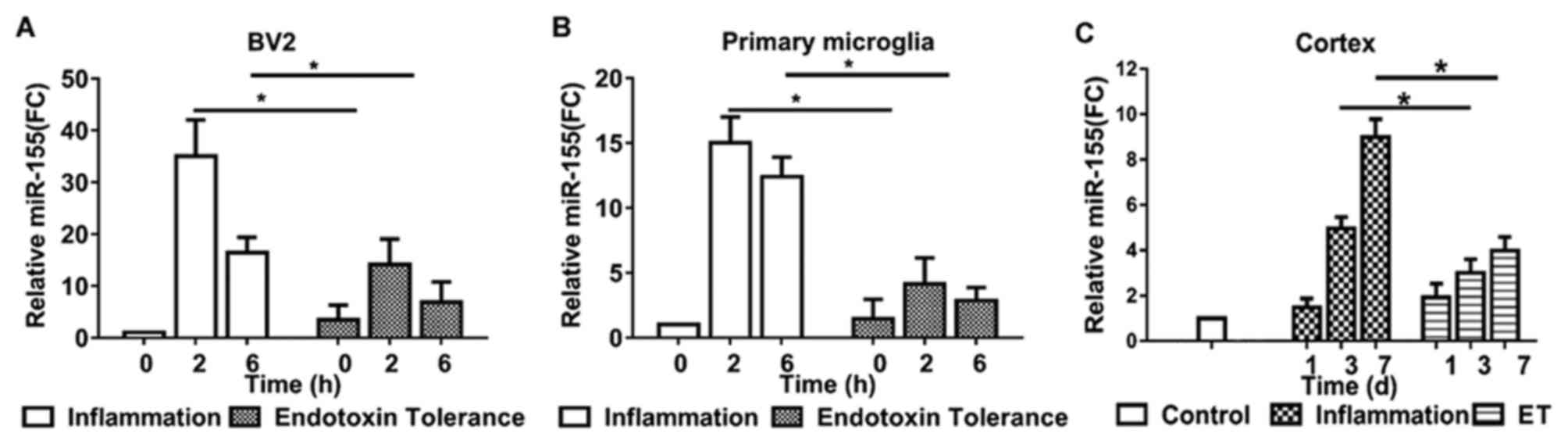
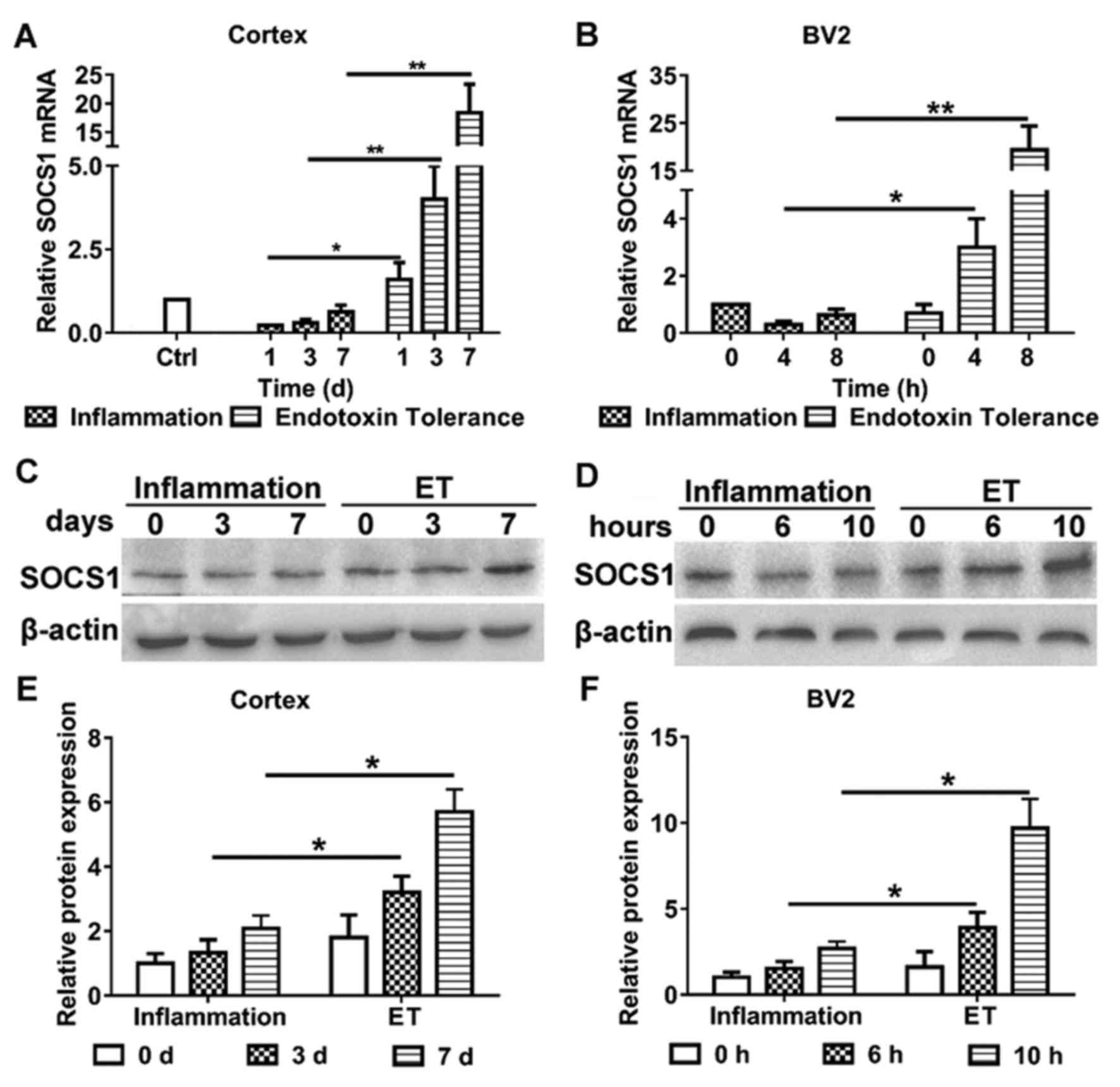
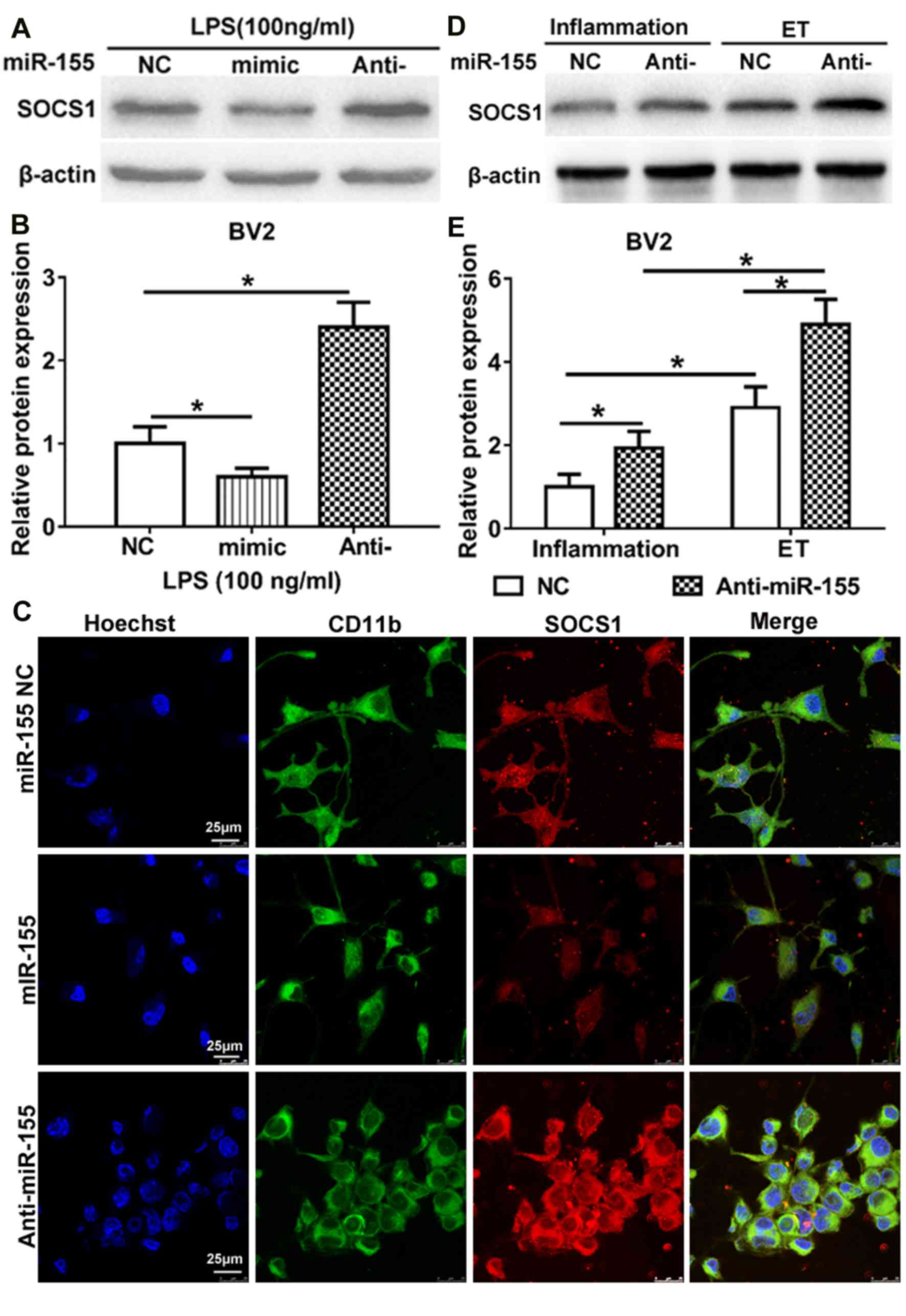
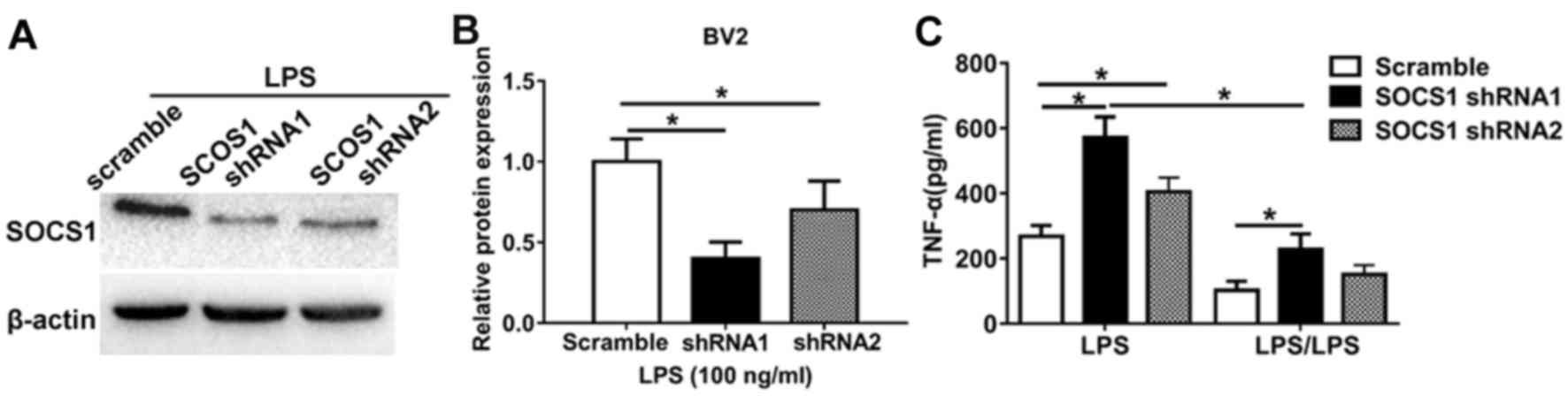
|
1
|
Wilson JX and Young GB: Progress in
clinical neurosciences: Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: Evolving
concepts. Can J Neurol Sci. 30:98–105. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Buttini M, Limonta S and Boddeke HW:
Peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide induces activation
of microglial cells in rat brain. Neurochem Int. 29:25–35. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nimmerjahn A, Kirchhoff F and Helmchen F:
Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain
parenchyma in vivo. Science. 308:1314–1318. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sparkman NL, Kohman RA, Scott VJ and Boehm
GW: Bacterial endotoxin-induced behavioral alterations in two
variations of the Morris water maze. Physiol Behav. 86:244–251.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Biswas SK and Lopez-Collazo E: Endotoxin
tolerance: New mechanisms, molecules and clinical significance.
