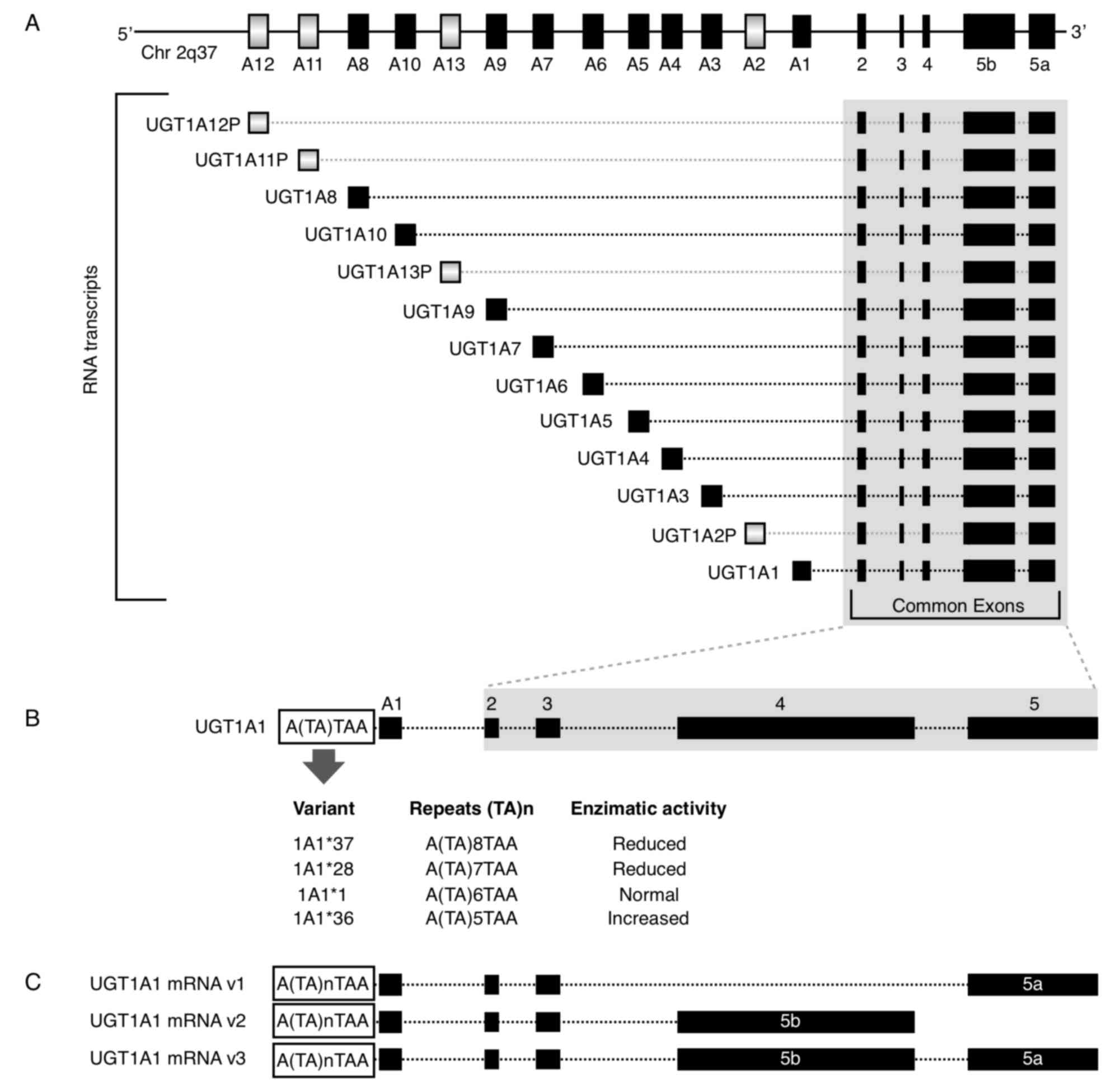
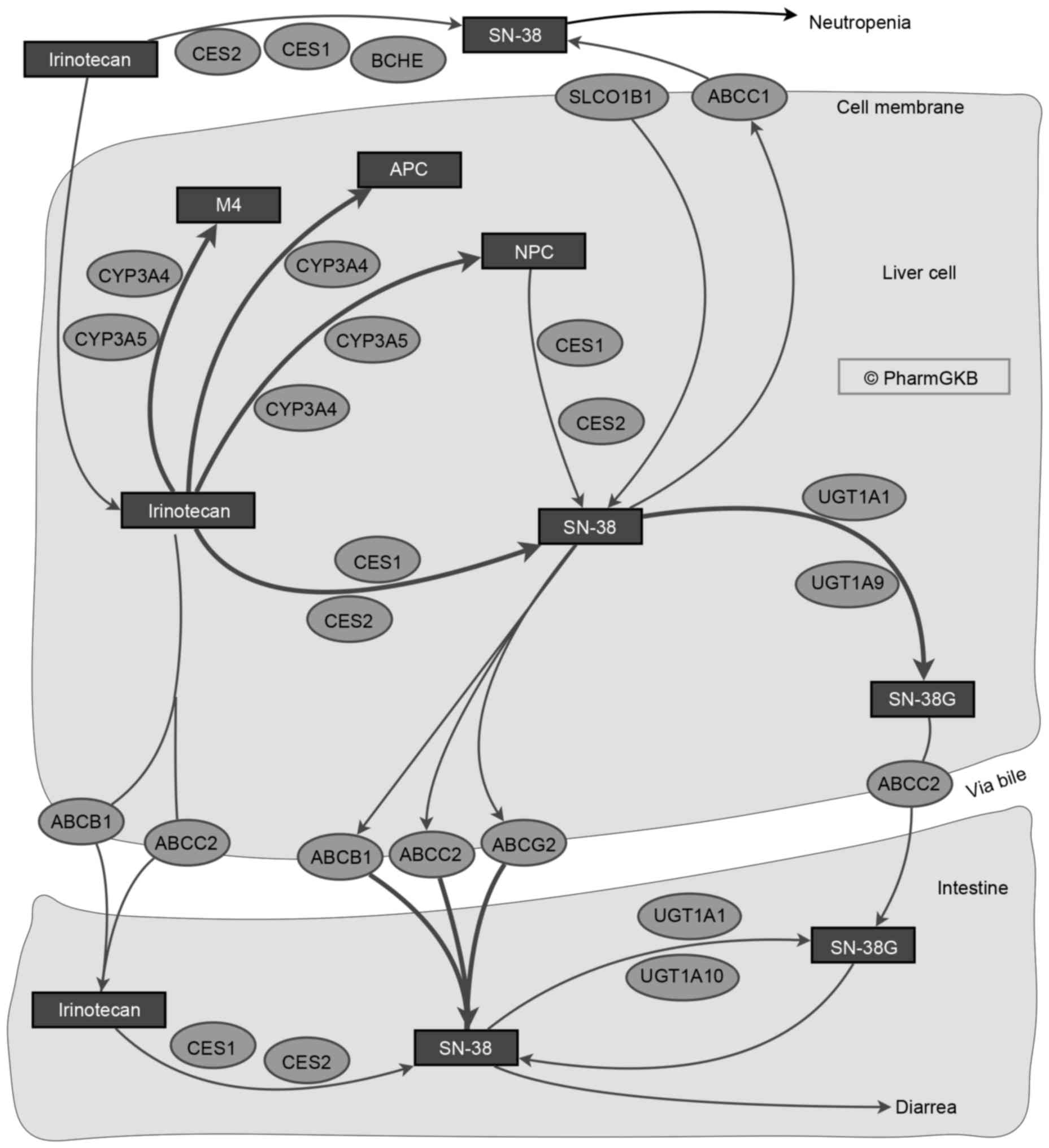
|
1
|
Obach RS: Pharmacologically active drug
metabolites: Impact on drug discovery and pharmacotherapy.
Pharmacol Rev. 65:578–640. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Laizure SC, Herring V, Hu Z, Witbrodt K
and Parker RB: The role of human carboxylesterases in drug
metabolism: Have we overlooked their importance? Pharmacotherapy.
