Introduction
Cyclosporin A (CsA) is widely used as an
immunosuppressor, but clinical study found that after organ
transplantation diabetes mellitus associated with the use of
immunosuppressants (1,2). New-onset diabetes mellitus (NODM) is an
important complication among patients receiving immunosuppressants.
Clinical studies have found that CsA induces hyperglycemia and
decreased plasma insulin levels in organ transplant patients
(3–5). The diabetogenicity of cyclosporin has
been attributed to both impaired insulin sensitivity and β cell
function (6–8). Animal experiments have confirmed that
CsA induces insulin resistance by decreasing the cell surface
availability of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) (9). Some research suggests that CsA and
tacrolimus are Ca2+ inhibitors. They likely affect
insulin secretion in β cell function, but previous studies have
confirmed that CsA maybe induces β cell apoptosis by other
mechanisms. Therefore, this research aims to confirm CsA induces β
cell apoptosis by specific inhibition of PPIB which could cause the
proinsulin misfolded. It is important to know the mechanism of CsA
and prevent NODM.
Recent studies have demonstrated that CsA adversely
affects pancreatic β cells and activates endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
stress and the unfolded protein response (UPR), thus leading to
cell death (10). However, the
mechanisms through how CsA induces ER stress remain largely
unknown, but the ER stress in β cells could be caused by misfolded
proinsulin. Pancreatic islet β cells synthesize and secrete insulin
and regulate blood glucose concentrations. The post-translational
modification of insulin involves two steps. First, insulin mRNA is
translated as a single-chain precursor called preproinsulin, and
the removal of this precursor's signal peptide during insertion
into the ER generates proinsulin (11). Second, proinsulin is cleaved into
insulin and C-peptide. There are three intramolecular disulfide
bonds in proinsulin and insulin molecules; these bonds are
important for insulin bioactivity. Similarly to disulfide bonds in
many secretory proteins, these bonds help to stabilize molecules
before and after secretion. The proinsulin molecule is folded in
the ER; during this process, the three aforementioned
evolutionarily conserved disulfide bonds are formed. Properly
folded proinsulin forms dimers and exits the ER, trafficking
through the golgi complex into secretory granules, where prohormone
convertases (PC1/3 and PC2) (12),
in concert with carboxypeptidase E (CPE), process proinsulin into
C-peptide and two-chain mature insulin, which is stored in insulin
granules (13).
PPIase family proteins are isomerases that shuffle
disulfide bonds and allow proinsulin molecules to potentially reach
their native conformation. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase b
(PPIB) is a member of the cyclophilin-type PPIase family and
contributes to protein folding (14–16). If
proinsulin is not properly folded within the ER, ER stress-induced
cell apoptosis occurs. CsA is not only an immunosuppressant but
also a known inhibitor of PPIB (17,18).
PPIB may be the key player in CsA-induced β cell death and may be
involved in the molecular mechanism through which unfolded
proinsulin activates ER stress.
Materials and methods
Reagents and antibodies
CsA and palmitic acid (PA) were purchased from Sigma
(Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). PA/Bull Serum
Albumin (BSA) conjugates were prepared as described previously.
Briefly, a 100 mmol/l solution of PA in 0.1 N NaOH was incubated at
70°C for 30 min, and fatty acid soaps were then complexed with 5%
BSA in PBS at a 19:1 molar ratio of fatty acids to BSA. CsA was
dissolved in PBS to obtain a 10 mmol/l stock solution.
3-[4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT)
was obtained from Biosharp (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA). Primary
antibodies, including anti-insulin (1:1,000; cat. no. 8138),
anti-caspase-3 (1:2,000; cat. no. 9662), anti-phospho-PKR-like
endoplasmic reticulum kinase (p-PERK; 1:1,000 cat. no. 3179),
anti-PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK; 1:2,000; cat. no.
3192), anti-binding immunoglobulin protein (BIP; 1:3,000; cat. no.
3183), and anti-C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP; 1:3,000; cat. no.
2895) and anti-β-actin antibodies (1:5,000; cat. no. 3700), and
secondary antibodies anti-rabbit IgG (1:2,000; cat. no. 7074) and
anti-mouse IgG (1:2,000; cat. no. 7076) were obtained from Cell
Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA). Anti-C-peptide (cat. no.
ab14181; 1:1,000) and anti-PPIB primary antibodies (cat. no.
ab16045; 1:1,000) were obtained from Abcam (Cambridge, UK).
