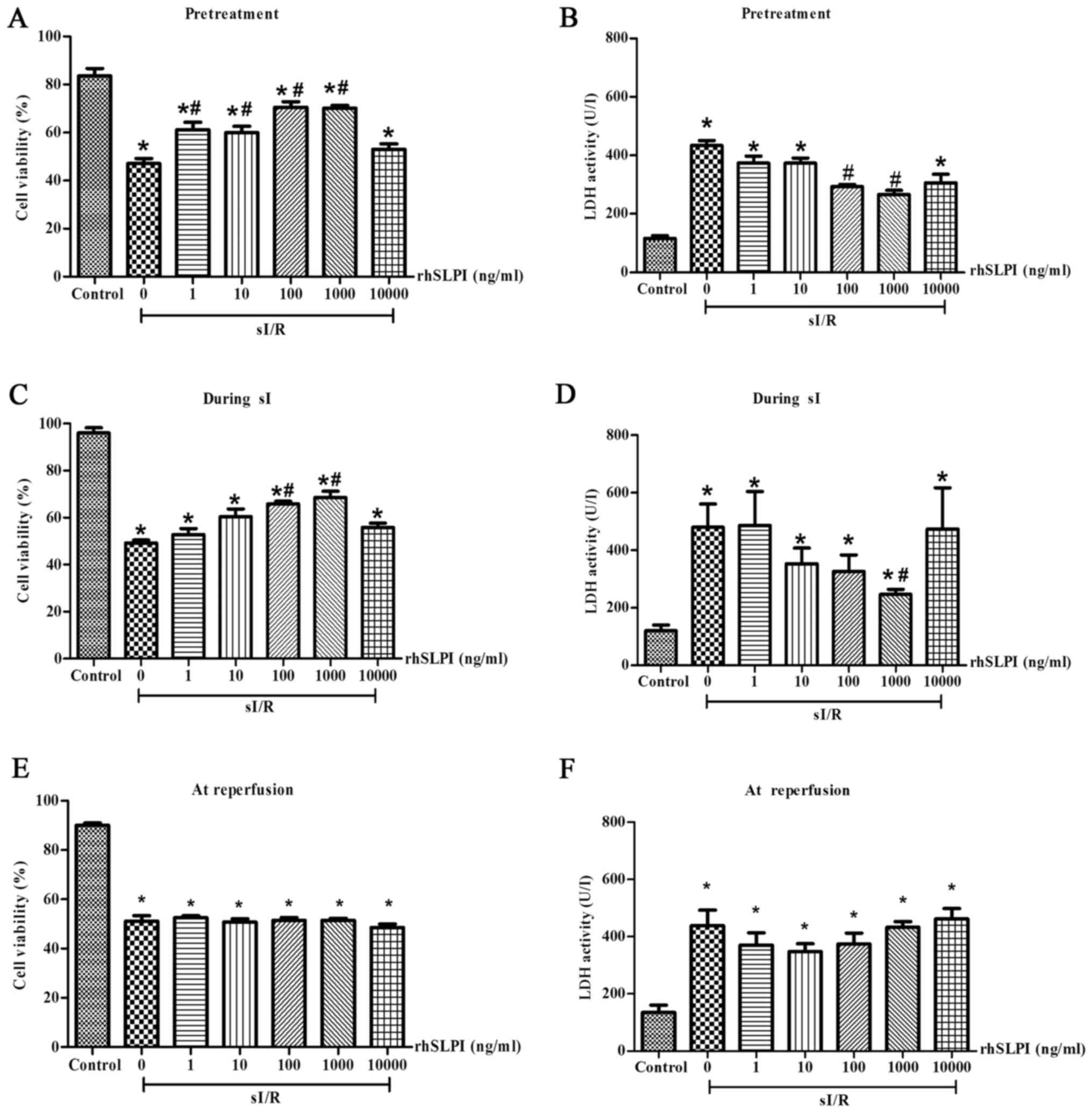
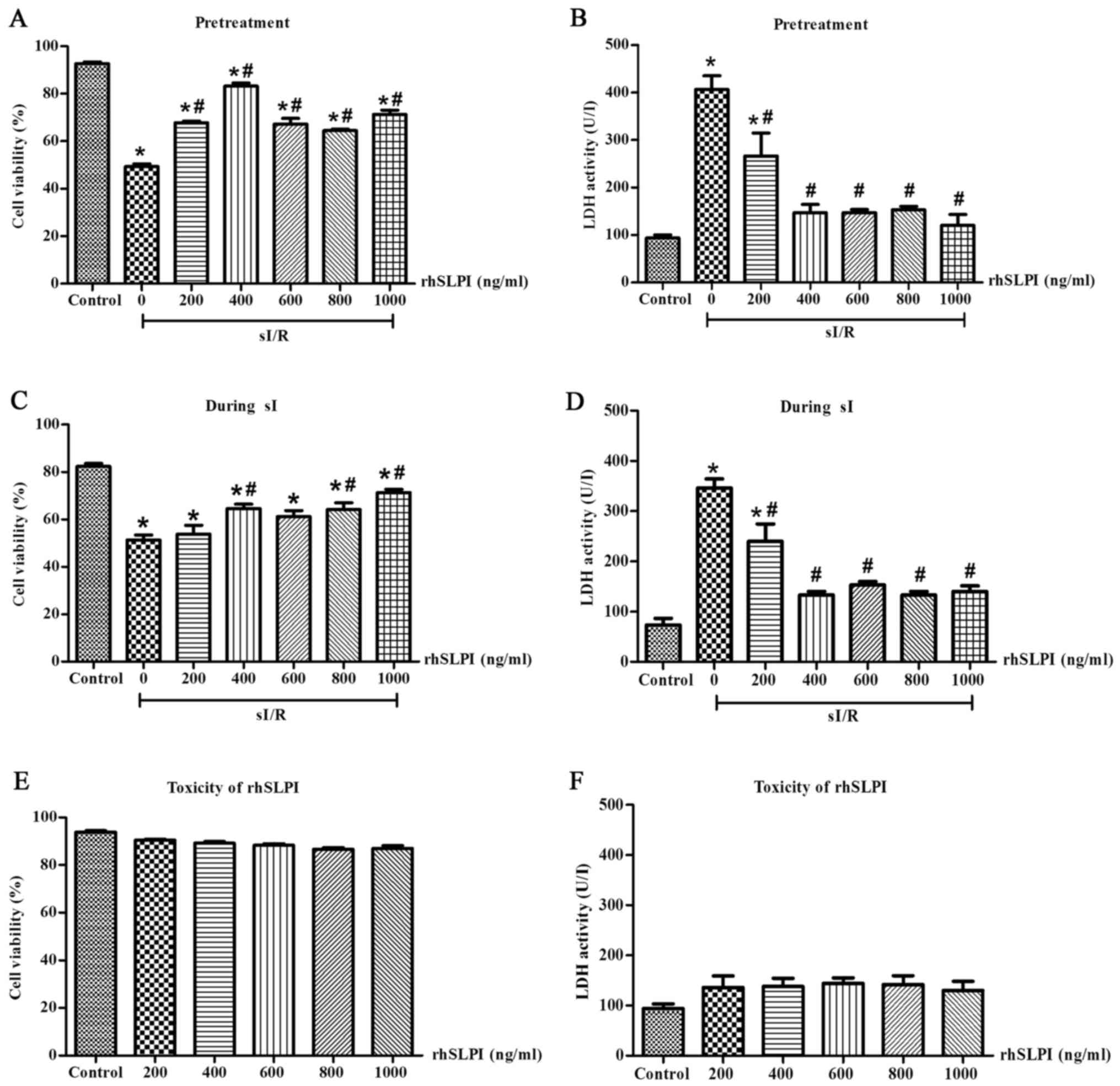
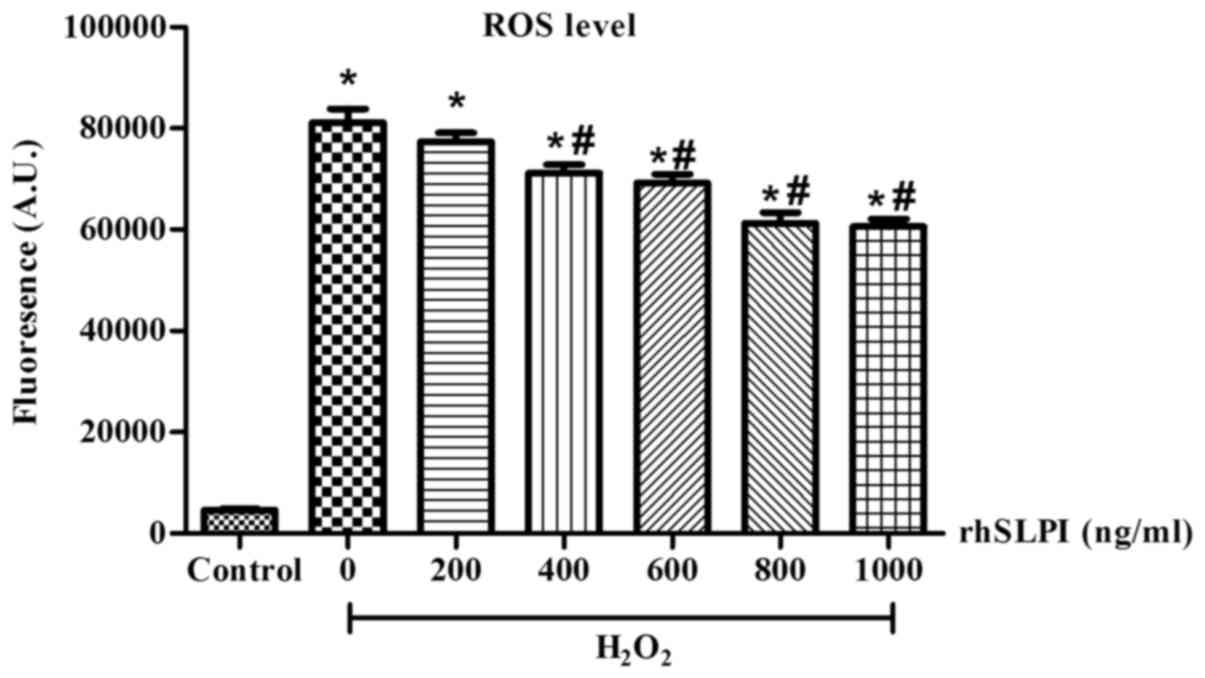
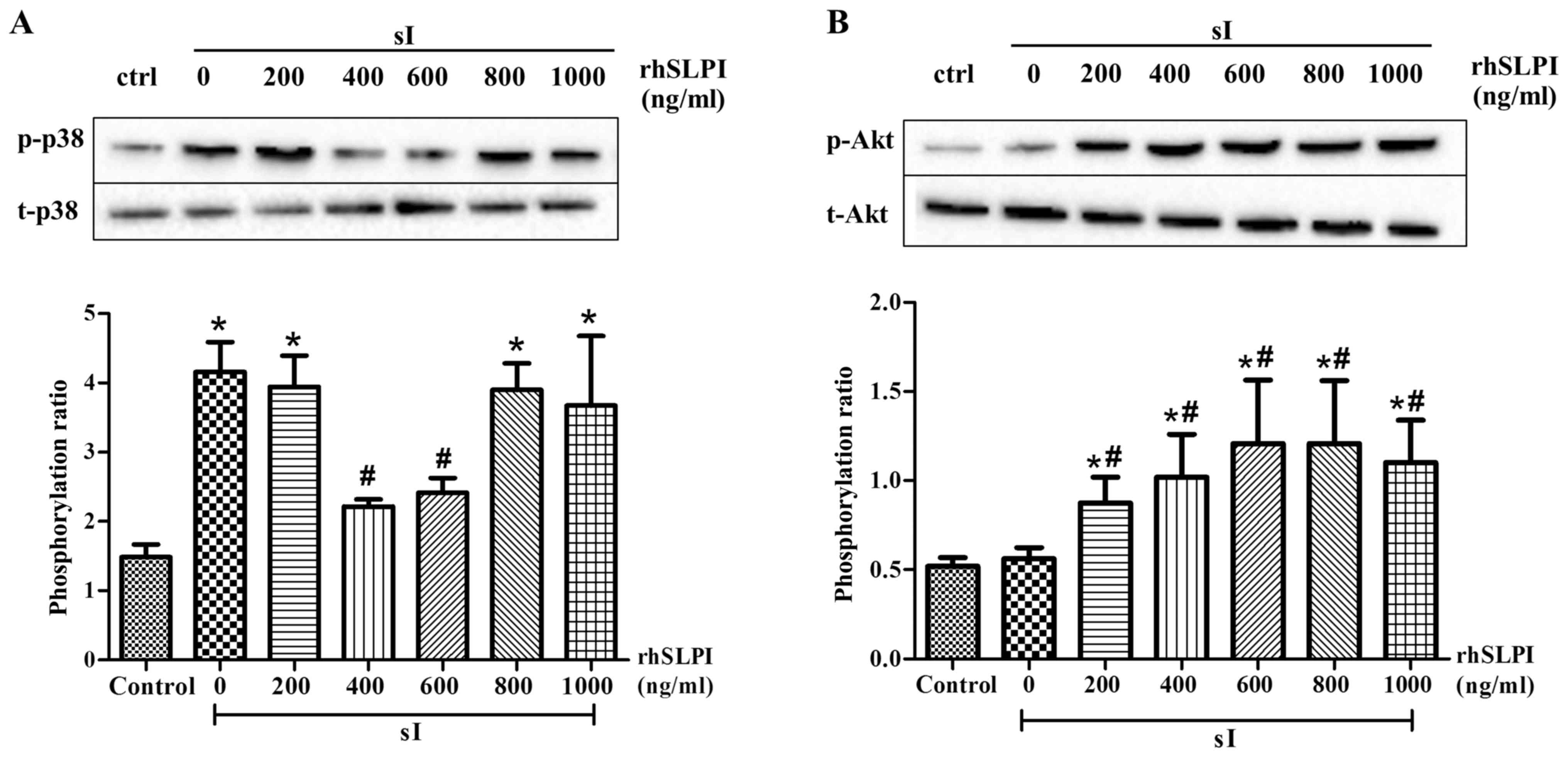
|
1
|
World Health Organization: World Health
Statistics 2008. Geneva: 2008
|
|
2
|
Writing Group Members, . Mozaffarian D,
Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de
Ferranti S, Després JP, et al: Heart disease and stroke
statistics-2016 update: A report from the american heart
association. Circulation. 133:e38–e360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jennings RB and Reimer KA: The cell
biology of acute myocardial ischemia. Annu Rev Med. 42:225–246.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yellon DM and Hausenloy DJ: Myocardial
reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 357:1121–1135. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Epelman S, Liu PP and Mann DL: Role of
innate and adaptive immune mechanisms in cardiac injury and repair.
Nat Rev Immunol. 15:117–129. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Boudoulas KD and Hatzopoulos AK: Cardiac