33:210–222. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gustavsson L: Pharmacogenomics in drug
developmentgenomics and proteomics for clinical discovery and
development. Springer; New York, NY: pp. 225–241. 2014
|
|
4
|
Rowland A, Miners JO and Mackenzie PI: The
UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: Their role in drug metabolism and
detoxification. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:1121–1132. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kaivosaari S, Finel M and Koskinen M:
N-glucuronidation of drugs and other xenobiotics by human and
animal UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Xenobiotica. 41:652–669. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ishii Y, Nurrochmad A and Yamada H:
Modulation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity by endogenous
compounds. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 25:134–148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chang TKH: Drug-metabolizing
enzymesHandbook of drug-nutrient interactions. Boullata IJ and
Armenti TV: Humana Press; Totowa, NJ: pp. 85–117. 2010
|
|
8
|
Mackenzie PI, Bock KW, Burchell B,
Guillemette C, Ikushiro S, Iyanagi T, Miners JO, Owens IS and
Nebert DW: Nomenclature update for the mammalian UDP
glycosyltransferase (UGT) gene superfamily. Pharmacogenet Genomics.
15:677–685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bosma PJ, Chowdhury JR, Bakker C, Gantla
S, de Boer A, Oostra BA, Lindhout D, Tytgat GN, Jansen PL, Elferink
Oude RP, et al: The genetic basis of the reduced expression of
bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 in Gilbert's syndrome. N
Engl J Med. 333:1171–1175. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barbarino JM, Haidar CE, Klein TE and
Altman RB: PharmGKB summary: Very important pharmacogene
information for UGT1A1. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 24:177–183. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou Y, Wang SN, Li H, Zha W, Peng Q, Li
S, Chen Y and Jin L: Quantitative trait analysis of polymorphisms
in two bilirubin metabolism enzymes to physiologic bilirubin levels
in Chinese newborns. J Pediatr. 165:1154–1160.e1. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bajro MH, Josifovski T, Panovski M,
Jankulovski N, Nestorovska AK, Matevska N, Petrusevska N and
Dimovski AJ: Promoter length polymorphism in UGT1A1 and the risk of
sporadic colorectal cancer. Cancer Genet. 205:163–167. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Monaghan G, Ryan M, Seddon R, Hume R and
Burchell B: Genetic variation in bilirubin
UPD-glucuronosyltransferase gene promoter and Gilbert's syndrome.
Lancet. 347:578–581. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shatalova EG, Loginov VI, Braga EA,
Kazubskaia TP, Sudomoina MA, Blanchard RL and Favorova OO:
Association of polymorphisms in SULT1A1 and UGT1A1 Genes with
breast cancer risk and phenotypes in Russian women. Mol Biol
(Mosk). 40:263–270. 2006.(In Russian). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen YH, Hung SC and Tarng DC: Serum
bilirubin links UGT1A1*28 polymorphism and predicts long-term
cardiovascular events and mortality in chronic hemodialysis
patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 6:567–574. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Petersen JP, Ebbesen F, Hollegaard MV,
Andersson S, Hougaard DM, Thorlacius-Ussing O and Henriksen TB:
UGT1A1*28 genotypes and respiratory disease in very preterm
infants: A cohort study. Neonatology. 109:124–129. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
do Sameiro-Faria M, Kohlova M, Ribeiro S,
Rocha-Pereira P, Teixeira L, Nascimento H, Reis F, Miranda V,
Bronze-da-Rocha E, Quintanilha A, et al: Potential cardiovascular
risk protection of bilirubin in end-stage renal disease patients
under hemodialysis. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1752862014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Torrecilla Lodoso B, Atance Palomo E,
Grande Camarena C, Díaz Fernández MC, Llanillo Hierro L, De la Vega
Bueno A, Remacha Frauca E, Bartolo Muñoz G and Vega Jara P:
Crigler-Najjar syndrome: Diagnosis and treatment. An Pediatr
(Barc). 65:73–78. 2006.(In Spanish). View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ciotti M, Chen F, Rubaltelli FF and Owens
IS: Coding defect and a TATA box mutation at the bilirubin
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene cause Crigler-Najjar type I
disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1407:40–50. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Petit FM, Hébert M, Gajdos V, Capel L,
M'Rad R and Labrune P: Large deletion in UGT1A1 gene encompassing
the promoter and the exon 1 responsible for Crigler-Najjar type I
syndrome. Haematologica. 93:1590–1591. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ko JS, Chang JY, Moon JS, Yang HR and Seo
JK: Molecular analysis of the UGT1A1 gene in Korean patients with
Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol
Nutr. 17:37–40. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen K, Jin M, Zhu Y, Jiang Q, Yu W, Ma X
and Yao K: Genetic polymorphisms of the uridine diphosphate
glucuronosyltransferase 1A7 and colorectal cancer risk in relation
to cigarette smoking and alcohol drinking in a Chinese population.
