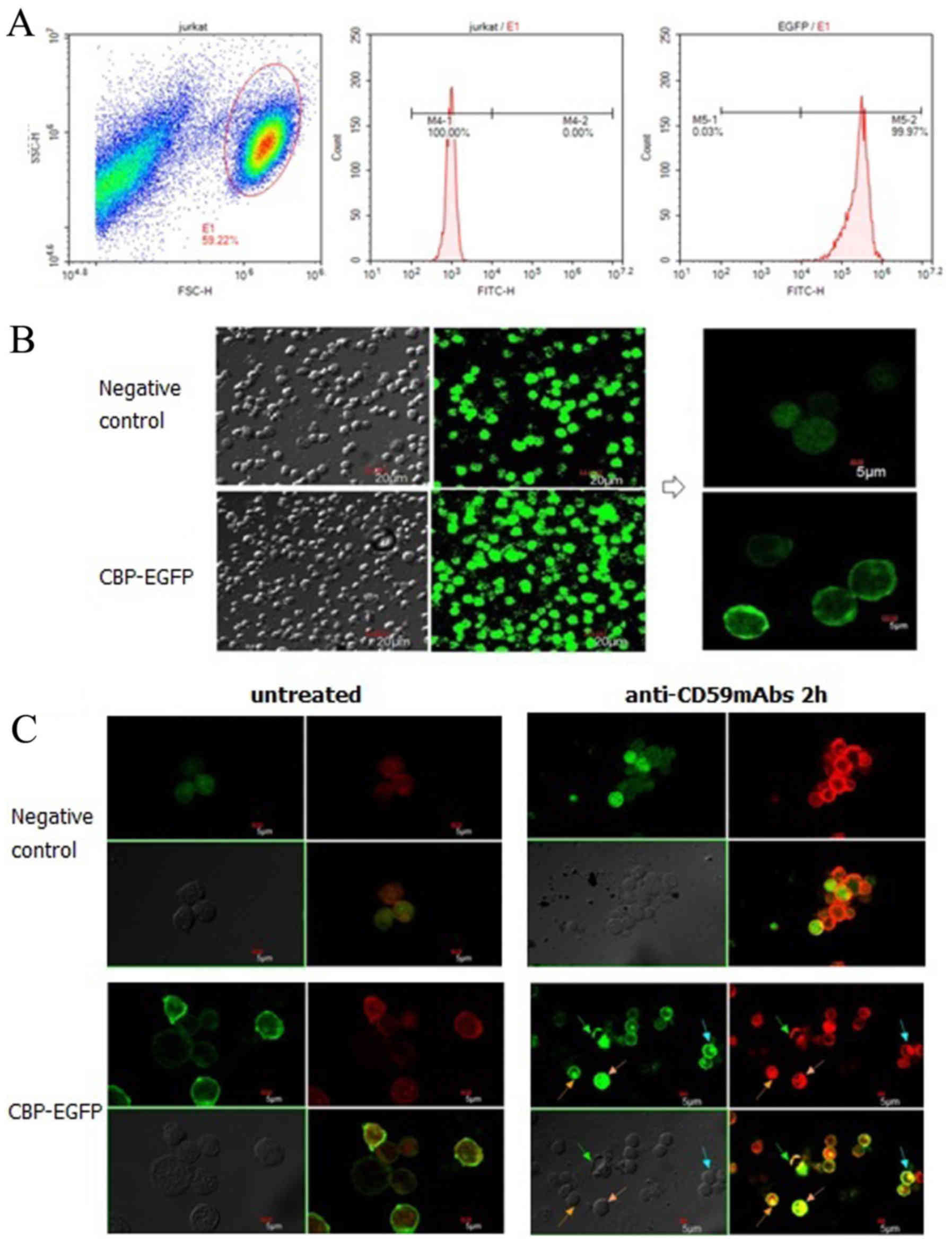
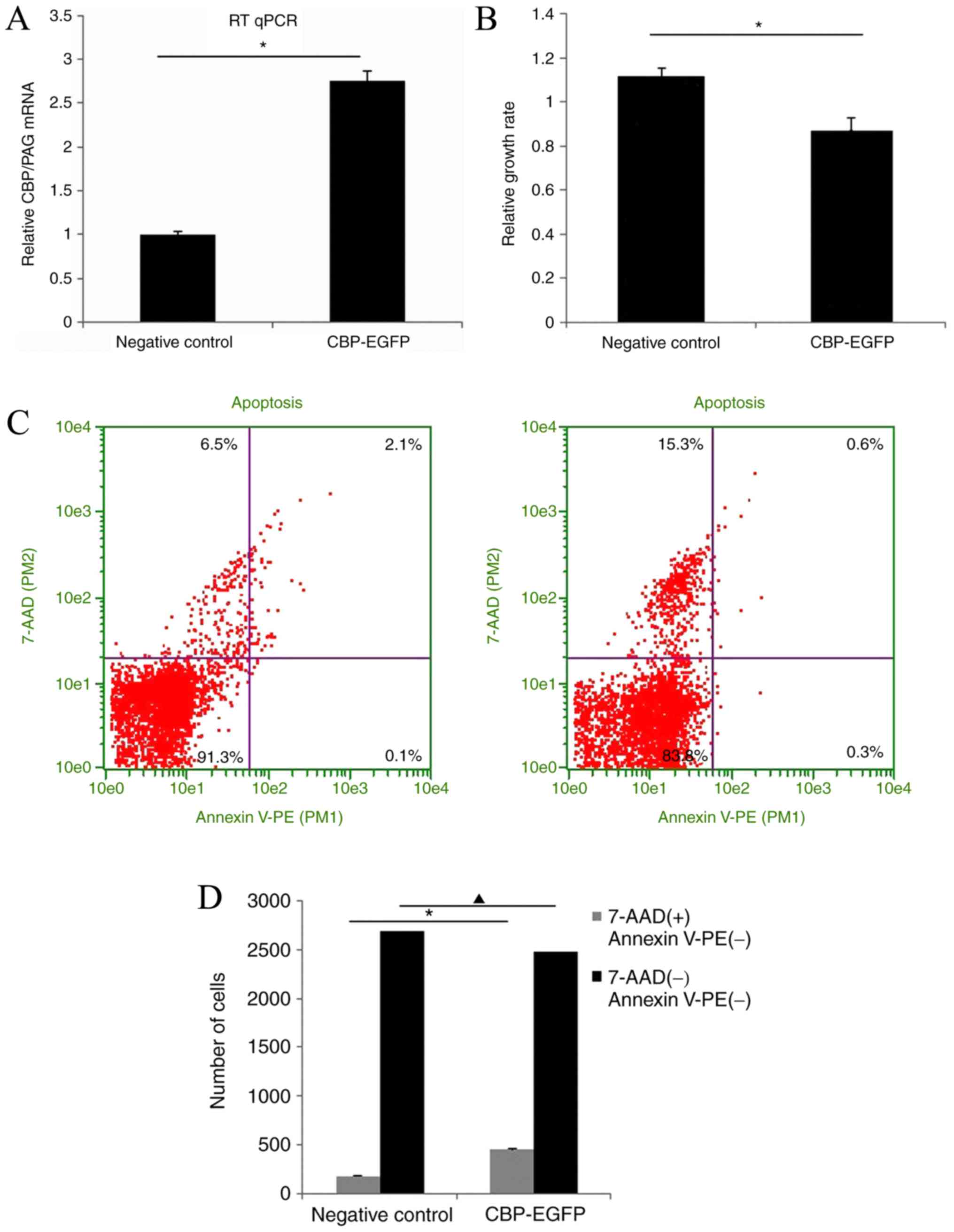
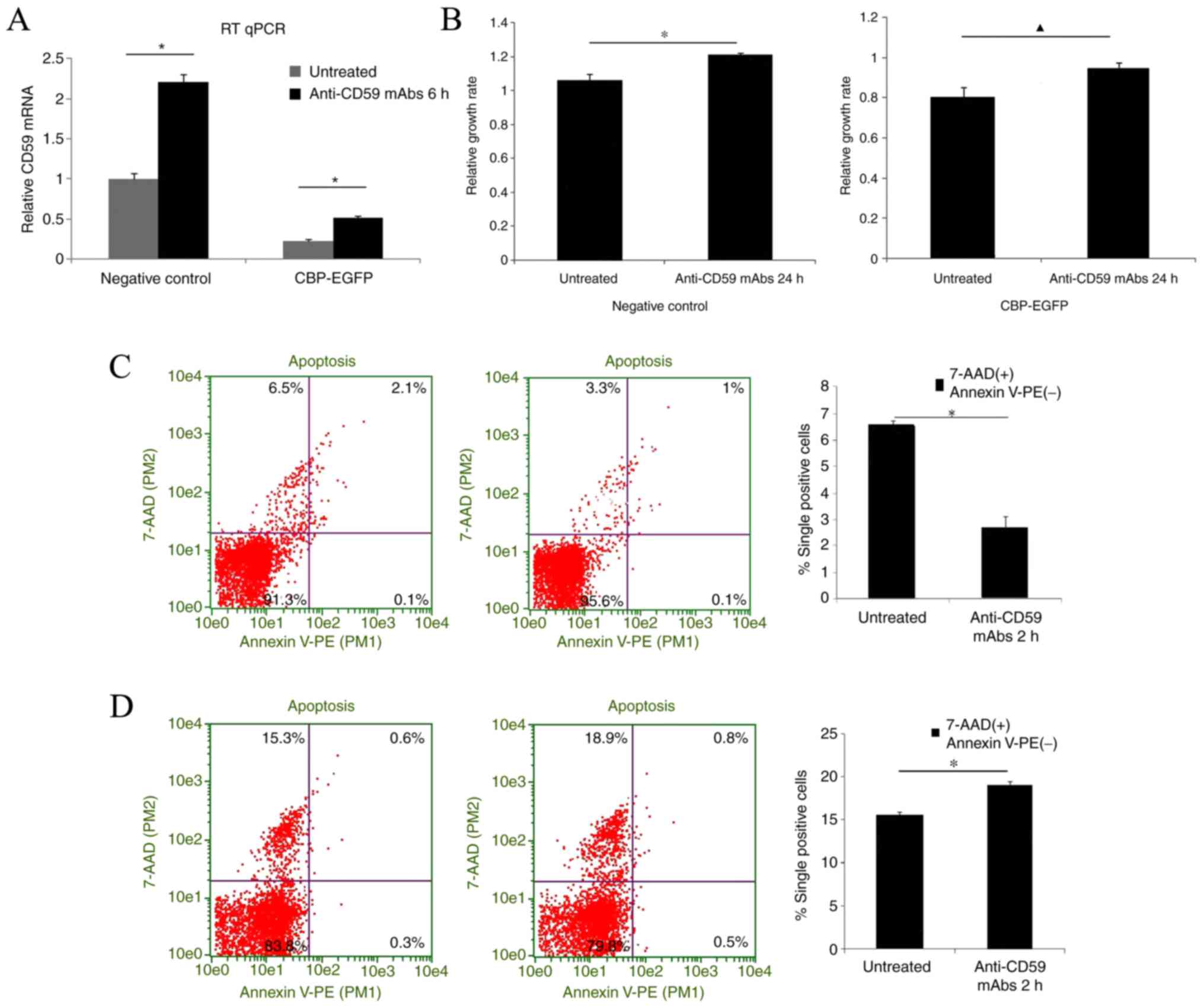
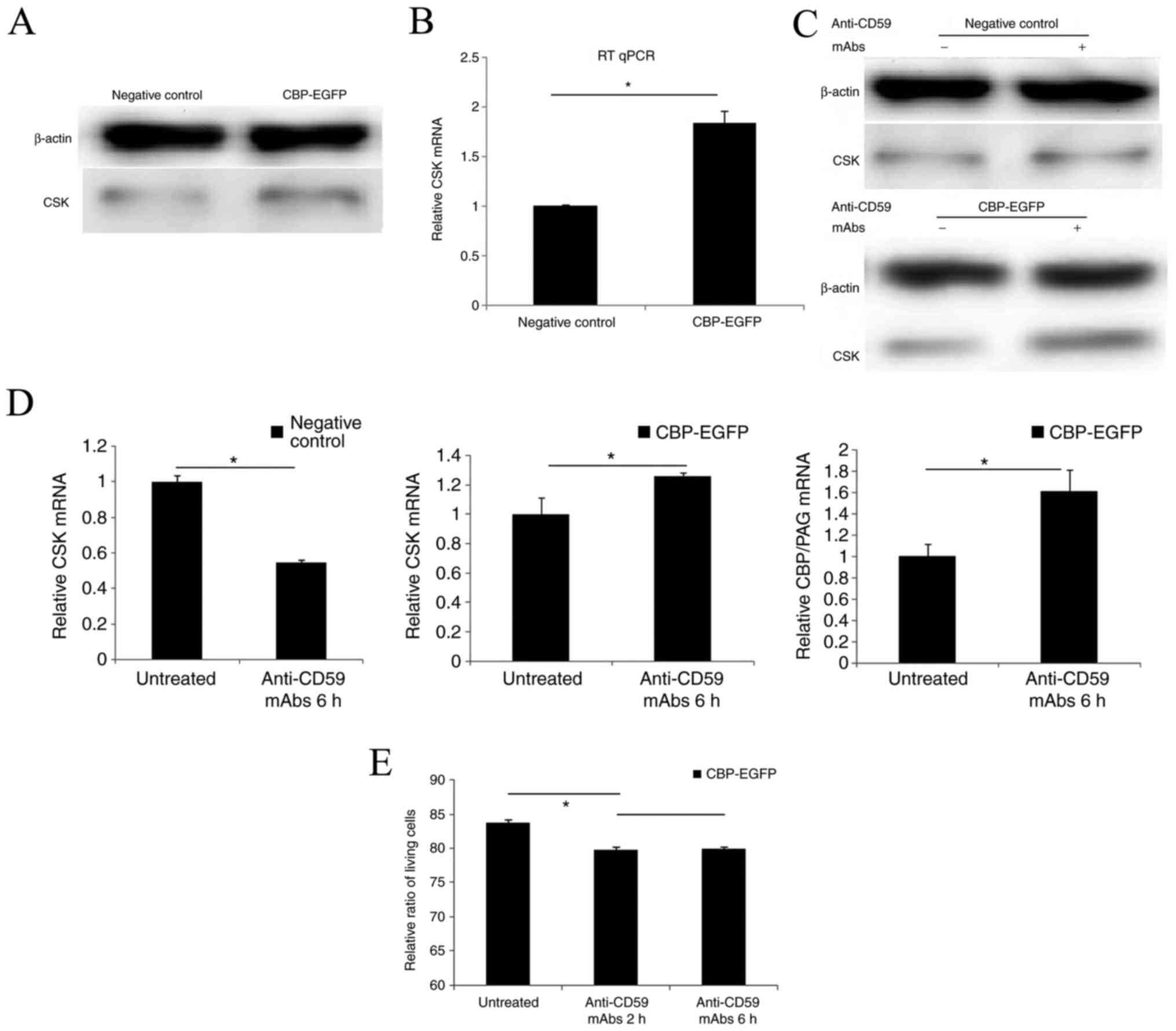
|
1
|
Kawabuchi M, Satomi Y, Takao T, Shimonishi
Y, Nada S, Nagai K, Tarakhovsky A and Okada M: Transmembrane
phosphoprotein Cbp regulates the activities of Src-family tyrosine
kinases. Nature. 404:999–1003. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brdicka T, Pavlistová D, Leo A, Bruyns E,
Korínek V, Angelisová P, Scherer J, Shevchenko A, Hilgert I, Cerný
J, et al: Phosphoprotein associated with glycosphingolipid-enriched
microdomains (PAG), a novel ubiquitously expressed transmembrane
adaptor protein, binds the protein tyrosine kinase csk and is
involved in regulation of T cell activation. J Exp Med.
