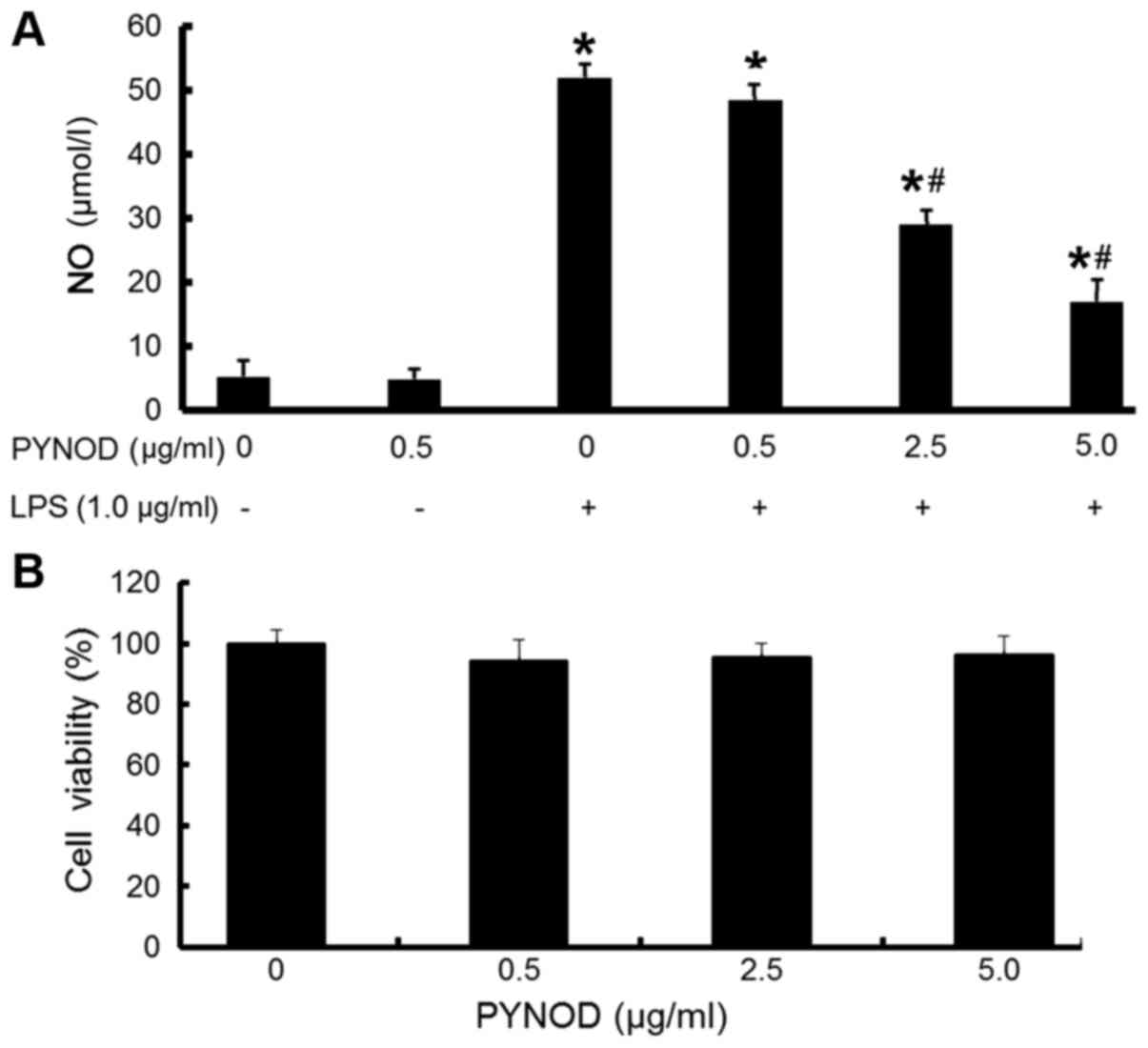
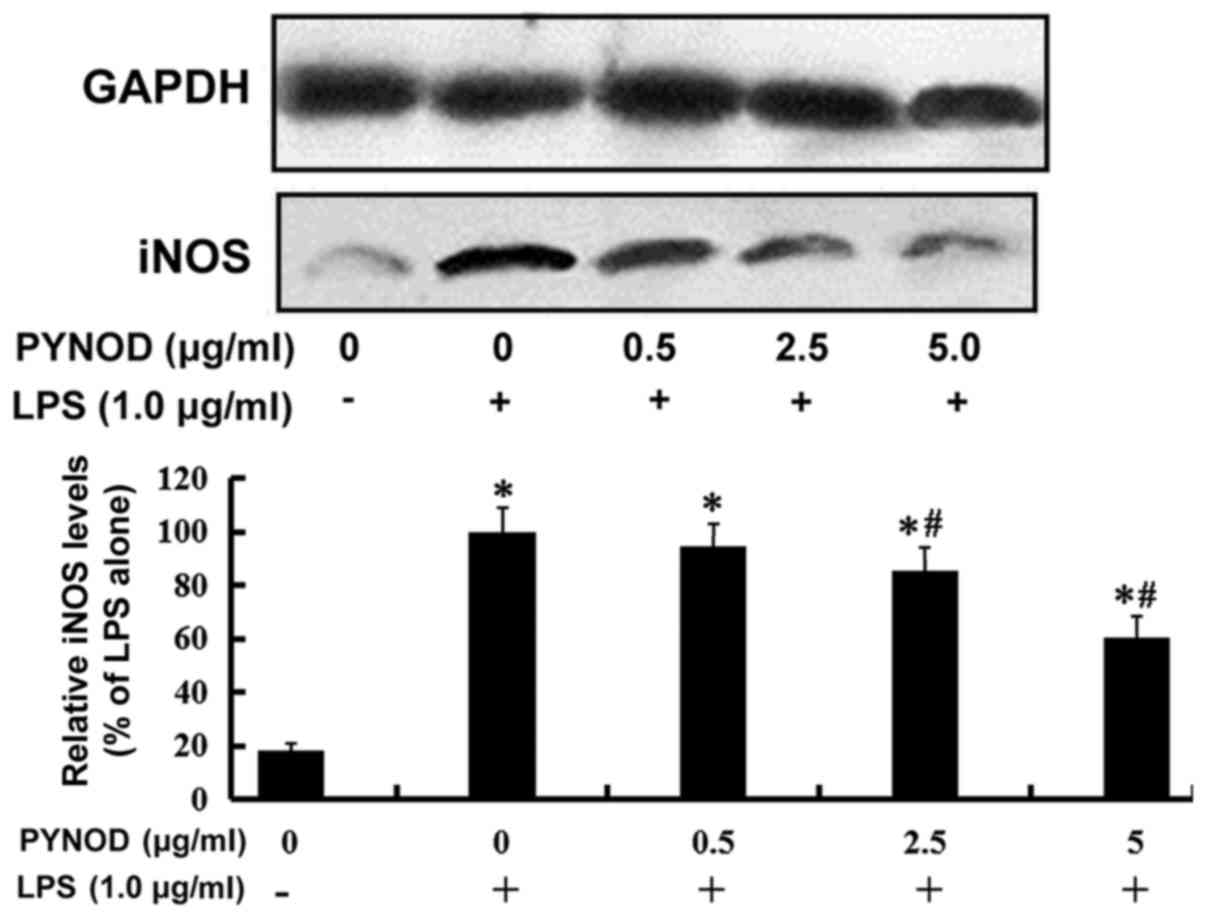
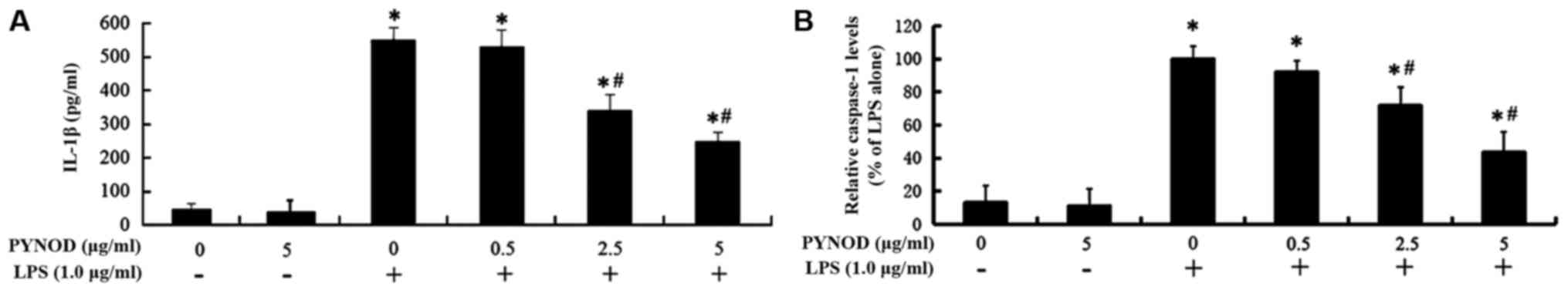
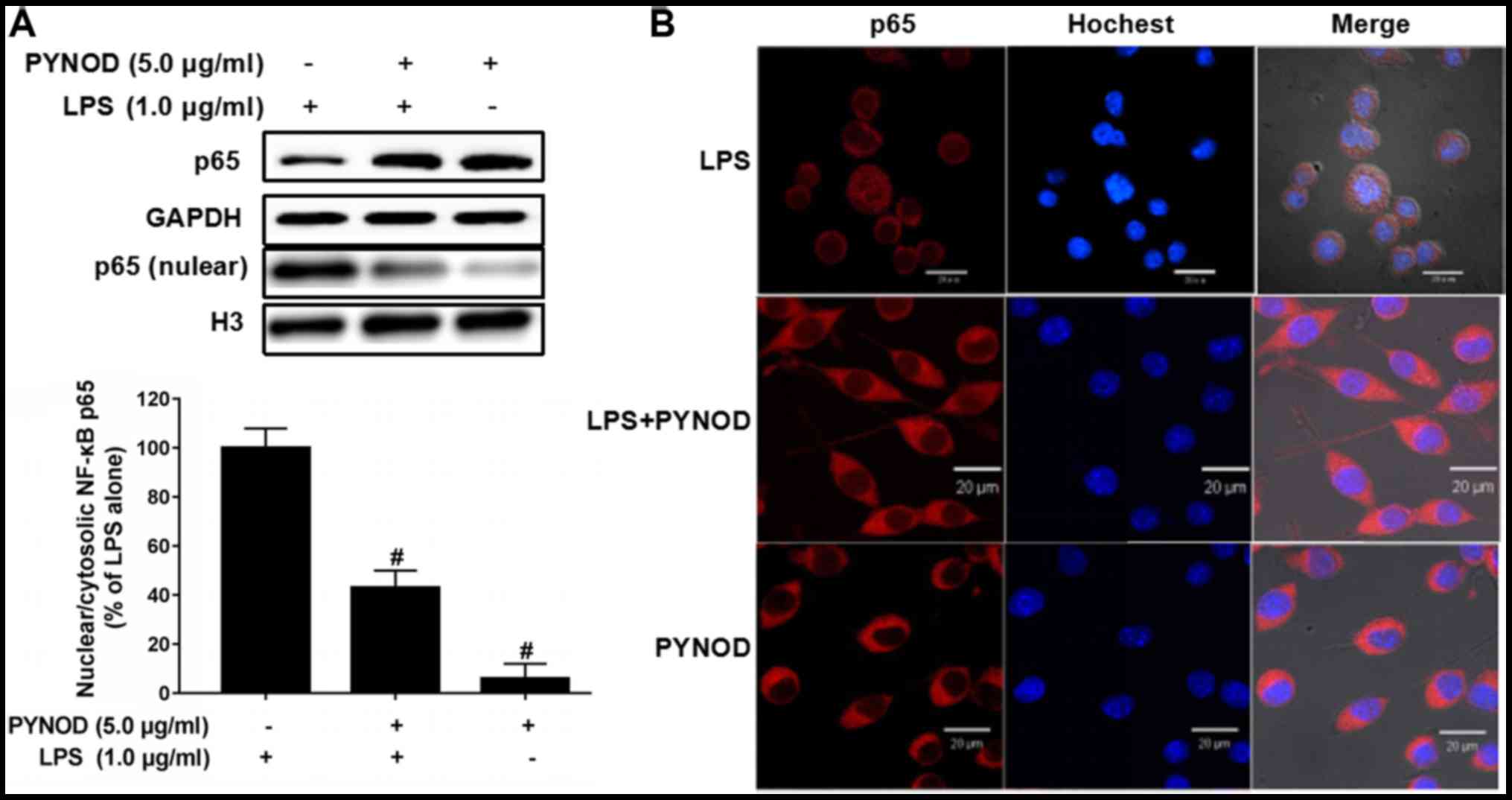
|
1
|
Pérez-Figueroa E, Torres J, Sánchez-Zauco
N, Contreras-Ramos A, Alvarez-Arellano L and Maldonado-Bernal C:
Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in human neutrophils by
Helicobacter pylori infection. Innate Immun. 22:103–112. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zambetti LP, Laudisi F, Licandro G,
Ricciardi-Castagnoli P and Mortellaro A: The rhapsody of NLRPs:
Master players of inflammation…and a lot more. Immunol Res.
53:78–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Caruso R, Warner N, Inohara N and Núñez G:
NOD1 and NOD2: Signaling, host defense and inflammatory disease.