Cell culture
MIN6 mouse insulinoma cells were obtained from the
Key Laboratory of Human Functional Genomics of Jiangsu Province,
Nanjing Medical University (Nanjing, China), and cultured in
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM), a high-glucose culture
medium, supplemented with 15% fetal bovine serum (both Gibco;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), 50 µmol/l
2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA), 100 U/ml penicillin
and 100 U/ml streptomycin (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
These cells were incubated in a humidified atmosphere of 5%
CO2 and 95% air at 37°C.
Cell viability assay
Cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of
103 cells per well and continuously exposed to CsA, PA
or a combination of both drugs. Twenty-four hours later, the cells
were treated with MTT (5 mg/ml) at 37°C for 4 h. Culture medium
containing MTT was discarded, and DMSO was added to each well to
dissolve the precipitate. Absorbance values were measured at a
spectral wavelength of 570 nm using a microplate reader after the
plates were incubated with vibration at 37°C for15 min.
Western blot analysis
After treatment, MIN6 cells (5×106 cells)
were washed with PBS three times and lysed in RIPA lysis buffer (25
mmol/l HEPES, 1.5% Triton X-100, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS,
0.5 M NaCl, 5 mmol/l EDTA, 50 mM NaF, 0.1 mmol/l sodium vanadate,
and 1 mmol/l phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, pH 7.8) on ice for 30
min. The cell lysate was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 30 min at
4°C, and the protein concentration in the supernatant was
determined via a BCA assay. Reducing loading buffer or non-reducing
loading buffer (lacked DTT and 2-mercaptoethanol; both Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology, Shanghai, China) was added to the
supernatant, which was subsequently boiled for 5 min and then
electrophoresed on a 12.5 or 10% SDS-PAGE gel. Proteins were
transferred to a PVDF membrane, and non-specific binding sites were
blocked with 5% nonfat dry milk in PBST (PBS containing 0.05%
Tween-20) for 2 h. The membrane was then incubated with primary
antibodies: Insulin, C-peptide, PPIB, caspase-3, p-PERK, PERK, BIP,
CHOP overnight at 4°C and then with peroxidase-conjugated secondary
antibodies at room temperature for 2 h. A sequential enhanced
chemiluminescence reagent was used to detect bands.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 22.0 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was
used to assess study data via one-way analysis of variance followed
by Dunnett's t-test or an LSD test. All experiments were performed
three times, and the results are presented as means ± standard
deviation. Differences were regarded as significant if
P<0.05.
Results
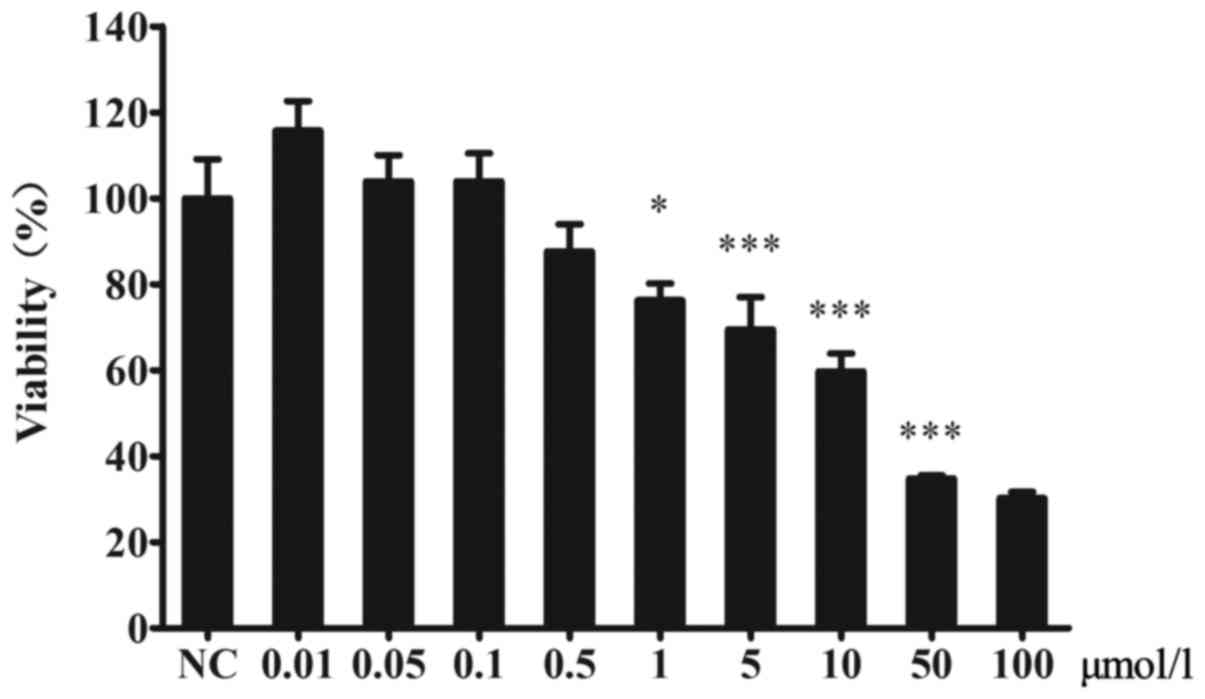
The effect of CsA on the viability of
MIN6 cells
The viability of MIN6 cells was decreased by CsA.
