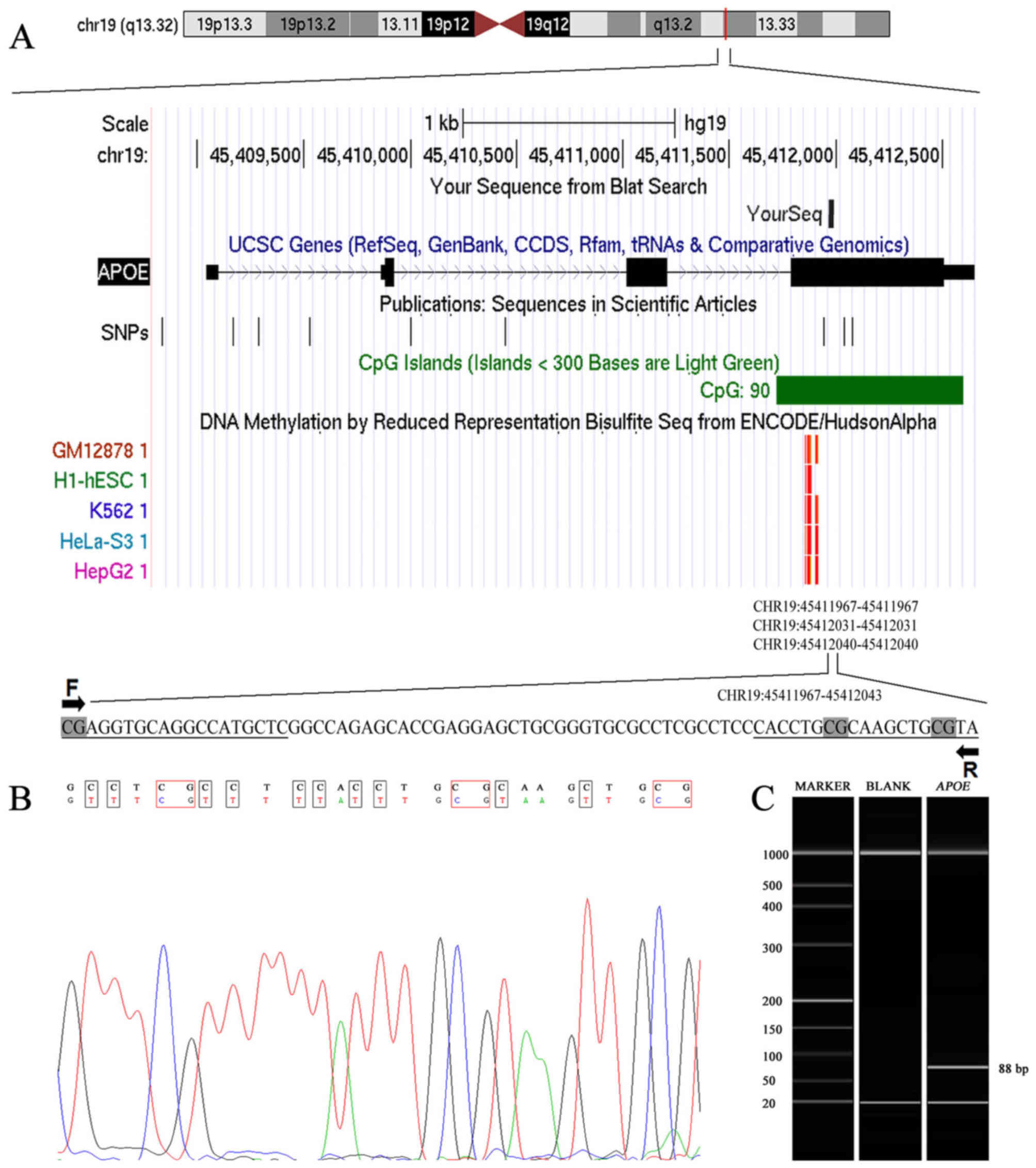
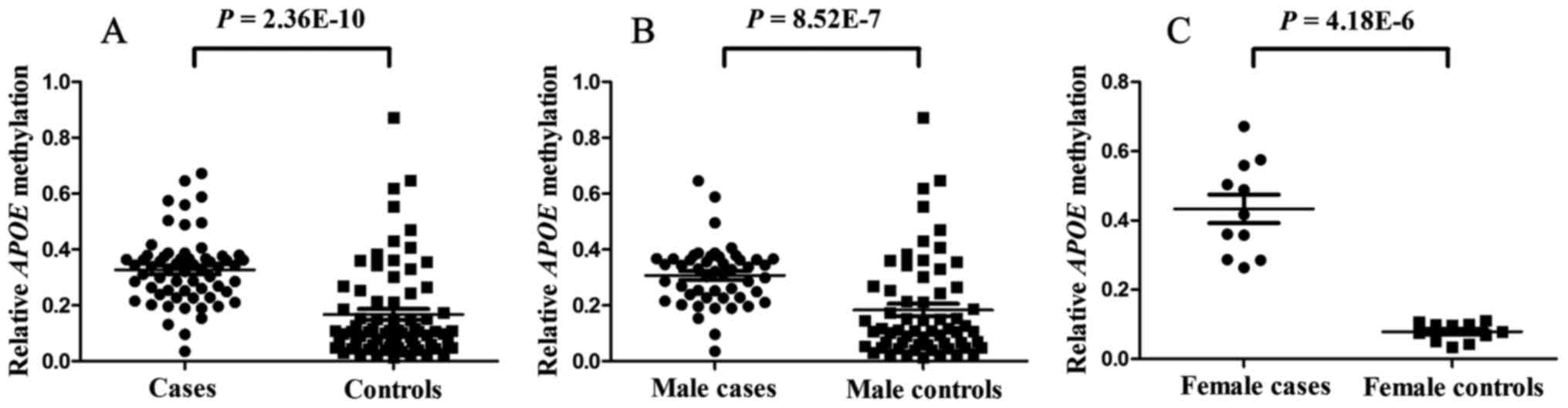
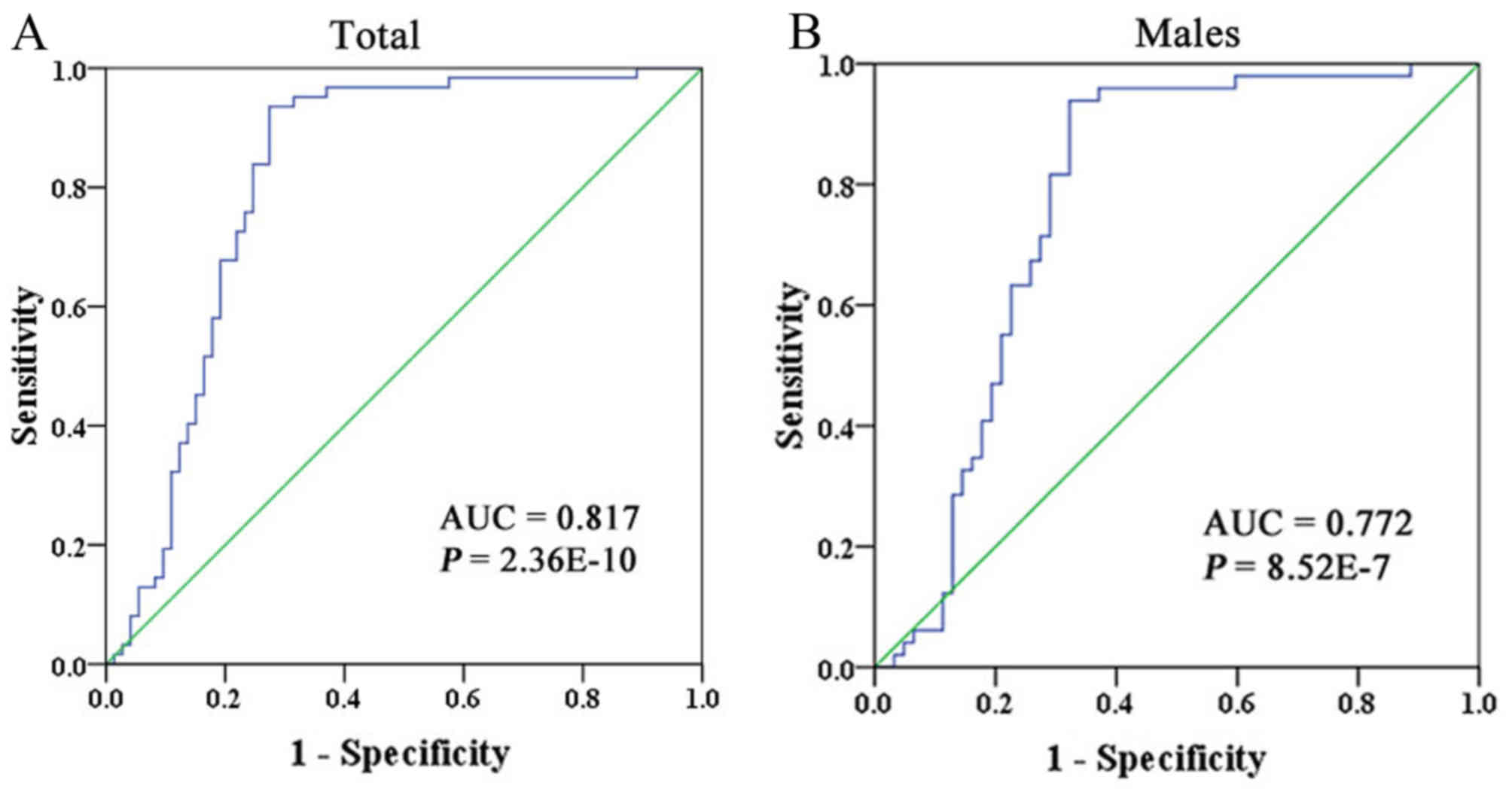
|
1
|
Shpyleva S, Ivanovsky S, de Conti A,
Melnyk S, Tryndyak V, Beland FA, James SJ and Pogribny IP:
Cerebellar oxidative DNA damage and altered DNA methylation in the
BTBR T+tf/J mouse model of autism and similarities with human post
mortem cerebellum. PLoS One. 9:e1137122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ginsberg MR, Rubin RA, Falcone T, Ting AH
and Natowicz MR: Brain transcriptional and epigenetic associations
with autism. PLoS One. 7:e447362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bird G and Cook R: Mixed emotions: The
contribution of alexithymia to the emotional symptoms of autism.
Transl Psychiatry. 3:e2852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Buescher AV, Cidav Z, Knapp M and Mandell
DS: Costs of autism spectrum disorders in the United Kingdom and
the United States. JAMA Pediatr. 168:721–728. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Howsmon DP, Kruger U, Melnyk S, James SJ
and Hahn J: Classification and adaptive behavior prediction of
children with autism spectrum disorder based upon multivariate data
analysis of markers of oxidative stress and DNA methylation. PLoS
Comput Biol. 13:e10053852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fernell E, Eriksson MA and Gillberg C:
Early diagnosis of autism and impact on prognosis: A narrative
review. Clin Epidemiol. 5:33–43. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen T, Giri M, Xia Z, Subedi YN and Li Y:
Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms of epilepsy: A review.
Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 13:1841–1859. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Esteller M: Profiling aberrant DNA
methylation in hematologic neoplasms: A view from the tip of the
iceberg. Clin Immunol. 109:80–88. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mill J, Tang T, Kaminsky Z, Khare T,
Yazdanpanah S, Bouchard L, Jia P, Assadzadeh A, Flanagan J,
Schumacher A, et al: Epigenomic profiling reveals DNA-methylation
changes associated with major psychosis. Am J Hum Genet.
