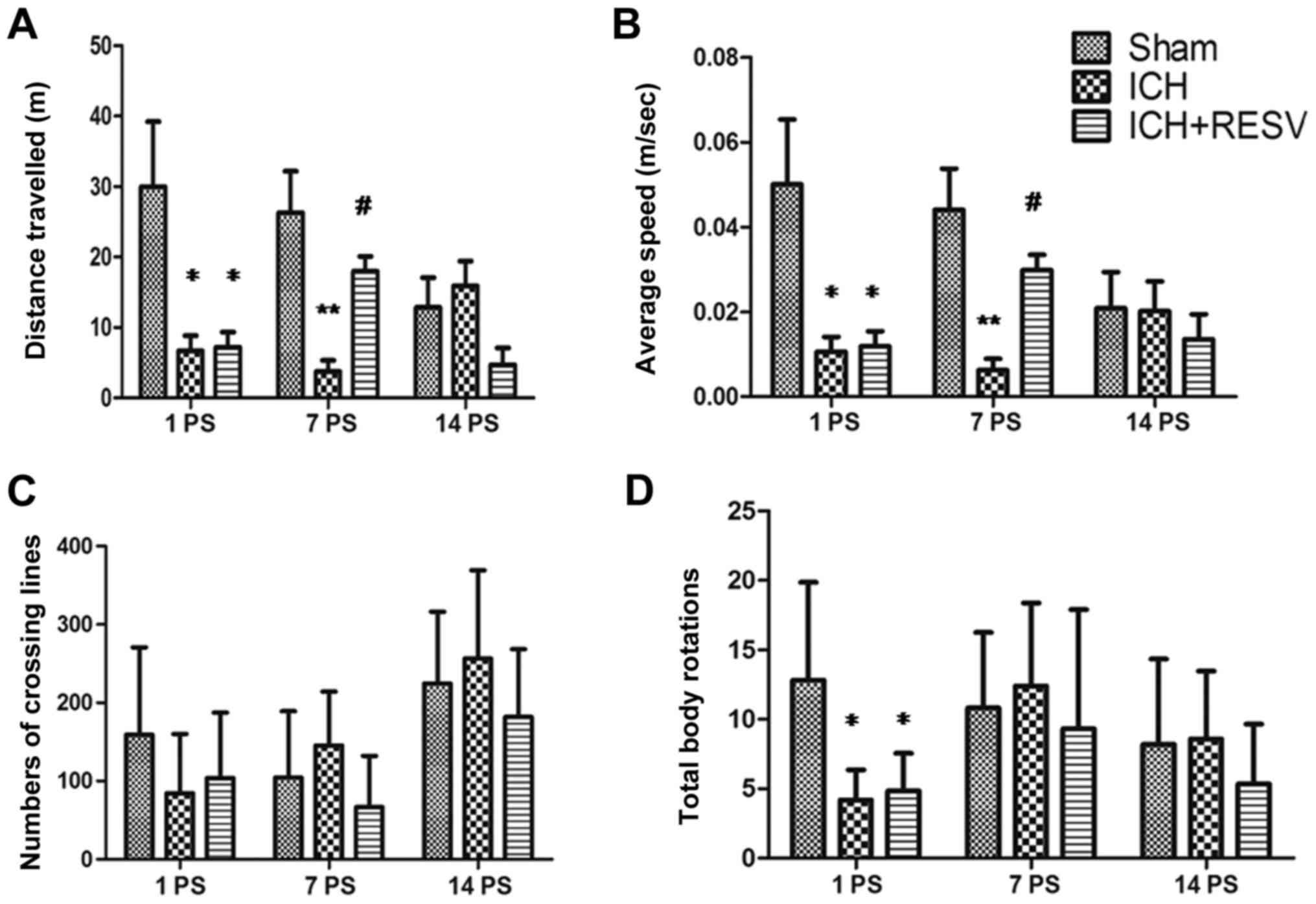
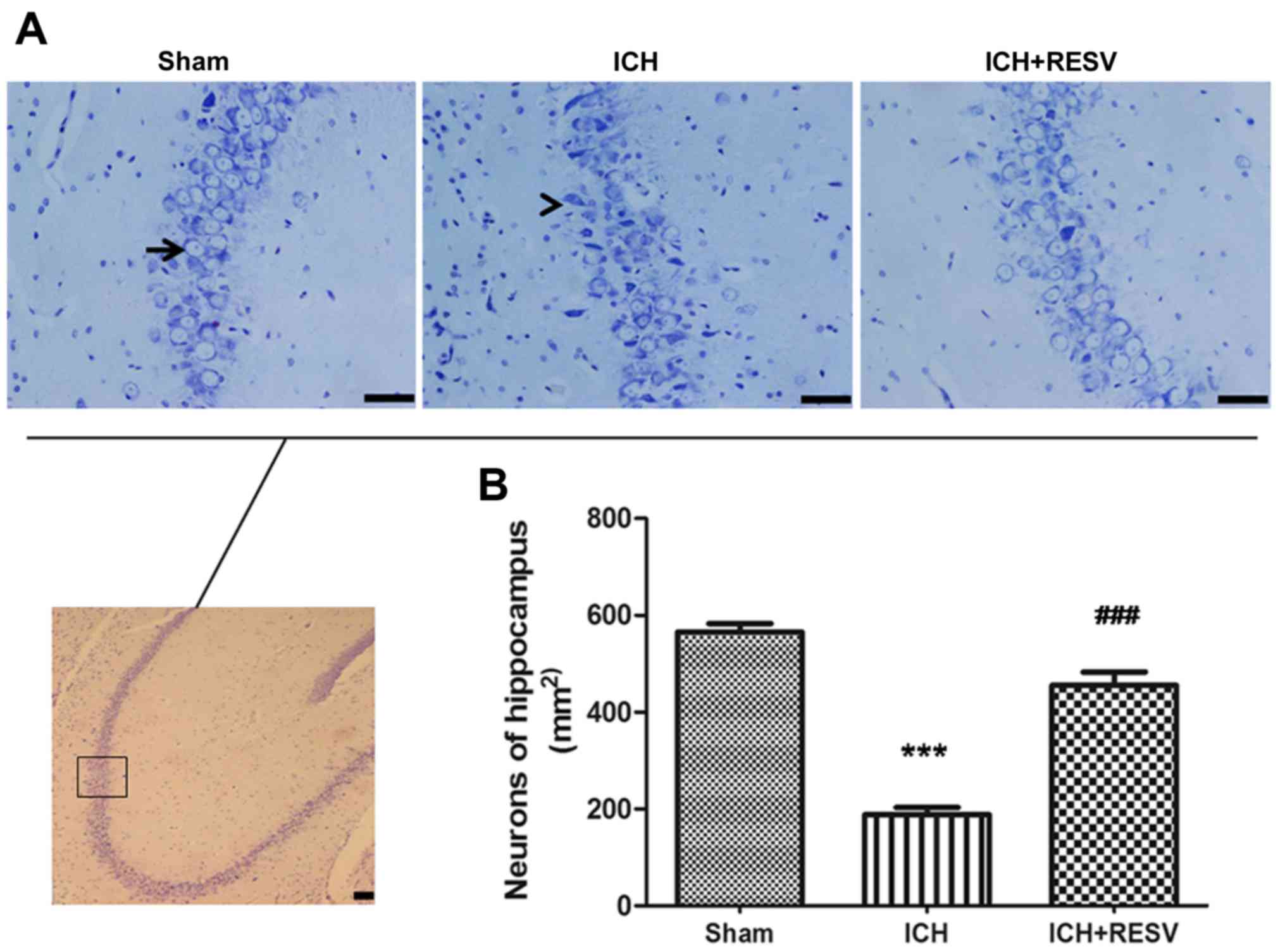
|
1
|
Rojas H, Lekic T, Chen W, Jadhav V, Titova
E, Martin RD, Tang J and Zhang J: The antioxidant effects of
melatonin after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Acta Neurochir
Suppl. 105:19–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu CH, Yang RL, Huang SY, Li HZ, Wang KY,
Yang DH, Yan XH, Xue XH, Wu SY, Wang JM, et al: Analysis of
thrombin-antithrombin complex contents in plasma and hematoma fluid
of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage patients after clot
removal. Eur J Neurol. 18:1060–1066. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kitaoka T, Hua Y, Xi G, Hoff JT and Keep
RF: Delayed argatroban treatment reduces edema in a rat model of
intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 33:3012–3018. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gu Y, Gong Y, Liu WQ, Keep RF, Xi G and
Hua Y: Zinc protoporphyrin attenuates white matter injury after
intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 121:199–202. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fung C, Murek M, Klinger-Gratz PP,
Fiechter M, Z'Graggen WJ, Gautschi OP, El-Koussy M, Gralla J,
Schaller K, Zbinden M, et al: Effect of decompressive craniectomy
on perihematomal edema in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage.