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:1036–1041. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vogel A, Kneip S, Barut A, Ehmer U, Tukey
RH, Manns MP and Strassburg CP: Genetic link of hepatocellular
carcinoma with polymorphisms of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
UGT1A7 gene. Gastroenterology. 121:1136–1144. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zheng Z, Park JY, Guillemette C, Schantz
SP and Lazarus P: Tobacco carcinogen-detoxifying enzyme UGT1A7 and
its association with orolaryngeal cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst.
93:1411–1418. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Strassburg CP, Vogel A, Kneip S, Tukey RH
and Manns MP: Polymorphisms of the human
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A7 gene in colorectal cancer.
Gut. 50:851–856. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vogel A, Ockenga J, Ehmer U, Barut A,
Kramer FJ, Tukey RH, Manns MP and Strassburg CP: Polymorphisms of
the carcinogen detoxifying UDP-glucuronosyltransferase UGT1A7 in
proximal digestive tract cancer. Z Gastroenterol. 40:497–502. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huangfu H, Pan H, Wang B, Wen S, Han R and
Li L: Association between UGT1A1 polymorphism and risk of laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
13:E1122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maruo Y, Morioka Y, Fujito H, Nakahara S,
Yanagi T, Matsui K, Mori A, Sato H, Tukey RH and Takeuchi Y:
Bilirubin uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase variation is
a genetic basis of breast milk jaundice. J Pediatr. 165:36–41.e1.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang H, Wang Q, Zheng L, Zheng XB, Lin M,
Zhan XF and Yang LY: Clinical significance of UGT1A1 genetic
analysis in chinese neonates with severe hyperbilirubinemia.
Pediatr Neonatol. 57:310–317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Azlin I, Wong FL, Ezham M, Hafiza A and
Ainoon O: Prevalence of uridine glucuronosyl transferase 1A1
(UGT1A1) mutations in Malay neonates with severe jaundice. Malays J
Pathol. 33:95–100. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu Z, Zhu K, Wang L, Liu Y and Sun J:
Association of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia with UGT1A1 gene
polymorphisms: A meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit. 21:3104–3114. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ando Y, Saka H, Asai G, Sugiura S,
Shimokata K and Kamataki T: UGT1A1 genotypes and glucuronidation of
SN-38, the active metabolite of irinotecan. Ann Oncol. 9:845–847.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Iyer L, King CD, Whitington PF, Green MD,
Roy SK, Tephly TR, Coffman BL and Ratain MJ: Genetic predisposition
to the metabolism of irinotecan (CPT-11). Role of uridine
diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase isoform 1A1 in the
glucuronidation of its active metabolite (SN-38) in human liver
microsomes. J Clin Invest. 101:847–854. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Innocenti F, Undevia SD, Iyer L, Chen PX,
Das S, Kocherginsky M, Karrison T, Janisch L, Ramírez J, Rudin CM,
et al: Genetic variants in the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 gene
predict the risk of severe neutropenia of irinotecan. J Clin Oncol.