Immunity. 41:898–908. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chavarría-Smith J and Vance RE: The NLRP1
inflammasomes. Immunol Rev. 265:22–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Garbarino-Pico E, Niu S, Rollag MD,
Strayer CA, Besharse JC and Green CB: Immediate early response of
the circadian polyA ribonuclease nocturnin to two extracellular
stimuli. RNA. 13:745–755. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kinoshita T, Wang Y, Hasegawa M, Imamura R
and Suda T: PYPAF3, a PYRIN-containing APAF-1-like protein, is a
feedback regulator of caspase-1-dependent interleukin-1beta
secretion. J Biol Chem. 280:21720–21725. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeng Q, Lu D, Tang Q, Tian L, Wang H, Tang
S and Hu C: Functional characterization of the p53 binding site in
the human PYNOD promoter. Hum Immunol. 73:355–363. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Hasegawa M, Imamura R, Kinoshita
T, Kondo C, Konaka K and Suda T: PYNOD, a novel Apaf-1/CED4-like
protein is an inhibitor of ASC and caspase-1. Int Immunol.
16:777–786. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Imamura R, Wang Y, Kinoshita T, Suzuki M,
Noda T, Sagara J, Taniguchi S, Okamoto H and Suda T:
Anti-inflammatory activity of PYNOD and its mechanism in humans and
mice. J Immunol. 184:5874–5884. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eisenbarth SC, Williams A, Colegio OR,
Meng H, Strowig T, Rongvaux A, Henao-Mejia J, Thaiss CA, Joly S,
Gonzalez DG, et al: NLRP10 is a NOD-like receptor essential to
initiate adaptive immunity by dendritic cells. Nature. 484:510–513.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu D, Rhebergen AM and Eisenbarth SC:
Licensing adaptive immunity by NOD-like receptors. Front Immunol.
4:4862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Krishnaswamy JK, Singh A, Gowthaman U, Wu
R, Gorrepati P, Nascimento Sales M, Gallman A, Liu D, Rhebergen AM,
Calabro S, et al: Coincidental loss of DOCK8 function in
NLRP10-deficient and C3H/HeJ mice results in defective dendritic
cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:3056–3061. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vacca M, Böhme J, Zambetti LP, Khameneh
HJ, Paleja BS, Laudisi F, Ho AWS, Neo K, Leong KWK, Marzuki M, et
al: NLRP10 enhances CD4+ T-cell-mediated IFNγ response via
regulation of dendritic cell-derived IL-12 release. Front Immunol.
8:14622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Imai K, Kotani T, Tsuda H, Mano Y, Nakano
T, Ushida T, Li H, Miki R, Sumigama S, Iwase A, et al:
Neuroprotective potential of molecular hydrogen against perinatal
brain injury via suppression of activated microglia. Free Radic
Biol Med. 91:154–163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zindler E and Zipp F: Neuronal injury in
chronic CNS inflammation. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol.
24:551–562. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baby N, Patnala R, Ling EA and Dheen ST:
Nanomedicine and its application in treatment of microglia-mediated
neuroinflammation. Curr Med Chem. 21:4215–4226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang LL, Zhou Y, Tian WD, Li HJ,
Kang-Chu-Li, Miao X, An GZ, Wang XW, Guo GZ and Ding GR:
Electromagnetic pulse activated brain microglia via the p38 MAPK
pathway. Neurotoxicology. 52:144–149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Papageorgiou IE, Lewen A, Galow LV,
Cesetti T, Scheffel J, Regen T, Hanisch UK and Kann O:
TLR4-activated microglia require IFN-γ to induce severe neuronal
dysfunction and death in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:212–217.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gu Y, Yang DK, Spinas E, Kritas SK,
Saggini A, Caraffa A, Antinolfi P, Saggini R and Conti P: Role of
TNF in mast cell neuroinflammation and pain. J Biol Regul Homeost
Agents. 29:787–791. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shih RH, Wang CY and Yang CM: NF-kappaB
signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: A mini review.
Front Mol Neurosci. 8:772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Frakes AE, Ferraiuolo L, Haidet-Phillips
AM, Schmelzer L, Braun L, Miranda CJ, Ladner KJ, Bevan AK, Foust
KD, Godbout JP, et al: Microglia induce motor neuron death via the
classical NF-κB pathway in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuron.
81:1009–1023. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Owens R, Grabert K, Davies CL, Alfieri A,
Antel JP, Healy LM and McColl BW: Divergent neuroinflammatory
regulation of microglial TREM expression and involvement of NF-κB.
