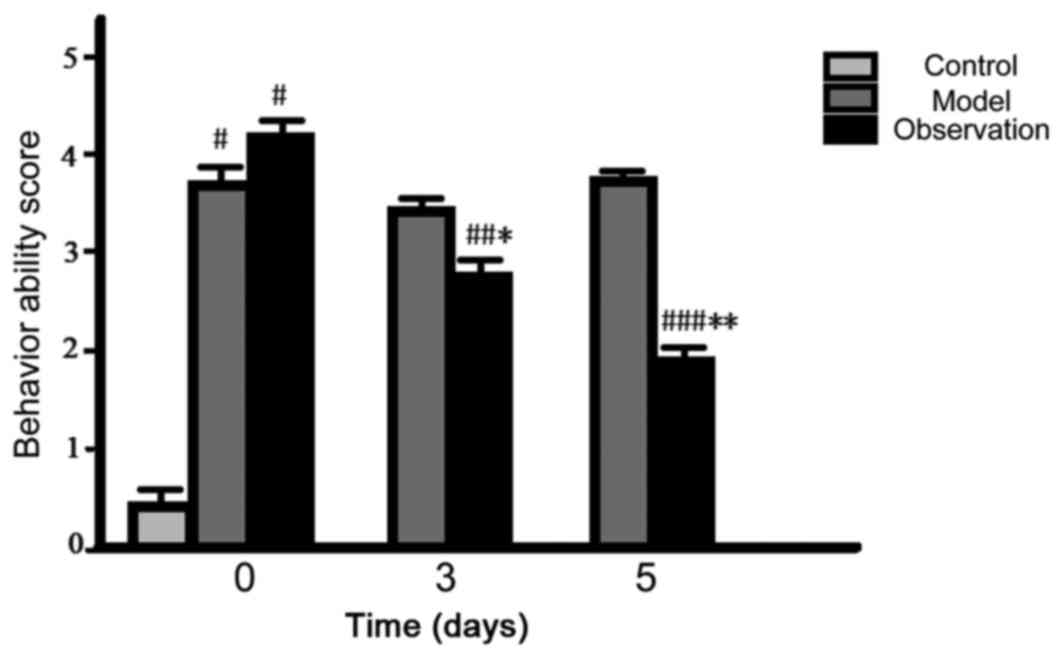
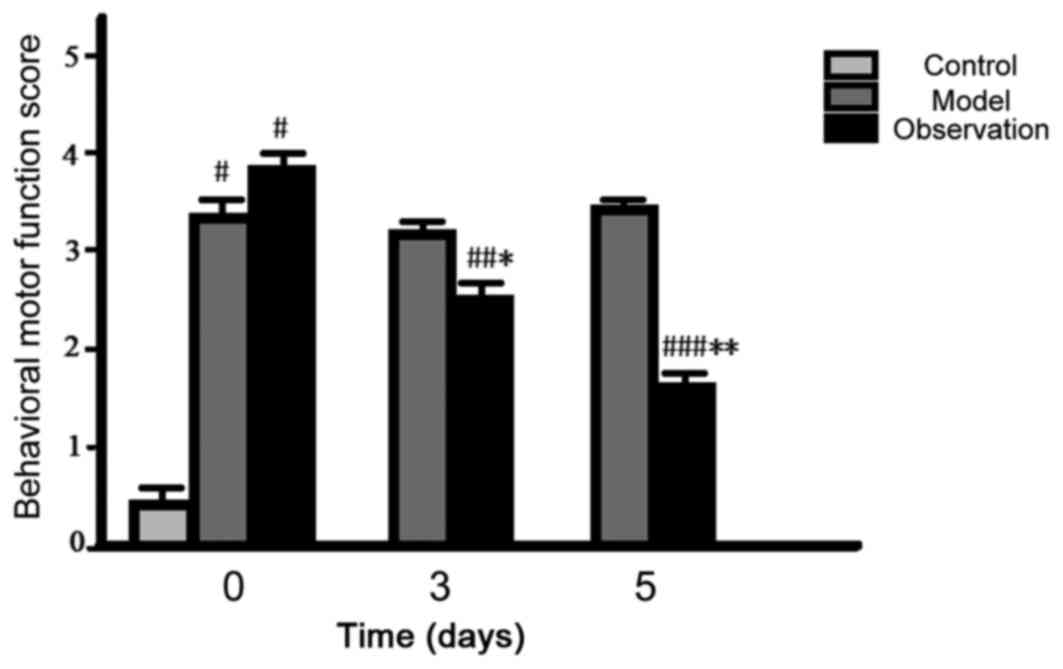
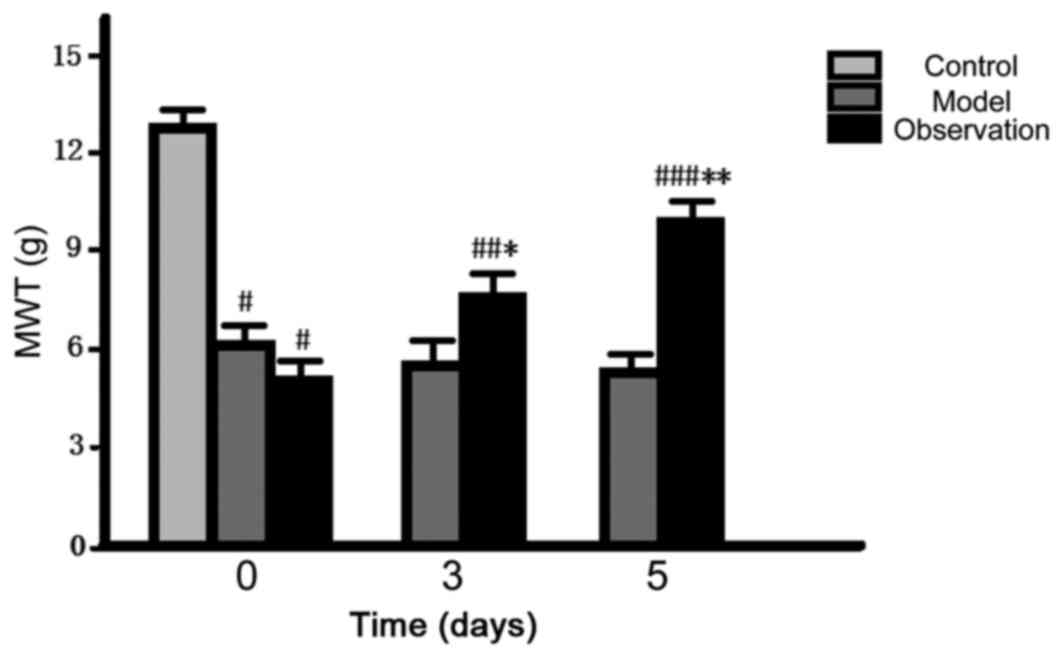
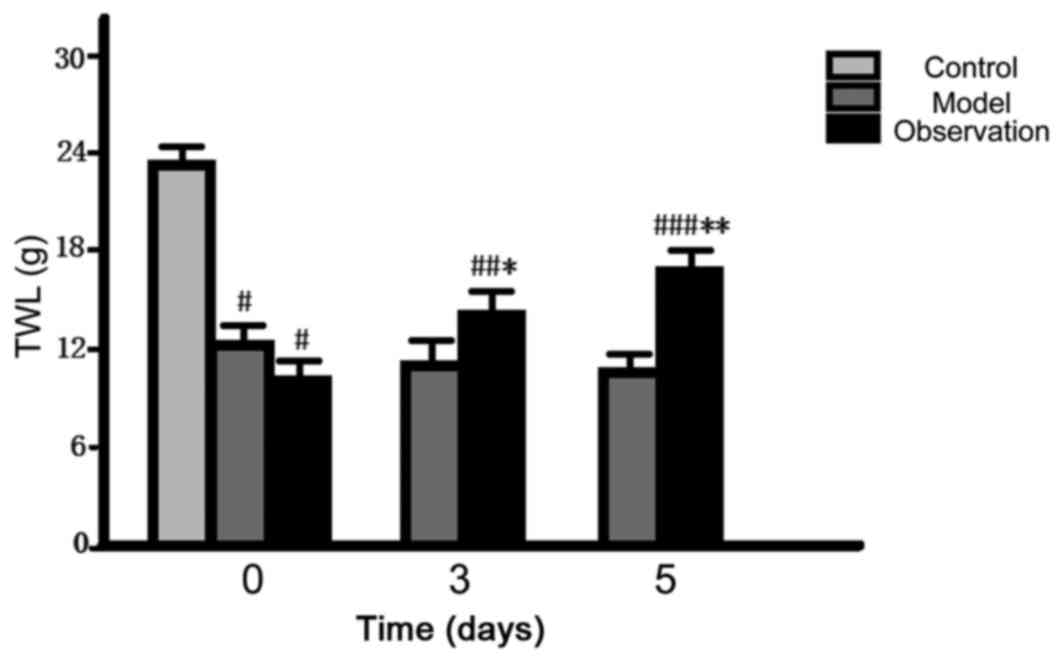
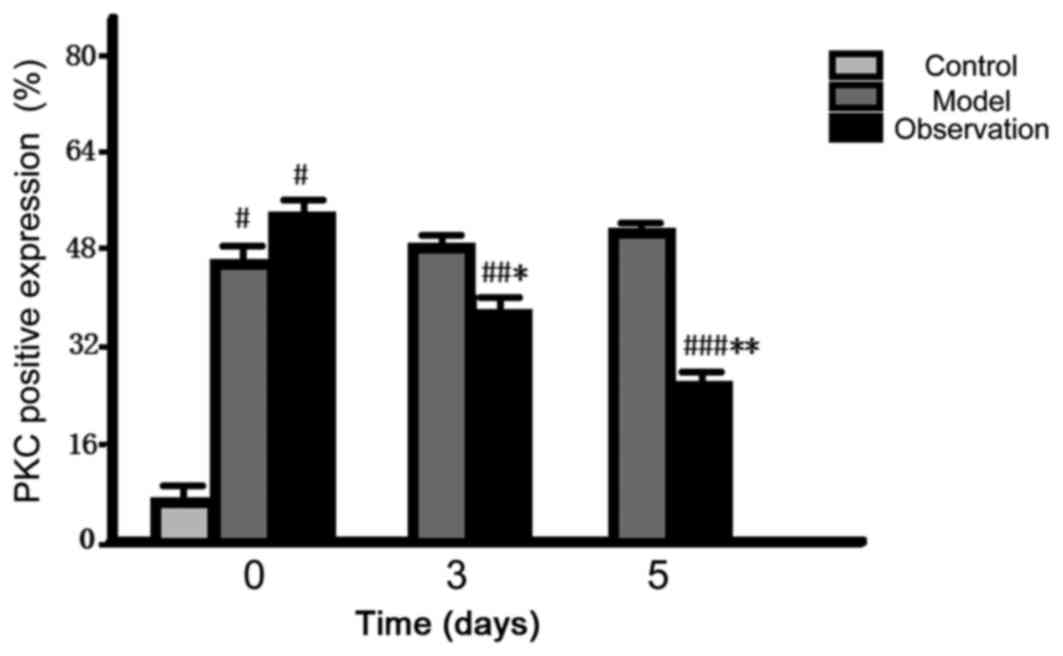
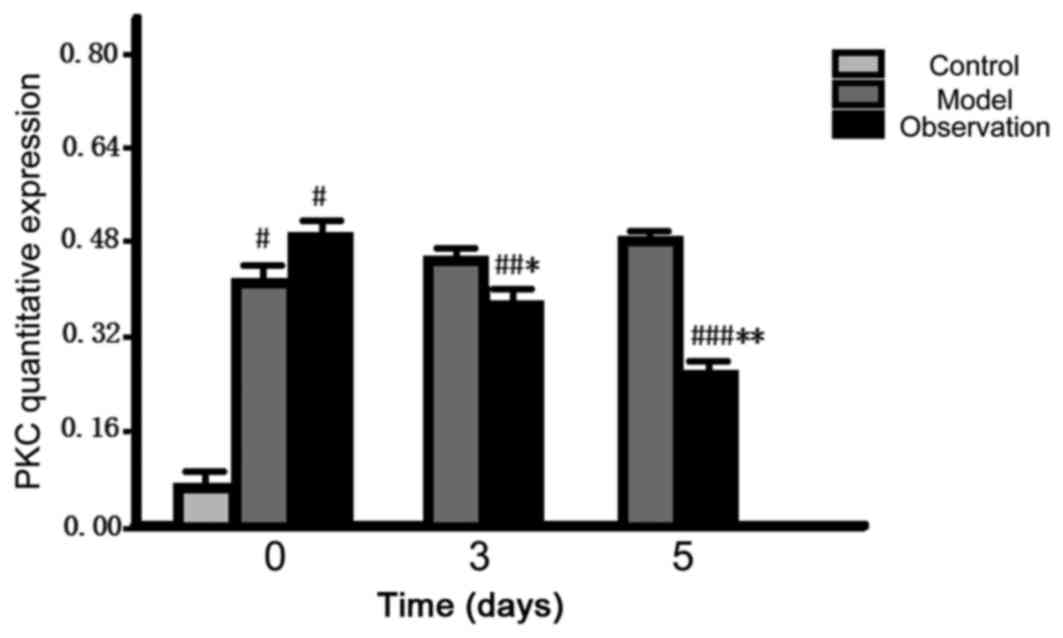
|
1
|
Ritter DM, Ho C, O'Leary ME and
Covarrubias M: Modulation of Kv3.4 channel N-type inactivation by
protein kinase C shapes the action potential in dorsal root
ganglion neurons. J Physiol. 590:145–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yan X, Yadav R, Gao M and Weng HR:
Interleukin-1beta enhances endocytosis of glial glutamate
transporters in the spinal dorsal horn through activating protein
kinase C. Glia. 62:1093–1109. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Garrity AG, Botta S, Lazar SB, Swor E,
Vanini G, Baghdoyan HA and Lydic R: Dexmedetomidine-induced
sedation does not mimic the neurobehavioral phenotypes of sleep in
sprague dawley rat. Sleep. 38:73–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Funai Y, Pickering AE, Uta D, Nishikawa K,
Mori T, Asada A, Imoto K and Furue H: Systemic dexmedetomidine
