Introduction
The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a novel
indicator of sub-clinical inflammation and has been identified as
an independent risk factor for postoperative outcome in patients
with various types of cancer (1).
Previous studies have demonstrated that an elevated NLR is a
significant adverse prognostic factor regarding overall survival
(OS), disease-free survival and progression-free survival of
metastatic or non-metastatic cancer patients (1). For liver cancer, Xue et al
(2) performed a meta-analysis of 26
studies comprising 4,461 patients, which indicated that a high NLR
was independently associated with poor OS and disease-free
survival. For colorectal cancer, Walsh et al (3) reported that the pre-operative NLR is an
independent risk factor and a predictor of worse OS and
cancer-specific survival (CSS). The prognostic value of the NLR has
also been confirmed in other cancer types, including small-cell
lung (4), gastric (5) and ovarian cancer (6).
Previous studies have demonstrated that the
preoperative NLR is a predictor of post-operative outcomes in
patients with either non-metastatic (7,8) or
metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) (9,10). To
date, several scoring systems and nomograms have been developed to
improve the accuracy of survival prediction for localized RCC,
including the Stage, Size, Grade, and Necrosis Score (SSIGN)
(11), the Leibovich score as a
modified version of the SSIGN score (12), the University of the California Los
Angeles Integrated Staging System (13) and Karakiewicz's nomogram (14). These predictive models include the
pathological tumor-nodes-metastasis (pTNM) stage and clinical
criteria (Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group or Karnofsky),
histological grading criteria (Fuhrman), imaging parameters (e.g.
tumor size) and biological criteria (e.g. hemoglobin, neutrophils).
However, the NLR has not been included in any of the abovementioned
prognostic scoring systems for RCC. As a sensitive indicator of the
inflammatory status, the NLR may be influenced by various clinical
factors. Several studies have confirmed the significant association
between the NLR and diabetes mellitus (DM) (15,16). In
addition, previous meta-analyses have indicated that DM increases
the risk of the occurrence of RCC (17,18);
furthermore, the increasing incidence of pre-existing DM may
increase the incidence of RCC. The aim of the present study was to
explore whether DM affects the NLR-based evaluation of the
prognosis of patients with RCC after surgery.
Patients and methods
Patients
The present study retrospectively reviewed 662
consecutive patients with non-metastatic RCC treated with
nephrectomy between January 2004 and July 2014 at the Department of
Urology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical
University, Wenzhou, China). Clinical data, including
clinicopathologic and hematologic records, were collected and
retrospectively analyzed.
Follow-up
Patients were generally followed up every 3–6 months
for the first 2 years and annually thereafter by performing blood
and urine tests, cystoscopy and image examination. Information on
patient death was obtained from outpatient medical records,
telephone interviews or the patient's social security death index.
The OS was defined as the interval from the time-point of surgery
to the date of death from all causes and metastasis-free survival
(MFS) was defined as the interval from surgery to the date of
recurrence of radiologically or histologically confirmed distant
metastasis, according to the treating physician's assessment and
radiologic criteria. The primary endpoint of the present study was
MFS.
Statistical analysis
The NLR was calculated as the neutrophil count
divided by the lymphocyte count. X-tile software (version 3.6.1;
Yale University, New Haven CT, USA) was applied to calculate the
discriminatory ability of NLR to identify the optimal cutoff value.
The association of the clinicopathologic characteristics with low
and high NLR was assessed using either Fisher's exact test or the
Student's t-test and Pearson's Chi-square test. Kaplan-Meier
survival curves were drawn to estimate OS and MFS and significant
differences were determined using the log-rank test. Univariate
analysis was performed with using Cox logistic regression.
Variables with P<0.05 in the univariate analysis were included
in the subsequent multivariate analysis. Multivariate analysis was
performed using Cox regression analysis. All tests were two-sided
and P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference. Statistical analyses were performed using
the SPSS software package version 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY,
USA).
