Introduction
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a malignant
myeloproliferative disease characterized by an excessive and
unregulated production of myeloid leukemia cells in the bone marrow
(1,2), accounting for approximately 15% of
newly diagnosed cases of leukemia in adults (3). Furthermore, the treatment of CML is
problematic and its pathogenesis remains elusive (4). Therefore, it is important to elucidate
the key mechanism underlying CML for the development of effective
therapeutic strategies.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA recently
implicated in numerous biological processes through via regulating
gene expression (5–7). Accumulating studies have reported the
aberrant expression and key roles of several miRNAs in CML
(8–12). Exploration of key miRNAs associated
with CML development has become a hot topic of research. Recently,
the critical functions of miR-574-3p in numerous cancers have been
illustrated. For instance, miR-574-3p was down-regulated in bladder
cancer cells and overexpression of miR-574-3p significantly
inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion
(13). miR-574-3p is identified as
potential novel prognostic marker for breast cancer by next
generation sequencing profiling (14), which is also able to modulate
tamoxifen response in breast cancer (15). Reduced expression of miR-574-3p is
observed in the early stages of gastric cancer and overexpression
of miR-574-3p inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of
gastric cancer SGC7901 cells in vitro (16). Nevertheless, the roles of miR-574-3p
in regulating the development of CML remain unclear.
In the present study, the expression of miR-574-3p
in peripheral blood obtained from CML patients was detected. Then
miR-574-3p was overexpressed and suppressed in CML K562 cells to
further investigate the effects of miR-574-3p on cell proliferation
and apoptosis. Moreover, luciferase reporter assay was performed to
investigate whether interleukin-6 (IL6) was a target of miR-574-3p.
Besides, it is reported that IL6 can regulate the activation of
JAK/STAT3 pathway in CML development (17), thus the regulatory relationship
between miR-574-3p and IL6/Janus kinase/signal transducer and
activator of transcription-3 (JAK/STAT3) pathway was explored. All
efforts of our study were to elucidate the potential roles and
regulatory mechanism of miR-574-3p in CML development.
Materials and methods
Patient samples
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of
San Er Ling Yi Hospital Affiliated to School of Medicine, Xi'an
Jiaotong University, and each patient provided written informed
consent. A total of 36 consecutive, treatment naive patients who
were diagnosed with CML in our hospital and 8 healthy volunteers
were enrolled in our study. Peripheral blood was then obtained from
CML patients and healthy volunteers and the serum was collected by
centrifugation at 1,500 g for 10 min at 4°C. Finally, serum were
portioned in aliquots and stored at 80°C until subsequently
use.
Cell culture and transfection
Human CML cell line K562 (American Type Culture
Collection, Manassas, VA, USA) was cultured in Roswell Park
Memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640 medium (HyClone, Logan, UT, USA)
supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Sigma, USA) in a 5%
CO2 humidified incubator at 37°C.
The miR-574-3p mimics, miR-574-3p inhibitor or their
corresponding controls were synthesized by Shanghai GenePharma Co.,
Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Vector pcDNA-IL6 was constructed by
inserting the coding oligonucleotides of IL6 into pcDNA3.1 vector
(Invitrogen, Shanghai, China) for overexpression of IL6. Small
interference RNAs (siRNAs) targeting IL6 (si-IL6) and corresponding
control siRNAs (si-control) were designed and synthesized by
RiboBio (Gungdong, China). For cell transfection, K562 cells
(6×104 cells per well) were seeded in a 24-well plate
and then transfected with 50 nM of miR-574-3p mimics or mimic
control, miR-574-3p inhibitor or inhibitor control, pcDNA-IL6 or
blank vector, and si-IL6 or si-control using Lipofectamine 2000
(Invitrogen, Shanghai, China) in accordance with the manufacturer's
protocols. After 48 h of transfection, cells were harvested for
subsequent analysis.
Dual luciferase reporter assay
Complementary oligonucleotides containing the
miR-574-3p target site from IL6 (IL6 3′UTR-wt) and the mutated
3′UTR of IL6 (IL6 3′UTR-mut) containing a mutated miR-574-3p target
sequence with identical flanking nucleotides were synthesized by
Invitrogen (Shanghai, China). Oligonucleotides were then inserted
into the 3′UTR of the pMIR-REPORT luciferase reporter vector
(Ambion, Austin, Texas, USA) to construct a luciferase reporter.
pMIR-REPORT Beta-gal was used as the internal control. K562 cells
were cultured into a 24-well plate and then cotransfected with
miR-574-3p mimic or mimic control and pMIR 3′UTR clones or pMIR
Beta-gal for 24 h using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Shanghai,
China). The luciferase and b-galactosidase activity were then
quantified using Dual-Light System chemiluminescent reporter gene
assay (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).
MTT assay
The cell viability of K562 cells were detected by
the 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazo-liumbromide
(MTT) assay. After transfection, 6×104 cells were plated
into 6-well plates. At 1, 2, 3 days after transfection, 10 mg/ml of
MTT solution (Sigma, USA) was added into each well and cultured the
cells for 12 h. Then 200 µl of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, Sigma,
USA) was added into each well for 20 min to dissolve the formazan
crystals. The absorbance at 490 nm was finally detected.
