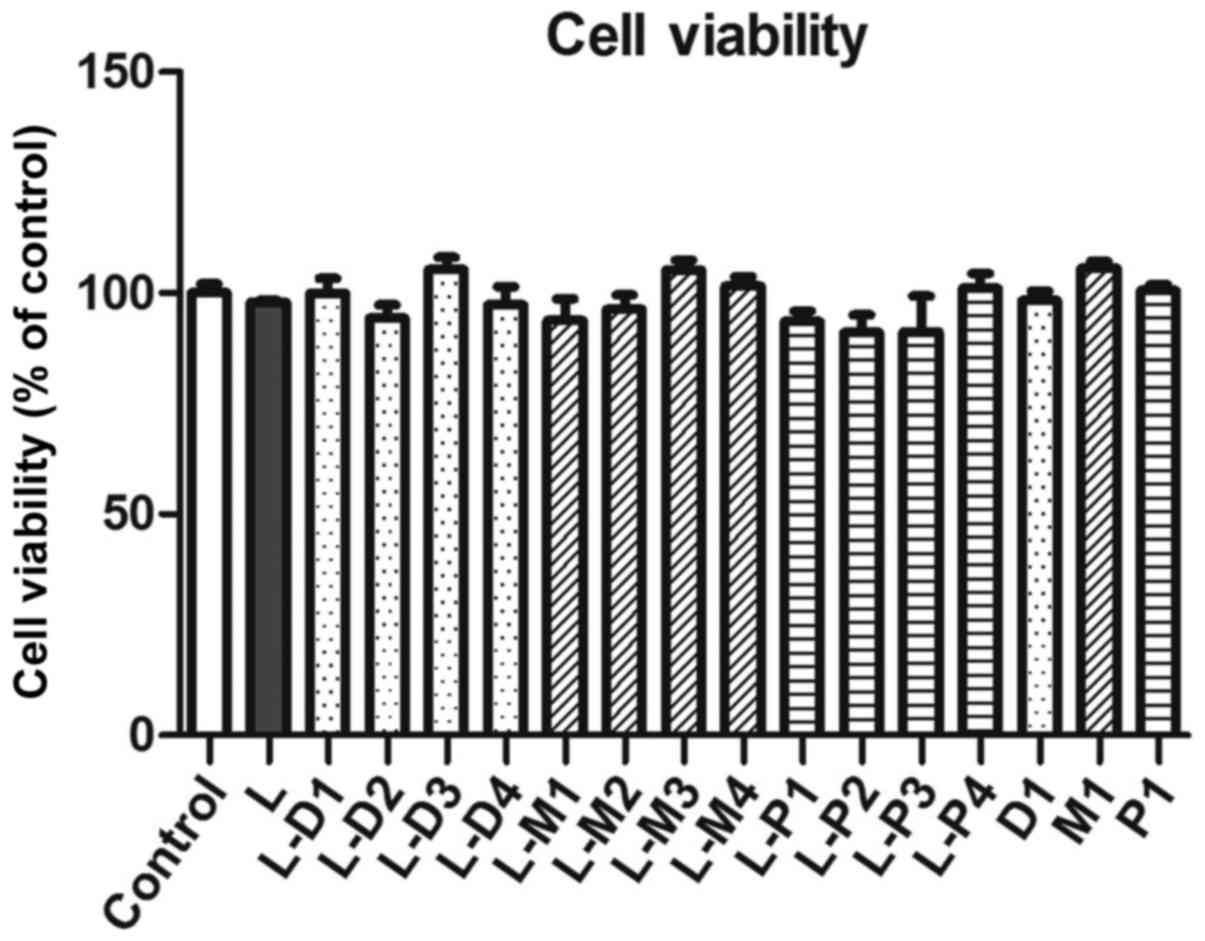
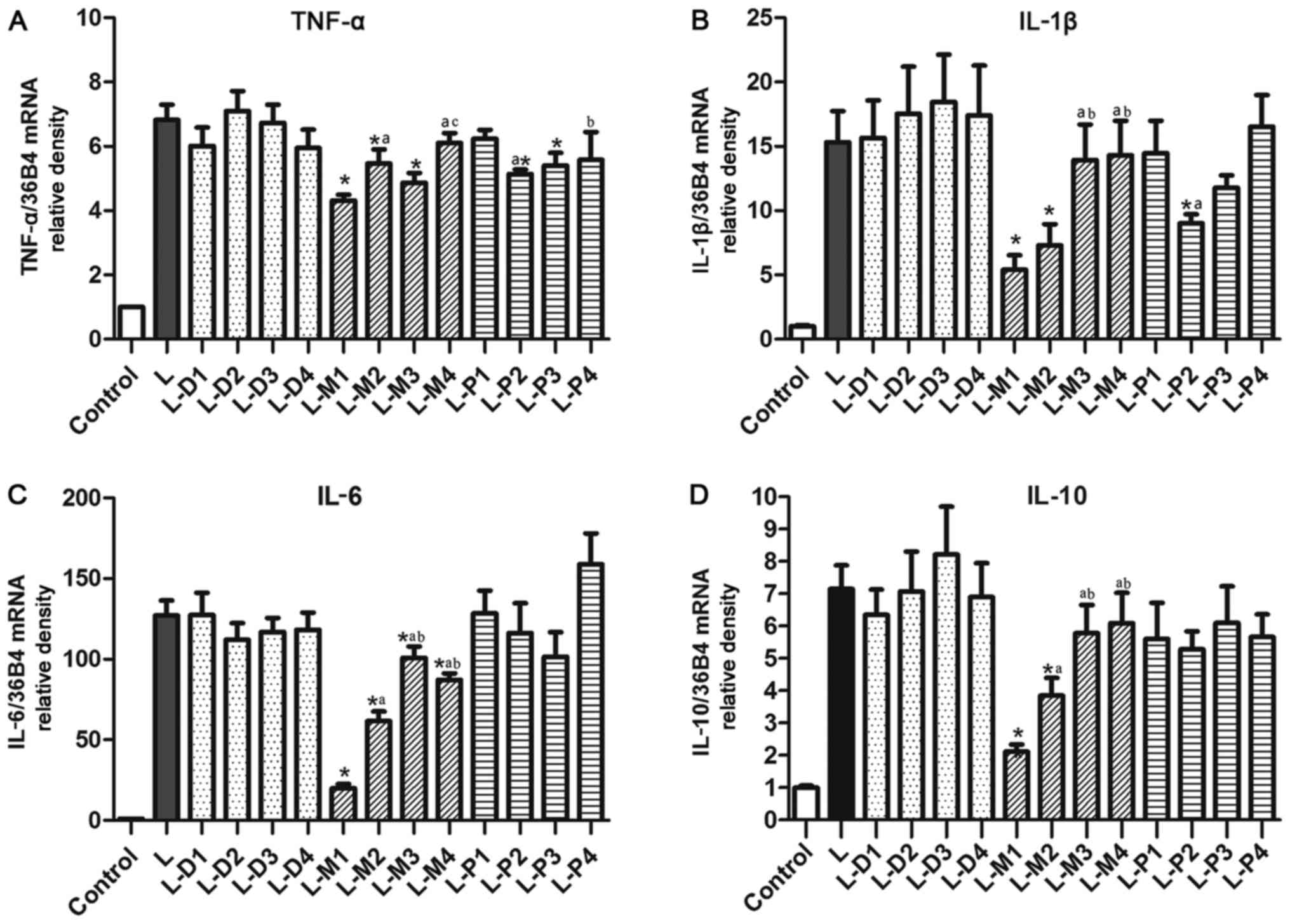
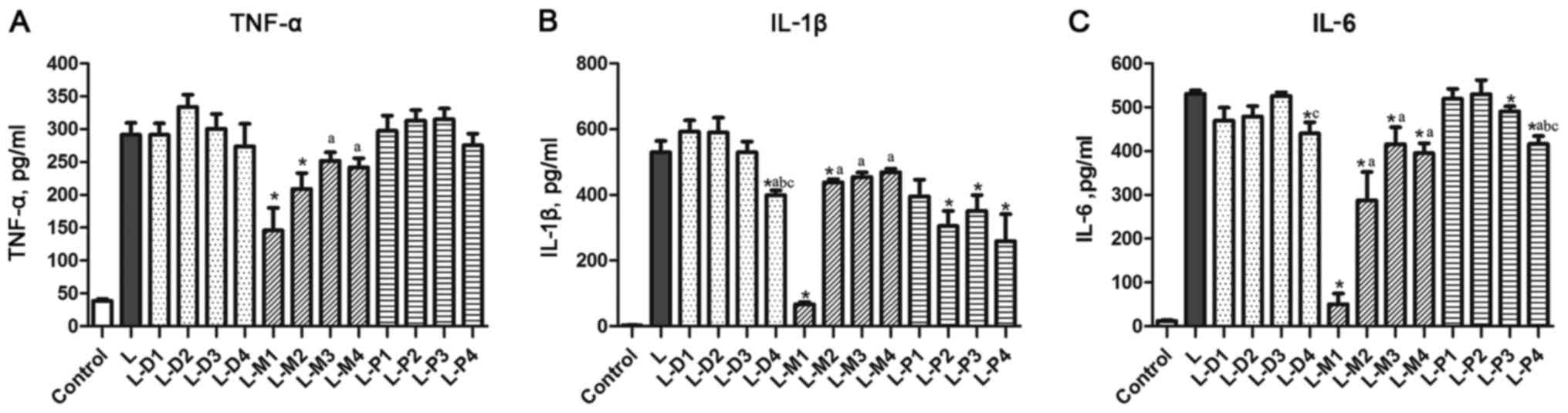
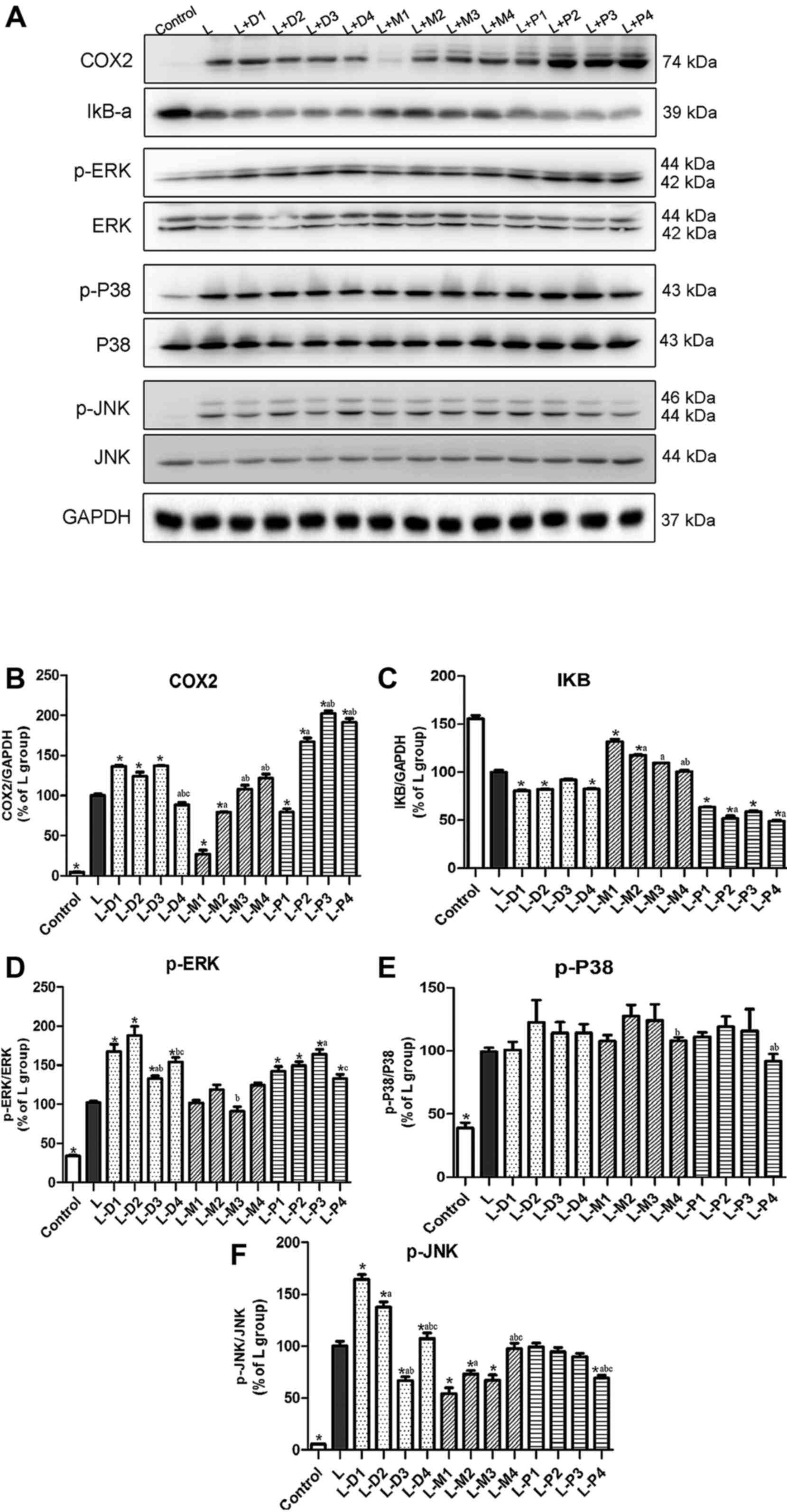
|
1
|
Yuki K, Soriano SG and Shimaoka M:
Sedative drug modulates T-cell and lymphocyte function-associated
antigen-1 function. Anesth Analg. 112:830–838. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pandharipande PP, Sanders RD, Girard TD,
McGrane S, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, Herr DL, Maze M and Ely EW:
MENDS investigators: Effect of dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam on
outcome in patients with sepsis: An a priori-designed analysis of
the MENDS randomized controlled trial. Crit Care. 14:R382010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ruokonen E, Parviainen I, Jakob SM, Nunes
S, Kaukonen M, Shepherd ST, Sarapohja T, Bratty JR and Takala J:
‘Dexmedetomidine for Continuous Sedation’ Investigators:
Dexmedetomidine versus propofol/midazolam for long-term sedation