PLoS One. 11:e01491692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dragone T, Cianciulli A, Calvello R, Porro
C, Trotta T and Panaro MA: Resveratrol counteracts
lipopolysaccharide-mediated microglial inflammation by modulating a
SOCS-1 dependent signaling pathway. Toxicol In Vitro. 28:1126–1135.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bobermin LD, Wartchow KM, Flores MP, Leite
MC, Quincozes-Santos A and Goncalves CA: Ammonia-induced oxidative
damage in neurons is prevented by resveratrol and lipoic acid with
participation of heme oxygenase 1. Neurotoxicology. 49:28–35. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang T, Gao D, Jiang X, Hu S, Zhang L and
Fei Z: Resveratrol inhibits oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced
MMP-3 expression and cell apoptosis in primary cortical cells via
the NF-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 10:1065–1071. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nguyen JK, Jorfi M, Buchanan KL, Park DJ,
Foster EJ, Tyler DJ, Rowan SJ, Weder C and Capadona JR: Influence
of resveratrol release on the tissue response to mechanically
adaptive cortical implants. Acta Biomater. 29:81–93. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Virgili M and Contestabile A: Partial
neuroprotection of in vivo excitotoxic brain damage by chronic
administration of the red wine antioxidant agent, trans-resveratrol
in rats. Neurosci Lett. 281:123–126. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ren J, Fan C, Chen N, Huang J and Yang Q:
Resveratrol pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischemic injury by
upregulating expression of transcription factor Nrf2 and HO-1 in
rats. Neurochem Res. 36:2352–2362. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu C, Shi Z, Fan L, Zhang C, Wang K and
Wang B: Resveratrol improves neuron protection and functional
recovery in rat model of spinal cord injury. Brain Res.
1374:100–109. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Davinelli S, Sapere N, Zella D, Bracale R,
Intrieri M and Scapagnini G: Pleiotropic protective effects of
phytochemicals in Alzheimer's disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2012:3865272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Y, Wang R, Chen C, Du X, Ruan L, Sun J,
Li J, Zhang L, O'Donnell JM, Pan J and Xu Y: Antidepressant-like
effect of trans-resveratrol in chronic stress model: Behavioral and
neurochemical evidences. J Psychiatr Res. 47:315–322. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Della-Morte D, Dave KR, DeFazio RA, Bao
YC, Raval AP and Perez-Pinzon MA: Resveratrol pretreatment protects
rat brain from cerebral ischemic damage via a sirtuin 1-uncoupling
protein 2 pathway. Neuroscience. 159:993–1002. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJ, Duarte FV,
Martin-Montalvo A, North BJ, Agarwal B, Ye L, Ramadori G, Teodoro
JS, et al: SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial
effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab.
15:675–690. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ungvari Z, Bagi Z, Feher A, Recchia FA,
Sonntag WE, Pearson K, de Cabo R and Csiszar A: Resveratrol confers
endothelial protection via activation of the antioxidant
transcription factor Nrf2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
299:H18–H24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deinsberger W, Vogel J, Kuschinsky W, Auer
LM and Böker DK: Experimental intracerebral hemorrhage: Description
of a double injection model in rats. Neurol Res. 18:475–477. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
National Research Council: Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th edition. National Acadamies
Press; Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
20
|
Shao A, Wu H, Hong Y, Tu S, Sun X, Wu Q,
Zhao Q, Zhang J and Sheng J: Hydrogen-rich saline attenuated
subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced early brain injury in rats by
suppressing inflammatory response: Possible involvement of NF-κB
pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Mol Neurobiol. 53:3462–3476. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee HI, Park JH, Park MY, Kim NG, Park KJ,
Choi BT, Shin YI and Shin HK: Pre-conditioning with transcranial
low-level light therapy reduces neuroinflammation and protects
blood-brain barrier after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Restor
Neurol Neurosci. 34:201–214. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kettenmann H, Hanisch UK, Noda M and
Verkhratsky A: Physiology of microglia. Physiol Rev. 91:461–553.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tischer J, Krueger M, Mueller W,
Staszewski O, Prinz M, Streit WJ and Bechmann I: Inhomogeneous
distribution of Iba-1 characterizes microglial pathology in
Alzheimer's disease. Glia. 64:1562–1572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ahmed Z, Shaw G, Sharma VP, Yang C,
McGowan E and Dickson DW: Actin-binding proteins coronin-1a and
IBA-1 are effective microglial markers for immunohistochemistry. J
Histochem Cytochem. 55:687–700. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ducruet AF, Zacharia BE, Hickman ZL,
Grobelny BT, Yeh ML, Sosunov SA and Connolly ES Jr: The complement
cascade as a therapeutic target in intracerebral hemorrhage. Exp
Neurol. 219:398–403. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thiex R and Tsirka SE: Brain edema after
intracerebral hemorrhage: Mechanisms, treatment options, management
strategies, and operative indications. Neurosurg Focus. 22:E62007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hua Y, Wu J, Keep RF, Nakamura T, Hoff JT
and Xi G: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases in the brain after
intracerebral hemorrhage and thrombin stimulation. Neurosurgery.