Colony formation assay
The colony formation ability of K562 cells was also
detected. K562 cells in each group were diluted to 100 cells,
seeded in soft agar plates and cultured in complete medium for 12
days. When the cells in the largest dilution formed clones, clones
were then fixed with 100% methanol for 15 min. After that, cells
were stained with Giemsa (Sigma, USA) for 15 min. The number of
clones in 5 regions in each plate which were randomly selected was
counted under a microscope (IX83, Olympus). Three parallel
experiments were conducted for each sample.
Detection of cell apoptosis using flow
cytometry
The apoptosis of K562 cells was measured using
Annexin V labeling BD Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)
assay kit (Becton Dickinson, NJ, USA). In brief, a total of
5×105 cells were harvested after transfection of 48 h.
Cells were stained with 5 µl Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide
(PI) in the dark for 15 min. Within 1 h, the apoptotic cells were
sent out by means of Flow BD Fac Canto II flow-cytometer (Becton
Dickinson, NJ, USA). According to the fluorescence intensity, the
apoptotic cells (annexin V-positive and PI-negative) were finally
analyzed with a CellQuest 3.0 software (Becton Dickinson, NJ,
USA).
RNA extraction and quantitative
real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from peripheral blood and
K562 cells using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, Shanghai, China) and
their quality was measured using ultraviolet spectrophotometer (SMA
400 UV-VIS, Merinton, Shanghai, China). First-strand cDNA was then
synthesized using a High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit
(Invitrogen, Shanghai, China). To detect the expressions of
miR-574-3p and IL6, qRT-PCR was performed using the SYBR ExScript
RT-qPCR Kit (Takara, China) by means of the ABI PRISM 7300 Fast
Real-Time PCR System (Ambion, Foster City, CA, USA). Moreover,
analysis of melting curve was conducted at the end of each PCR to
detect the specificity of the PCR products. U6 and
Phosphoglyceraldehyde dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as the
internal control for miR-574-3p and IL6, respectively. Finally, the
relative expression of miR-574-3p and IL6 was calculated with
2−ΔΔCt method.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
(ELISA) assay
Peripheral blood (2 ml) was then obtained from CML
patients and healthy volunteers and the serum was collected by
centrifugation at 350 g for 10 min. The concentration of IL6 was
then determined with a commercially available ELISA kit (Genzyme,
Boston, MA) according to the manufacturer's protocols.
Western blot analysis
Total proteins in whole-cell lysates of K562 cells
were obtained using radioimmunoprecipitation buffer (RIPA) (Sangon
Biotech, Shanghai, China) containing protease inhibitor cocktail
(GE Healthcare, Buckinghamshire, UK) on ice for 20 min. After
estimating the protein concentration by Bradford reagent (Biorad
laboratories, CA, USA), equal quantities of protein extracts were
separated in a 10% SDS-PAGE and then electrically transferred to
polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Amersham, GE, Buckinghamshire,
UK). After blocked with 5% blocking agent, the membranes were
immunoblotted with primary antibodies, including anti-IL6,
anti-JAK1, anti-p-JAK1, anti-JAK2, anti-p-JAK2, anti-STAT3,
anti-p-STAT3 and anti-β-actin (1:1,000, cell signaling, MA, USA)
overnight at 4°C in shaker. β-actin was used as the loading
control. The membranes were then incubated with secondary
horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibody (1:5,000, cell
signaling, MA, USA) for 1 h. Lastly, the membranes were visualized
with Amersham ECL Detection Agent (GE, Buckinghamshire, UK) by
exposure to hyperfilm (GE, Buckinghamshire, UK) in the dark
room.
Statistical analysis
Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation
(SD) and their normal distribution was conducted using one-sample
K-S test. Significant differences between groups were assessed
using Student's t-test. All statistical analyses were performed
using SPSS 18.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL) and P<0.05 was considered
statistical significant.