191:1591–1604. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oneyama C, Iino T, Saito K, Suzuki K,
Ogawa A and Okada M: Transforming potential of Src family kinases
is limited by the cholesterol-enriched membrane microdomain. Mol
Cell Biol. 29:6462–6472. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu W, Harrison SC and Eck MJ:
Three-dimensional structure of the tyrosine kinase c-Src. Nature.
385:595–602. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Itoh K, Sakakibara M, Yamasaki S, Takeuchi
A, Arase H, Miyazaki M, Nakajima N, Okada M and Saito T: Cutting
edge: Negative regulation of immune synapse formation by anchoring
lipid raft to cytoskeleton through Cbp-EBP50-ERM assembly. J
Immunol. 168:541–544. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Torgersen KM, Vang T, Abrahamsen H, Yaqub
S, Horejsí V, Schraven B, Rolstad B, Mustelin T and Taskén K:
Release from tonic inhibition of T cell activation through
transient displacement of C-terminal Src kinase (Csk) from lipid
rafts. J Biol Chem. 276:29313–29318. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kanou T, Oneyama C, Kawahara K, Okimura A,
Ohta M, Ikeda N, Shintani Y, Okumura M and Okada M: The
transmembrane adaptor Cbp/PAG1 controls the malignant potential of
human non-small cell lung cancers that have c-src upregulation. Mol
Cancer Res. 9:103–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oneyama C, Hikita T, Enya K, Dobenecker
MW, Saito K, Nada S, Tarakhovsky A and Okada M: The lipid
raft-anchored adaptor protein Cbp controls the oncogenic potential
of c-Src. Mol Cell. 30:426–436. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smida M, Cammann C, Gurbiel S, Kerstin N,
Lingel H, Lindquist S, Simeoni L, Brunner-Weinzierl MC, Suchanek M,
Schraven B and Lindquist JA: PAG/Cbp suppression reveals a
contribution of CTLA-4 to setting the activation threshold in T
cells. Cell Commun Signal. 11:282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shi XX, Gao MH, Li XP, Zhang B and Wang
QB: Knocking down human CD59 gene expression decreased protection
to complement-mediated cytolysis. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 24:1164–1166. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Farkas I, Baranyi L, Ishikawa Y, Okada N,
Bohata C, Budai D, Fukuda A, Imai M and Okada H: CD59 blocks not
only the insertion of C9 into MAC but inhibits ion channel
formation by homologous C5b-8 as well as C5b-9. J Physiol.