58:542–550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xi G, Keep RF and Hoff JT: Mechanisms of
brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol.
5:53–63. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shao AW, Wu HJ, Chen S, Ammar AB, Zhang JM
and Hong Y: Resveratrol attenuates early brain injury after
subarachnoid hemorrhage through inhibition of NF-κB-dependent
inflammatory/MMP-9 pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 20:182–185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Koronowski KB, Dave KR, Saul I, Camarena
V, Thompson JW, Neumann JT, Young JI and Perez-Pinzon MA:
Resveratrol preconditioning induces a novel extended window of
ischemic tolerance in the mouse brain. Stroke. 46:2293–2298. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin CJ, Chen TH, Yang LY and Shih CM:
Resveratrol protects astrocytes against traumatic brain injury
through inhibiting apoptotic and autophagic cell death. Cell Death
Dis. 5:e11472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ghaiad HR, Nooh MM, El-Sawalhi MM and
Shaheen AA: Resveratrol promotes remyelination in cuprizone model
of multiple sclerosis: Biochemical and histological study. Mol
Neurobiol. 54:3219–3229. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu L, Wang S, Xu R, Zheng J, Tang J, Tang
X and Zhang D: Experimental intracerebral haemorrhage: Description
of a semi-coagulated autologous blood model in rats. Neurol Res.
37:874–879. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paylor R, Spencer CM, Yuva-Paylor LA and
Pieke-Dahl S: The use of behavioral test batteries, II: Effect of
test interval. Physiol Behav. 87:95–102. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Arteaga O, Revuelta M, Urigüen L, Álvarez
A, Montalvo H and Hilario E: Pretreatment with resveratrol prevents
neuronal injury and cognitive deficits induced by perinatal
hypoxia-ischemia in rats. PLoS One. 10:e01424242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang X, Wu Q, Zhang Q, Lu Y, Liu J, Li W,
Lv S, Zhou M, Zhang X and Hang C: Resveratrol attenuates early
brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage via
inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Front Neurosci.
11:6112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang XS, Li W, Wu Q, Wu LY, Ye ZN, Liu
JP, Zhuang Z, Zhou ML, Zhang X and Hang CH: Resveratrol attenuates
acute inflammatory injury in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage
in rats via inhibition of TLR4 pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 17:pii:
E13312016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ayub A, Poulose N and Raju R: Resveratrol
improves survival and prolongs life following hemorrhagic shock.
Mol Med. 21:305–312. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Q, Yuan L, Zhang Q, Gao Y, Liu G,
Xiu M, Wei X, Wang Z and Liu D: Resveratrol attenuates
hypoxia-induced neurotoxicity through inhibiting microglial
activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:578–587. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Turner RS, Thomas RG, Craft S, van Dyck
CH, Mintzer J, Reynolds BA, Brewer JB, Rissman RA, Raman R, Aisen
PS, et al: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
resveratrol for Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 85:1383–1391. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li R, Ma K, Zhao H, Feng Z, Yang Y, Ge H,
Zhang X, Tang J, Yin Y, Liu X, et al: Cattle encephalon glycoside
and ignotin reduced white matter injury and prevented
post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus in a rat model of intracerebral
hemorrhage. Sci Rep. 6:359232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee HJ, Lim IJ, Lee MC and Kim SU: Human
neural stem cells genetically modified to overexpress brain-derived
neurotrophic factor promote functional recovery and neuroprotection
in a mouse stroke model. J Neurosci Res. 88:3282–3294. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|