Results
miR-574-3p was down-regulated in
peripheral blood obtained from CML patients
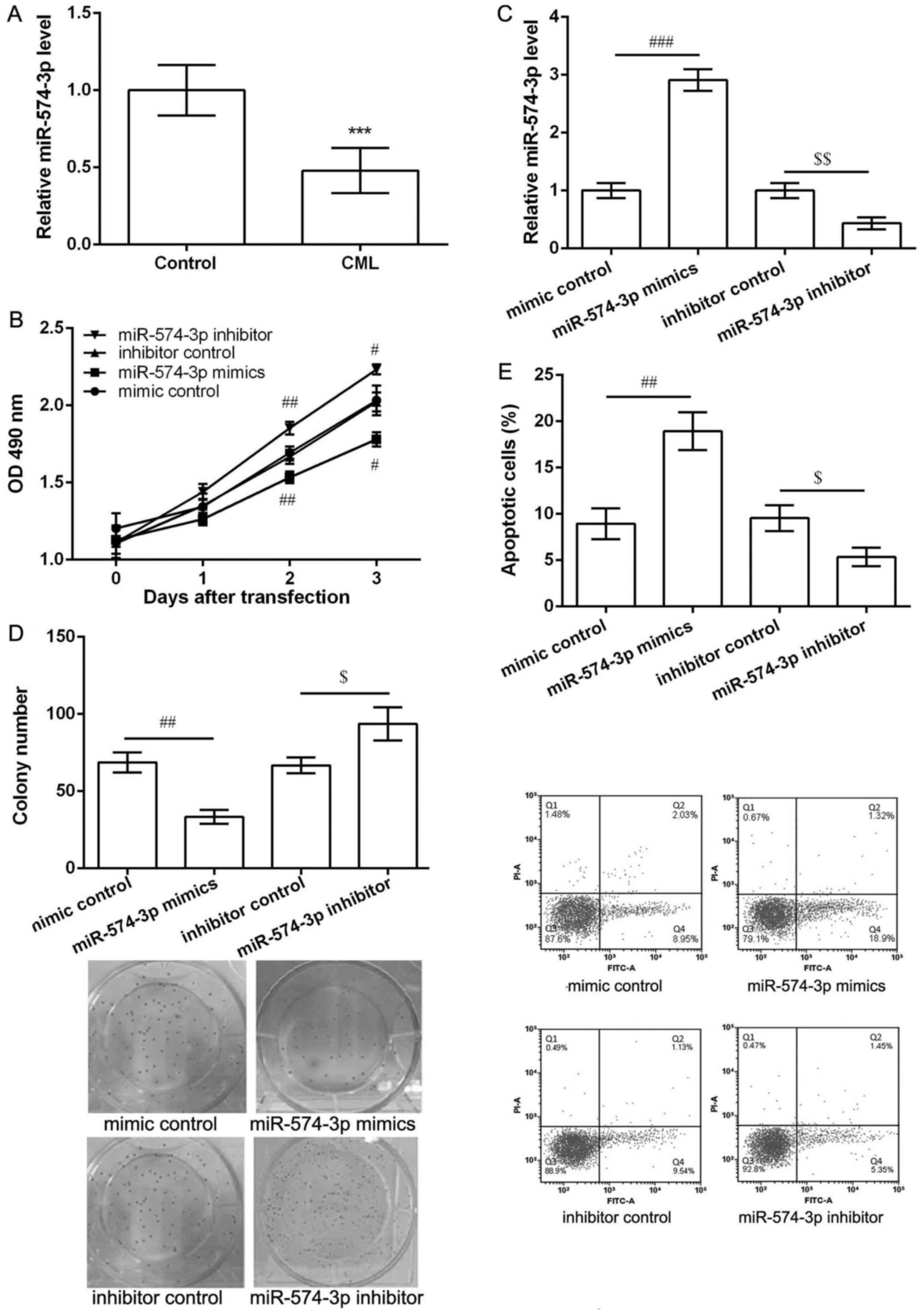
As shown in Fig. 1A,
the expression of miR-574-3p in peripheral blood obtained from CML
patients was significantly lower than that in healthy controls
(P<0.05), indicating miR-574-3p may be involved in the
development and progression of CML. Overexpression of miR-574-3p
inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis of K562 cells.
To investigate the potential effects of miR-574-3p
in CML, K562 cells were transfected with miR-574-3p mimic, mimic
control, miR-574-3p inhibitor and inhibitor control. The results of
MTT assay showed that after 2 and 3 days of transfection,
miR-574-3p mimics significantly inhibited cell viability while
miR-574-3p inhibitor markedly enhanced cell viability when compared
with their corresponding controls (P<0.05, Fig. 1B). In comparison with their
corresponding control groups, miR-574-3p expression was
significantly increased in miR-574-3p mimic group, while obviously
decreased in miR-574-3p inhibitor group after 2 days of
transfection (P<0.05, Fig. 1C).
Thus, colony formation assay and flow cytometry were further
performed the cell proliferation and apoptosis after 2 days of
transfection. The results showed miR-574-3p mimics decreased the
number of colony (P<0.05, Fig.
1D) and induced cell apoptosis (P<0.05, Fig. 1E) significantly compared with mimic
control. Moreover, miR-574-3p inhibitor resulted in opposite
effects on colony number and cell apoptosis (Fig. 1D and E).
