Introduction
Kümmell disease is a delayed complication of
osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (VCF) and was first
described by Hermann Kümmell in 1895 (1,2). It is
routinely encountered in patients suffering from long-term
osteoporosis or following spinal injury (3). It may lead to back pain, spinal canal
stenosis or neurological deficits that negatively impact quality of
life and increase the risk of disability, morbidity and mortality
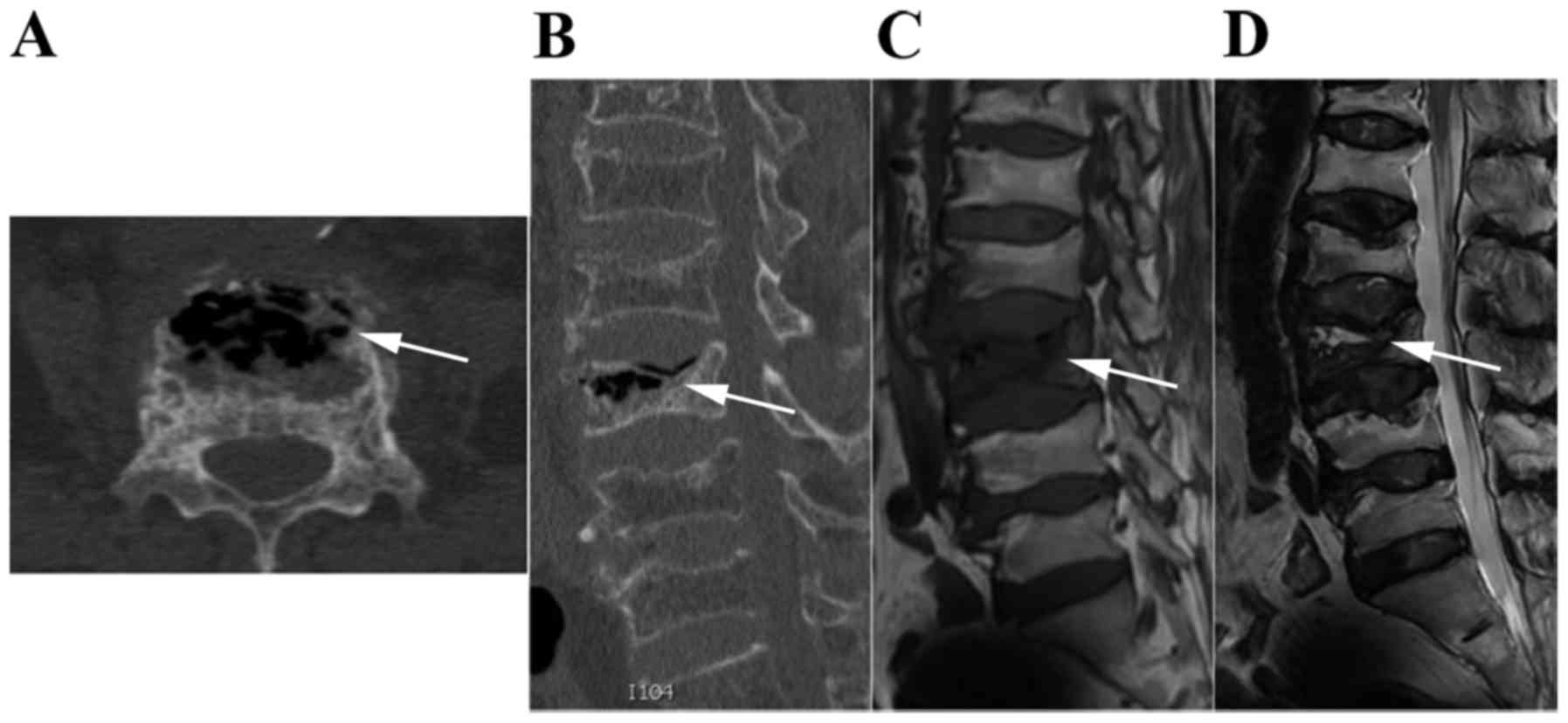
(4–6). The intravertebral cleft, formed through
osteonecrosis absorption, is an important radiographic feature in
diagnosing Kümmell disease (3). The
rapid development of advanced imaging technology has allowed for an
improved diagnosis of Kümmell disease (7).
Traditional surgical interventions may be the first
treatment choice for a majority of patients, as conservative
treatments, including analgesics and bed rest, exhibit little
benefit in pain relief (8). However,
shortcomings of open surgery, including major trauma and long
recovery times are concerns for patients (9). Minimally invasive treatment approaches
have become widely accepted by patients. Percutaneous kyphoplasty
(PKP) serves an important role in pain relief and vertebrae
strengthening in benign and malignant spinal lesions (10–12).
Compared with traditional open surgery, PKP results in decreased
wounds and allows for earlier mobilization, which is conducive to
faster recovery (10). PKP has been
used in the treatment of Kümmell disease since 2005 and substantial
work has been performed to evaluate its efficacy and safety
(13,14). However, to the best of the present
authors' knowledge, there are few studies evaluating long-term
follow-up (>2 years), including a study by Zhang et al
(15) with a follow-up time of 19.3
months. The association between cement injection volume and the
degree of pain relief in patients with Kümmell disease remains
unclear.
In the current study 50 patients with Kümmell
disease that were treated with PKP were enrolled and a 2-year
follow-up analysis was conducted. The aim of the present study was
to assess the efficacy and safety of PKP as treatment and to
explore the potential correlation between cement volume and pain
relief levels. The present study may be regarded as a reference for
facilitating pain relieve in the treatment of patients with Kümmell
disease.