22:1382–1388. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lankisch TO, Schulz C, Zwingers T,
Erichsen TJ, Manns MP, Heinemann V and Strassburg CP: Gilbert's
syndrome and irinotecan toxicity: Combination with
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A7 variants increases risk. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:695–701. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jinno H, Tanaka-Kagawa T, Hanioka N, Saeki
M, Ishida S, Nishimura T, Ando M, Saito Y, Ozawa S and Sawada J:
Glucuronidation of 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin (SN-38), an
active metabolite of irinotecan (CPT-11), by human UGT1A1 variants,
G71R, P229Q, and Y486D. Drug Metab Dispos. 31:108–113. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wen F and Li Q: Treatment dilemmas of
cetuximab combined with chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 22:5332–5341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu C, Tang X, Qu Y, Keyoumu S, Zhou N and
Tang Y: UGT1A1 gene polymorphism is associated with toxicity and
clinical efficacy of irinotecan-based chemotherapy in patients with
advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 78:119–130.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pacheco PR, Brilhante MJ, Ballart C,
Sigalat F, Polena H, Cabral R, Branco CC and Mota-Vieira L: UGT1A1,
UGT1A6 and UGT1A7 genetic analysis: Repercussion for irinotecan
pharmacogenetics in the Sao Miguel Island population (Azores,
Portugal). Mol Diagn Ther. 13:261–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rotger M, Taffe P, Bleiber G, Gunthard HF,
Furrer H, Vernazza P, Drechsler H, Bernasconi E, Rickenbach M and
Telenti A: Swiss HIV Cohort Study: Gilbert syndrome and the
development of antiretroviral therapy-associated
hyperbilirubinemia. J Infect Dis. 192:1381–1386. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lankisch TO, Moebius U, Wehmeier M,
Behrens G, Manns MP, Schmidt RE and Strassburg CP: Gilbert's
disease and atazanavir: From phenotype to
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase haplotype. Hepatology. 44:1324–1332.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Romero-Lorca A, Novillo A, Gaibar M,
Bandrés F and Fernández-Santander A: Impacts of the glucuronidase
genotypes UGT1A4, UGT2B7, UGT2B15 and UGT2B17 on tamoxifen
metabolism in breast cancer patients. PLoS One. 10:e01322692015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sutiman N, Lim JS, Muerdter TE, Singh O,
Cheung YB, Ng RCH, Yap YS, Wong NS, Ang PCS, Dent R, et al:
Pharmacogenetics of UGT1A4, UGT2B7 and UGT2B15 and their influence
on tamoxifen disposition in asian breast cancer patients. Clin
Pharmacokinet. 55:1239–1250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Goey AK and Figg WD: UGT genotyping in
belinostat dosing. Pharmacol Res. 105:22–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Goey AK, Sissung TM, Peer CJ, Trepel JB,
Lee MJ, Tomita Y, Ehrlich S, Bryla C, Balasubramaniam S, Piekarz R,
et al: Effects of UGT1A1 genotype on the pharmacokinetics,
pharmacodynamics, and toxicities of belinostat administered by
48-hour continuous infusion in patients with cancer. J Clin
Pharmacol. 56:461–473. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Court MH, Freytsis M, Wang X, Peter I,
Guillemette C, Hazarika S, Duan SX, Greenblatt DJ and Lee WM: Acute
Liver Failure Study Group: The UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) 1A
polymorphism c.2042C>G (rs8330) is associated with increased
human liver acetaminophen glucuronidation, increased UGT1A exon
5a/5b splice variant mRNA ratio, and decreased risk of
unintentional acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 345:297–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kaplan M, Hammerman C and Maisels MJ:
Bilirubin genetics for the nongeneticist: Hereditary defects of
neonatal bilirubin conjugation. Pediatrics. 111:886–893. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jancova P, Anzenbacher P and
Anzenbacherova E: Phase II drug metabolizing enzymes. Biomed Pap
Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 154:103–116. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tourancheau A, Margaillan G, Rouleau M,
Gilbert I, Villeneuve L, Lévesque E, Droit A and Guillemette C:
Unravelling the transcriptomic landscape of the major phase II
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase drug metabolizing pathway using
targeted RNA sequencing. Pharmacogenomics J. 16:60–70. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Girard H, Lévesque E, Bellemare J,
Journault K, Caillier B and Guillemette C: Genetic diversity at the
UGT1 locus is amplified by a novel 3′ alternative splicing
mechanism leading to nine additional UGT1A proteins that act as
regulators of glucuronidation activity. Pharmacogenet Genomics.