Results
Clinicopathological
characteristics
A total of 662 consecutive patients were included in
the current study, with 243 (36.71%) females and 419 (63.29%)
males. The mean age of the cohort was 61.70 (12.65) years. To
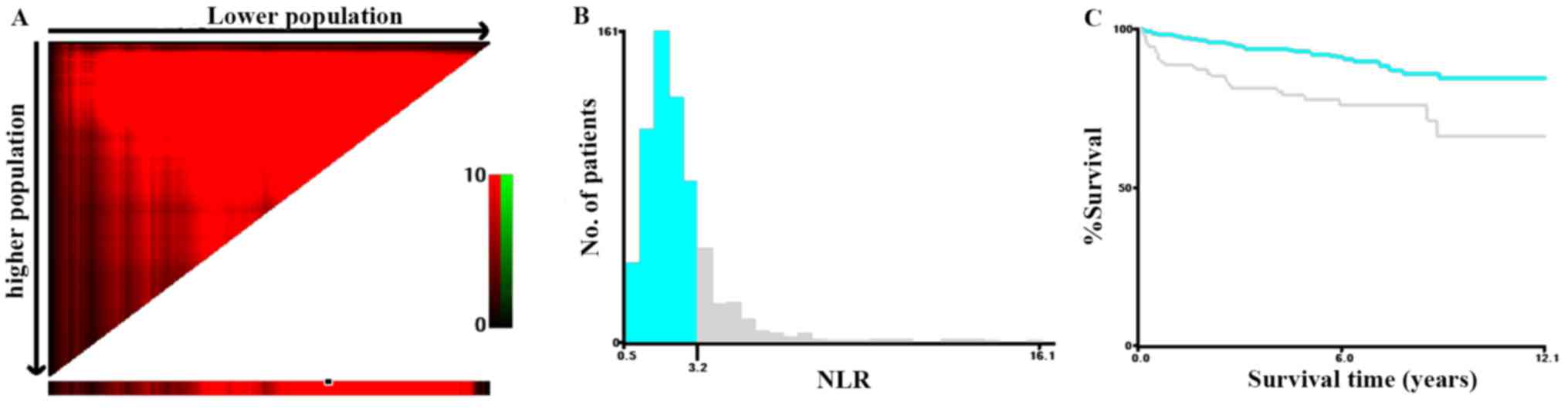
determine the most suitable cutoff value for NLR, X-tile software
was applied with the MFS as the endpoint, and a cutoff value of
NLR=3.2 was obtained (Fig. 1). The
χ2 log-rank value of NLR was 21.15. Therefore, patients
were divided into two groups according to the cutoff value:
NLR<3.2 and NLR≥3.2. The patient population comprised 519
patients (78.40%) with a low NLR and 143 (21.60%) with a high NLR.
A total of 662 patients with non-metastatic RCC, with a mean
follow-up duration of 59.21 months (median, 50.35 months; range,
30.30–85.08 months) were included in the present study. During the
follow-up, 74 patients (11.18%) experienced distant metastasis and
60 (9.06%) died, of which 41 cases (6.19%) were cancer-specific
deaths. The baseline clinicopathologic characteristics are
summarized in Table I. Patients with
a high NLR were more likely to be older, and had higher neutrophil
and lower lymphocyte counts, as well as an advanced pathologic T
stage and tumor grade (all P<0.05). The two groups were
comparable with regard to sex, American Society of
Anesthesiologists (ASA) grade, body mass index (BMI), type of
surgery, mean tumor size, histologic subtype, platelet count and
history of DM.
 | Table I.Patient characteristics and influence
of the NLR. |
Table I.
Patient characteristics and influence
of the NLR.