Patients and methods
Patients
Between September 2012 and December 2014, 50
patients (female, 38; male, 12) diagnosed with Kümmell disease
underwent PKP treatment at the First Hospital of China Medical
University (Shenyang, China). Patients with neurological deficits,
history of spinal surgery, infection or tumor were excluded. All
patients provided written informed consent prior to surgery and the
current study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the
First Hospital of China Medical University (Shenyeng, China). A
total of 62 vertebral lesions were treated, including thoracic (T)8
(n=1), T9 (n=4), T10 (n=9), T11 (n=4), T12 (n=11), lumbar (L)1
(n=12), L2 (n=13), L3 (n=6) and L4 (n=2). A total of 41 patients
exhibited single lesions, 6 patients exhibited two lesions and 3
lesions were observed in 3 patients. Patients were aged between
56–85 years, with 69.00±7.17 years mean age. All patients suffered
from varying degrees of back pain and leg weakness for 1–12 months;
the mean duration of pain was 5.1±1.2 months. Patient demographics
are presented in Table I. A total of
35 patients had a history of trauma, whereas 15 patients had no
obvious inciting event. In all patients pain increased during
activity and eased at rest according to their pain reception. Some
patients (90%; 45/50) were treated conservatively with bed rest or
medical therapies with transient pain relief, but progressive pain
developed following an asymptomatic period (5–7 days). All patients
were diagnosed by X-ray, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic
resonance imaging (Fig. 1).
