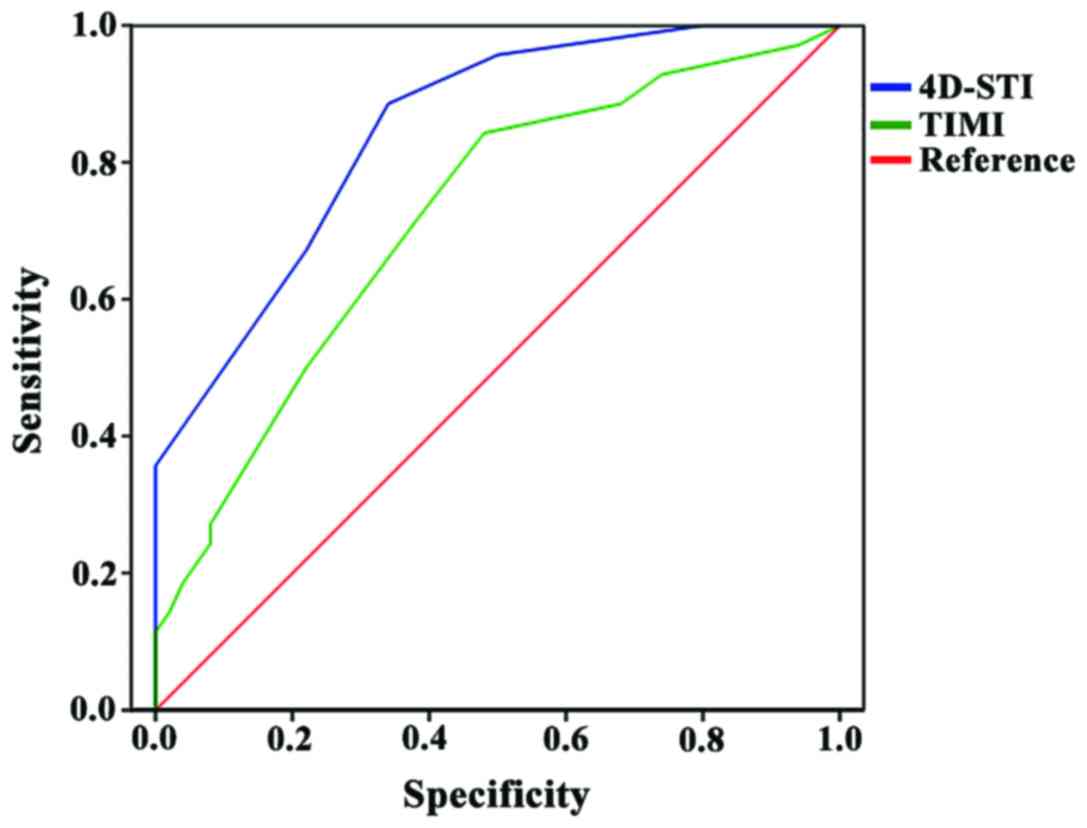
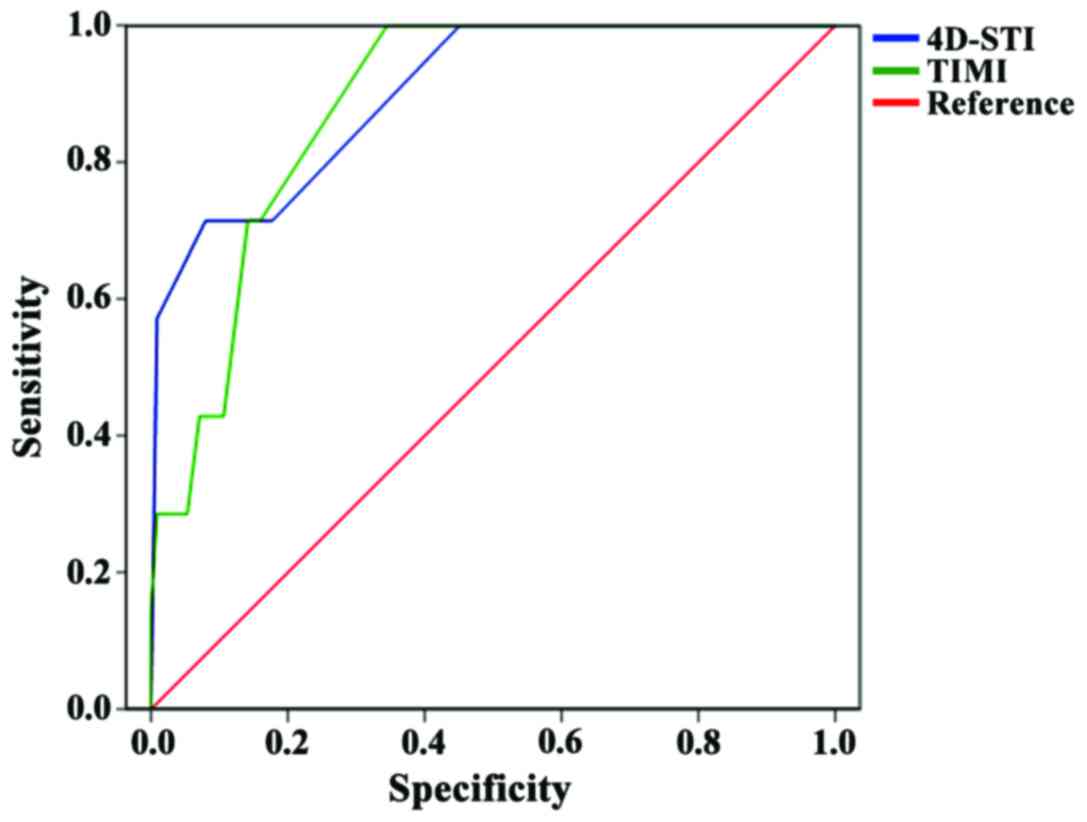
|
1
|
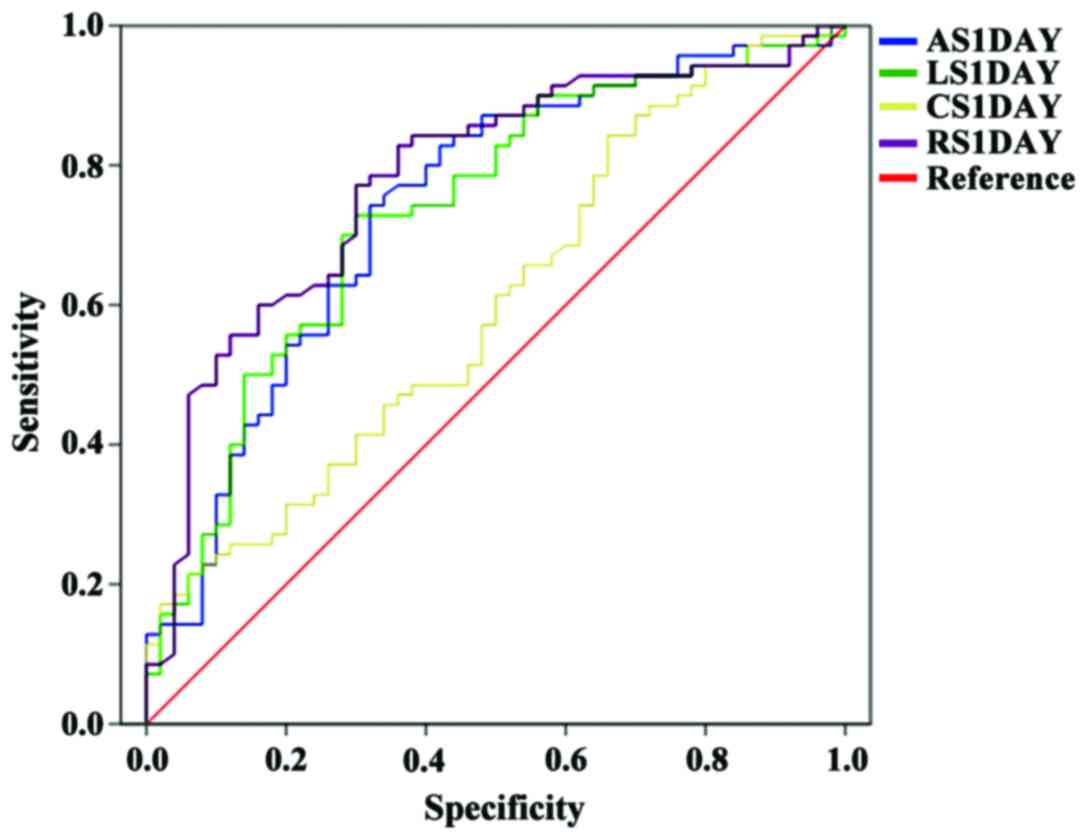
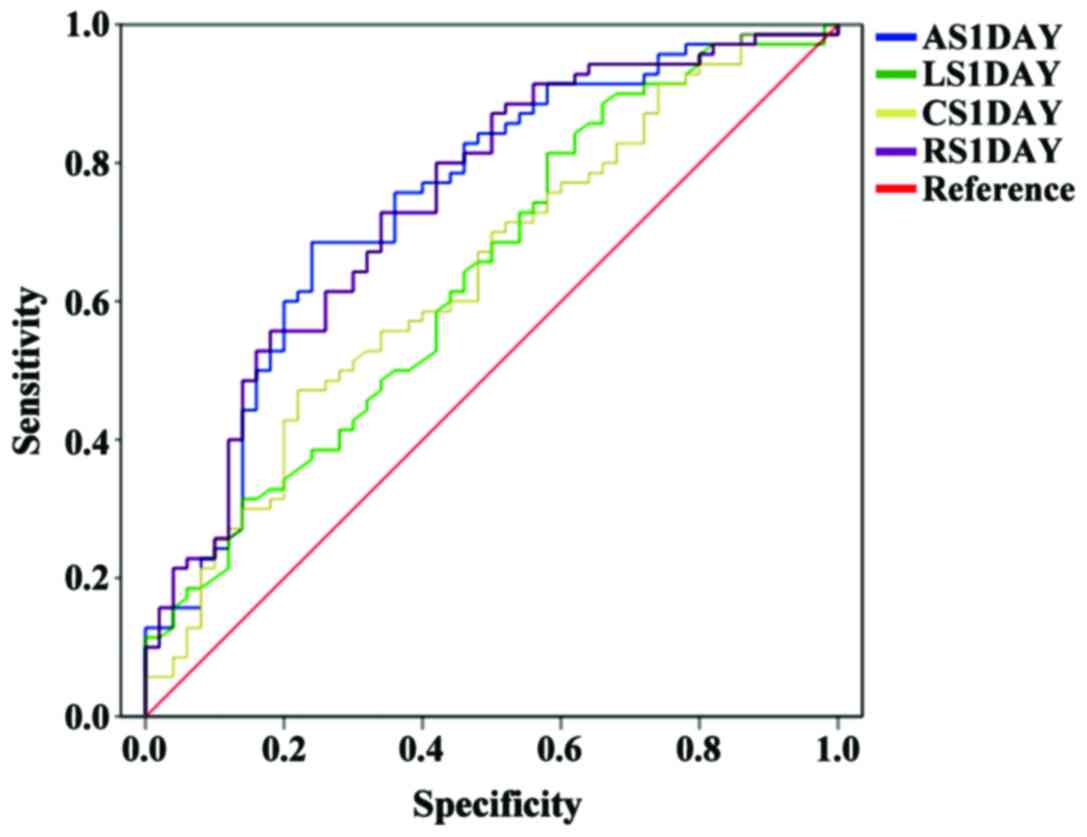
Abbasnezhad M, Soleimanpour H, Sasaie M,
Golzari SE, Safari S, Soleimanpour M and Esfanjani Mehdizadeh R:
Comparison of prediction between TIMI (thrombolysis in myocardial
infarction) risk score and modified TIMI risk score in discharged
patients from Emergency Department with atypical chest pain. Iran
Red Crescent Med J. 16:e139382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Correia LCL, Garcia G, Kalil F, Ferreira
F, Carvalhal M, Oliveira R, Silva A, Vasconcelos I, Henri C and
Noya-Rabelo M: Prognostic value of TIMI score versus GRACE score in
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Arq Bras Cardiol.