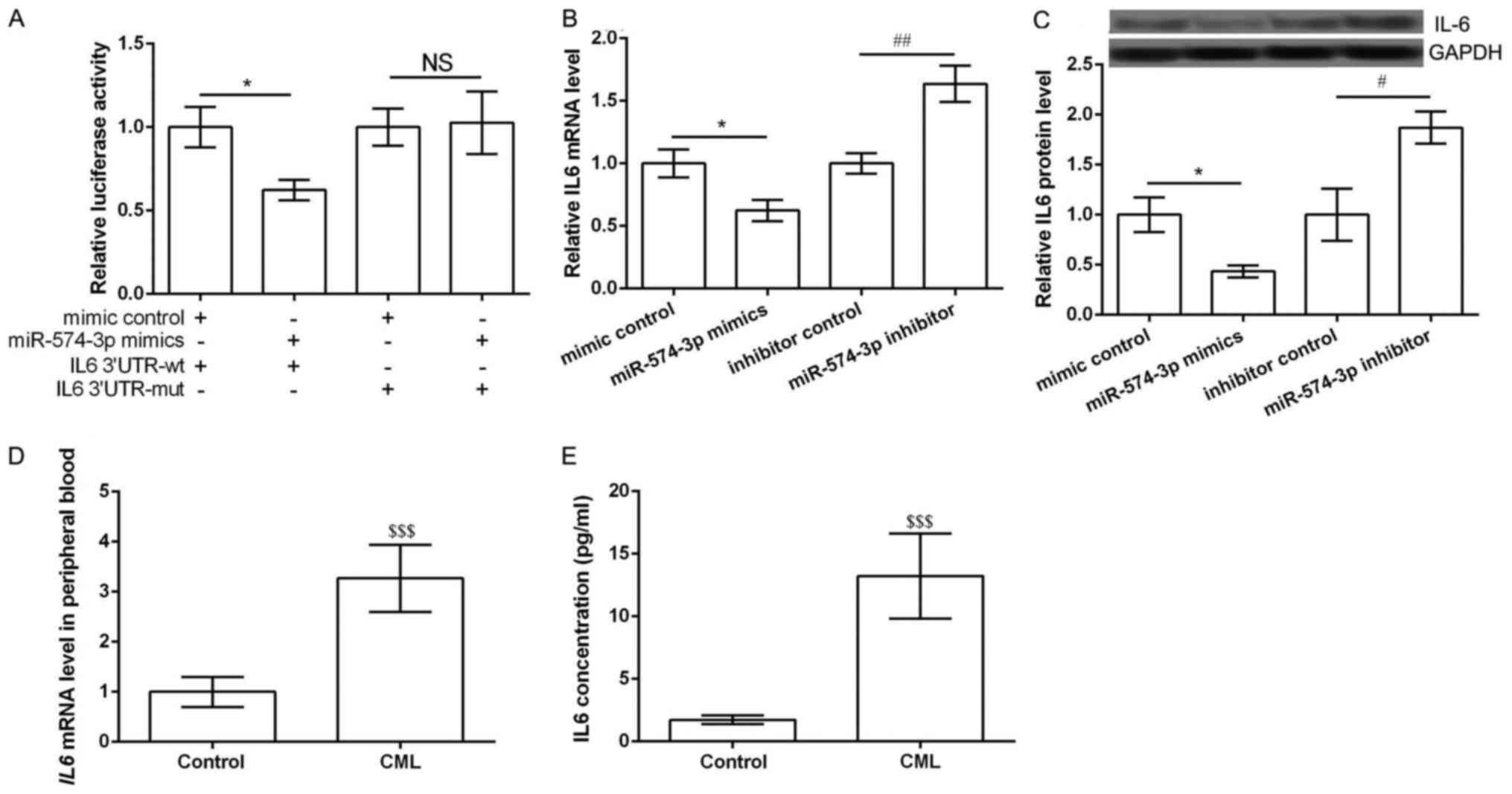
IL6 was the direct target of
miR-574-3p
According to the information of TargetScanHuman, IL6
was the predicted as a potential target of miR-574-3p. Luciferase
report assay was performed to further verify the predicted results.
Expected results was obtained that miR-574-3p mimic significantly
inhibited the luciferase report activity of IL6 3′UTR-wt rather
than IL6 3′UTR-mut (P<0.05, Fig.
2A). Then qRT-PCR and western blot were performed to detect the
expression of IL6 in different transfected groups. The results
showed the expression of IL6 in both mRNA and protein levels was
significantly inhibited in miR-574-3p mimic group compared with
that in mimic control group, while was markedly increased in
miR-574-3p inhibitor group compared with that in inhibitor control
group (P<0.05, Fig. 2B and C).
Notably, the mRNA expression of IL6 in peripheral blood obtained
from CML patients and healthy controls was detected. Expected
results were obtained that IL6 expression was significantly higher
than that in healthy controls (P<0.05, Fig. 2D). ELISA assay also showed similar
results that the concentration of IL6 was significantly higher than
that in healthy controls (P<0.05, Fig. 2E). These data indicated that IL6 was
the direct target of miR-574-3p and its expression was negatively
regulated by miR-574-3p.