 | Table I.Clinical characteristics of patients
with Kümmell disease (n=50). |
Table I.
Clinical characteristics of patients
with Kümmell disease (n=50).
| Characteristics | Patients, n (%) |
|---|
| Age, years |
|
|
55–65 | 14 (28) |
|
66–75 | 24 (48) |
|
76–85 | 12 (24) |
| Gender |
|
| Male | 12 (24) |
|
Female | 38 (76) |
| Vertebral lesions
treated, n |
|
| 1 | 41 (82) |
| 2 | 6 (12) |
| 3 | 3 (6) |
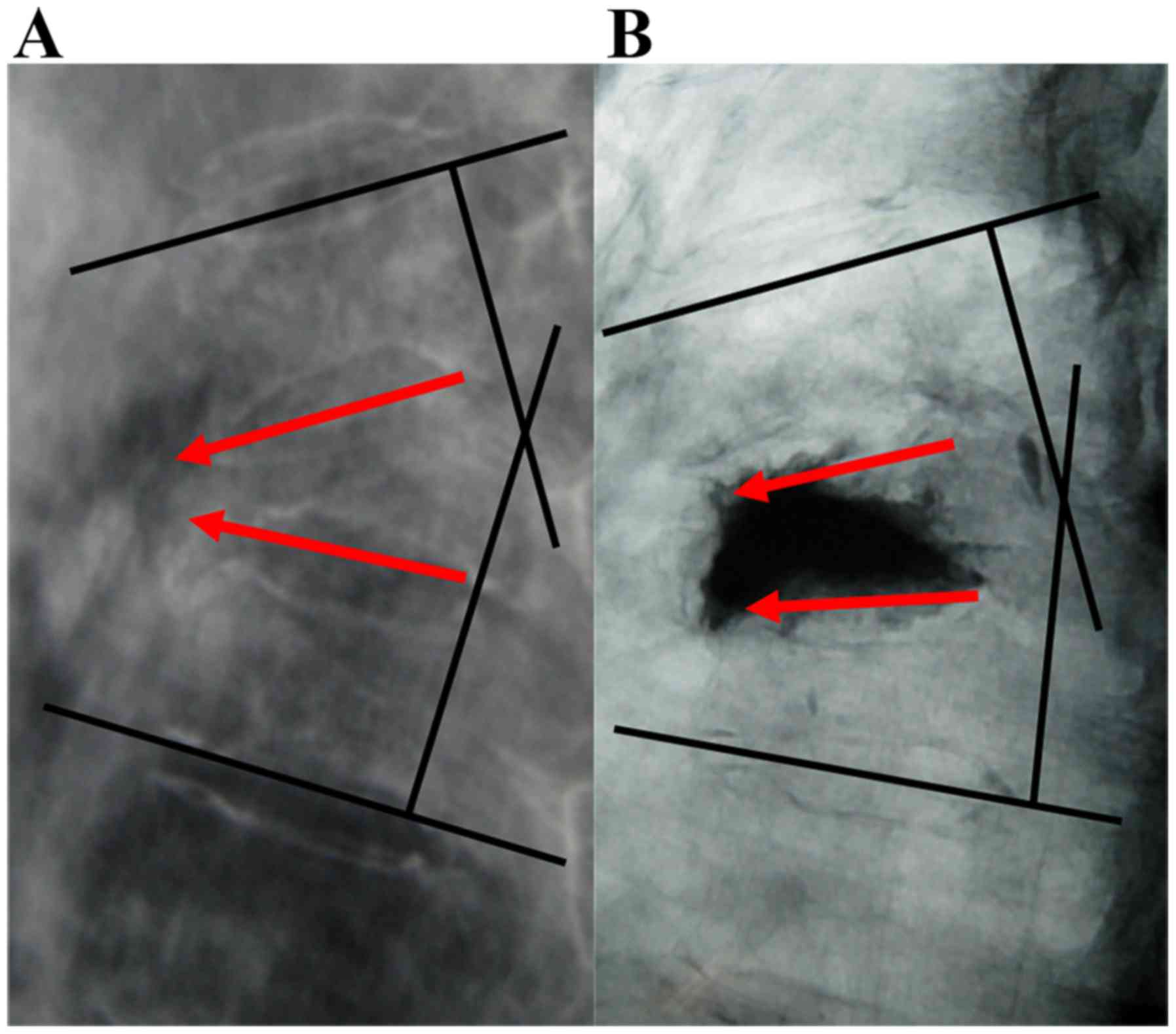
PKP procedure
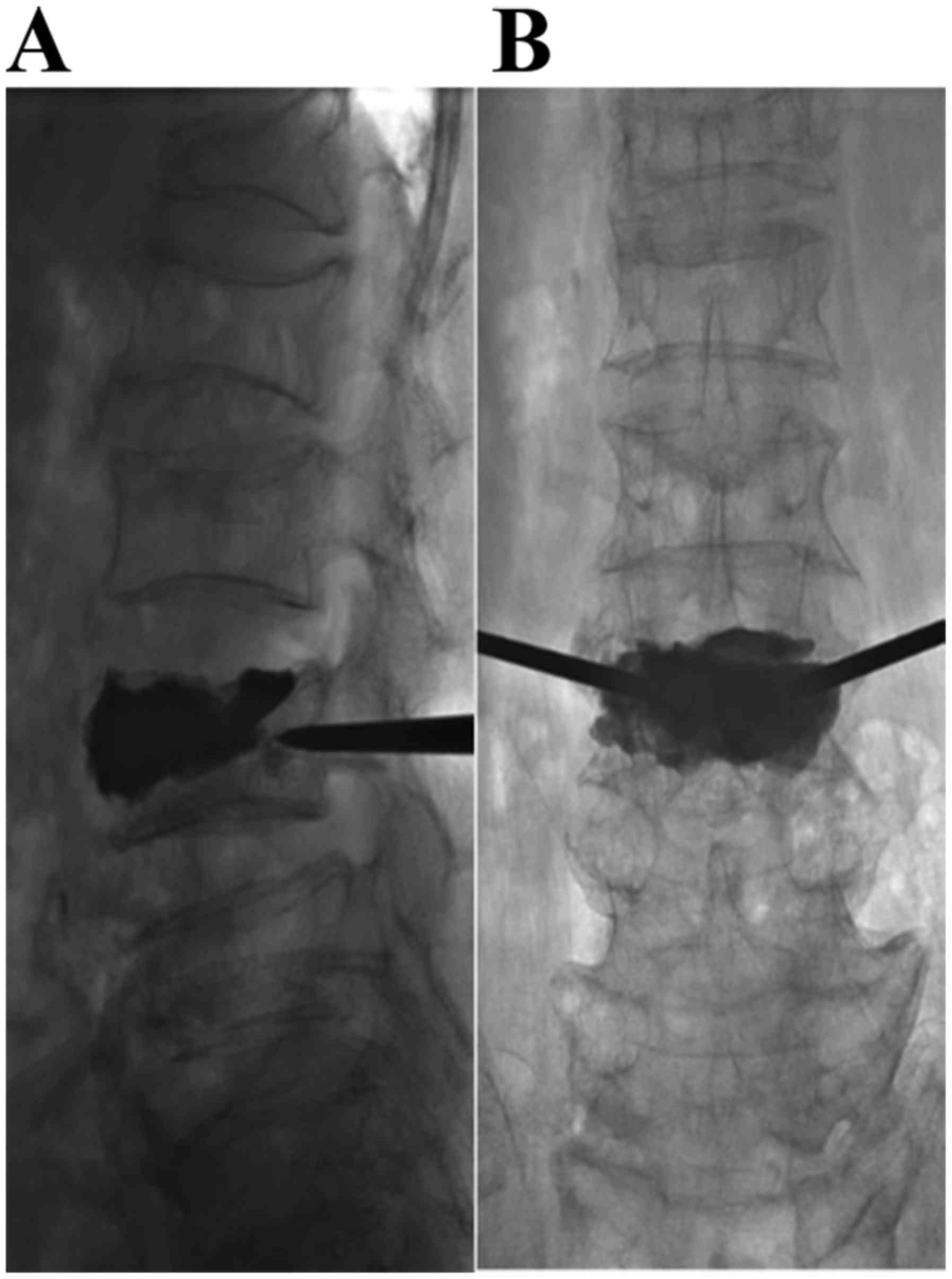
The PKP procedure was performed as previously
described (10). Under local
anesthesia, puncture needles were inserted bilaterally through the
pedicle of the vertebral arch under fluoroscopic guidance. Needles
penetrated into the vertebral body and at 1/3 of the distance from
the posterior wall, a 3-dimensional CT was recorded to monitor the
efficacy and safety of the puncture. Puncture needles further
continued to infix to the anterior. Subsequently, a balloon was
inserted into the vertebra to restore vertebral body height and to
create a cavity in the vertebra for the injection of cement. Next,
polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA; Heraeus Medical GmbH, Wehrheim,
Germany) and non-ionic contrast medium (Heraeus Medical GmbH) were
prepared at 26 g/10 ml and injected into the vertebra using a bone
cement injector under fluoroscopic monitoring (Fig. 2). Upon hardening of PMMA, the
injector was removed. Following the procedure, patients remained in
bed for ≥6 h and vital signs, neurological status, urine output and
sensory and motor function were monitored. Patients were