repair and regeneration: The Rubik's cube of cell therapy for heart
disease. Dis Model Mech. 2:344–358. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jordan JE, Zhao ZQ and Vinten-Johansen J:
The role of neutrophils in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Cardiovasc Re. 43:860–878. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kuckleburg CJ and Newman PJ: Neutrophil
proteinase 3 acts on protease-activated receptor-2 to enhance
vascular endothelial cell barrier function. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 33:275–284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bouchard D, Morisset D, Bourbonnais Y and
Tremblay GM: Proteins with whey-acidic-protein motifs and cancer.
Lancet Oncol. 7:167–174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Majchrzak-Gorecka M, Majewski P, Grygier
B, Murzyn K and Cichy J: Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor
(SLPI), a multifunctional protein in the host defense response.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 28:79–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moreau T, Baranger K, Dadé S,
Dallet-Choisy S, Guyot N and Zani ML: Multifaceted roles of human
elafin and secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor (SLPI), two
serine protease inhibitors of the chelonianin family. Biochimie.
90:284–295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Doumas S, Kolokotronis A and Stefanopoulos
P: Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial roles of secretory leukocyte
protease inhibitor. Infect Immun. 73:1271–1274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schneeberger S, Hautz T, Wahl SM,
Brandacher G, Sucher R, Steinmassl O, Steinmassl P, Wright CD,
Obrist P, Werner ER, et al: The effect of secretory leukocyte
protease inhibitor (SLPI) on ischemia/reperfusion injury in cardiac
transplantation. Am J Transplant. 8:773–782. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jacquet S, Nishino Y, Kumphune S, Sicard
P, Clark JE, Kobayashi KS, Flavell RA, Eickhoff J, cotton M and
Marber MS: The role of RIP2 in p38 MAPK activation in the stressed
heart. J Biol Chem. 283:11964–11971. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kumphune S, Bassi R, Jacquet S, Sicard P,
Clark JE, Verma S, Avkiran M, O'Keefe SJ and Marber MS: A chemical
genetic approach reveals that p38alpha MAPK activation by
diphosphorylation aggravates myocardial infarction and is prevented
by the direct binding of SB203580. J Biol Chem. 285:2968–2975.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cowan B, Baron O, Crack J, Coulber C,
Wilson GJ and Rabinovitch M: Elafin, a serine elastase inhibitor,
attenuates post-cardiac transplant coronary arteriopathy and
reduces myocardial necrosis in rabbits afer heterotopic cardiac
transplantation. J Clin Invest. 97:2452–2468. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tiefenbacher CP, Ebert M, Niroomand F,
Batkai S, Tillmanns H, Zimmermann R and Kübler W: Inhibition of
elastase improves myocardial function after repetitive ischaemia
and myocardial infarction in the rat heart. Pflugers Arch.
