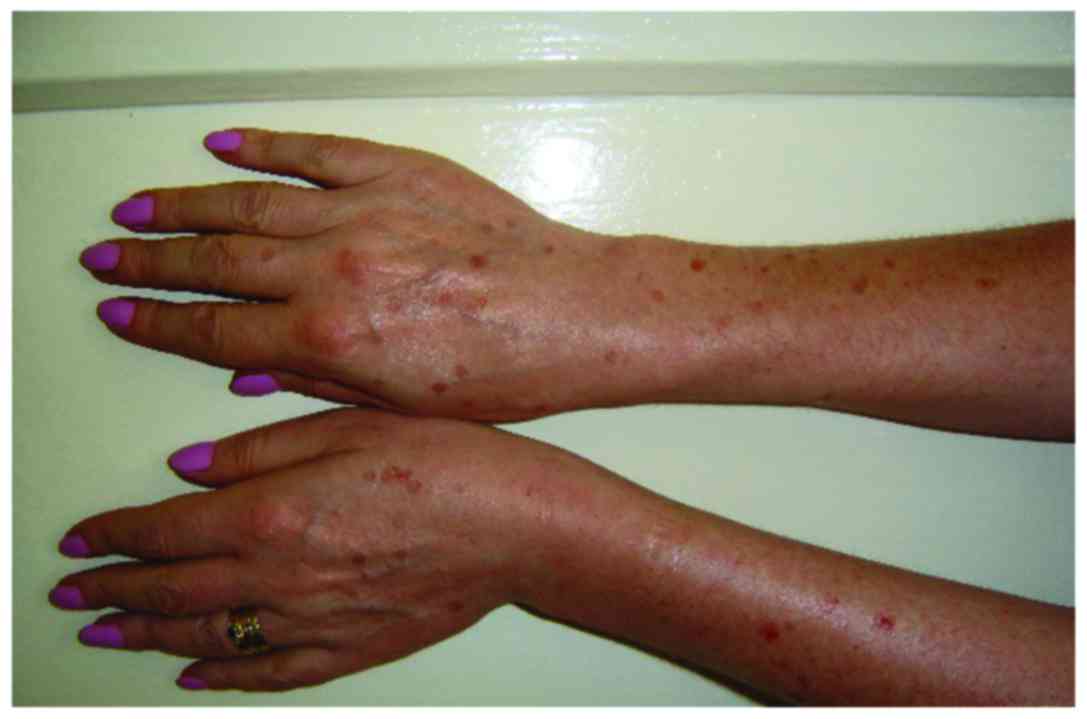
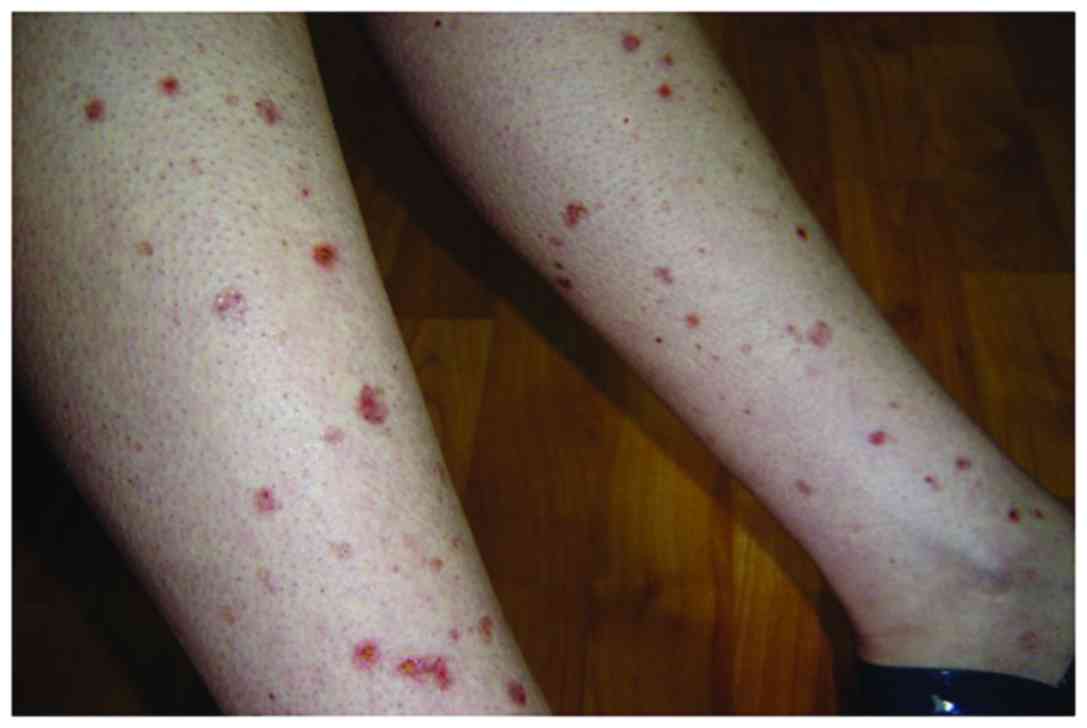
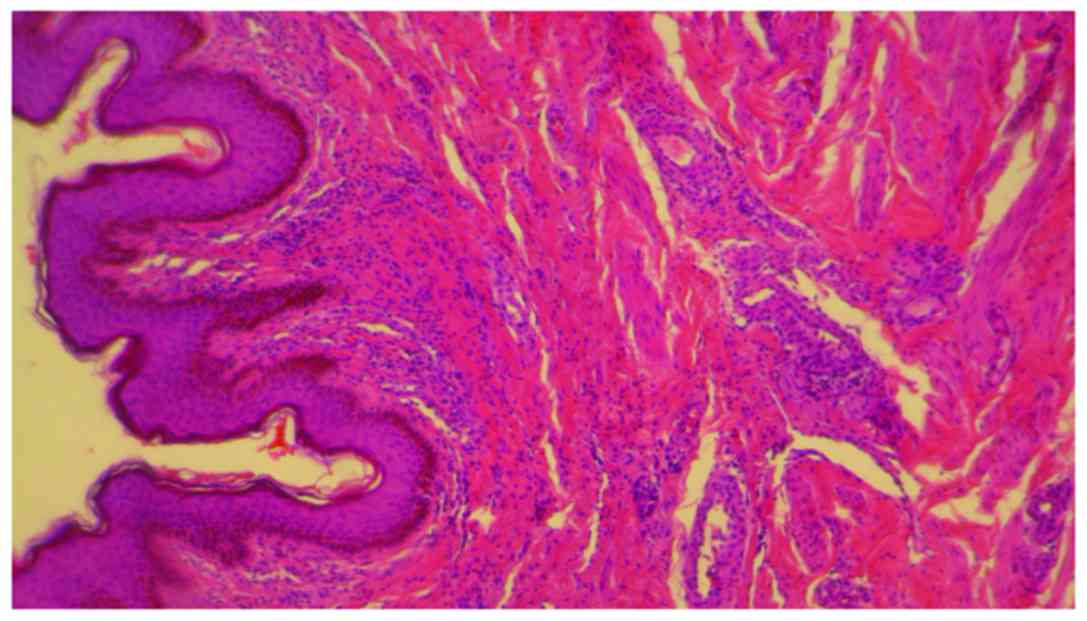
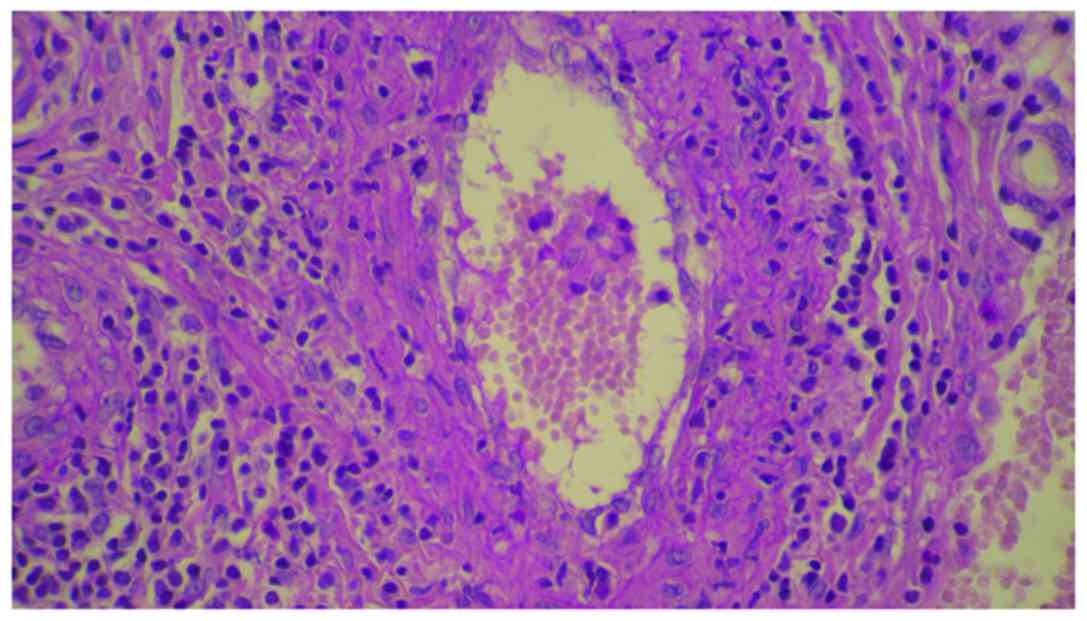
|
1
|
Brandi G, Venturi M, Dika E, Maibach H,
Patrizi A and Biasco G: Cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis due
to erlotinib: Just an adverse event or also a putative marker of
drug efficacy? Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 32:336–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Faye E, Bondon-Guitton E, Olivier-Abbal P
and Montastruc JL: French Network of Regional Pharmacovigilance
Centers: Spontaneous reporting of serious cutaneous reactions with
protein kinase inhibitors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 69:1819–1826.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sawada T, Suehiro M and Hiranuma O:
Cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis associated with erlotinib.