during mechanical ventilation. Int Care Med. 35:282–290. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jung HS, Joo JD, Jeon YS, Lee JA, Kim DW,
In JH, Rhee HY and Choi JW: Comparison of an intraoperative
infusion of dexmedetomidine or remifentanil on perioperative
haemodynamics, hypnosis and sedation and postoperative pain
control. J Int Med Res. 39:1890–1899. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roquilly A, Josien R and Asehnoune K:
Midazolam impairs immune functions: It's time to take care of
dendritic cells. Anesthesiology. 114:237–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lai YC, Tsai PS and Huang CJ: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on regulating endotoxin-induced up-regulation of
inflammatory molecules in murine macrophages. J Surg Res.
154:212–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lipscomb MF and Masten BJ: Dendritic
cells: Immune regulators in health and disease. Physiol Rev.
82:97–130. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blanco P, Palucka AK, Pascual V and
Banchereau J: Dendritic cells and cytokines in human inflammatory
and autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 19:41–52.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dowling D, Hamilton CM and O'Neill SM: A
comparative analysis of cytokine responses, cell surface marker
expression and MAPKs in DCs matured with LPS compared with a panel
of TLR ligands. Cytokine. 41:254–262. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Neves BM and Cruz MV: Differential roles
of PI3-Kinase, MAPKs and NF-kappaB on the manipulation of dendritic
cell T(h)1/T(h)2 cytokine/chemokine polarizing profile. Mol
Immunol. 46:2481–2492. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim SF: The nitric oxide-mediated
regulation of prostaglandin signaling in medicine. Vitam Horm.
96:211–245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aktan F: iNOS-mediated nitric oxide
production and its regulation. Life Sci. 75:639–653. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nakahara T, Moroi Y, Uchi H and Furue M:
Differential role of MAPK signaling in human dendritic cell
maturation and Th1/Th2 engagement. J Dermatol Sci. 42:1–11. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen RM, Chen TG, Chen TL, Lin LL, Chang
CC, Chang HC and Wu CH: Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects
of propofol on lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1042:262–271. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim SN, Son SC, Lee SM, Kim CS, Yoo DG,
Lee SK, Hur GM, Park JB and Jeon BH: Midazolam inhibits
proinflammatory mediators in the lipopolysaccharide-activated
macrophage. Anesthesiology. 105:105–110. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peng M, Wang YL, Wang CY and Chen C:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
proinflammatory response in primary microglia. J Surg Res.