433:563–570. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hoffmeyer MR, Scalia R, Ross CR, Jones SP
and Lefer DJ: PR-39, a potent neutrophil inhibitor, attenuates
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 279:H2824–H2828. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ueno M, Moriyama Y, Toda R, Yotsumoto G,
Yamamoto H, Fukumoto Y, Sakasegawa K, Nakamura K and Sakata R:
Effect of a neutrophil elastase inhibitor (ONO-5046 Na) on
ischemia/reperfusion injury using the left-sided heterotopic canine
heart transplantation model. J Heart Lung Transplant. 20:889–896.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schneeberger S, Brandacher G, Mark W,
Amberger A and Margreiter R: Protease inhibitors as a potential
target in modulation of postischemic inflammation. Drug News
Perspect. 15:568–574. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lentsch AB, Yoshidome H, Warner RL, Ward
PA and Edwards MJ: Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor in mice
regulates local and remote organ inflammatory injury induced by
hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. Gastroenterology. 117:953–961. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McKiernan PJ, McElvaney NG and Greene CM:
SLPI and inflammatory lung disease in females. Biochem Soc Trans.
39:1421–1426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ding A, Thieblemont N, Zhu J, Jin F, Zhang
J and Wright S: Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor interferes
with uptake of lipopolysaccharide by macrophages. Infect Immun.
67:4485–4489. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Taggart CC, Cryan SA, Weldon S, Gibbons A,
Greene CM, Kelly E, Low TB, O'neill SJ and McElvaney NG: Secretory
leucoprotease inhibitor binds to NF-kappaB binding sites in
monocytes and inhibits p65 binding. J Exp Med. 202:1659–1668. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McElvaney NG, Nakamura H, Birrer P, Hébert
CA, Wong WL, Alphonso M, Baker JB, Catalano MA and Crystal RG:
Modulation of airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis. In vivo
suppression of interleukin-8 levels on the respiratory epithelial
surface by aerosolization of recombinant secretory leukoprotease
inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 90:1296–1301. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Adapala VJ, Buhman KK and Ajuwon KM: Novel
anti-inflammatory role of SLPI in adipose tissue and its regulation
by high fat diet. J Inflamm (Lond). 8:52011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mueller AM, Pedré X, Stempfl T, Kleiter I,
Couillard-Despres S, Aigner L, Giegerich G and Steinbrecher A:
Novel role for SLPI in MOG-induced EAE revealed by spinal cord
expression analysis. J Neuroinflammation. 5:202008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McGarry N, Greene CM, McElvaney NG, Weldon
S and Taggart CC: The ability of secretory leukocyte protease
inhibitor to inhibit apoptosis in monocytes is independent of its
antiprotease activity. J Immunol Res. 2015:5073152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Subramaniyam D, Hollander C, Westin U,
Erjefält J, Stevens T and Janciauskiene S: Secretory leukocyte
protease inhibitor inhibits neutrophil apoptosis. Respirology.
16:300–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Seto T, Takai T, Ebihara N, Matsuoka H,
Wang XL, Ishii A, Ogawa H, Murakami A and Okumura K: SLPI prevents
cytokine release in mite protease-exposed conjunctival epithelial
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 379:681–685. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee SY, Nho TH, Choi BD, Jeong SJ, Lim DS
and Jeong MJ: Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor reduces
inflammation and alveolar bone resorption in LPS-induced
periodontitis in rats and in MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts. Animal Cells
Systems. 20:344–352. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hoffman JW Jr, Gilbert TB, Poston RS and
Silldorff EP: Myocardial reperfusion injury: Etiology, mechanisms,
and therapies. J Extra Corpor Technol. 36:391–411. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Raedschelders K, Ansley DM and Chen DD:
The cellular and molecular origin of reactive oxygen species
generation during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Pharmacol
Ther. 133:230–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gottlieb RA: Cell death pathways in acute
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther.
16:233–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lucchesi BR: Myocardial ischemia,
reperfusion and free radical injury. Am J Cardiol. 65:14I–23I.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Venardos KM, Perkins A, Headrick J and
Kaye DM: Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, antioxidant enzyme
systems, and selenium: A review. Curr Med Chem. 14:1539–1549. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: A neglected therapeutic target. J Clin
Invest. 123:92–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ferrari R, Agnoletti L, Comini L, Gaia G,
Bachetti T, Cargnoni A, Ceconi C, Curello S and Visioli O:
Oxidative stress during myocardial ischaemia and heart failure. Eur
Heart J. 19 Suppl B:B2–B11. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gillissen A, Birrer P and McElvaney NG:
Recombinant secretory leukoprotease inhibitor augments glutathione
levels in lung epithelial lining fluid. J Appl Physiol (1985).