administered 250 ml mannitol (20%; Zhejiang Huakang Pharmaceutical
Co., Ltd., Huabu, China) and 80 mg solumedrol (Pfizer, Inc., New
York, NY, USA) once daily for 3 days following surgery to prevent
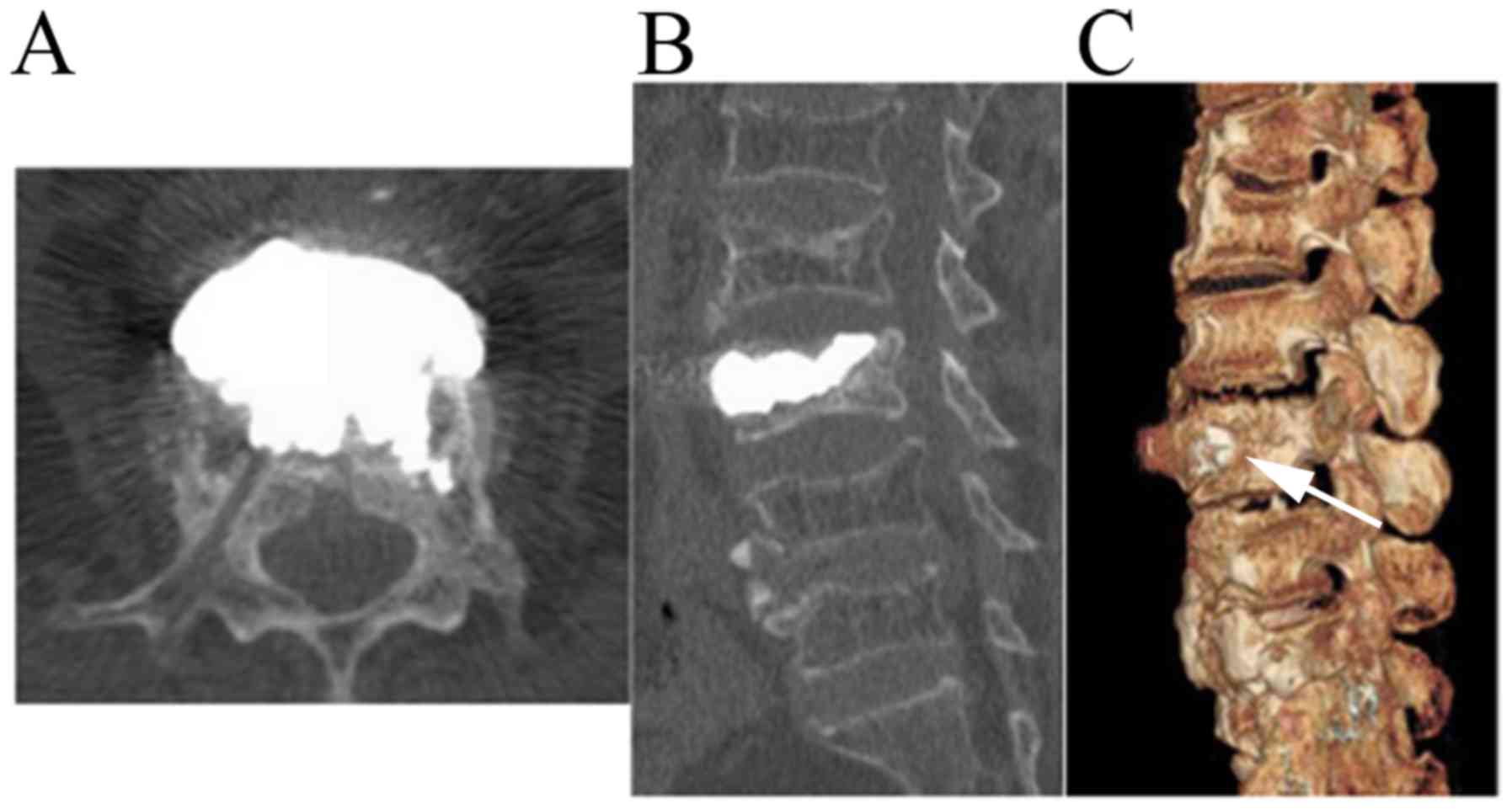
and treat spinal cord edema. Representative images are presented in
Fig. 3.
Efficacy and safety evaluation
To evaluate the efficacy of PKP treatment in
patients with Kümmell disease, the Visual Analog Scale (VAS; 0, no
pain; 10, worst pain) (10),
Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) (16), kyphotic angle (Cobb's angle),
anterior and posterior vertebral height and injected cement volume
were analyzed. VAS and ODI analyses were performed preoperatively
and 3 days, 3 months and 1 and 2 years following surgery via
outpatient review or telephone interview. Cobb's angle and anterior
and posterior vertebral height data were collected radiographically
preoperatively and at 3 months and 1 and 2 years following surgery.
PKP safety was assessed by evaluating for pre- and postoperative
complications, including cement leakage, spinal cord compression
and inflammation. Inflammation assessment was based on serum white
blood cells and inflammatory factors, including C-reactive
protein.
In addition, the correlation between injected volume
of cement and variation in VAS was evaluated. The variation of VAS
over the 2-year follow-up was defined as: δVAS=(VAS at 2-years
follow-up)-(VAS prior to surgery). Correlation between cement
injection volume and variation of VAS was assessed using Spearman
analysis (GraphPad Prism 5; GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA,
USA).