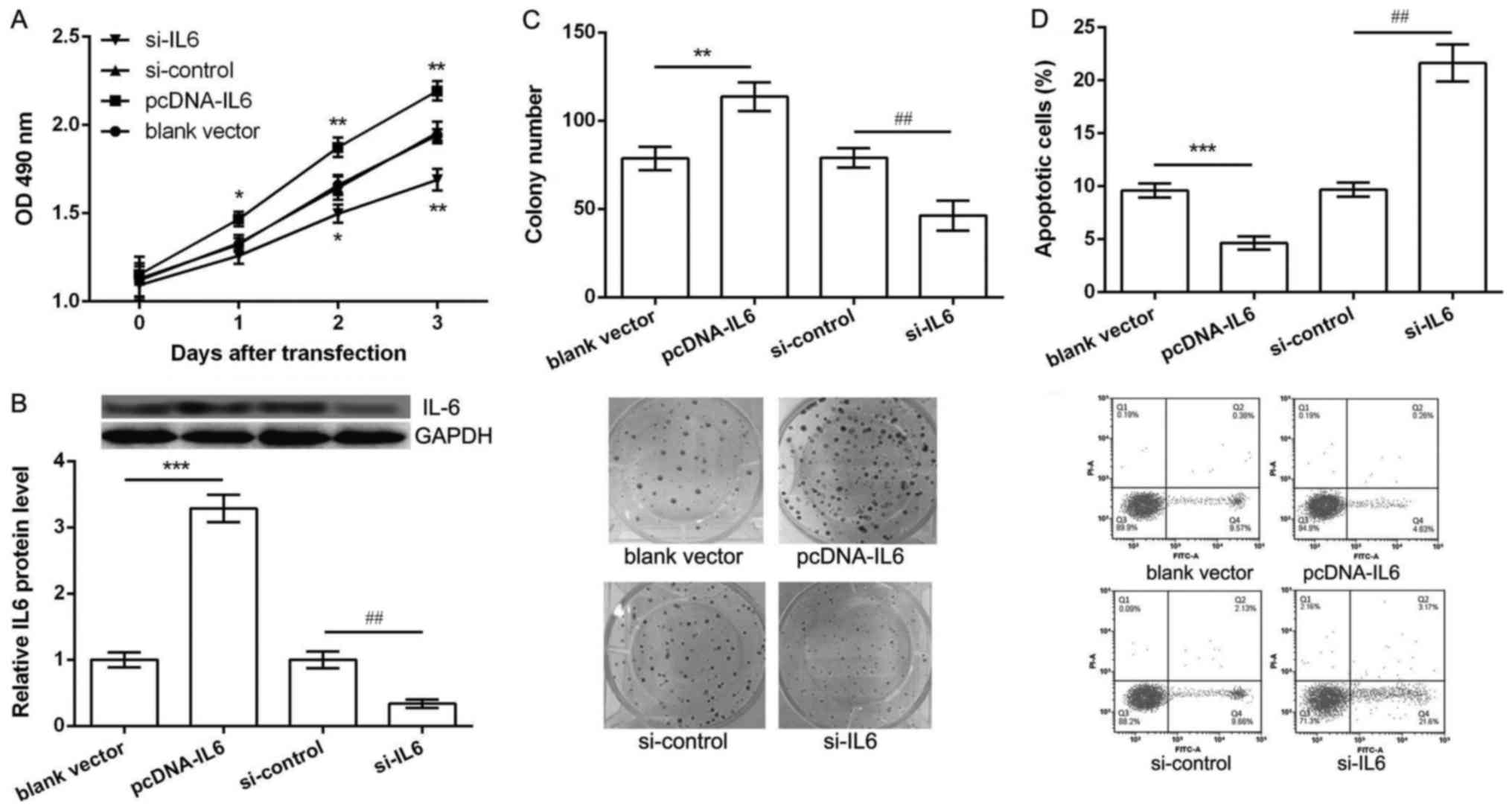
Overexpression of IL6 promoted
proliferation and inhibited apoptosis of K562 cells
We further investigated whether dys-regulation of
IL6 could also regulate K562 cell proliferation and apoptosis.
Thus, K562 cells were transfected with pcDNA-IL6, blank vector,
si-IL6 and si-control. As shown in Fig.
3A, when compared with their corresponding controls,
overexpression of IL6 could significantly increase K562 cell
viability after 2 and 3 days of pcDNA-IL6 transfection, while
knockdown of IL6 resulted in a significantly decrease of cell
viability after 2 and 3 days of si-IL6 transfection (P<0.05). In
addition, after 2 days of transfection, the protein expression of
IL6 was significantly up-regulated in pcDNA-IL6 group and obvious
down-regulated in si-IL6 group in comparison with their
corresponding control groups (P<0.05, Fig. 3B). Besides, the results of colony
formation assay and flow cytometry showed, after 2 days of
pcDNA-IL6 transfection, the number of colony was significantly
increased (P<0.05, Fig. 3C) and
apoptotic cells were markedly decreased (P<0.05, Fig. 3D). However, opposite effects were
observed after 2 days of si-IL6 transfection (Fig. 1D and E). These data indicated that
overexpression of IL6 promoted proliferation and inhibited
apoptosis of K562 cells, which was opposite with the function of
miR-574-3p overexpression.