There were no significant differences between the CsA and control
groups at CsA concentrations lower than 1 µmol/l (Fig. 1).
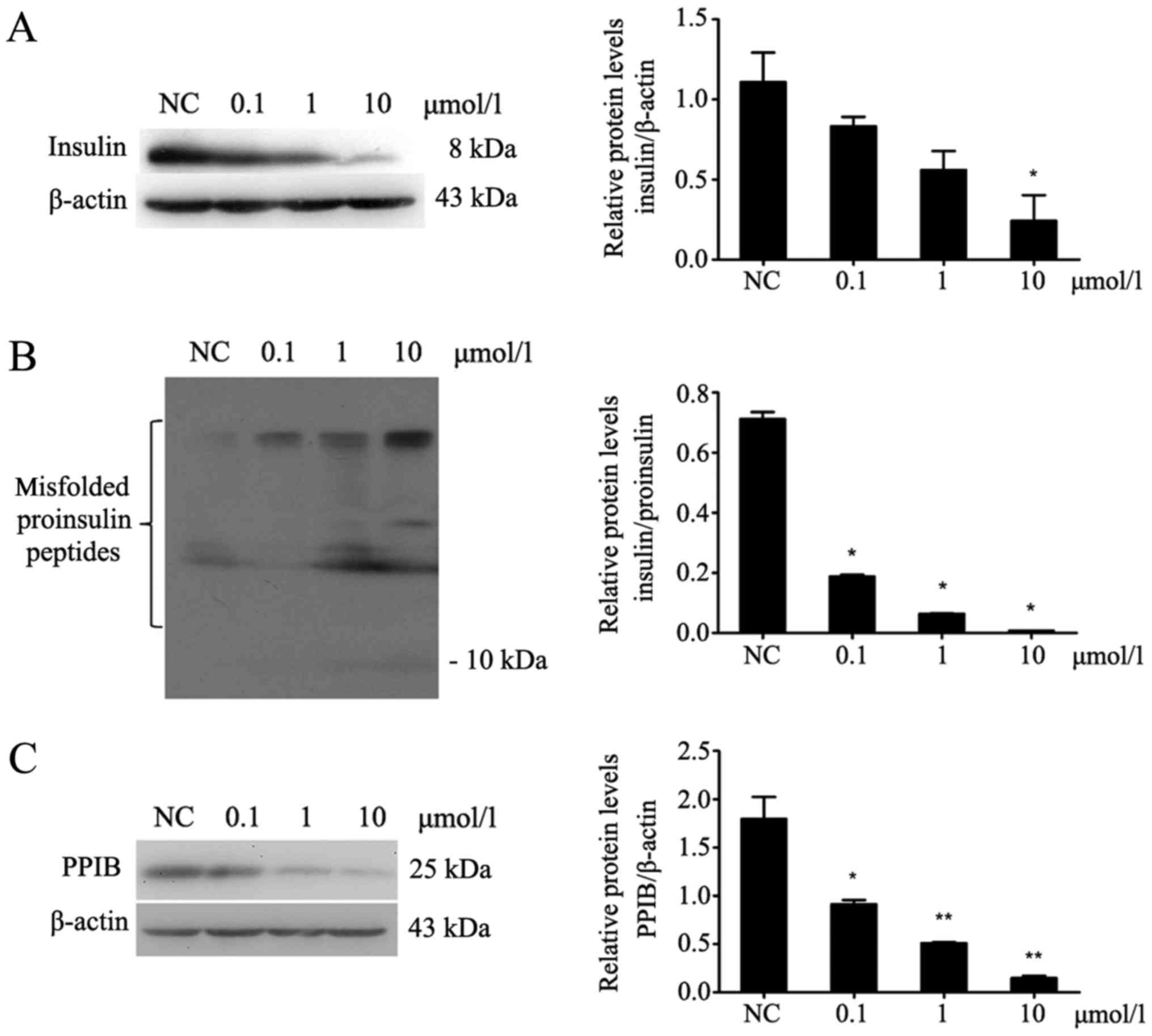
CsA inhibits the expression of insulin
and PPIB and increases the misfolding of proinsulin peptides in
MIN6 cells
After MIN6 cells were treated with different
concentrations of CsA for 24 h (Fig.