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as the mean ± standard
deviation. All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad
Prism 5 (GraphPad Software, Inc.). A comparison of preoperative and
postoperative continuous variables was performed using one-way
analysis of variance followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test.
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
Follow-up times for patients who
underwent PKP treatment
All PKP treatment procedures were successful.
Clinical assessments, including pain problem, physical ability
index and imaging, were conducted preoperatively and 3 days, 3
months, 1 year and 2 years following surgery via outpatient review
or telephone interview. All 50 patients were available for
follow-up during the 2-year period.
PKP improves VAS scores in patients
with Kümmell disease
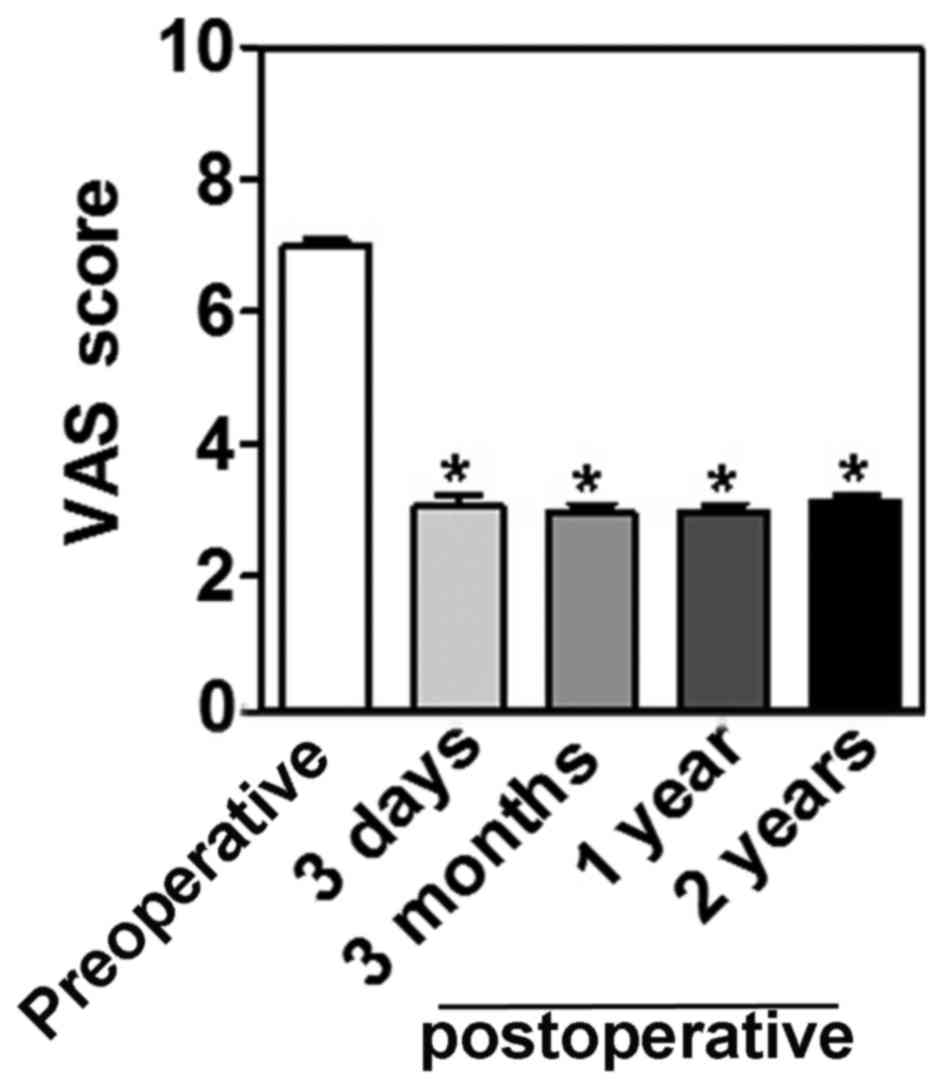
VAS was used to quantify the severity of pain. All
patients reported pain relief preoperatively and 3 days, 3 months,
1 year and 2 years following PKP. The preoperative VAS score was
7.00±0.78, which decreased significantly to 3.10±0.93 at 3 days
following surgery (P<0.05; Fig.
4). Following this initial decrease, VAS scores remained at a
stable level with 2.98±0.84, 2.98±0.77 and 3.14±0.67 at 3 months, 1
and 2 years following surgery, respectively (Fig. 4).