179:e219–e225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ueshima H, Inada T and Shingu K:
Suppression of phagosome proteolysis and Matrigel migration with
the α2-adrenergic receptor agonist dexmedetomidine in murine
dendritic cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 35:558–566. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ohta N, Ohashi Y, Takayama C, Mashimo T
and Fujino Y: Midazolam suppresses maturation of murine dendritic
cells and priming of lipopolysaccharide-induced t helper 1-type
immune response. Anesthesiology. 114:355–362. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brown M, Zhang Y, Dermine S, de Wynter EA,
Hart C, Kitchener H, Stern PL, Skinner MA and Stacey SN: Dendritic
cells infected with recombinant fowlpox virus vectors are potent
and long-acting stimulators of transgene-specific class I
restricted T lymphocyte activity. Gene Ther. 7:1680–1689. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dyck JB, Maze M, Haack C, Azarnoff DL,
Vuorilehto L and Shafer SL: Computer-controlled infusion of
intravenous dexmedetomidine hydrochloride in adult human
volunteers. Anesthesiology. 78:821–828. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Swart EL, Zuideveld KP, de Jongh J, Danhof
M, Thijs LG and van Schijndel Strack RM: Population pharmacodynamic
modelling of lorazepam- and midazolam-induced sedation upon
long-term continuous infusion in critically ill patients. Eur J
Clin Pharmacol. 62:185–194. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gepts E, Camu F, Cockshott ID and Douglas
EJ: Disposition of propofol administered as constant rate
intravenous infusions in humans. Anesth Analg. 66:1256–1263. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meng ZX, Li S, Wang L, Ko HJ, Lee Y, Jung
DY, Okutsu M, Yan Z, Kim JK and Lin JD: Baf60c drives glycolytic
metabolism in the muscle and improves systemic glucose homeostasis
through Deptor-mediated Akt activation. Nat Med. 19:640–645. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arend WP, Palmer G and Gabay C: IL-1,
IL-18 and IL-33 families of cytokines. Immunol Rev. 223:20–38.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Inada T, Kubo K, Ueshima H and Shingu K:
Intravenous anesthetic propofol suppresses prostaglandin E2
production in murine dendritic cells. J Immunotoxicol. 8:359–366.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ren K and Torres R: Role of
interleukin-1beta during pain and inflammation. Brain Res Rev.
60:57–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zelová H and Hošek J: TNF-α signalling and
inflammation: Interactions between old acquaintances. Inflamm Res.
62:641–651. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Scheller J, Garbers C and Rose-John S:
Interleukin-6: From basic biology to selective blockade of
pro-inflammatory activities. Semin Immunol. 26:2–12. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
González-Correa JA, Cruz-Andreotti E,
Arrebola MM, López-Villodres JA, Jódar M and De La Cruz JP: Effects
of propofol on the leukocyte nitric oxide pathway: In vitro and ex
vivo studies in surgical patients. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch
Pharmacol. 376:331–339. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen RM, Wu GJ, Tai YT, Sun WZ, Lin YL,
Jean WC and Chen TL: Propofol reduces nitric oxide biosynthesis in
lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages by downregulating the
expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Arch Toxicol.
77:418–423. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peng M, Ye JS, Wang YL, Chen C and Wang
CY: Posttreatment with propofol attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced up-regulation of inflammatory molecules
in primary microglia. Inflamm Res. 63:411–418. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chiu WT, Lin YL, Chou CW and Chen RM:
Propofol inhibits lipoteichoic acid-induced iNOS gene expression in
macrophages possibly through downregulation of toll-like receptor
2-mediated activation of Raf-MEK1/2-ERK1/2-IKK-NFκB. Chem Biol
Interact. 181:430–439. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee CJ, Tai YT, Lin YL and Chen RM:
Molecular mechanisms of propofol-involved suppression of no
biosynthesis and inducible iNOS gene expression in LPS-stimulated
macrophage-like raw 264.7 cells. Shock. 33:93–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Faugaret D, Lemoine R, Baron C, Lebranchu
Y and Velge-Roussel F: Mycophenolic acid differentially affects
dendritic cell maturation induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha
and lipopolysaccharide through a different modulation of MAPK
signaling. Mol Immunol. 47:1848–1859. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nakahara T, Uchi H, Urabe K, Chen Q, Furue
M and Moroi Y: Role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase on
lipopolysaccharide induced maturation of human monocyte-derived
dendritic cells. Int Immunol. 16:1701–1709. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jin Y, Wi HJ, Choi MH, Hong ST and Bae YM:
Regulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and TGF-β in mouse
dendritic cells through treatment with Clonorchis sinensis crude
antigen. Exp Mol Med. 46:e742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Handley ME, Thakker M, Pollara G, Chain BM
and Katz DR: JNK activation limits dendritic cell maturation in
response to reactive oxygen species by the induction of apoptosis.
Free Radic Biol Med. 38:1637–1652. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kadoi Y, Saito S, Kawauchi C, Hinohara H
and Kunimoto F: Comparative effects of propofol vs. dexmedetomidine
on cerebrovascular carbon dioxide reactivity in patients with
septic shock. Br J Anaesth. 100:224–229. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jakob S, Ruokonen E, Grounds RM, Sarapohja
T, Garratt C, Pocock SJ, Bratty JR and Takala J: Dexmedetomidine
for Long-Term Sedation Investigators: Dexmedetomidine vs. midazolam
or propofol for sedation during prolonged mechanical ventilation:
Two randomized controlled trials. JAMA. 307:1151–1160. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|