2), the protein expression of PPIB was decreased (P<0.05;
Fig. 2C). Additionally, insulin
expression in MIN6 cells was decreased (P<0.05; Fig. 2A), whereas the expression of
misfolded proinsulin peptides was increased (P<0.05; Fig. 2B).
CsA and PA upregulate ER stress and
the expression of apoptosis-related proteins
Cells were treated with CsA, PA or a combination of
both drugs for 24 h (Fig. 3).
Cleaved caspase-3, p-PERK, PERK, BIP and CHOP were upregulated
after the cells were exposed to CsA or PA (P<0.05; Fig. 3A and C). Thus, CsA and PA induced ER
stress-related apoptosis in MIN6 cells. The expression of PPIB and
insulin was inhibited by treatment with these two drugs.
Additionally, both CsA and PA caused the upregulation of misfolded
proinsulin peptides but the downregulation of insulin expression
(P<0.05; Fig. 3B).
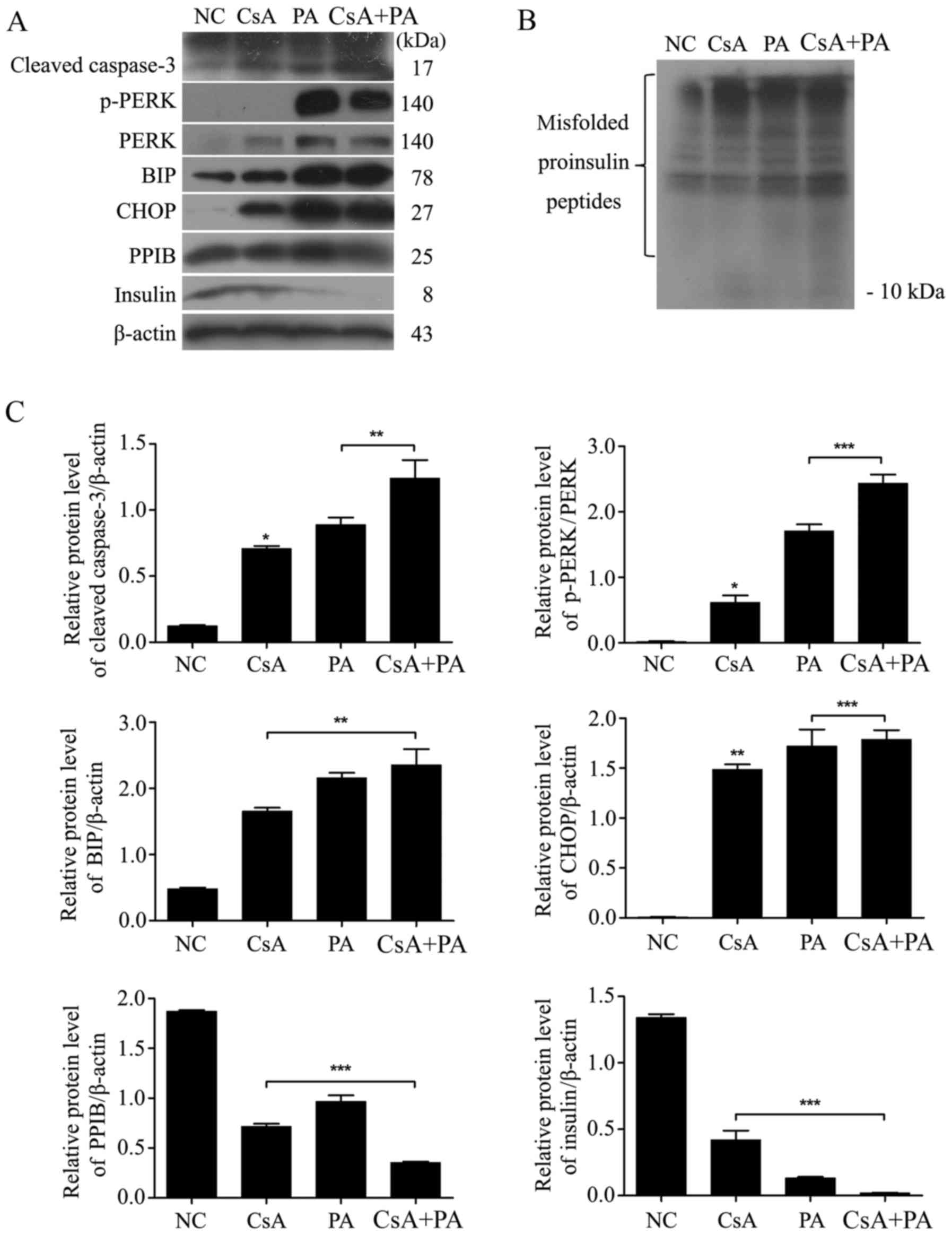 | Figure 3.CsA and PA upregulate ER stress and
the expression of apoptosis-associated proteins. (A) MIN6 cells
were treated with 1 µmol/l CsA, 0.5 mmol/l PA or a combination of
the two for 24 h. The expression of ER stress-induced cell
apoptosis-associated proteins (cleaved caspase-3, p-PERK, PERK, BIP
and CHOP) and insulin was then determined via a western blot assay.
(B) Misfolded proinsulin peptides were detected via a non-reducing
western blot assay. (C) The relative protein levels of cleaved
caspase-3, p-PERK, BIP and CHOP were upregulated, and those of PPIB
and insulin were downregulated. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and
***P<0.001 vs. NC, or as indicated. NC, normal control; CsA,
cyclosporin A; PA, palmitic acid; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; p-,
phosphorylated; PERK, protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum
kinase; BIP, binding immunoglobulin protein; CHOP, C/EBP homologous
protein; PPIB, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase B. |
Discussion
Cyclophilins are a family of proteins present in
vertebrates and other organisms. They bind to CsA, an
immunosuppressant that is commonly used to suppress rejection after
organ transplantation (19–20). The molecular mechanisms of
CsA-induced β cell apoptosis probably involve the downregulation of
cyclophilins.
This study in our research, MIN6 cells were treated
with different concentrations of CsA (0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5,
10, 50 and 100 µmol/l). There were no significant differences
between the control and 1 µmol/l CsA group. The results reveal
after treatment with CsA concentrations lower than 1 µmol/l. There
is a limitation of the current study, we should be confirmed the
apoptosis in some ways such as flow cytometry, but we have already
detected the expression of cleaved caspase-3. MIN6 cells were
treated with CsA for 24 h has obviously changes in apoptosis. So we
chose this time point (other time points not show). We used chose
three concentrations of CsA (0.1, 1 and 10 µmol/l) to study the
resultant effects on proinsulin folding.
In order to reveal the molecular mechanism of CsA
induced MIN6 apoptosis, proinsulin folding and UPR were detected.
Reducing and non-reducing SDS-PAGE assays were used to examine the
expression of misfolded proinsulin peptides. The reducing SDS-PAGE
buffer contained mercaptoethanol, which reduces disulfide bonds and
breaks down the complex structure of proinsulin. Meanwhile the
non-reducing SDS-PAGE-based western blot assay does not break
misfolded peptides into monomers (21,22).