103:98–106. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yeh YT, Liu CW, Li AH, Ke SR, Liu YH, Chen
KC, Liao PC and Wu YW: Rapid early triage by Leukocytosis and the
thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) risk score for
ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous
coronary intervention: An observational study. Medicine
(Baltimore). 95:e28572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Worner F, Cequier A, Bardají A, Bodí V,
Bover R, Martínez-Sellés M, Sabaté M, Sionis A, de Prada Vázquez
JA, Arós F, et al: Spanish Society of Cardiology Working Group on
the Clinical Practice Guidelines for ST-Elevation Acute Coronary
Syndrome; Group of Expert Reviewers for the Clinical Practice
Guidelines for ST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome; Spanish
Society of Cardiology Clinical Practice Guidelines Committee:
Comments on the ESC guidelines for the management of acute
myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment
elevation. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 66:5–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng TO and Zhao D: Current practice on
the management of acute coronary syndrome in China. Int J Cardiol.
169:1–6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Karabinos I, Grassos C, Kostaki P and
Kranidis A: Echocardiography in the evaluation of a hypertensive
patient: An invaluable tool or simply following the routine?
Hellenic J Cardiol. 54:47–57. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Na JP, Shin KC, Kim S, Park YS, Chung SP,
Park IC, Park JM and Kim MJ: Performance of reperfusion therapy and
hospital mortality in ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients
with non-chest pain complaints. Yonsei Med J. 55:617–624. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Singh V and Cohen MG: Therapy in
ST-elevation myocardial infarction: Reperfusion strategies,
pharmacology and stent selection. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc
Med. 16:3022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
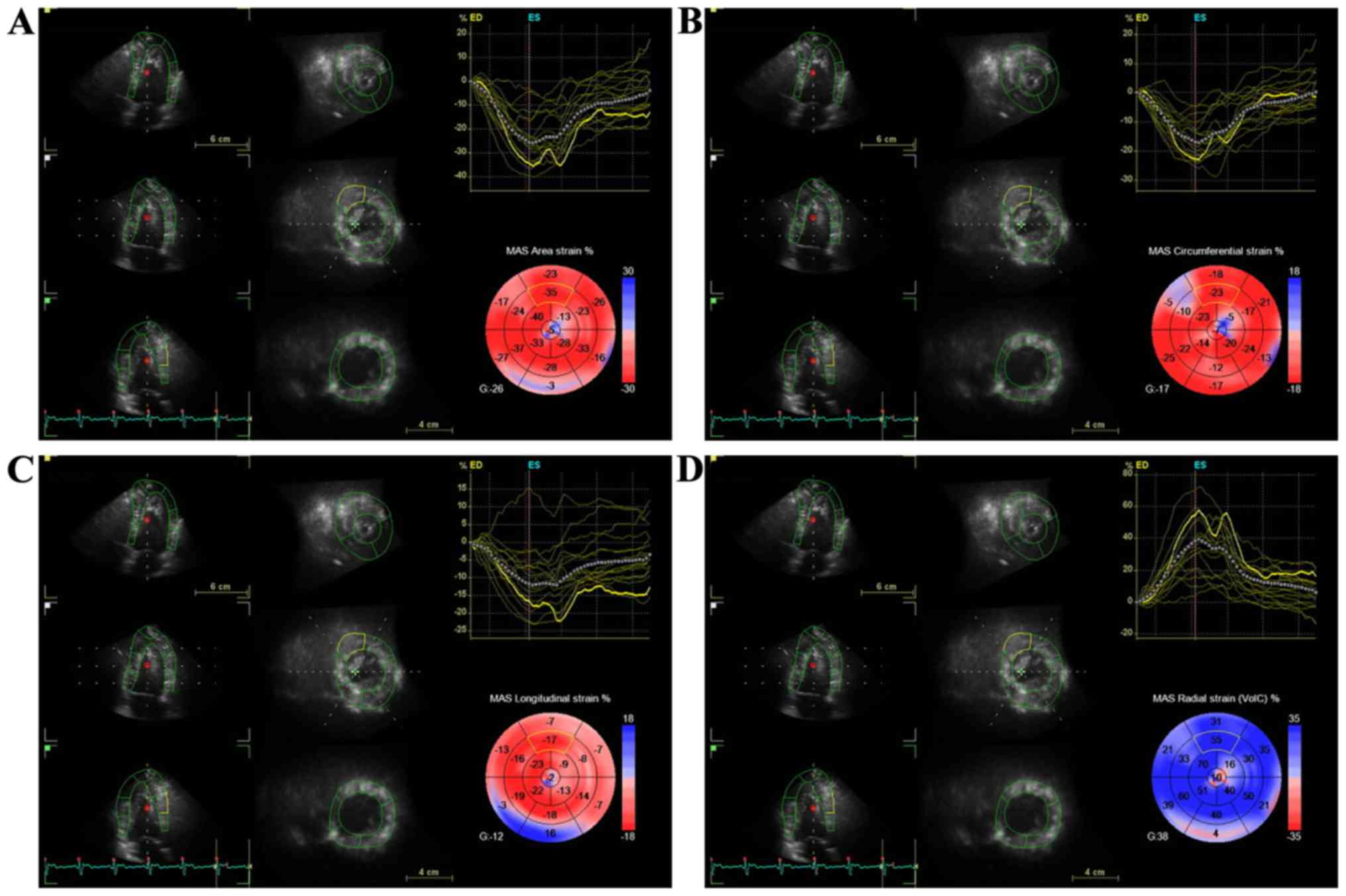
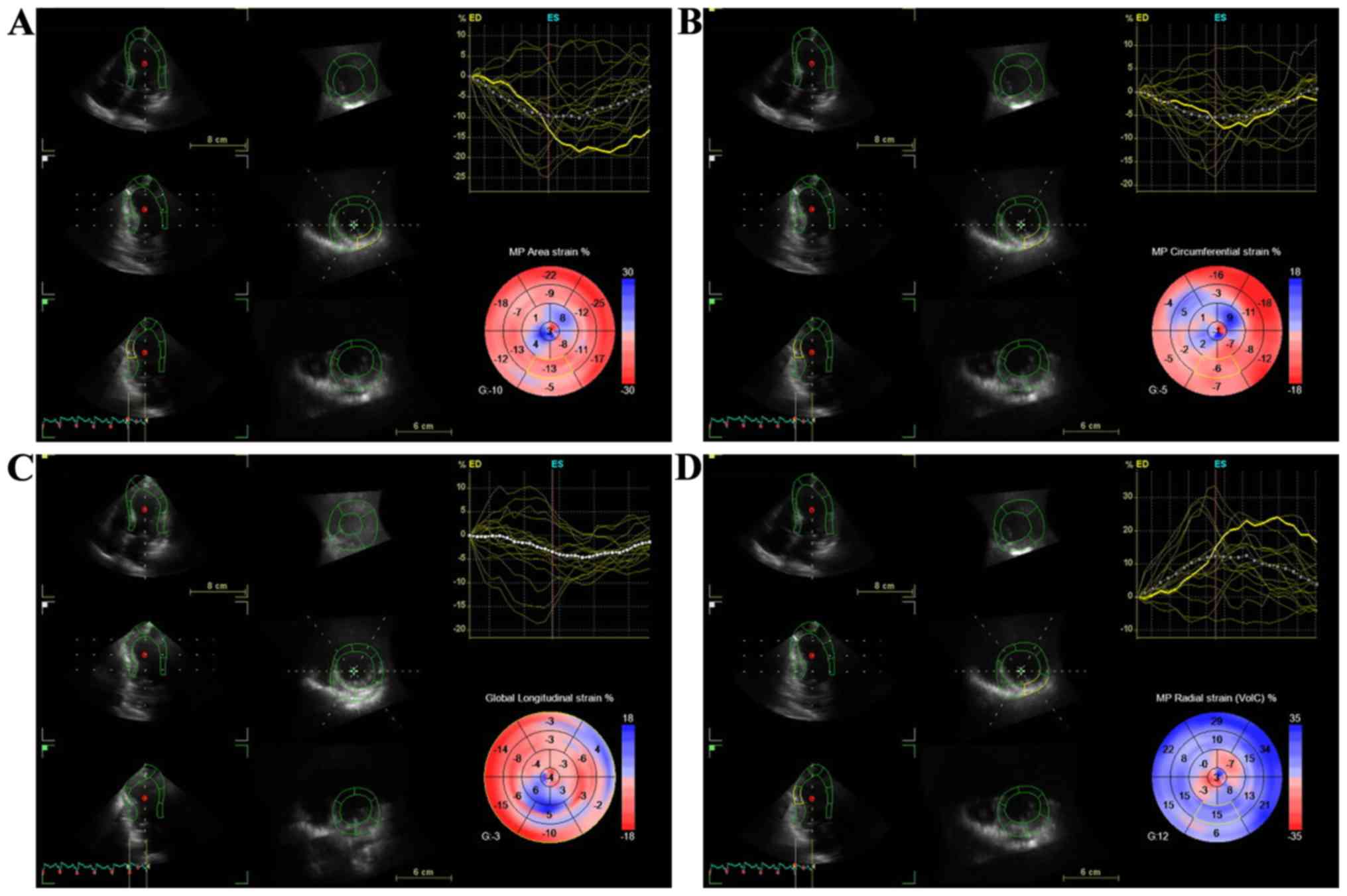
Szymczyk E, Lipiec P, Michalski B,
Szymczyk K, Shim A, Woźniakowski B, Rotkiewicz A, Stefańczyk L and
Kasprzak JD: 2D speckle tracking echocardiography for the
assessment of regional contractile reserve after myocardial
infarction. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 17:374–381. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abduch MC, Alencar AM, Mathias W Jr and
Vieira ML: Cardiac mechanics evaluated by speckle tracking
echocardiography. Arq Bras Cardiol. 102:403–412. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reant P, Barbot L, Touche C, Dijos M,
Arsac F, Pillois X, Landelle M, Roudaut R and Lafitte S: Evaluation
of global left ventricular systolic function using
three-dimensional echocardiography speckle-tracking strain
parameters. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 25:68–79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kilickesmez Orta K, Baydar O, Bostan C,
Coskun U and Kucukoglu S: Four-dimensional speckle tracking
echocardiography in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Echocardiography. 32:1547–1553. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Smith BC, Dobson G, Dawson D,
Charalampopoulos A, Grapsa J and Nihoyannopoulos P:
Three-dimensional speckle tracking of the right ventricle: Toward
optimal quantification of right ventricular dysfunction in
pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 64:41–51. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Popovic B, Girerd N, Rossignol P, Agrinier
N, Camenzind E, Fay R, Pitt B and Zannad F: Prognostic value of the
thrombolysis in myocardial infarction risk score in ST-elevation
myocardial infarction patients with left ventricular dysfunction
(from the EPHESUS Trial). Am J Cardiol. 118:1442–1447. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feder SL, Schulman-Green D, Geda M,
Williams K, Dodson JA, Nanna MG, Allore HG, Murphy TE, Tinetti ME,
Gill TM, et al: Physicians' perceptions of the thrombolysis in
myocardial infarction (TIMI) risk score in older adults with acute
myocardial infarction. Heart Lung. 44:376–381. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|