augments inhibitory synaptic transmission in the superficial dorsal
horn through activation of descending noradrenergic control: An in
vivo patch-clamp analysis of analgesic mechanisms. Pain.
155:617–628. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu B, Zhang WS, Yang JL, Xu H, Deng XM and
Zhang YQ: Dexmedetomidine blocks thermal hyperalgesia and spinal
glial activation in rat model of monoarthritis. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
31:523–530. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hwang W, Lee J, Park J and Joo J:
Dexmedetomidine versus remifentanil in postoperative pain control
after spinal surgery: A randomized controlled study. BMC
Anesthesiol. 15:212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Velázquez KT, Mohammad H and Sweitzer SM:
Protein kinase C in pain: Involvement of multiple isoforms.
Pharmacol Res. 55:578–589. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bu F, Tian H, Gong S, Zhu Q, Xu GY, Tao J
and Jiang X: Phosphorylation of NR2B NMDA subunits by protein
kinase C in arcuate nucleus contributes to inflammatory pain in
rats. Sci Rep. 5:159452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim JYV, Tillu DV, Quinn TL, Mejia GL, Shy
A, Asiedu MNK, Murad E, Schumann AP, Totsch SK, Sorge RE, et al:
Spinal dopaminergic projections control the transition to
pathological pain plasticity via a D1/D5-mediated mechanism. J
Neurosci. 35:6307–6317. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mo G, Grant R, O'Donnell D, Ragsdale DS,
Cao CQ and Séguéla P: Neuropathic Nav1.3-mediated sensitization to
P2X activation is regulated by protein kinase C. Mol Pain.
7:142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Melemedjian OK, Tillu DV, Asiedu MN,
Mandell EK, Moy JK, Blute VM, Taylor CJ, Ghosh S and Price TJ: BDNF
regulates atypical PKC at spinal synapses to initiate and maintain
a centralizedchronic pain state. Mol Pain. 9:122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu X, Hang LH, Wang H, Shao DH, Xu YG, Cui
W and Chen Z: Intranasally administered adjunctive dexmedetomidine
reduces perioperative anesthetic requirements in general
anesthesia. Yonsei Med J. 57:998–1005. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
You HJ, Lei J, Xiao Y, Ye G, Sun ZH, Yang
L and Niu N: Pre-emptive analgesia and its supraspinal mechanisms:
Enhanced descending inhibition and decreased descending
facilitation by dexmedetomidine. J Physiol. 594:1875–1890. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ni J, Wei J, Yao Y, Jiang X, Luo L and Luo
D: Effect of dexmedetomidine on preventing postoperative agitation
in children: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 10:e01284502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eskandr A and Maseeh SA: The effect of
dexmedetomidine on lumbar epidural injection for failed back
surgery syndrome. Anesthesiol Res Pract.
2016:71980482016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iirola T, Aantaa R, Laitio R, Kentala E,
Lahtinen M, Wighton A, Garratt C, Ahtola-Sätilä T and Olkkola:
Pharmacokinetics of prolonged infusion of high-dose dexmedetomidine
in critically ill patients. Crit Care. 15:R2572011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|