Proinsulin has two forms in the ER: the correctly folded monomer
and misfolded proinsulin peptides. Misfolded proinsulin peptides
produce insoluble polymers of various molecular weights (23). Only correctly folded monomers can be
cleaved into mature insulin (24).
Proinsulin peptides of different molecular weights can be detected
via a non-reducing western blot assay. Our results demonstrated
that CsA decreased the expression of insulin and increased the
expression of misfolded proinsulin peptides. These findings suggest
that in cells treated with CsA, insulin mRNA can be translated into
proinsulin; however, this proinsulin could not become insulin in
the ER. CsA also down regulated the expression of PPIB. PPIB could
potential be a key protein involved in proinsulin folding. We
revealed the relationship between proinsulin and PPIB, but further
studies are needed to investigate the potential direct association
between them.
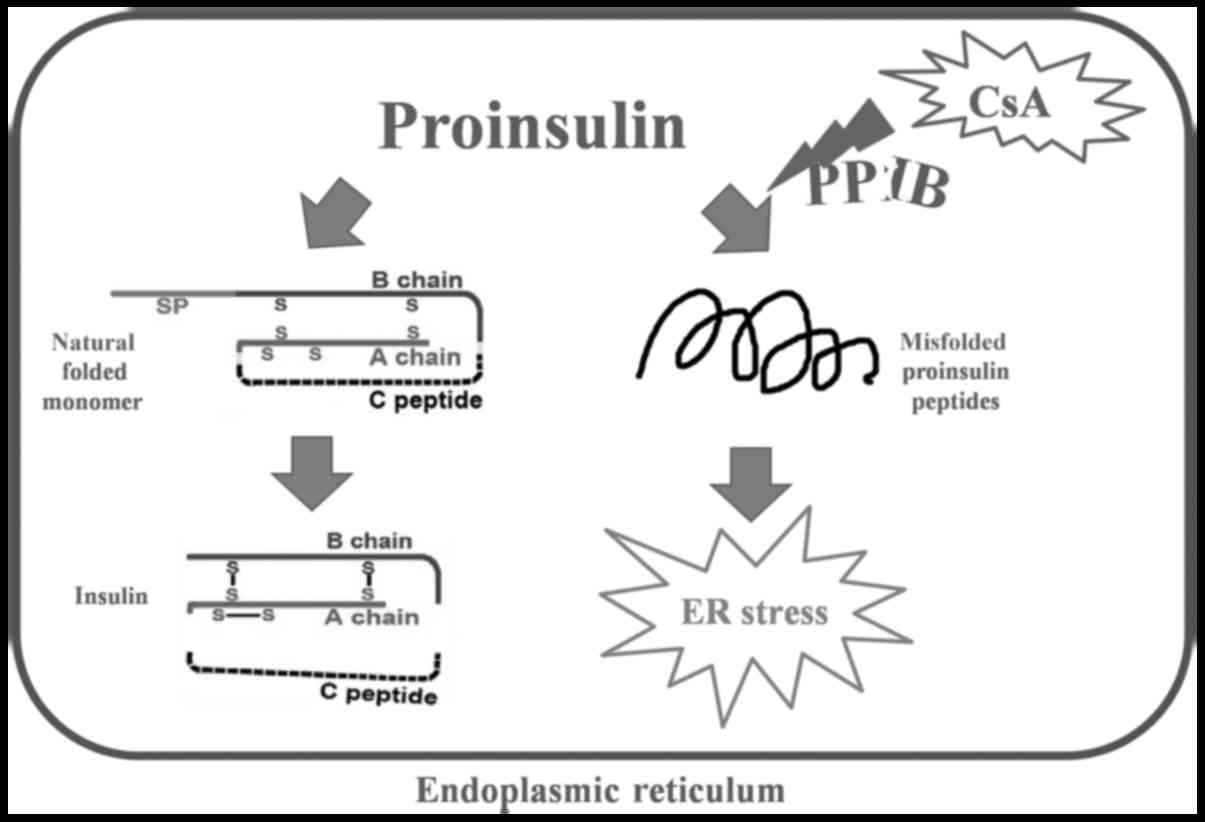
Proinsulin misfolding maybe the initial factor
causing β cell failure. If nonfunctional peptides accumulate in the
ER, ER stress-induced cell apoptosis occurs (25). To study the effect of misfolded
peptides in the ER. PA was used as a positive control for ER stress
(26,27). Certain ER stress-related proteins
were detected in response to PA treatment. CsA and PA can both
increase misfolded peptides, cleaved caspase-3, p-PERK, PERK, BIP
and CHOP. We was suggested to detect the mRNA levels at same time
to make a strong conclusion, and it will be accepted in further
research. These findings indicate that ER stress is activated in
response to an accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in
the lumen of the ER (28–30). Our data also revealed that ER stress
was induced by CsA and PA, both of which had similar effects on
proinsulin folding and ER stress (Fig.