539:537–545. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Murray EW and Robbins SM: Antibody
cross-linking of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked protein
CD59 on hematopoietic cells induces signaling pathways resembling
activation by complement. J Biol Chem. 273:25279–25284. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stulnig TM, Berger M, Sigmund T,
Raederstorff D, Stockinger H and Waldhäusl W: Polyunsaturated fatty
acids inhibit T cell signal transduction by modification of
detergent-insoluble membrane domains. J Cell Biol. 143:637–644.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Drbal K, Moertelmaier M, Holzhauser C,
Muhammad A, Fuertbauer E, Howorka S, Hinterberger M, Stockinger H
and Schütz GJ: Single-molecule microscopy reveals heterogeneous
dynamics of lipid raft components upon TCR engagement. Int Immunol.
19:675–684. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
de Wet B, Zech T, Salek M, Acuto O and
Harder T: Proteomic characterization of plasma membrane-proximal T
cell activation responses. J Biol Chem. 286:4072–4080. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Korty PE, Brando C and Shevach EM: CD59
functions as a signal-transducing molecule for human T cell
activation. J Immunol. 146:4092–4098. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deckert M, Ticchioni M, Mari B, Mary D and
Bernard A: The glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored CD59 protein
stimulates both T cell receptor zeta/ZAP-70-dependent and
-independent signaling pathways in T cells. Eur J Immunol.
25:1815–1822. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suzuki KG, Fujiwara TK, Edidin M and
Kusumi A: Dynamic recruitment of phospholipase C gamma at
transiently immobilized GPI-anchored receptor clusters induces
IP3-Ca2+ signaling: Single-molecule tracking study 2. J Cell Biol.
177:731–742. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xie XH, Gao MH, Zhang B, Wang MJ and Wang
J: Post-transcriptional CD59 gene silencing by siRNAs induces
enhanced human T lymphocyte response to tumor cell lysate-loaded
DCs. Cell Immunol. 274:1–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao M, Ji J, Wang B, Zhang B, Zhang S and
Qin Y: Localization and function of CD59 and Cbp in T lymphocytes.
Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 29:565–569. 2013.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stuart AD, Eustace HE, McKee TA and Brown
TD: A novel cell entry pathway for a DAF-using human enterovirus is
dependent on lipid rafts. J Virol. 76:9307–9322. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kalland ME, Solheim SA, Skånland SS,
Taskén K and Berge T: Modulation of proximal signaling in normal
and transformed B cells by transmembrane adapter Cbp/PAG. Exp Cell
Res. 318:1611–1619. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsuoka H, Nada S and Okada M: Mechanism
of Csk-mediated down-regulation of Src family tyrosine kinases in
epidermal growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem. 279:5975–5983.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takeuchi S, Takayama Y, Ogawa A, Tamura K
and Okada M: Transmembrane phosphoprotein Cbp positively regulates
the activity of the carboxyl-terminal Src kinase, Csk. J Biol Chem.
275:29183–29186. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
D'Oro U, Sakaguchi K, Appella E and
Ashwell JD: Mutational analysis of Lck in CD45-negative T cells:
Dominant role of tyrosine 394 phosphorylation in kinase activity.
Mol Cell Biol. 16:4996–5003. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elias D and Ditzel HJ: Fyn is an important
molecule in cancer pathogenesis and drug resistance. Pharmacol Res.