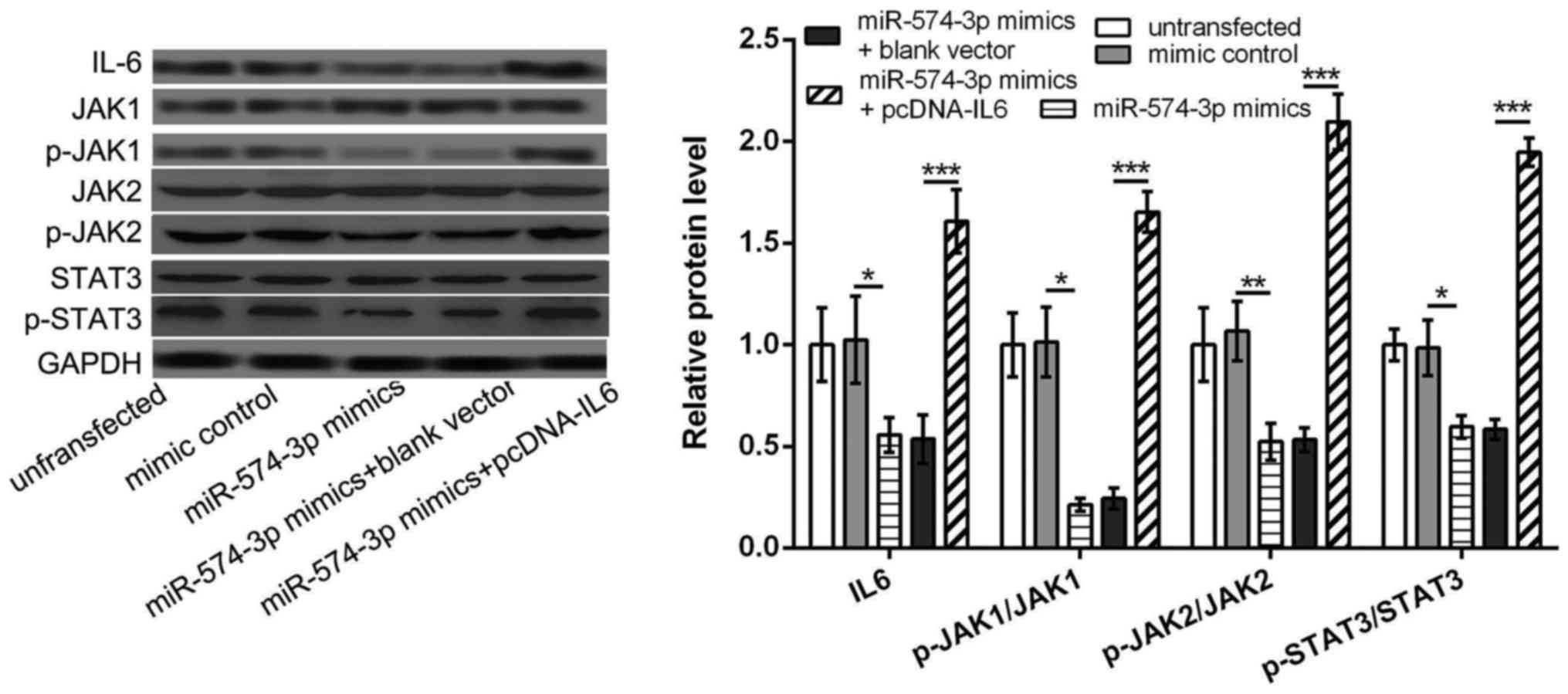
miR-574-3p targets IL6 to further
inhibit the activation of JAK/STAT3 pathway in K562 cells
We further investigated the relationship between
miR-574-3p and IL6/JAK/STAT3 pathway, aiming to elucidate the key
mechanism of miR-574-3p in CMI development. The results showed that
the protein levels of IL6, p-JAK1/JAK1, p-JAK2/JAK2 and
p-STAT3/STAT3 in miR-574-3p mimic group were all significantly
lower than that in mimic control group or untransfected group
(P<0.05, Fig. 4), indicating that
overexpression of miR-574-3p could inhibited the activation of
JAK/STAT3 pathway. However, the protein levels of IL6, p-JAK1/JAK1,
p-JAK2/JAK2 and p-STAT3/STAT3 were significantly increased in
miR-574-3p mimic+pcDNA-IL6 group in comparison with that in
miR-574-3p mimic group or miR-574-3p mimic+blank vector group
(P<0.05, Fig. 4), indicating that
overexpression of IL6 could reverse the inhibitory of miR-574-3p
overexpression on the activation of IL6/JAK/STAT3 pathway, and
miR-574-3p might inhibit the activation of JAK/STAT3 pathway in
K562 cells via targeting IL6.
Discussion
In the present study, miR-574-3p was down-regulated
in peripheral blood obtained from CML patients, and down-regulation
of miR-574-3p promoted proliferation and inhibited apoptosis of
K562 cells. In addition, IL6 was confirmed as a direct target of
miR-574-3p, and the effects of IL6 overexpression on K562 cell
proliferation and apoptosis were opposite with down-regulation of
miR-574-3p. Besides, the activation of JAK/STAT3 pathway induced by
miR-574-3p overexpression was rescued by overexpression of IL6.
These data imply that miR-574-3p may exert a tumor suppressor role
in K562 cells via regulating IL6/JAK/STAT3 pathway.
In previous studies, miR-574-3p has a
tumor-promoting role in human osteosarcoma (18), while exerts a tumor suppressor effect
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (19), indicating that miR-574-3p may play a
dual role in regulating cancer progression. Furthermore, it is
reported that aberrantly expression of miR-574-3p may play
functional roles in regulating the proliferation and metatasis of
gastric cancer (16). In our study,
miR-574-3p was down-regulated in peripheral blood obtained from CML
patients, and overexpression of miR-574-3p significantly inhibited
proliferation and induced apoptosis of K562 cells, indicating that
miR-574-3p may play a tumor suppressor role in CML development.