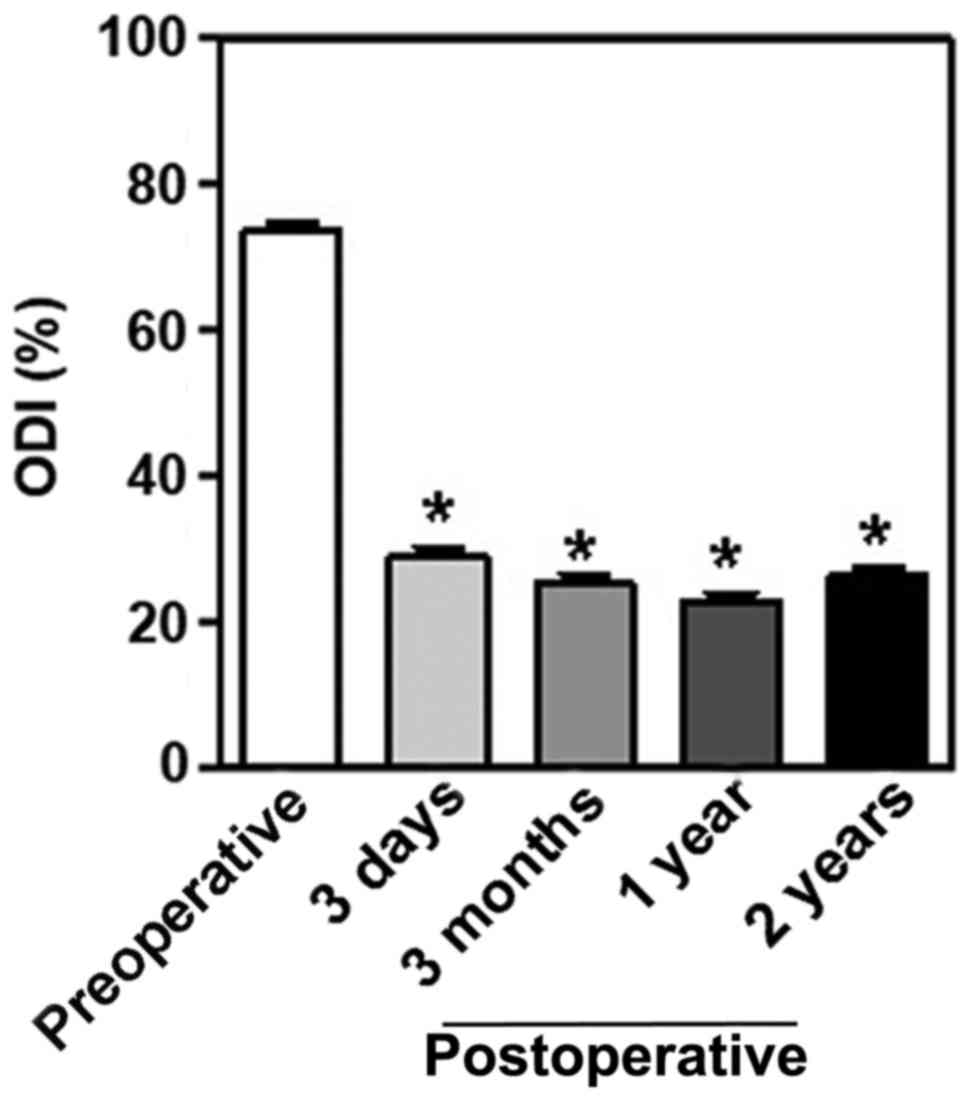
PKP improves ODI scores in patients
with Kümmell disease
General disability status was assessed by ODI. Over
the 2-year follow-up period, marked improvements in ODI were
observed following PKP treatment. ODI significantly decreased from
73.88±8.60 preoperatively to 29.2±8.98 at 3 days following surgery
(P<0.05) and remained at a similar level of 25.48±8.48
22.84±8.85 and 26.44±8.63 at 3 months and 1 and 2 years following
surgery, respectively (P<0.05 vs. preoperative; Fig. 5).
PKP positively affects the Cobb's
angle and vertebral heights in patients with Kümmell disease
The kyphotic angle has been defined as Cobb's angle
(10,17). In the current study, the preoperative
Cobb's angle in vertebral lesions significantly improved from
17.73±2.43 to 8.32±2.21° recorded at 3 months following surgery
based on lateral X-ray images (P<0.05; Fig. 6). Follow-up revealed that the Cobb's
angle still remained improved at the 1-year and 2-years checks with
9.55±2.82 and 10.27±3.22°, respectively (P<0.05 vs.
preoperative).
The anterior vertebral height exhibited a marked
increase following PKP. The anterior vertebral height was
14.25±2.64 mm prior to treatment and significantly increased to
18.03±2.77, 17.29±2.66 and 17.11±3.23 mm following PKP at 3 months,
1 and 2 years, respectively (all P<0.05). Unlike the marked
increase observed for the anterior vertebral height, the posterior
vertebral height exhibited no variations over the 2-year follow-up
period, with 20.23±1.89 mm preoperative and 21.04±1.55, 20.98±2.87
and 20.60±2.23 mm at 3 months, and 1 and 2 years following surgery,
respectively.
PKP is a safe treatment option for
patients with Kümmell disease
In 8 patients cement leakage was observed during PKP
surgery, including 3 paravertebral, 3 intradiscal and 2 intracanal
leakages. No neurological deficits were detected and no further
complications, including spinal cord compression, inflammation or
pulmonary embolism occurred following the 2-year follow-up.
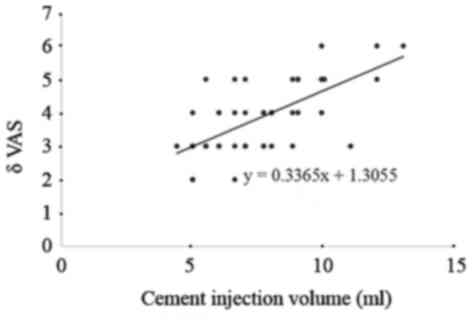
Cement injection volume is correlated
with pain relief
The mean injection volume of cement was 7.59±1.22 ml
(range, 4.40–13.00 ml). VAS scores ranged from 2.00–6.00
preoperatively Spearman analysis suggested that there was a
correlation between the volume of injected cement and VAS scores.
Correlation analysis revealed a correlation coefficient of R=0.67
(P<0.05; Fig. 7), indicating a
positive correlation between the injected cement volume and pain
relief effect. A larger amount of injected cement was correlated
with a greater improvement in VAS.
