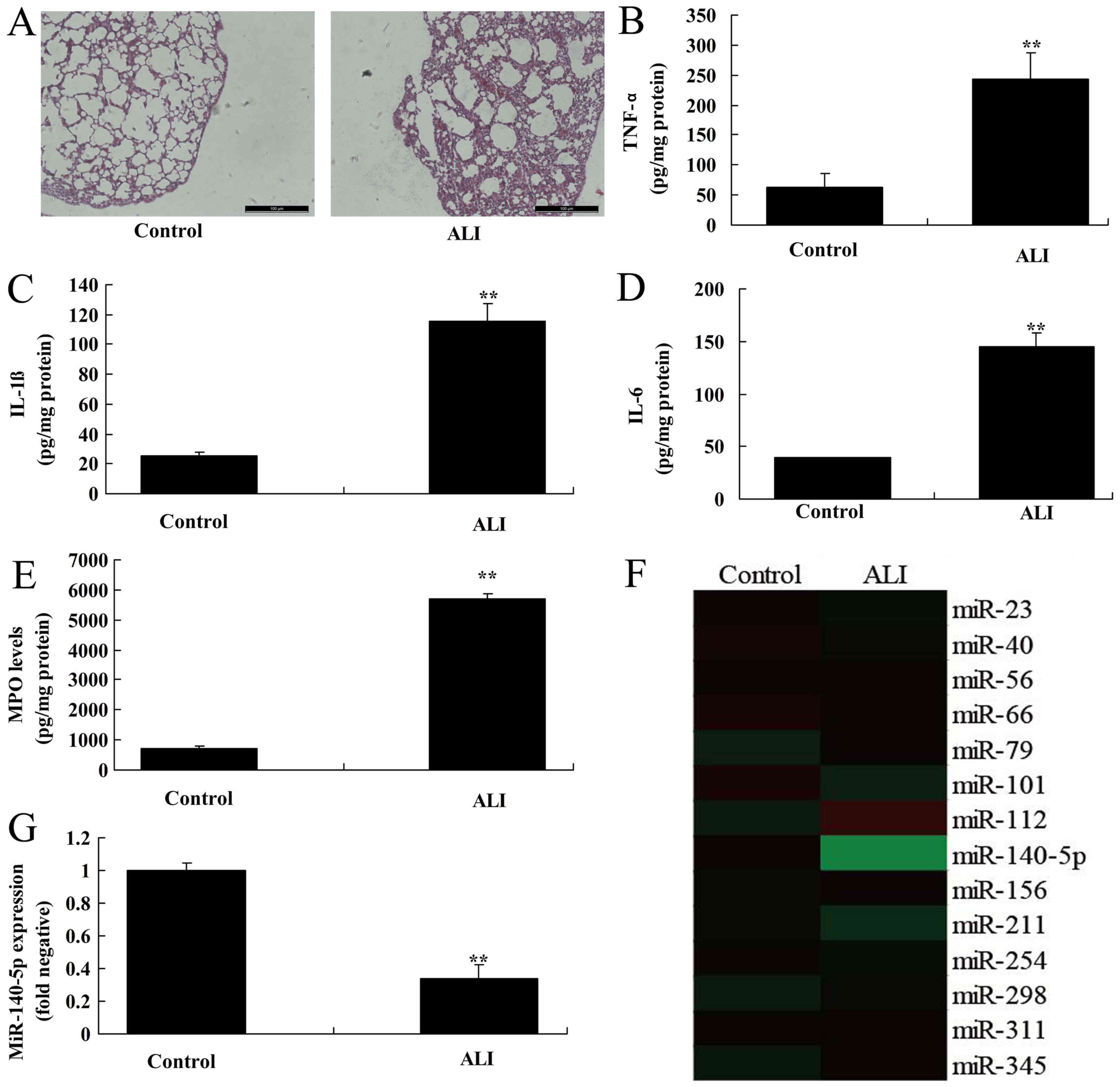
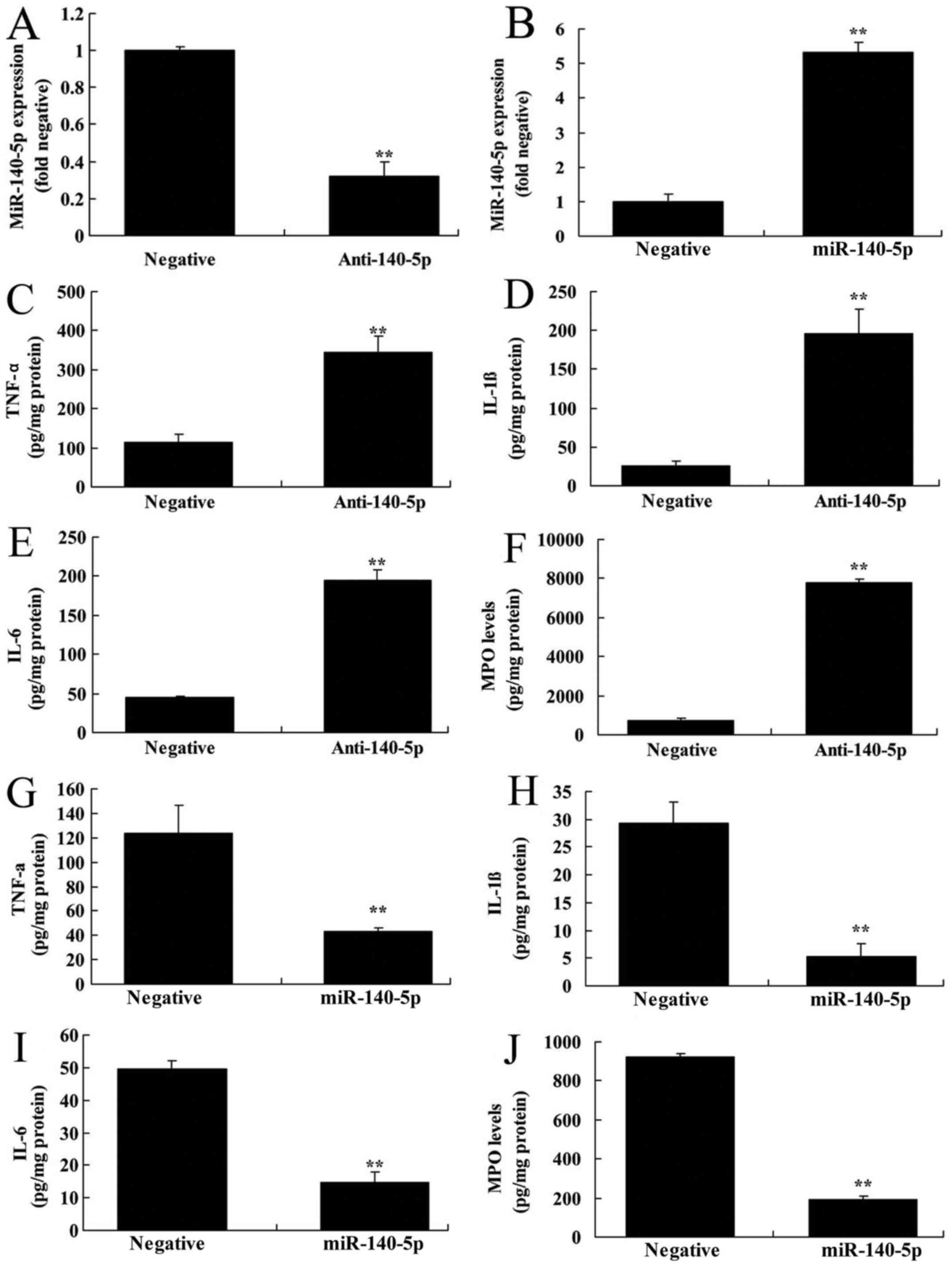
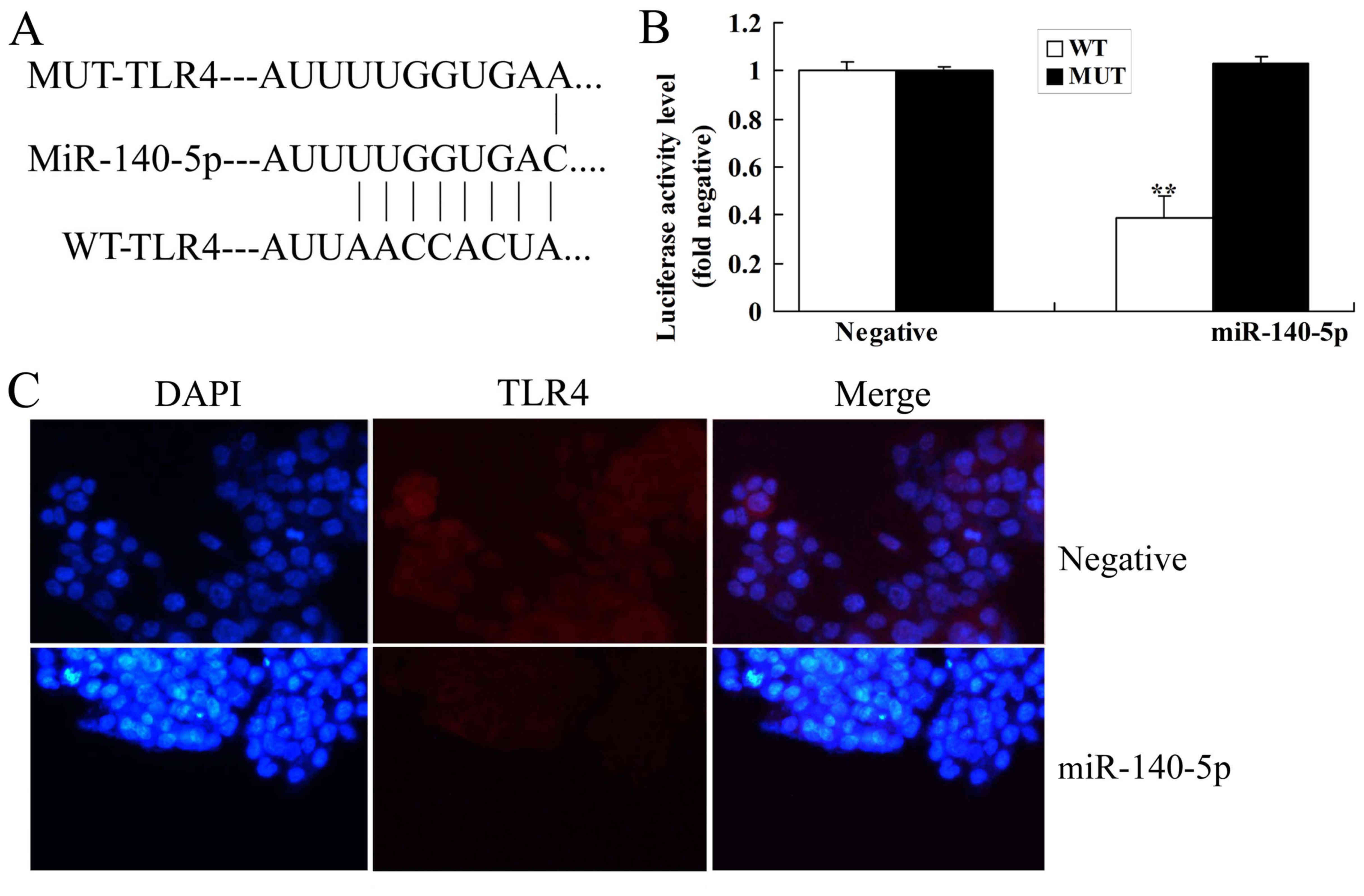
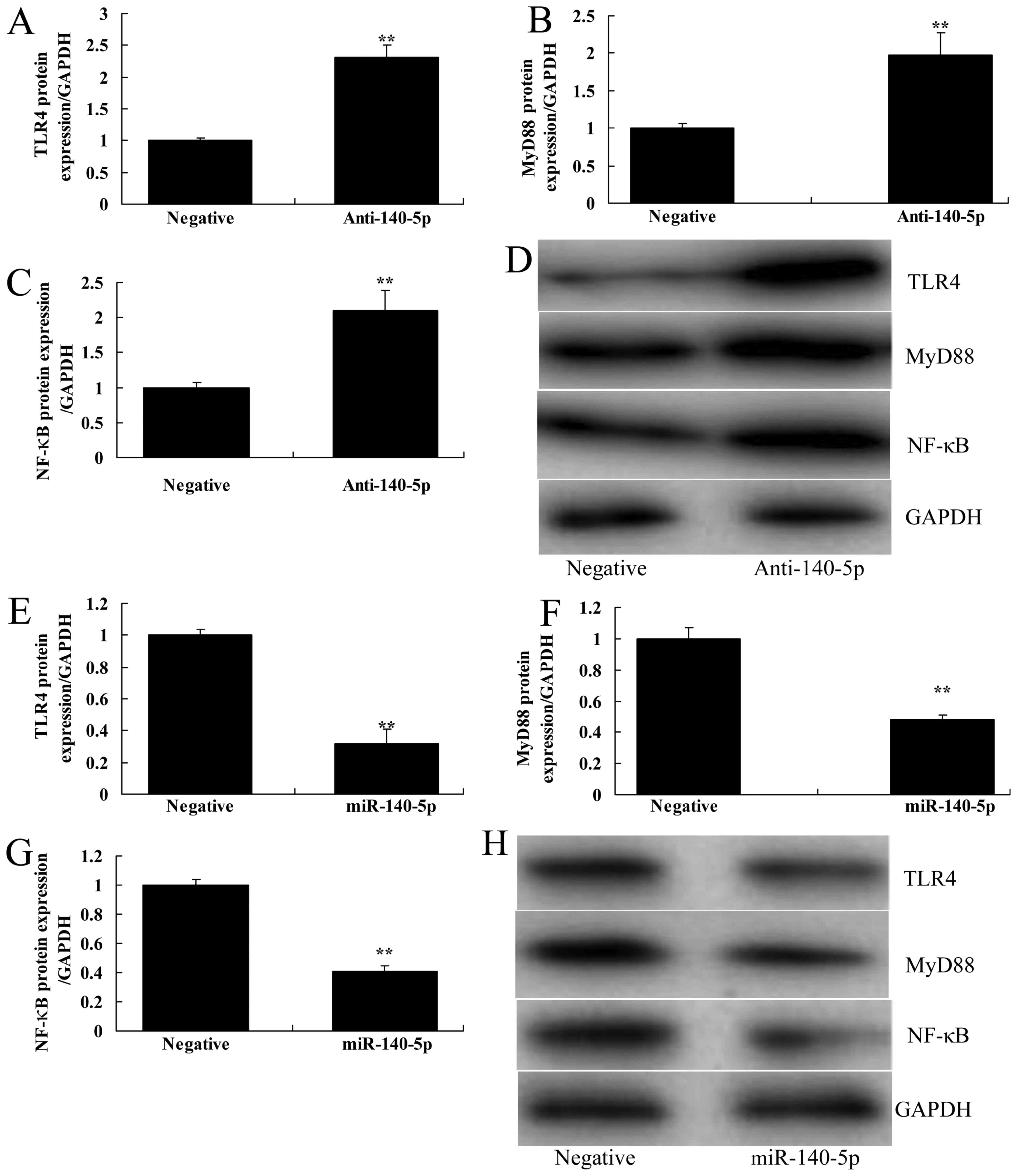
|
1
|
Stapleton RD, Dixon AE, Parsons PE, Ware
LB and Suratt BT: NHLBI Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Network: The association between BMI and plasma cytokine levels in
patients with acute lung injury. Chest. 138:568–577. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Z, Chen L and Ni H: The
effectiveness of Corticosteroids on mortality in patients with
acute respiratory distress syndrome or acute lung injury: A
secondary analysis. Sci Rep. 5:176542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Braunschweig CA, Sheean PM, Peterson SJ,
Perez Gomez S, Freels S, Lateef O, Gurka D and Fantuzzi G:
Intensive nutrition in acute lung injury: A clinical trial
(INTACT). JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 39:13–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li W, Qiu X, Jiang H, Han Y, Wei D and Liu
J: Downregulation of miR-181a protects mice from LPS-induced acute
lung injury by targeting Bcl-2. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1375–1382.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cao Y, Lyu YI, Tang J and Li Y: MicroRNAs:
Novel regulatory molecules in acute lung injury/acute respiratory
distress syndrome. Biomed Rep. 4:523–527. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang K, Gao B, Wei W, Li Z, Pan L, Zhang
J, Zhao Q, Chen W and Xu Z: Changed profile of microRNAs in acute
lung injury induced by cardio-pulmonary bypass and its mechanism
involved with SIRT1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:1104–1115.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X, Zhang L, Duan W, Liu B, Gong P,
Ding Y and Wu X: Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide by
inhibiting the NF-kappaB signalling pathway in LPS-induced acute
lung injury in a murine model. Mol Med Rep. 10:447–452. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He X, Qian Y, Li Z, Fan EK, Li Y, Wu L,
Billiar TR, Wilson MA, Shi X and Fan J: TLR4-upregulated IL-1beta
and IL-1RI promote alveolar macrophage pyroptosis and lung
inflammation through an autocrine mechanism. Sci Rep. 6:316632016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun XJ, Li XQ, Wang XL, Tan WF and Wang
JK: Sevoflurane inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB activation in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute inflammatory lung injury via
toll-like receptor 4 signaling. PLoS One. 10:e01227522015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y and Xu J: miR-140-5p regulates
hypoxia-mediated human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell
proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation by targeting Dnmt1 and
promoting SOD2 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 473:342–348.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feiner JR, Gropper MA, Toy P, Lieberman J,
Twiford J and Weiskopf RB: A clinical trial to detect subclinical
transfusion-induced lung injury during surgery. Anesthesiology.
123:126–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng G, Huang L, Tong H, Shu Q, Hu Y, Ge
M, Deng K, Zhang L, Zou B, Cheng B and Xu J: Treatment of acute
respiratory distress syndrome with allogeneic adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells: A randomized, placebo-controlled pilot
study. Respir Res. 15:392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nagy B Jr, Nagy B, Fila L, Clarke LA,
Gönczy F, Bede O, Nagy D, Újhelyi R, Szabó Á, Anghelyi A, et al:
Human epididymis protein 4: A novel serum inflammatory biomarker in
cystic fibrosis. Chest. 150:661–672. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li H, Guan SB, Lu Y and Wang F: miR-140-5p