In addition, miRNAs are implicated in numerous
biological processes through degrading or inhibiting the
translation of their target genes (20). In our study, IL6 was confirmed as a
direct target of miR-574-3p. The effects of overexpression of IL6
on the proliferation and apoptosis of K562 cells were opposite with
overexpression of miR-574-3p. IL-6, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, is
previously shown to play important roles in the pathogenesis of
hematological malignancies, including multiple myeloma (21). Maeda et al (22) confirmed that IL6 was implicated in
both myeloid expansion and lymphocytopenia. Reynaud et al
(23) demonstrated that IL6 could
control the cell fate of leukemic multipotent progenitor cells fate
and might serves as a positive feedback loop to sustain CML
development. IL-6 is also considered as a selective and prognostic
factor to address the follow-up in imatinib-treated CML patients
(24). Although the role of
miR-574-3p in CML has not been fully investigated, our results
prompt us to speculate that miR-574-3p may inhibit proliferation
and induce apoptosis of K562 cells through targeting IL6.
Furthermore, JAK/STAT signaling pathway has been
implicated in transmission of information carried by cytokines. It
is reported that JAK/STAT3 pathway can be activated by IL6, thus
contributes to the CML development (17). Kumar et al (25), also demonstrated that IL-6 can induce
JAK/STAT and MAPK pathways, thus have a key role in deciphering the
CML progression stages. In addition, STAT5 is found to play a
critical role in regulating growth and apoptosis of the CML
leukaemic cells (26). JAK/STAT3
pathway is shown to be a key mechanism to mediate
cryptotanshinone-induced apoptosis of CML K562 cells (27). Besides, capsaicin can induce
apoptosis and inhibit proliferation of K562 leukemic cells through
affecting miR-520a-5p/STAT3 interaction (28). Bortezomib can induce apoptosis of
K562 leukemic cells by interacting with JAK/STAT pathway (29). JAK/STAT signaling pathway is found to
mediate sehydrocostus lactone-suppressed proliferation of CML cells
(30). In this study, overexpression
of miR-574-3p could inhibit the activation of JAK/STAT3 pathway,
which was rescued by overexpression of IL6. Therefore, we speculate
that miR-574-3p may exert a tumor suppressor role in K562 cells via
regulating IL6/JAK/STAT3 pathway, which are still needed to be
further investigated.
In conclusion, our results indicate that
overexpression of miR-574-3p may inhibit proliferation and induce
apoptosis of K562 cells via suppressing the activation of
IL6/JAK/STAT3 pathway. miR-574-3p may serve as a potential target
for the treatment of CML.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The analyzed data sets generated during the present
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
HY, JZ and XX conceived and designed the
experiments. HY, FZ and YS performed the experiments. JL and FZ
analyzed the data. HY and XX wrote and revised the manuscript. All
authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of San Er Ling Yi Hospital Affiliated to School of
Medicine, Xi'an Jiaotong University, and each patient provided
written informed consent.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Aquino SS, Gonçalves RP and Silva LB: The
pharmacotherapeutic follow-up of patients with chronic myeloid
leukemia (CML) on imatinib mesylate therapy. Rev Bras Hematol
Hemoter. 31:137–142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Marzag H: Développement de nouvelles
réactions éco-compatibles: Application à la synthèse de molécules
bioactives. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Jabbour E and Kantarjian H: Chronic
myeloid leukemia: 2014 update on diagnosis, monitoring, and
management. Am J Hematol. 89:547–556. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holyoake TL, Jiang X, Drummond MW, Eaves
AC and Eaves CJ: Elucidating critical mechanisms of deregulated
stem cell turnover in the chronic phase of chronic myeloid
leukemia. Leukemia. 16:549–558. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chu Y, Zhu H, Lv L, Zhou Y and Huo J:
MiRNAs in oesophageal squamous cancer. Neth J Med. 71:69–75.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mo MH, Chen L, Fu Y, Wang W and Fu SW:
Cell-free circulating miRNA biomarkers in cancer. J Cancer.
3:432–448. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Reddy KB: MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer.
Cancer Cell Int. 15:382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arya D, Sachithanandan SP, Ross C,
Palakodeti D, Li S and Krishna S: MiRNA182 regulates percentage of
myeloid and erythroid cells in chronic myeloid leukemia. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e25472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xishan Z, Ziying L, Jing D and Gang L:
MicroRNA-320a acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting BCR/ABL
oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia. Sci Rep. 5:124602015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Y, Song Y, Ma W, Zheng W and Yin H:
Decreased microRNA-30a levels are associated with enhanced ABL1 and
BCR-ABL1 expression in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res.