Discussion
The current study demonstrated that PKP may be an
effective treatment for patients with Kümmell disease. It resulted
in rapid pain relief, improvement in quality of life based on VAS
and ODI scores, correction of kyphosis and vertebral height
restoration with complications in 16% patients (8/50).
Postoperative follow-ups at 2 years revealed maintenance of pain
relief and improvement of disability. Additionally, it was
determined that bilateral puncture and injection of larger volumes
of bone cement, which completely filled all cracks, resulted in
improved pain relief.
In recent years, Kümmell disease has been diagnosed
with increasing frequency due to disease progression and
radiographic characteristics (1,2). The
traditional disease course may include minor trauma, an
asymptomatic period and the development of continuous
activity-associated pain (18). A
major factor causing pain in patients with Kümmell disease is
micro-movement of vertebral fractures (19). The elimination of micro-fractures and
stabilization of vertebral lesions results in the reduction of
severe pain (20–22). An intravertebral cleft provoked by
trauma is considered to be the most dominant feature in diagnosing
Kümmell disease and the incidence rate is 79% (6,7,9,23). As a
vertebral fracture occurs, gas enters the subchondral cleft and
forms a specific gas phenomenon emitting a lower intravertebral
signal visible in MR imaging (24).
In quick succession, extensive fluid accumulates in the cleft as
part of the process of avascular necrosis of the vertebral bodies
(25,26). The cleft may lead to vertebral
collapse and spinal canal stenosis, aggravating clinical symptoms
(1).
A multitude of treatment options for patients with
Kümmell disease exist, including conservative treatment (bed rest,
narcotic analgesics), surgical intervention and less invasive
interventional therapy, including nerve blockage. However,
conservative treatments exhibit minimal impact on pain relief for
symptoms attributed to intervertebral instability (27). Surgical intervention remains
challenging owing to comorbidities secondary to osteoporosis
(28). PKP is increasingly accepted
as an alterative treatment due to its minimally invasive nature and
early postoperative mobilization (29). In the current study, PKP effectively
stabilized collapsed vertebrae and strengthened intervertebral
stability resulting in clinical improvement of affected patients
with minimal complications.
Over the 2-year follow-up period, VAS scores had
significantly decreased following surgery. Maximal pain relief is
attributed to the stabilization of the spine, a key principle in
PKP (30). Lower levels of pain
improved the quality of life as evident from the significant
decrease in ODI scores following surgery. Radiographic data further
confirmed the effects of PKP on clinical outcomes. The kyphotic
angle decreased following surgery and the anterior vertebral height
improved over two years. Previous research indicated that the rate
of cement leakage associated to PKP was 25% (31), while in the current study cement
leakage occurred 16% patients. No severe neurological deterioration
was observed in patients experiencing cement leakage. Other
complications, including spinal cord compression, inflammation and
pulmonary embolism were not observed.
To the best of the authors' knowledge, the current
study, for the first time, identified a positive correlation
between the volume of bone cement and pain relief measured by VAS.
It is suggested that this was because a certain volume of bone
cement was needed to successfully fill fracture cracks.
Additionally, sufficient cement fused with vertebral lesions also
contributes to bear balanced stress, but too much cement can
increase the risk of leakage. Hence, the movement of cement during
surgery was tightly monitored to prevent leakage.
Although PKP was effective in the treatment of
patients with Kümmell disease, it also had exhibited limitations.
Patients with severe spinal cord compression, neurological deficits
or a history of spinal surgery were excluded from the current
study, as the goal of PKP was primarily to strengthen vertebrae
without aiming for neurological restoration. Additionally, the
current study included a limited sample size of 50 patients.
In summary, the present study indicated that PKP is
an effective treatment for patients with Kümmell disease by not
only relieving pain but also by contributing to restoring the
physiologic angle of the spine with only minor complications.
Additionally, a positive correlation between volume of injected
cement and the degree of pain relief was determined. The current
study may be used as a reference for cement dosing and associated
increased pain relieve in PKP treatment.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Chunbiao Li for
his help with the language editing of the manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during the present
study are included in this published article.
Authors' contributions
KX and BF designed the experiments. BF, YX and LZ
performed PKP treatments. GL and ZT conducted the follow-ups. FC
analyzed data and performed the statistical analysis. All authors
read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The current study was approved by the Institutional
Review Board in the First Hospital of China Medical University
(Shenyeng, China).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Kim YC, Kim YH and Ha KY: Pathomechanism
of intravertebral clefts in osteoporotic compression fractures of
the spine. Spine J. 14:659–666. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang G, Yang H and Chen K: Osteoporotic
vertebral compression fractures with an intravertebral cleft
treated by percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br.
92:1553–1557. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matzaroglou C, Georgiou CS, Panagopoulos
A, Assimakopoulos K, Wilke HJ, Habermann B, Panos G and Kafchitsas
K: Kümmell's disease: Clarifying the mechanisms and patients'
inclusion criteria. Open Orthop J. 8:288–297. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang X, Hu W, Yu J, Wang Z and Wang Y: An
effective treatment option for kümmell disease with neurological
deficits: Modified transpedicular subtraction and disc osteotomy
combined with long-segment fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
41:E923–E930. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ruan J, Gong X, Kong J, Wang H, Zheng X
and Chen T: Effect of B vitamin (folate, B6, and B12)
supplementation on osteoporotic fracture and bone turnover markers:
A meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit. 21:875–881. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen GD, Lu Q, Wang GL, Zou J, Yang HL,
Yang Y and Luo ZP: Percutaneous kyphoplasty for kümmell disease
with severe spinal canal stenosis. Pain Physician. 18:E1021–E1028.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ito Y, Hasegawa Y, Toda K and Nakahara S:
Pathogenesis and diagnosis of delayed vertebral collapse resulting
from osteoporotic spinal fracture. Spine J. 2:101–106. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang GQ, Gao YZ, Zheng J, Luo JP, Tang C,
Chen SL, Wang HQ, Liu K and Xie RG: Posterior decompression and
short segmental pedicle screw fixation combined with vertebroplasty
for Kummell's disease with neurological deficits. Exp Ther Med.