100:250–254. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Appleby MW, Gross JA, Cooke MP, Levin SD,
Qian X and Perlmutter RM: Defective T cell receptor signaling in
mice lacking the thymic isoform of p59fyn. Cell. 70:751–763. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Filby A, Seddon B, Kleczkowska J, Salmond
R, Tomlinson P, Smida M, Lindquist JA, Schraven B and Zamoyska R:
Fyn regulates the duration of TCR engagement needed for commitment
to effector function. J Immunol. 179:4635–4644. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sugie K, Jeon MS and Grey HM: Activation
of naïve CD4 T cells by anti-CD3 reveals an important role for Fyn
in Lck-mediated signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:14859–14864.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chan AC, Irving BA, Fraser JD and Weiss A:
The zeta chain is associated with a tyrosine kinase and upon T-cell
antigen receptor stimulation associates with ZAP-70, a 70-kDa
tyrosine phosphoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:9166–9170.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Kadlecek TA, Au-Yeung BB,
Goodfellow HE, Hsu LY, Freedman TS and Weiss A: ZAP-70: An
essential kinase in T-cell signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 2:a0022792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Williams BL, Schreiber KL, Zhang W, Wange
RL, Samelson LE, Leibson PJ and Abraham RT: Genetic evidence for
differential coupling of Syk family kinases to the T-cell receptor:
Reconstitution studies in a ZAP-70-deficient Jurkat T-cell line.
Mol Cell Biol. 18:1388–1399. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lindquist JA, Simeoni L and Schraven B:
Transmembrane adapters: Attractants for cytoplasmic effectors.
Immunol Rev. 191:165–182. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Boggon TJ and Eck MJ: Structure and
regulation of Src family kinases. Oncogene. 23:7918–7927. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Palacios EH and Weiss A: Function of the
Src-family kinases, Lck and Fyn, in T-cell development and
activation. Oncogene. 23:7990–8000. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zamoyska R, Basson A, Filby A, Legname G,
Lovatt M and Seddon B: The influence of the src-family kinases, Lck
and Fyn, on T cell differentiation, survival and activation.
Immunol Rev. 191:107–118. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nika K, Soldani C, Salek M, Paster W, Gray
A, Etzensperger R, Fugger L, Polzella P, Cerundolo V, Dushek O, et
al: Constitutively active Lck kinase in T cells drives antigen
receptor signal transduction. Immunity. 32:766–777. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Martin GS: The hunting of the Src. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 2:467–475. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lipp AM, Juhasz K, Paar C, Ogris C,
Eckerstorfer P, Thuenauer R, Hesse J, Nimmervoll B, Stockinger H,
Schütz GJ, et al: Lck mediates signal transmission from CD59 to the
TCR/CD3 pathway in Jurkat T cells. PLoS One. 9:e859342014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Monleón I, Martínez-Lorenzo MJ, Anel A,
Lasierra P, Larrad L, Piñeiro A, Naval J and Alava MA: CD59
cross-linking induces secretion of APO2 ligand in overactivated
human T cells. Eur J Immunol. 30:1078–1087. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Longhi MP, Sivasankar B, Omidvar N, Morgan
BP and Gallimore A: Cutting edge: Murine CD59a modulates antiviral
CD4+ T cell activity in a complement-independent manner.
J Immunol. 175:7098–7102. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sivasankar B, Longhi MP, Gallagher KM,
Betts GJ, Morgan BP, Godkin AJ and Gallimore AM: CD59 blockade
enhances antigen-specific CD4+ T cell responses in
humans: A new target for cancer immunotherapy? J Immunol.
182:5203–5207. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Legembre P, Daburon S, Moreau P, Moreau JF
and Taupin JL: Modulation of Fas-mediated apoptosis by lipid rafts
in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 176:716–720. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mitchell JS, Kanca O and McIntyre BW:
Lipid microdomain clustering induces a redistribution of antigen
recognition and adhesion molecules on human T lymphocytes. J
Immunol. 168:2737–2744. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao M, Wang L, Wang B, Cong B and Zhang S:
Mutation of palmitoylation site of linker for activation of T cells
inhibits signal transduction mediated by glycosyl phosphatidyl
inositol-anchored CD59 in T cells. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 31(1013–1016): 10212015.(In Chinese).
|
|
47
|
Zhang W, Trible RP and Samelson LE: LAT
palmitoylation: Its essential role in membrane microdomain
targeting and tyrosine phosphorylation during T cell activation.
Immunity. 9:239–246. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lin J, Weiss A and Finco TS: Localization
of LAT in glycolipid-enriched microdomains is required for T cell
activation. J Biol Chem. 274:28861–28864. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|