75:825–832. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Masterson CH, O'Toole DP and Laffey JP:
Over expression of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI)
and glutathione peroxidase-3 (GPX3) attenuate inflammation and
oxidant-mediated pulmonary epithelial injuryAmerican Thoracic
Society 2012 International Conference. San Francisco, California:
2012
|
|
41
|
Kaiser RA, Lyons JM, Duffy JY, Wagner CJ,
McLean KM, O'Neill TP, Pearl JM and Molkentin JD: Inhibition of p38
reduces myocardial infarction injury in the mouse but not pig after
ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
289:H2747–H2751. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gorog DA, Tanno M, Cao X, Bellahcene M,
Bassi R, Kabir AM, Dighe K, Quinlan RA and Marber MS: Inhibition of
p38 MAPK activity fails to attenuate contractile dysfunction in a
mouse model of low-flow ischemia. Cardiovasc Res. 61:123–131. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ma XL, Kumar S, Gao F, Louden CS, Lopez
BL, Christopher TA, Wang C, Lee JC, Feuerstein GZ and Yue TL:
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase decreases
cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improves cardiac function after
myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation. 99:1685–1691.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kumphune S, Chattipakorn S and
Chattipakorn N: Role of p38 inhibition in cardiac
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 68:513–524.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kumphune S, Surinkaew S, Chattipakorn SC
and Chattipakorn N: Inhibition of p38 MAPK activation protects
cardiac mitochondria from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharm Biol.
53:1831–1841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu L, Li F, Zhao G, Yang Y, Jin Z, Zhai M,
Yu W, Zhao L, Chen W, Duan W and Yu S: Protective effect of
berberine against myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury: Role of
Notch1/Hes1-PTEN/Akt signaling. Apoptosis. 20:796–810. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mullonkal CJ and Toledo-Pereyra LH: Akt in
ischemia and reperfusion. J Invest Surg. 20:195–203. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fujio Y, Nguyen T, Wencker D, Kitsis RN
and Walsh K: Akt promotes survival of cardiomyocytes in vitro and
protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mouse heart.
Circulation. 101:660–667. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Armstrong SC: Protein kinase activation
and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res.
61:427–436. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Surinkaew S, Kumphune S, Chattipakorn S
and Chattipakorn N: Inhibition of p38 MAPK during ischemia, but not
reperfusion, effectively attenuates fatal arrhythmia in
ischemia/reperfusion heart. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 61:133–141.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu SZ, Tao LY, Wang JN, Xu ZQ, Wang J, Xue
YJ, Huang KY, Lin JF, Li L and Ji KT: Amifostine pretreatment
attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting
apoptosis and oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:41308242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang P, Liu X, Huang G, Bai C, Zhang Z
and Li H: Barbaloin pretreatment attenuates myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury via activation of AMPK. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 490:1215–1220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jones SP, Trocha SD and Lefer DJ:
Pretreatment with simvastatin attenuates myocardial dysfunction
after ischemia and chronic reperfusion. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 21:2059–2064. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen H, Liu S, Liu X, Yang J, Wang F, Cong
X and Chen X: lysophosphatidic acid pretreatment attenuates
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in the immature hearts of
rats. Front Physiol. 8:1532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ke Z, Liu J, Xu P, Gao A, Wang L and Ji L:
The cardioprotective effect of icariin on ischemia-reperfusion
injury in isolated rat heart: Potential involvement of the PI3K-Akt
signaling pathway. Cardiovasc Ther. 33:134–140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Skrzypiec-Spring M, Grotthus B, Szelag A
and Schulz R: Isolated heart perfusion according to
Langendorff-still viable in the new millennium. J Pharmacol Toxicol
Methods. 55:113–126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Herr DJ, Aune SE and Menick DR: Induction
and assessment of ischemia-reperfusion injury in
langendorff-perfused rat hearts. J Vis Exp. 27:e529082015.
|
|
58
|
Csonka C, Kupai K, Kocsis GF, Novák G,
Fekete V, Bencsik P, Csont T and Ferdinandy P: Measurement of
myocardial infarct size in preclinical studies. J Pharmacol Toxicol
Methods. 61:163–170. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|