| Factor | Total (n=662) | NLR<3.2
(n=519) | NLR≥3.2 (n=143) | P-value |
|---|
| Age (years) | 61.70±12.65 | 61.10±12.42 | 63.90±13.27 | 0.019 |
| Sex |
|
|
| 0.203 |
|
Female | 243 (36.71) | 197 (37.96) | 46 (32.17) |
|
| Male | 419 (63.29) | 322 (62.04) | 97 (67.83) |
|
| ASA grade |
|
|
| 0.110 |
| I | 85 (12.84) | 72 (13.87) | 13 (9.09) |
|
| II | 532 (80.36) | 416 (80.16) | 116 (81.12) |
|
|
III | 45 (6.80) | 31 (5.97) | 14 (9.79) |
|
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.16±3.04 | 23.26±3.12 | 22.82±2.71 | 0.130 |
| Type of
surgery |
|
|
| 0.262 |
| Partial
nephrectomy | 143 (21.60) | 117 (22.54) | 26 (18.18) |
|
| Radical
nephrectomy | 519 (78.40) | 402 (77.46) | 117 (81.82) |
|
| Mean tumor size
(SD; cm) | 4.91 (3.42) | 4.85 (3.46) | 5.14 (3.30) | 0.375 |
| Pathological T
stage |
|
|
| 0.046 |
|
pT1 | 514 (77.64) | 415 (79.96) | 99 (69.23) |
|
|
pT2 | 77 (11.63) | 56 (10.79) | 21 (14.69) |
|
|
pT3 | 62 (9.37) | 42 (8.09) | 20 (13.98) |
|
|
pT4 | 9 (1.36) | 6 (1.16) | 3 (2.10) |
|
| Fuhrman grade |
|
|
| 0.005 |
| 1 | 210 (31.72) | 173 (33.33) | 37 (25.87) |
|
| 2 | 282 (42.60) | 229 (44.12) | 53 (37.06) |
|
| 3 | 148 (22.36) | 101 (19.46) | 47 (32.87) |
|
| 4 | 22 (3.32) | 16 (3.09) | 6 (4.20) |
|
| Histologic
subtype |
|
|
| 0.682 |
| Clear
cell carcinoma | 581 (87.76) | 454 (87.48) | 127 (88.81) |
|
|
Papillary carcinoma | 41 (6.20) | 31 (5.97) | 10 (6.99) |
|
|
Chromophobe carcinoma | 36 (5.44) | 31 (5.97) | 5 (3.50) |
|
|
Collecting duct carcinoma | 1 (0.15) | 1 (0.19) | 0 (0.00) |
|
|
Unclassified carcinoma | 3 (0.45) | 2 (0.39) | 1 (0.70) |
|
| Mean nutrophil
count ×109 (mean; SD) | 4.12±1.68 | 3.63±1.15 | 5.88±2.08 | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte count
×109 (mean; SD) | 1.78±0.62 | 1.93±0.58 | 1.22±0.39 | <0.001 |
| Platelet count
(mean; SD) | 216.46±70.66 | 213.97±68.01 | 225.48±79.13 | 0.085 |
| Diabetes
mellitus |
|
|
| 0.938 |
| No | 438 (66.16) | 343 (66.09) | 95 (66.43) |
|
|
Yes | 224 (33.84) | 176 (33.91) | 48 (33.57) |
|
Factors affecting OS in total
subjects
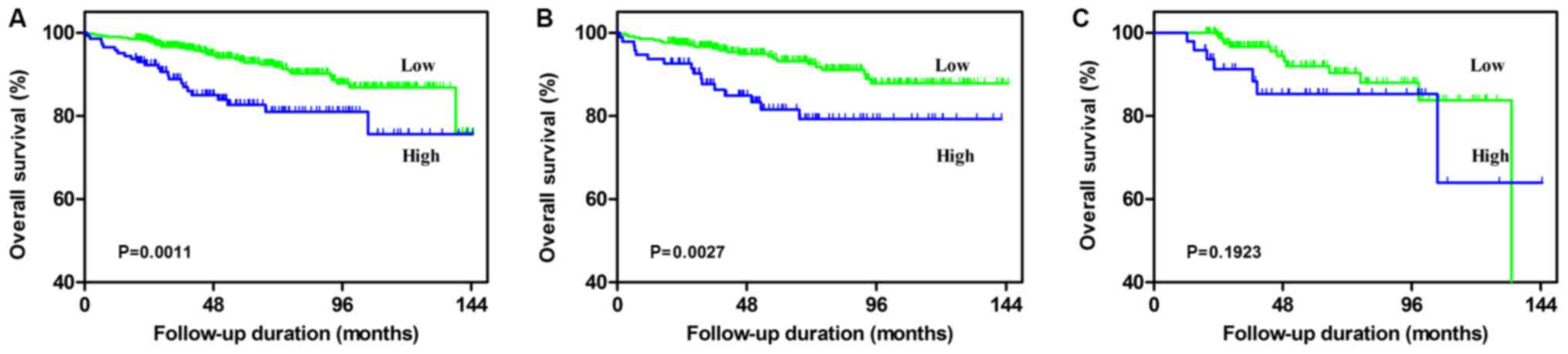
Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to
determine the predictive value of the NLR value regarding the
clinical prognosis of patients with RCC. According to the
univariate analysis, an NLR of ≥3.2, a higher age (≥65 years), a
higher ASA grade (≥III), a higher BMI (≥25 kg/m2), a