82:696–711. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng J, Wang Y, Zhou K, Wang L, Li J,
Zhuang Q, Xu X, Xu L, Zhang K, Dai D, et al: Male-specific
association between dopamine receptor D4 gene methylation and
schizophrenia. PLoS One. 9:e891282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dai D, Cheng J, Zhou K, Lv Y, Zhuang Q,
Zheng R, Zhang K, Jiang D, Gao S and Duan S: Significant
association between DRD3 gene body methylation and schizophrenia.
Psychiatry Res. 220:772–777. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yuksel Elagoz M, Yuceturk B, Karatas OF,
Ozen M and Dogangun B: The altered promoter methylation of oxytocin
receptor gene in autism. J Neurogenet. 30:280–284. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lintas C, Sacco R and Persico AM:
Differential methylation at the RELN gene promoter in temporal
cortex from autistic and typically developing post-puberal
subjects. J Neurodev Disord. 8:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu L, Wang X, Li XL, Towers A, Cao X,
Wang P, Bowman R, Yang H, Goldstein J, Li YJ and Jiang YH:
Epigenetic dysregulation of SHANK3 in brain tissues from
individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Hum Mol Genet.
23:1563–1578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tamboli IY, Heo D and Rebeck GW:
Extracellular proteolysis of apolipoprotein E (apoE) by secreted
serine neuronal protease. PLoS One. 9:e931202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Raiford KL, Shao Y, Allen IC, Martin ER,
Menold MM, Wright HH, Abramson RK, Worley G, DeLong GR, Vance JM,
et al: No association between the APOE gene and autism. Am J Med
Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 125B:57–60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Foraker J, Millard SP, Leong L, Thomson Z,
Chen S, Keene CD, Bekris LM and Yu CE: The APOE gene is
differentially methylated in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis.
48:745–755. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Napoli E, Ross-Inta C, Wong S, Hung C,
Fujisawa Y, Sakaguchi D, Angelastro J, Omanska-Klusek A, Schoenfeld
R and Giulivi C: Mitochondrial dysfunction in Pten
haplo-insufficient mice with social deficits and repetitive
behavior: Interplay between Pten and p53. PLoS One. 7:e425042012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Giunco CT, de Oliveira AB, Carvalho-Salles
AB, Souza DS, Silva AE, da Rocha SS and Fett-Conte AC: Association
between APOE polymorphisms and predisposition for autism. Psychiatr
Genet. 19:3382009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kristensen LS, Mikeska T, Krypuy M and
Dobrovic A: Sensitive melting analysis after real time-methylation
specific PCR (SMART-MSP): High-throughput and probe-free
quantitative DNA methylation detection. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:e422008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen X, Hu H, Liu J, Yang Y, Liu G, Ying
X, Chen Y, Li B, Ye C, Wu D and Duan S: FOXF2 promoter methylation
is associated with prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176922302017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang Y and Mahley RW: Apolipoprotein E:
Structure and function in lipid metabolism, neurobiology, and
Alzheimer's diseases. Neurobiol Dis. 72:3–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu S, Park S, Allington G, Prelli F, Sun
Y, Sun Y, Martá-Ariza M, Scholtzova H, Biswas G2, Brown B, Verghese
PB, et al: Targeting Apolipoprotein E/Amyloid β Binding by Peptoid
CPO_Aβ17-21 P Ameliorates Alzheimer's disease related pathology and
cognitive decline. Sci Rep. 7:80092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao N, Liu CC, Qiao W and Bu G:
Apolipoprotein E, Receptors, and Modulation of Alzheimer's Disease.
Biol Psychiatry. 83:347–357. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Folmsbee SS, Wilcox DR, Tyberghein K, De
Bleser P, Tourtellotte WG, van Hengel J, van Roy F and Gottardi CJ:
αT-catenin in restricted brain cell types and its potential
connection to autism. J Mol Psychiatry. 4:22016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Blomqvist ME, Andreasen N, Bogdanovic N,
Blennow K, Brookes AJ and Prince JA: Genetic variation in CTNNA3
encoding alpha-3 catenin and Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett.