17:1077–1089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Landrum MJ, Lee JM, Riley GR, Jang W,
Rubinstein WS, Church DM and Maglott DR: ClinVar: Public archive of
relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic
Acids Res. 42:(Database Issue). D980–D985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Beutler E, Gelbart T and Demina A: Racial
variability in the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 (UGT1A1) promoter:
A balanced polymorphism for regulation of bilirubin metabolism?
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:8170–8174. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sai K and Saito Y: Ethnic differences in
the metabolism, toxicology and efficacy of three anticancer drugs.
Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 7:967–988. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Canu G, Minucci A, Zuppi C and Capoluongo
E: Gilbert and Crigler Najjar syndromes: An update of the
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) gene mutation database.
Blood Cells Mol Dis. 50:273–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Memon N, Weinberger BI, Hegyi T and
Aleksunes LM: Inherited disorders of bilirubin clearance. Pediatr
Res. 79:378–386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Maisels MJ: Managing the jaundiced
newborn: A persistent challenge. CMAJ. 187:335–343. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Seco ML, del Río E, Barceló MJ, Remacha A,
Ginovart G, Moliner E and Baiget M: Interest in the study of
genetic variants of the promoter region of the UGT1A1 gene in
neonatal jaundice. An Esp Pediatr. 56:139–143. 2002.(In Spanish).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ramos-Leví AM, Bernabeu I, Sampedro-Núñez
M and Marazuela M: Genetic predictors of response to different
medical therapies in acromegaly. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci.
138:85–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Köhle C, Möhrle B, Münzel PA, Schwab M,
Wernet D, Badary OA and Bock KW: Frequent co-occurrence of the TATA
box mutation associated with Gilbert's syndrome (UGT1A1*28) with
other polymorphisms of the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase-1 locus
(UGT1A6*2 and UGT1A7*3) in Caucasians and Egyptians. Biochem
Pharmacol. 65:1521–1527. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bosma PJ: Inherited disorders of bilirubin
metabolism. J Hepatol. 38:107–117. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Rodrigues C, Vieira E, Santos R, de
Carvalho J, Santos-Silva A, Costa E and Bronze-da-Rocha E: Impact
of UGT1A1 gene variants on total bilirubin levels in Gilbert
syndrome patients and in healthy subjects. Blood Cells Mol Dis.
48:166–172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ciotti M, Werlin SL and Owens IS: Delayed
response to phenobarbital treatment of a Crigler-Najjar type II
patient with partially inactivating missense mutations in the
bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene. J Pediatr Gastroenterol
Nutr. 28:210–213. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Maruo Y, Nakahara S, Yanagi T, Nomura A,
Mimura Y, Matsui K, Sato H and Takeuchi Y: Genotype of UGT1A1 and
phenotype correlation between Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II and
Gilbert syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31:403–408. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bosma PJ, Chowdhury NR, Goldhoorn BG,
Hofker MH, Elferink Oude RP, Jansen PL and Chowdhury JR: Sequence
of exons and the flanking regions of human
bilirubin-UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene complex and
identification of a genetic mutation in a patient with
Crigler-Najjar syndrome, type I. Hepatology. 15:941–947. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bosma PJ, Goldhoorn B, Elferink Oude RP,
Sinaasappel M, Oostra BA and Jansen PL: A mutation in bilirubin
uridine 5′-diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase isoform 1 causing
Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II. Gastroenterology. 105:216–220.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Petit F, Gajdos V, Capel L, Parisot F,
Myara A, Francoual J and Labrune P: Crigler-Najjar type II syndrome
may result from several types and combinations of mutations in the
UGT1A1 gene. Clin Genet. 69:525–527. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Servedio V, d'Apolito M, Maiorano N,
Minuti B, Torricelli F, Ronchi F, Zancan L, Perrotta S, Vajro P,
Boschetto L and Iolascon A: Spectrum of UGT1A1 mutations in
Crigler-Najjar (CN) syndrome patients: Identification of twelve
novel alleles and genotype-phenotype correlation. Hum Mutat.