4).
The purpose of this paper is to prove that the
proinsulin-fold disorder and endoplasmic reticulum stress occur at
the same time. A reasonable possible mechanism between proinsulin
and endoplasmic reticulum stress was mentioned in this manuscript.
Further research is needed to confirm the potential mechanism. In
conclusion, CsA induces β cell dysfunction and downregulates the
expression of PPIB. The reasonable underlying mechanism of this
phenomenon may be that PPIB-related proinsulin misfolding induces
ER stress in β cells.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge The Key
Laboratory of TCM Syndrome and Treatment of Yingbing of State
Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Nanjing, China) and
Research Center of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases (Jiangsu,
China) for the use of their laboratories. In addition, the authors
would like to thank Dr Xingjia Li, Dr Yu Chen, Dr Yijiao Xu and Dr
Wanwei Yang (Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of
Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Nanjing
University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China) for their useful
advice and assistance.
Funding
The present study was supported by The National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81270861) and
Foundation Research Project of Jiangsu Province (The Natural
Science Fund, grant no. BK2012887).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
GC, JW and CL designed research. XW, DZ, XM and QW
performed the experiments. CF analyzed the data, and XW and CF
wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and
reviewed the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Shivaswamy V, Boerner B and Larsen J:
Post-transplant diabetes mellitus: Causes, treatment, and impact on
outcomes. Endocr Rev. 37:37–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang X, Hu YC, Zhang RY, Jin DX, Jiang Y,
Zhang HN and Cong HL: Effect of cyclosporin A intervention on the
immunological mechanisms of coronary heart disease and restenosis.
Exp Ther Med. 12:3242–3248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bhat M, Pasini E, Copeland J, Angeli M,
Husain S, Kumar D, Renner E, Teterina A, Allard J, Guttman DS and
Humar A: Impact of immunosuppression on the metagenomic composition
of the intestinal microbiome: A systems biology approach to
post-transplant diabetes. Sci Rep. 7:102772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Azzi JR, Sayegh MH and Mallat SG:
Calcineurin inhibitors: 40 years later, can't live without. J
Immunol. 191:5785–5791. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Langsford D and Dwyer K: Dysglycemia after
renal transplantation: Definition, pathogenesis, outcomes, and
implications for management. World J Diabetes. 6:1132–1151. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Montero N and Pascual J: Immunosuppression
and Post-transplant Hyperglycemia. Curr Diabetes Rev. 11:144–154.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Palepu S and Prasad GV: New-onset diabetes
mellitus after kidney transplantation: Current status and future
directions. World J Diabetes. 6:445–455. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Øzbay LA, Smidt K, Mortensen DM, Carstens
J, Jørgensen KA and Rungby J: Cyclosporin and tacrolimus impair
insulin secretion and transcriptional regulation in INS-1E
beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 162:136–146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pereira MJ, Palming J, Rizell M, Aureliano
M, Carvalho E, Svensson MK and Eriksson JW: Cyclosporine A and
tacrolimus reduce the amount of GLUT4 at the cell surface in human
adipocytes: Increased endocytosis as a potential mechanism for the
diabetogenic effects of immunosuppressive agents. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 99:E1885–E1894. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bai Y, Wei Y, Wu L, Wei J, Wang X and Bai
Y: C/EBP β mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress regulated
inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation in
LPS-stimulated human periodontal ligament cells. Int J Mol Sci.