Trends Immunol. 30:475–487. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Foster SL, Hargreaves DC and Medzhitov R:
Gene-specific control of inflammation by TLR-induced chromatin
modifications. Nature. 447:972–978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Medvedev AE, Lentschat A, Wahl LM,
Golenbock DT and Vogel SN: Dysregulation of LPS-induced Toll-like
receptor 4-MyD88 complex formation and IL-1 receptor-associated
kinase 1 activation in endotoxin-tolerant cells. J Immunol.
169:5209–5216. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li L, Cousart S, Hu J and McCall CE:
Characterization of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase in
normal and endotoxin-tolerant cells. J Biol Chem. 275:23340–23345.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kobayashi K, Hernandez LD, Galán JE,
Janeway CA Jr, Medzhitov R and Flavell RA: IRAK-M is a negative
regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell. 110:191–202. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zacharioudaki V, Androulidaki A, Arranz A,
Vrentzos G, Margioris AN and Tsatsanis C: Adiponectin promotes
endotoxin tolerance in macrophages by inducing IRAK-M expression. J
Immunol. 182:6444–6451. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Piao W, Song C, Chen H, Diaz MA, Wahl LM,
Fitzgerald KA, Li L and Medvedev AE: Endotoxin tolerance
dysregulates MyD88- and Toll/IL-1R domain-containing adapter
inducing IFN-beta-dependent pathways and increases expression of
negative regulators of TLR signaling. J Leukoc Biol. 86:863–875.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Porta C, Rimoldi M, Raes G, Brys L, Ghezzi
P, Di Liberto D, Dieli F, Ghisletti S, Natoli G, De Baetselier P,
et al: Tolerance and M2 (alternative) macrophage polarization are
related processes orchestrated by p50 nuclear factor kappaB. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:14978–14983. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Von Knethen AA and Brüne B: Delayed
activation of PPARgamma by LPS and IFN-gamma attenuates the
oxidative burst in macrophages. FASEB J. 15:535–544. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ryo A, Suizu F, Yoshida Y, Perrem K, Liou
YC, Wulf G, Rottapel R, Yamaoka S and Lu KP: Regulation of
NF-kappaB signaling by Pin1-dependent prolyl isomerization and
ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65/RelA. Mol Cell. 12:1413–1426.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He Y, Zhang W, Zhang R, Zhang H and Min W:
SOCS1 inhibits tumor necrosis factor-induced activation of ASK1-JNK
inflammatory signaling by mediating ASK1 degradation. J Biol Chem.
281:5559–5566. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baker BJ, Akhtar LN and Benveniste EN:
SOCS1 and SOCS3 in the control of CNS immunity. Trends Immunol.
30:392–400. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marine JC, Topham DJ, McKay C, Wang D,
Parganas E, Stravopodis D, Yoshimura A and Ihle JN: SOCS1
deficiency causes a lymphocyte-dependent perinatal lethality. Cell.