25:3252005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Fang JL and Lazarus P: Correlation between
the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT1A1) TATAA box polymorphism and
carcinogen detoxification phenotype: significantly decreased
glucuronidating activity against benzo(a)pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol(−)
in liver microsomes from subjects with the UGT1A1*28 variant.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 13:102–109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Thibaudeau J, Lépine J, Tojcic J, Duguay
Y, Pelletier G, Plante M, Brisson J, Têtu B, Jacob S, Perusse L, et
al: Characterization of common UGT1A8, UGT1A9, and UGT2B7 variants
with different capacities to inactivate mutagenic 4-hydroxylated
metabolites of estradiol and estrone. Cancer Res. 66:125–133. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Guillemette C, Bélanger A and Lépine J:
Metabolic inactivation of estrogens in breast tissue by
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase enzymes: An overview. Breast Cancer
Res. 6:246–254. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Eskandari-Nasab E, Hashemi M, Rezaei H,
Fazaeli A, Mashhadi MA, Moghaddam SS, Arbabi F, Jahantigh M and
Taheri M: Evaluation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 2B17 (UGT2B17)
and dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) genes deletion and the
expression level of NGX6 mRNA in breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep.
39:10531–10539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
McCarty MF: ‘Iatrogenic Gilbert
syndrome’-a strategy for reducing vascular and cancer risk by
increasing plasma unconjugated bilirubin. Med Hypotheses.
69:974–994. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wallner M, Marculescu R, Doberer D, Wolzt
M, Wagner O, Vitek L, Bulmer AC and Wagner KH: Protection from
age-related increase in lipid biomarkers and inflammation
contributes to cardiovascular protection in Gilbert's syndrome.
Clin Sci (Lond). 125:257–264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zucker SD, Horn PS and Sherman KE: Serum
bilirubin levels in the U.S. population: Gender effect and inverse
correlation with colorectal cancer. Hepatology. 40:827–835. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Glimelius B, Garmo H, Berglund A,
Fredriksson LA, Berglund M, Kohnke H, Byström P, Sørbye H and
Wadelius M: Prediction of irinotecan and 5-fluorouracil toxicity
and response in patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
Pharmacogenomics J. 11:61–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ushijima K, Kamura T, Tamura K, Kuzuya K,
Sugiyama T, Noda K and Ochiai K: Docetaxel/irinotecan combination
chemotherapy in platinum/taxane-refractory and -resistant ovarian
cancer: JGOG/WJGOG intergroup study. Int J Clin Oncol. 18:126–131.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Osawa K: Gene polymorphisms and
chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi.
12:837–840. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yang C, Liu Y, Xi WQ, Zhou CF, Jiang JL,
Ma T, Ye ZB, Zhang J and Zhu ZG: Relationship between UGT1A1*6/*28
polymorphisms and severe toxicities in Chinese patients with
pancreatic or biliary tract cancer treated with
irinotecan-containing regimens. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:3677–3683.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Phelip JM, Mineur L, De la Fouchardière C,
Chatelut E, Quesada JL, Roblin X, Pezet D, Mendoza C, Buc E and
Rivoire M: High resectability rate of initially unresectable
colorectal liver metastases after UGT1A1-adapted high-dose
irinotecan combined with LV5FU2 and cetuximab: A multicenter phase
II study (ERBIFORT). Ann Surg Oncol. 23:2161–2166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Chiorean EG, Sanghani S, Schiel MA, Yu M,
Burns M, Tong Y, Hinkle DT, Coleman N, Robb B, LeBlanc J, et al:
Phase II and gene expression analysis trial of neoadjuvant
capecitabine plus irinotecan followed by capecitabine-based
chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: Hoosier
oncology group GI03-53. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 70:25–32. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Whirl-Carrillo M, McDonagh EM, Hebert JM,
Gong L, Sangkuhl K, Thorn CF, Altman RB and Klein TE:
Pharmacogenomics knowledge for personalized medicine. Clin
Pharmacol Ther. 92:414–417. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lowenberg D, Thorn CF, Whirl-Carrillo M,
Ramirez J, Gong L, Marsh S, Schuetz EG, Dolan ME, Innocenti F,
McLeod HL and Ratain MJ: Irinotecan Pathway, Pharmacokinetics:
Pharmacogenomics Knowledge Base (PharmGKB) and Stanford University.
https://www.pharmgkb.org/pathway/PA2001December
19–2016
|
|
83
|
Marsh S and Hoskins JM: Irinotecan
pharmacogenomics. Pharmacogenomics. 11:1003–1010. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Satoh T, Ura T, Yamada Y, Yamazaki K,
Tsujinaka T, Munakata M, Nishina T, Okamura S, Esaki T, Sasak Y, et
al: Genotype-directed, dose-finding study of irinotecan in cancer
patients with UGT1A1*28 and/or UGT1A1*6 polymorphisms. Cancer Sci.