358:220–222. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martin ER, Bronson PG, Li YJ, Wall N,
Chung RH, Schmechel DE, Small G, Xu PT, Bartlett J, Schnetz-Boutaud
N, et al: Interaction between the alpha-T catenin gene (VR22) and
APOE in Alzheimer's disease. J Med Genet. 42:787–792. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Persico AM, D'Agruma L, Zelante L,
Militerni R, Bravaccio C, Schneider C, Melmed R, Trillo S,
Montecchi F, Elia M, et al: Enhanced APOE2 transmission rates in
families with autistic probands. Psychiatr Genet. 14:73–82. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jaenisch R and Bird A: Epigenetic
regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic
and environmental signals. Nat Genet. 33 Suppl:S245–S254. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tamura Y, Kunugi H, Ohashi J and Hohjoh H:
Epigenetic aberration of the human REELIN gene in psychiatric
disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 12(519): 593–600. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zilberman D, Gehring M, Tran RK, Ballinger
T and Henikoff S: Genome-wide analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana DNA
methylation uncovers an interdependence between methylation and
transcription. Nat Genet. 39:61–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang X, Yazaki J, Sundaresan A, Cokus S,
Chan SW, Chen H, Henderson IR, Shinn P, Pellegrini M, Jacobsen SE
and Ecker JR: Genome-wide high-resolution mapping and functional
analysis of DNA methylation in arabidopsis. Cell. 126:1189–1201.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Suzuki M, Takeda S, Teraoka-Nishitani N,
Yamagata A, Tanaka T, Sasaki M, Yasuda N, Oda M, Okano T, Yamahira
K, et al: Cadmium-induced malignant transformation of rat liver
cells: Potential key role and regulatory mechanism of altered
apolipoprotein E expression in enhanced invasiveness. Toxicology.
382:16–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Juneja M, Sharma S and Mukherjee SB:
Sensitivity of the autism behavior checklist in Indian autistic
children. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 31:48–49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dykens EM, Roof E, Hunt-Hawkins H, Dankner
N, Lee EB, Shivers CM, Daniell C and Kim SJ: Diagnoses and
characteristics of autism spectrum disorders in children with
Prader-Willi syndrome. J Neurodev Disord. 9:182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nordin V and Gillberg C: Autism spectrum
disorders in children with physical or mental disability or both.
II: Screening aspects. Dev Med Child Neurol. 38:314–324. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
García-López C and Narbona J: Clinical
usefulness of IDEA and CARS: Concordance with DSM-IV-TR in children
and adolescents with suspicion of PDD. An Pediatr (Barc). 80:71–76.
2014.(In Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hayek J, Cervellati C, Crivellari I,
Pecorelli A and Valacchi G: Lactonase activity and
lipoprotein-phospholipase A2 as possible novel serum biomarkers for
the differential diagnosis of autism spectrum disorders and rett
syndrome: Results from a pilot study. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:56940582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mundalil Vasu M, Anitha A, Thanseem I,
Suzuki K, Yamada K, Takahashi T, Wakuda T, Iwata K, Tsujii M,
Sugiyama T and Mori N: Serum microRNA profiles in children with
autism. Mol Autism. 5:402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hicks SD, Ignacio C, Gentile K and
Middleton FA: Salivary miRNA profiles identify children with autism
spectrum disorder, correlate with adaptive behavior, and implicate
ASD candidate genes involved in neurodevelopment. BMC Pediatr.
16:522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
El-Ansary AK, Ben Bacha AG and Al-Ayadhi
LY: Proinflammatory and proapoptotic markers in relation to mono
and di-cations in plasma of autistic patients from Saudi Arabia. J
Neuroinflammation. 8:1422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu P, Cao Z and Wu S: New progress of
epigenetic biomarkers in urological cancer. Dis Markers.
2016:98640472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tsui NB, Ng EK and Lo YM: Stability of
endogenous and added RNA in blood specimens, serum, and plasma.
Clin Chem. 48:1647–1653. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|