5:517–522. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu AM, Chi YL and Ni WF: Vertebral
compression fracture with intravertebral vacuum cleft sign:
Pathogenesis, image, and surgical intervention. Asian Spine J.
7:148–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen F, Xia YH, Cao WZ, Shan W, Gao Y,
Feng BO and Wang D: Percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of
spinal metastases. Oncol Lett. 11:1799–1806. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu CW, Hsieh MK, Chen LH, Niu CC, Fu TS,
Lai PL, Chen WJ, Chen WC and Lu ML: Percutaneous balloon
kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures.
BMC Surg. 14:32014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Gu YF, Sun ZK, Wu CG, Li YD, Wang W,
Chen YC and Lu J: Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty with
and without interventional tumour removal for malignant vertebral
compression fractures with symptoms of neurological compression.
Eur Radiol. 23:2754–2763. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chin DK, Kim YS, Cho YE and Shin JJ:
Efficacy of postural reduction in osteoporotic vertebral
compression fractures followed by percutaneous vertebroplasty.
Neurosurgery. 58:695–700. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang GL, Zhu XS and Gan MF: Balloon
kyphoplasty for osteoporotic kümmell disease. Bone. 47:s385–s485.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Fan Y, He X, Meng Y, Huang Y, Jia
S, Du J, Wu Q and Hao D: Is percutaneous kyphoplasty the better
choice for minimally invasive treatment of neurologically intact
osteoporotic Kümmell's disease? A comparison of two minimally
invasive procedures. Int Orthop. 42:1321–1326. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zou D, Zhang K and Ren Y: Therapeutic
effects of PKP on chronic painful osteoporotic vertebral
compression fractures with or without intravertebral cleft. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 8:15780–15786. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cobb J: Outline for the study of
scoliosis. AAOS Instr Course Lect. 5:261–275. 1948.
|
|
18
|
Kim DY, Lee SH, Jang JS, Chung SK and Lee
HY: Intravertrbral vacuum phenomenon in osteoporotic compression
fractures: Report of 67 cases with quantitative evaluation of
intravertebral instability. J Neurosurg (1 Suppl Spine).
100:S24–S31. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen L, Dong R, Gu Y and Feng Y:
Comparison between balloon kyphoplasty and short segmental fixation
combined with vertebroplasty in the treatment of Kummell's disease.
Pain Physician. 18:373–381. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang G, Yang H, Meng B, Zhu X, Zou J, Gan
M, Mei X, Chen K and Tang T: Post-traumatic osteoporotic vertebral
osteonecrosis treated using balloon kyphoplasty. J Clin Neurosci.
18:664–668. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barr JD, Barr MS, Lemley TJ and MaCann RM:
Percutaneous vertebroplasty for pain relief and spinal
stabilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:923–928. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu BS, Tang TS, Hu YC, Ni CF and Yang HL:
Vertebroplasty for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture.
Chin J Orthop. 22:738–742. 2002.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Matzaroglou C, Georgiou CS, Wilke HJ,
Assimakopoulos K, Karageorgos A, Konstantinou D, Velissaris D,
Panagiotopoulos E and Kafchitsas K: Kümmell's disease: Is ischemic
necrosis or vertebral ‘microcracking’ the first step in the
sequence? Med Hypotheses. 80:5052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oka M, Matsusako M, Kobayashi N, Uemura A
and Numaguchi Y: Intravertebral cleft sign on fat-suppressed
contrast-enhanced MR: Correlation with cement distribution pattern
on Percutaneous vertebroplasty. Acad Radiol. 12:992–999. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baur A, Stäbler A, Arbogast S, Duerr HR,
Bartl R and Reiser M: Acute osteoporotic and neoplastic vertebral
compression fractures: Fluid sign at MR imaging. Radiology.
225:730–735. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dupuy DE, Palmer WE and Rosenthal DI:
Vertebral fluid collection associated with vertebral collapse. AJR
Am J Roentgenol. 167:1535–1538. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakamae T, Fujimoto Y, Yamada K and
Matsuura M: The cause of delayed neruologic deficits following
osteoporotic vertebral pseudoarthrosis. Spine J. 14:97S2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cho Y: Corpectomy and circumferential
fusion for advanced thoracolumbar Kümmell's disease. Musculoskelet
Surg. 101:269–274. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang GQ, Gao YZ, Chen SL, Ding S, Gao K
and Wang HQ: Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty and
percutaneous kyphoplasty for the management of kümmell's disease: A
retrospective study. Indian J Orthop. 49:577–582. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu CW, Hsieh MK, Chen LH, Niu CC, Fu TS,
Lai PL, Chen WJ, Chen WC and Lu ML: Percutaneous balloon
kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures.
BMC Surg. 14:32014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang GL, Yang HL and Meng B: Kyphoplasty
for osteoporotic kummell's disease. Chin J Spine Spinal Cord.
21:46–49. 2011.
|