inhibits synovial fibroblasts proliferation and inflammatory
cytokines secretion through targeting TLR4. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:208–214. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chi X, Wei X, Gao W, Guan J, Yu X, Wang Y,
Li X and Cai J: Dexmedetomidine ameliorates acute lung injury
following orthotopic autologous liver transplantation in rats
probably by inhibiting Toll-like receptor 4-nuclear factor kappa B
signaling. J Transl Med. 13:1902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu DD, Cao G, Han LK, Ye YL, Zhang Q,
Sima YH and Ge WH: Flavonoids from Radix Tetrastigmae improve
LPS-induced acute lung injury via the TLR4/MD-2-mediated pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 14:1733–1741. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu L, Xue T, Zhang J and Qu J: Knockdown
of versican V1 induces a severe inflammatory response in
LPS-induced acute lung injury via the TLR2-NF-κB signaling pathway
in C57BL/6J mice. Mol Med Rep. 13:5005–5012. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun DG, Xin BC, Wu D, Zhou L, Wu HB, Gong
W and Lv J: miR-140-5p-mediated regulation of the proliferation and
differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells occurs through the
lipopolysaccharide/toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Eur J
Oral Sci. 125:419–425. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang Q, Yi M, Guo Q, Wang C, Wang H, Meng
S, Liu C, Fu Y, Ji H and Chen T: Protective effects of polydatin on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through
TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:370–376. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tianzhu Z and Shumin W: Esculin inhibits
the inflammation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via
regulation of TLR/NF-κB pathways. Inflammation. 38:1529–1536. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang X, Sun CY, Zhang YB, Guo HZ, Feng
XX, Peng SZ, Yuan J, Zheng RB, Chen WP, Su ZR and Huang XD: Kegan
Liyan oral liquid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury through inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway
and MMP-9 expression. J Ethnopharmacol. 186:91–102. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jude JA, Dileepan M, Subramanian S, Solway
J, Panettieri RA Jr, Walseth TF and Kannan MS: miR-140-3p
regulation of TNF-α-induced CD38 expression in human airway smooth
muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 303:L460–L468.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|