Front Cell Neurosci. 11:562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiong JY, Li SC, Sun YX, Zhang XS, Dong
ZZ, Zhong P and Sun XR: Long-term treadmill exercise improves
spatial memory of male APPswe/PS1dE9 mice by regulation of BDNF
expression and microglia activation. Biol Sport. 32:295–300. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li JY, Ma SS, Huang QY and Li MT: The
function of neuroinflammation in parkinson disease. Sheng Li Ke Xue
Jin Zhan. 46:175–179. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rangarajan P, Karthikeyan A, Lu J, Ling EA
and Dheen ST: Sirtuin 3 regulates Foxo3a-mediated antioxidant
pathway in microglia. Neuroscience. 311:398–414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gravel M, Béland LC, Soucy G, Abdelhamid
E, Rahimian R, Gravel C and Kriz J: IL-10 controls early microglial
phenotypes and disease onset in ALS caused by misfolded superoxide
dismutase 1. J Neurosci. 36:1031–1048. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gendelman HE and Mosley RL: A perspective
on roles played by innate and adaptive immunity in the pathobiology
of neurodegenerative disorders. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.
10:645–650. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Murphy N, Grehan B and Lynch MA: Glial
uptake of amyloid beta induces NLRP3 inflammasome formation via
cathepsin-dependent degradation of NLRP10. Neuromolecular Med.
16:205–215. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Henn A, Lund S, Hedtjärn M, Schrattenholz
A, Pörzgen P and Leist M: The suitability of BV2 cells as
alternative model system for primary microglia cultures or for
animal experiments examining brain inflammation. ALTEX. 26:83–94.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Blasko I, Apochal A, Boeck G, Hartmann T,
Grubeck-Loebenstein B and Ransmayr G: Ibuprofen decreases
cytokine-induced amyloid beta production in neuronal cells.
Neurobiol Dis. 8:1094–1101. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kiyota T, Ingraham KL, Swan RJ, Jacobsen
MT, Andrews SJ and Ikezu T: AAV serotype 2/1-mediated gene delivery
of anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 enhances neurogenesis and
cognitive function in APP+PS1 mice. Gene Ther. 19:724–733. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
White PA, Oliveira RC, Oliveira AP,
Serafini MR, Araújo AA, Gelain DP, Moreira JC, Almeida JR, Quintans
JS, Quintans-Junior LJ and Santos MR: Antioxidant activity and
mechanisms of action of natural compounds isolated from lichens: A
systematic review. Molecules. 19:14496–14527. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
McCarthy RC, Lu DY, Alkhateeb A, Gardeck
AM, Lee CH and Wessling-Resnick M: Characterization of a novel
adult murine immortalized microglial cell line and its activation
by amyloid-beta. J Neuroinflammation. 13:212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang WY, Tan MS, Yu JT and Tan L: Role of
pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer's
disease. Ann Transl Med. 3:1362015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Muriel P: NF-kappaB in liver diseases: A
target for drug therapy. J Appl Toxicol. 29:91–100. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu L, Li L, Medeiros LJ and Young KH:
NF-κB signaling pathway and its potential as a target for therapy
in lymphoid neoplasms. Blood Rev. 31:77–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Habashi Abbasi S, Sabouni F, Moghimi A and
Majd Ansari S: Modulation of lipopolysaccharide stimulated nuclear
factor kappa B mediated iNOS/NO production by bromelain in rat
primary microglial cells. Iran Biomed J. 20:33–40. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bi W, Zhu L, Jing X, Zeng Z, Liang Y, Xu
A, Liu J, Xiao S, Yang L, Shi Q, et al: Rifampicin improves
neuronal apoptosis in LPS-stimulated co-cultured BV2 cells through
inhibition of the TLR-4 pathway. Mol Med Rep. 10:1793–1799. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lo Frederick C, Ning X, Gonzales C and
Ozenberger BA: Induced expression of death domain genes NALP1 and
NALP5 following neuronal injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
366:664–669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nagyőszi P, Nyúl-Tóth Á, Fazakas C,
Wilhelm I, Kozma M, Molnár J, Haskó J and Krizbai IA: Regulation of
NOD-like receptors and inflammasome activation in cerebral
endothelial cells. J Neurochem. 135:551–564. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nyúl-Tóth Á, Kozma M, Nagyőszi P, Nagy K,
Fazakas C, Haskó J, Molnár K, Farkas AE, Végh AG, Váró G, et al:
Expression of pattern recognition receptors and activation of the
non-canonical inflammasome pathway in brain pericytes. Brain Behav
Immun. 64:220–231. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|