37:349–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu Y, Yang L, Zhao M, Zhu S, Kang R,
Vernon P, Tang D and Cao L: Targeting microRNA-30a-mediated
autophagy enhances imatinib activity against human chronic myeloid
leukemia cells. Leukemia. 26:1752–1760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Zhao L, Li N, Miao Y, Zhou H and Jia
L: miR-9 regulates the multidrug resistance of chronic myelogenous
leukemia by targeting ABCB1. Oncol Rep. 37:2193–2200. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tatarano S, Chiyomaru T, Kawakami K,
Enokida H, Yoshino H, Hidaka H, Nohata N, Yamasaki T, Gotanda T,
Tachiwada T, et al: Novel oncogenic function of mesoderm
development candidate 1 and its regulation by MiR-574-3p in bladder
cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 40:951–959. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Krishnan P, Ghosh S, Wang B, Li D,
Narasimhan A, Berendt R, Graham K, Mackey JR, Kovalchuk O and
Damaraju S: Next generation sequencing profiling identifies
miR-574-3p and miR-660-5p as potential novel prognostic markers for
breast cancer. BMC Genomics. 16:7352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ujihira T, Ikeda K, Suzuki T, Yamaga R,
Sato W, Horie-Inoue K, Shigekawa T, Osaki A, Saeki T, Okamoto K, et
al: MicroRNA-574-3p, identified by microRNA library-based
functional screening, modulates tamoxifen response in breast
cancer. Sci Rep. 5:76412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su Y, Ni Z, Wang G, Cui J, Wei C, Wang J,
Yang Q, Xu Y and Li F: Aberrant expression of microRNAs in gastric
cancer and biological significance of miR-574-3p. Int
Immunopharmacol. 13:468–475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma L, Zhu Z, Jiang L, Sun X, Lu X, Zhou M,
Qian S and Jianyong L: Matrine suppresses cell growth of human
chronic myeloid leukemia cells via its inhibition of the
interleukin-6/Janus activated kinase/signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 signaling cohort. Leuk Lymphoma.
56:2923–2930. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu H, Liu X, Zhou J, Chen X and Zhao J:
miR-574-3p acts as a tumor promoter in osteosarcoma by targeting
SMAD4 signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 12:5247–5253. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Okumura T, Kojima H, Miwa T, Sekine S,
Hashimoto I, Hojo S, Nagata T and Shimada Y: The expression of
microRNA 574-3p as a predictor of postoperative outcome in patients
with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol.
14:2282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamasaki T, Kim EJ, Cerutti H and Ohama T:
Argonaute3 is a key player in miRNA-mediated target cleavage and
translational repression in Chlamydomonas. Plant J. 85:258–268.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hong DS, Angelo LS and Kurzrock R:
Interleukin-6 and its receptor in cancer: Implications for
translational therapeutics. Cancer. 110:1911–1928. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maeda K, Baba Y, Nagai Y, Miyazaki K,
Malykhin A, Nakamura K, Kincade PW, Sakaguchi N and Coggeshall KM:
IL-6 blocks a discrete early step in lymphopoiesis. Blood.
106:879–885. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reynaud D, Pietras E, Barry-Holson K, Mir
A, Binnewies M, Jeanne M, Sala-Torra O, Radich JP and Passegué E:
IL-6 controls leukemic multipotent progenitor cell fate and
contributes to chronic myelogenous leukemia development. Cancer
Cell. 20:661–673. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ciarcia R, Vitiello MT, Galdiero M,
Pacilio C, Iovane V, d'Angelo D, Pagnini D, Caparrotti G, Conti D,
Tomei V, et al: Imatinib treatment inhibit IL-6, IL-8, NF-KB and
AP-1 production and modulate intracellular calcium in CML patients.
J Cell Physiol. 227:2798–2803. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kumar H, Tichkule S, Raj U, Gupta S,
Srivastava S and Varadwaj PK: Effect of STAT3 inhibitor in chronic
myeloid leukemia associated signaling pathway: A mathematical
modeling, simulation and systems biology study. 3 Biotech.
6:402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baśkiewicz-Masiuk M and Machaliński B: The
role of the STAT5 proteins in the proliferation and apoptosis of
the CML and AML cells. Eur J Haematol. 72:420–429. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jung JH, Kwon TR, Jeong SJ, Kim EO, Sohn
EJ, Yun M and Kim SH: Apoptosis induced by tanshinone IIA and
cryptotanshinone is mediated by distinct JAK/STAT3/5 and SHP1/2
signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:8056392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kaymaz BT, Cetintaş VB, Aktan C and Kosova
B: MicroRNA-520a-5p displays a therapeutic effect upon chronic
myelogenous leukemia cells by targeting STAT3 and enhances the
anticarcinogenic role of capsaicin. Tumor Biol. 35:8733–8742. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Selvi N, Kaymaz BT, Gündüz C, Aktan Ç,
Kiper HD, Şahin F, Cömert M, Selvi AF, Kosova B and Saydam G:
Bortezomib induces apoptosis by interacting with JAK/STAT pathway
in K562 leukemic cells. Tumor Biol. 35:7861–7870. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cai H, Qin X and Yang C: Dehydrocostus
lactone suppresses proliferation of human chronic myeloid leukemia
cells through Bcr/Abl-JAK/STAT signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem.
118:3381–3390. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|