98:609–616. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gingras S, Parganas E, de Pauw A, Ihle JN
and Murray PJ: Re-examination of the role of suppressor of cytokine
signaling 1 (SOCS1) in the regulation of toll-like receptor
signaling. J Biol Chem. 279:54702–54707. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mujtaba MG, Flowers LO, Patel CB, Patel
RA, Haider MI and Johnson HM: Treatment of mice with the suppressor
of cytokine signaling-1 mimetic peptide, tyrosine kinase inhibitor
peptide, prevents development of the acute form of experimental
allergic encephalomyelitis and induces stable remission in the
chronic relapsing/remitting form. J Immunol. 175:5077–5086. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang FJ, Steeg PS, Price JE, Chiu WT,
Chou PC, Xie K, Sawaya R and Huang S: Molecular basis for the
critical role of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 in melanoma
brain metastasis. Cancer Res. 68:9634–9642. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Quinn EM, Wang J and Redmond HP: The
emerging role of microRNA in regulation of endotoxin tolerance. J
Leukoc Biol. 91:721–727. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nahid MA, Satoh M and Chan EK: MicroRNA in
TLR signaling and endotoxin tolerance. Cell Mol Immunol. 8:388–403.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Androulidaki A, Iliopoulos D, Arranz A,
Doxaki C, Schworer S, Zacharioudaki V, Margioris AN, Tsichlis PN
and Tsatsanis C: The kinase Akt1 controls macrophage response to
lipopolysaccharide by regulating microRNAs. Immunity. 31:220–231.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alexander M, Ramstead AG, Bauer KM, Lee
SH, Runtsch MC, Wallace J, Huffaker TB, Larsen DK, Tolmachova T,
Seabra MC, et al: Rab27-dependent exosome production inhibits
chronic inflammation and enables acute responses to inflammatory
stimuli. J Immunol. 199:3559–3570. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Saura J, Tusell JM and Serratosa J:
High-yield isolation of murine microglia by mild trypsinization.
Glia. 44:183–189. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
AnimalsGuide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US). ISBN-13:
978-0-309-15400-0. 2011, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
O'Connell RM, Chaudhuri AA, Rao DS and
Baltimore D: Inositol phosphatase SHIP1 is a primary target of
miR-155. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:7113–7118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
O'Connell RM, Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Cheng
G and Baltimore D: MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage
inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:1604–1609. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cardoso AL, Guedes JR, de Almeida Pereira
L and de Lima Pedroso MC: miR-155 modulates microglia-mediated
immune response by down-regulating SOCS-1 and promoting cytokine
and nitric oxide production. Immunology. 135:73–88. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Staedel C and Darfeuille F: MicroRNAs and
bacterial infection. Cell Microbiol. 15:1496–1507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
de Yébenes VG, Bartolomé-Izquierdo N and
Ramiro AR: Regulation of B-cell development and function by
microRNAs. Immunol Rev. 253:25–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kumar A, Stoica BA, Loane DJ, Yang M,
Abulwerdi G, Khan N, Kumar A, Thom SR and Faden AI:
Microglial-derived microparticles mediate neuroinflammation after
traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation. 14:472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wen Y, Zhang X, Dong L, Zhao J, Zhang C
and Zhu C: Acetylbritannilactone modulates MicroRNA-155-mediated
inflammatory response in ischemic cerebral tissues. Mol Med.
21:197–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Doxaki C, Kampranis SC, Eliopoulos AG,
Spilianakis C and Tsatsanis C: Coordinated regulation of miR-155
and miR-146a genes during induction of endotoxin tolerance in
macrophages. J Immunol. 195:5750–5761. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Neagos J, Standiford TJ, Newstead MW, Zeng
X, Huang SK and Ballinger MN: Epigenetic regulation of tolerance to
toll-like receptor ligands in alveolar epithelial cells. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 53:872–881. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Prinz M and Priller J: Microglia and brain
macrophages in the molecular age: From origin to neuropsychiatric
disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 15:300–312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|