17:3852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu M, Wright J, Guo H, Xiong Y and Arvan
P: Proinsulin entry and transit through the endoplasmic reticulum
in pancreatic beta cells. Vitam Horm. 95:35–62. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ozawa S, Katsuta H, Suzuki K, Takahashi K,
Tanaka T, Sumitani Y, Nishida S, Yoshimoto K and Ishida H:
Estimated proinsulin processing activity of prohormone convertase
(PC) 1/3 rather than PC2 is decreased in pancreatic β-cells of type
2 diabetic patients. Endocr J. 61:607–614. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang X, Yuan Q, Tang W, Gu J, Osei K and
Wang J: Substrate-favored lysosomal and proteasomal pathways
participate in the normal balance control of insulin precursor
maturation and disposal in β-cells. PLoS One. 6:e276472011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim G, Kim JY and Choi HS: Peptidyl-prolyl
cis/trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 as a therapeutic target in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biol Pharm Bull. 38:975–979. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren LQ, Liu W, Li WB, Liu WJ and Sun L:
Peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase activity and molecular evolution
of vertebrate cyclophilin A. Yi Chuan. 38:736–745. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Humbert MV, Mendoza Almonacid HL, Jackson
AC, Hung MC, Bielecka MK, Heckels JE and Christodoulides M: Vaccine
potential of bacterial macrophage infectivity potentiator
(MIP)-like peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase) proteins.
Expert Rev Vaccines. 14:1633–1649. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cho KI, Orry A, Park SE and Ferreira PA:
Targeting the cyclophilin domain of Ran-binding protein 2 (Ranbp2)
with novel small molecules to control the proteostasis of STAT3,
hnRNPA2B1 and M-opsin. ACS Chem Neurosci. 6:1476–1485. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ernst K, Langer S, Kaiser E, Osseforth C,
Michaelis J, Popoff MR, Schwan C, Aktories K, Kahlert V, Malesevic
M, et al: Cyclophilin-facilitated membrane translocation as
pharmacological target to prevent intoxication of mammalian cells
by binary clostridial actin ADP-ribosylated toxins. J Mol Biol.
427:1224–1238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tafazoli A: Cyclosporine use in
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Pharmacokinetic approach.
Immunotherapy. 7:811–836. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Z and Zhang L: Treatment effect of
cyclosporine A in patients with painful bladder
syndrome/interstitial cystitis: A systematic review. Exp Ther Med.
12:445–450. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang J and Osei K: Proinsulin maturation
disorder is a contributor to the defect of subsequent conversion to
insulin in β-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 411:150–155. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Chen Y, Yuan Q, Tang W, Zhang X
and Osei K: Control of precursor maturation and disposal is an
early regulative mechanism in the normal insulin production of
pancreatic β-cells. PLoS One. 6:e194462011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yuan Q, Tang W, Zhang X, Hinson JA, Liu C,
Osei K and Wang J: Proinsulin atypical maturation and disposal
induces extensive defects in mouse Ins2+/Akita β-cells. PLoS One.
7:e350982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fu Z, Gilbert ER and Liu D: Regulation of
insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell
dysfunction in diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev. 9:25–53. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chan JY, Luzuriaga J, Maxwell EL, West PK,
Bensellam M and Laybutt DR: The balance between adaptive and
apoptotic unfolded protein responses regulates β-cell death under
ER stress conditions through XBP1, CHOP and JNK. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 413:189–201. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu C, Cui S, Zong C, Gao W, Xu T, Gao P,
Chen J, Qin D, Guan Q, Liu Y, et al: The orphan nuclear receptor
NR4A1 protects pancreatic β-cells from endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
stress-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 290:20687–20699. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kwak HJ, Choi HE, Jang J, Park SK, Bae YA
and Cheon HG: Bortezomib attenuates palmitic acid-induced ER
stress, inflammation and insulin resistance in myotubes via AMPK
dependent mechanism. Cell Signal. 28:788–797. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oh YS, Lee YJ, Kang Y, Han J, Lim OK and
Jun HS: Exendin-4 inhibits glucolipotoxic ER stress in pancreatic β
cells via regulation of SREBP1c and C/EBPβ transcription factors. J
Endocrinol. 216:343–352. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cumaoglu A, Arıcıoglu A and Karasu C:
Redox status related activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and
apoptosis caused by 4-hydroxynonenal exposure in INS-1 cells.
Toxicol Mech Methods. 24:362–367. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Reid DW, Chen Q, Tay AS, Shenolikar S and
Nicchitta CV: The unfolded protein response triggers selective mRNA
release from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 158:1362–1374. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|