102:1868–1873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Atasilp C, Chansriwong P, Sirachainan E,
Reungwetwattana T, Chamnanphon M, Puangpetch A, Wongwaisayawan S
and Sukasem C: Correlation of UGT1A1(*)28 and (*)6 polymorphisms
with irinotecan-induced neutropenia in Thai colorectal cancer
patients. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 31:90–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Pichereau S, Le Louarn A, Lecomte T,
Blasco H, Le Guellec C and Bourgoin H: Cost-Effectiveness of
UGT1A1*28 genotyping in preventing severe neutropenia following
FOLFIRI therapy in colorectal cancer. J Pharm Pharm Sci.
13:615–625. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Paulík A, Grim J and Filip S: Predictors
of irinotecan toxicity and efficacy in treatment of metastatic
colorectal cancer. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 55:153–159. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Banerjee SS, Aher N, Patil R and Khandare
J: Poly(ethylene glycol)-prodrug conjugates: Concept, design, and
applications. J Drug Deliv. 2012:1039732012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Giustina A, Ambrosio MR, Peccoz Beck P,
Bogazzi F, Cannavo' S, De Marinis L, De Menis E, Grottoli S and
Pivonello R: Use of Pegvisomant in acromegaly. An Italian society
of endocrinology guideline. J Endocrinol Invest. 37:1017–1030.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Buchfelder M, Schlaffer S, Droste M, Mann
K, Saller B, Brübach K, Stalla GK and Strasburger CJ:
GermanPegvisomant Observational Study: The German ACROSTUDY: Past
and present. Eur J Endocrinol. 161 Suppl 1:S3–S10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Mallea-Gil MS, Bernabeu I, Spiraquis A,
Avangina A, Loidi L and Ballarino C: Pegvisomant-induced
cholestatic hepatitis in an acromegalic patient with UGT1A1 () 28
mutation. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2016:20871022016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Bernabeu I, Marazuela M, Lucas T, Loidi L,
Alvarez-Escolá C, Luque-Ramírez M, Fernandez-Rodriguez E, Paniagua
AE, Quinteiro C and Casanueva FF: Pegvisomant-induced liver injury
is related to the UGT1A1*28 polymorphism of Gilbert's syndrome. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 95:2147–2154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Filopanti M, Barbieri AM, Mantovani G,
Corbetta S, Gasco V, Ragonese M, Martini C, Bogazzi F, Colao A,
Ferone D, et al: Role of UGT1A1 and ADH gene polymorphisms in
pegvisomant-induced liver toxicity in acromegalic patients. Eur J
Endocrinol. 170:247–254. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Bernabeu I, Cameselle-Teijeiro J,
Casanueva FF and Marazuela M: Pegvisomant-induced cholestatic
hepatitis with jaundice in a patient with Gilbert's syndrome. Eur J
Endocrinol. 160:869–872. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Park WB, Choe PG, Song KH, Jeon JH, Park
SW, Kim HB, Kim NJ, Oh MD and Choe KW: Genetic factors influencing
severe atazanavir-associated hyperbilirubinemia in a population
with low UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1*28 allele frequency. Clin
Infect Dis. 51:101–106. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Choe PG, Park WB, Song JS, Kim NH, Song
KH, Park SW, Kim HB, Kim NJ and Oh MD: Incidence of
atazanavir-associated hyperbilirubinemia in Korean HIV patients: 30
months follow-up results in a population with low
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase1A1*28 allele frequency. J Korean Med
Sci. 25:1427–1430. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Sanchez-Dominguez CN, Gallardo-Blanco HL,
Rodriguez-Rodriguez AA, Vela-Gonzalez AV and Sanchez-Dominguez M:
Nanoparticles vs. cancer: A multifuncional tool. Curr Top Med Chem.
14:664–675. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|