Indian J Dermatol. 61:2382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Boeck S, Wollenberg A and Heinemann V:
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis during treatment with the oral EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib. Ann Oncol. 18:1582–1583. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rezaković S, Paštar Z, Bukvić Mokos Z,
Pavliša G and Kovačević S: Erlotinib-induced rosacea-like
dermatitis. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 24:65–69. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rungtrakulchai R and Rerknimitr P:
Erlotinib induced target-like purpura. Dermatol Online J.
20:62014.
|
|
7
|
Zhu H, Zhu Z, Huang W, Cheng X, He J,
Xiong C and Han J: Common and uncommon adverse cutaneous reactions
to erlotinib: A study of 20 Chinese patients with cancer. Cutan
Ocul Toxicol. 37:96–99. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Panebianco M, Ragazzi M, Asensio NM,
Pagano M, Gnoni R and Boni C: A case of necrotizing vasculitis with
panniculitis, during sorafenib treatment for hepatocellular
carcinoma, appeared in disease progression. J Gastrointest Oncol.
5:E121–E124. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karadimou A, Migou M, Economidi A,
Stratigos A, Kittas C, Dimopoulos MA and Bamias A: Leukocytoclastic
vasculitis after long-term treatment with sunitinib: A case report.
Case Rep Oncol. 4:385–391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takahashi Y, Ebi N, Yamaguchi O, Fukusho
R, Sugimoto Y and Tsuruno K: A case of cutaneous vasculitis caused
by erlotinib treatment and a review of literature. Nihon Kokyuki
Gakkai Zasshi. 49:663–666. 2011.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hakeem AH, Aziz SA, lone AR, Bhat GM, Wani
B and Hussain I: Erlotinib induced vasculitis. JMSCR. 3:3890–3895.
2015.
|
|
12
|
Su BA, Shen WL, Chang ST, Feng LY, Wu CJ
and Feng YH: Successful rechallenge with reduced dose of erlotinib
in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma who developed
erlotinib-associated leukocytoclastic vasculitis: A case report.
Oncol Lett. 3:1280–1282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yuba T, Nagata K, Shiotsu S, Okano A,
Hatsuse M, Murakami S, Morihara K and Shimazaki C: Henoch-Schönlein
purpura induced by erlotinib (Tarceva): A case report. Nihon
Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 48:81–85. 2010.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin F, Zhu H, Kong L and Yu J: A spectrum
of cutaneous toxicities from erlotinib may be a robust clinical
marker for non-small-cell lung therapy: A case report and
literature review. Onco Targets Ther. 8:943–946. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu HB, Wu Y, Lv TF, Yao YW, Xiao YY, Yuan
DM and Song Y: Skin rash could predict the response to EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitor and the prognosis for patients with
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
PLoS One. 8:e551282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brănișteanu DE, Ianoşi SL, Dimitriu A,
Stoleriu G, Oanţǎ A and Brănișteanu DC: Drug-induced Rowell
syndrome, a rare and difficult to manage disease: A case report.
Exp Ther Med. 15:785–788. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gheorghe I, Tatu AL, Lupu I, Thamer O,
Cotar AI, Pircalabioru GG, Popa M, Cristea VC, Lazar V and
Chifiriuc MC: Molecular characterization of virulence and
resistance features in Staphylococcus aureus clinical
strains isolated from cutaneous lesions in patients with drug
adverse reactions. Rom Biotechnol Lett. 22:12321–12327. 2017.
|