larger mean tumor size (≥7 cm), a higher pathological T stage (≥3)
and a higher Fuhrman grade (≥3) were significantly associated with
poorer OS (all P<0.05; Table II
and Fig. 2A). Multivariate analysis
revealed that an NLR of ≥3.2, a higher age (≥65 years), a higher
BMI (≥25 kg/m2), a larger mean tumor size (≥7 cm), a
higher pathological T stage (≥3) and higher a Fuhrman grade (≥3)
were independent negative prognostic factors regarding OS.
 | Table II.Univariate and multivariate analysis
of the predictive value of clinicopathological parameters for the
overall survival of patients with renal cell carcinoma. |
Table II.
Univariate and multivariate analysis
of the predictive value of clinicopathological parameters for the
overall survival of patients with renal cell carcinoma.
|
| Total | With diabetes
mellitus | Without diabetes
mellitus |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Factor | Univariate analysis
HR (95% CI), P-value | Multivariate
analysis HR (95% CI), P-value | Univariate analysis
HR (95% CI), P-value | Multivariate
analysis HR (95% CI), P-value | Univariate analysis
HR (95% CI), P-value | Multivariate
analysis HR (95% CI), P-value |
|---|
| Sex (male vs.
female) | 1.50 (0.86–2.64),
0.155 |
| 2.95 (0.86–10.14),
0.085 |
| 1.16 (0.61–2.22),
0.652 |
|
| Age (≥65 vs. <65
years) | 4.00 (2.19–7.28),
<0.001 | 3.27 (1.77–6.04),
<0.001 | 3.81 (1.26–11.54),
0.018 | 4.64 (1.47–14.70),
0.009 | 4.01 (1.96–8.20),
<0.001 | 3.08 (1.46–6.50),
0.003 |
| ASA grade (≥III vs.
<III) | 3.33 (1.55–5.80),
0.001 | 1.61 (0.82–3.18),
0.169 | 1.37 (0.38–4.95),
0.632 |
| 4.22 (1.94–9.16),
<0.001 | 2.56 (1.08–6.07),
0.032 |
| BMI (≥25 vs. <
25 kg/m2) | 0.28 (0.11–0.70),
0.006 | 0.27 (0.11–0.67),
0.005 | 0.48 (0.16–1.45),
0.192 |
| 0.10 (0.01–0.70),
0.020 | 0.10 (0.01–0.70),
0.021 |
| Type of surgery
(partial nephrectomy vs. radical nephrectomy) | 0.51 (0.22–1.18),
0.115 |
| 0.62 (0.14–2.69),
0.521 |
| 0.47 (0.17–1.32),
0.152 |
|
| Mean tumor size (≥7
vs. <7 cm) | 2.96 (1.75–5.01),
<0.001 | 2.02 (1.17–3.48),
0.012 | 1.42 (0.51–3.99),
0.505 |
| 3.84 (2.05–7.19),
<0.001 | 3.15 (1.59–6.25),
0.001 |
| Pathological T
stage (≥3 vs. <3) | 4.40 (2.50–7.74),
<0.001 | 3.24 (1.80–5.85),
<0.001 | 5.98 (1.64–21.82),
0.007 | 9.77 (2.45–39.02),
0.001 | 4.82 (2.51–9.26),
<0.001 | 2.83 (1.38–5.83),
0.005 |
| Fuhrman grade (≥3
vs. <3) | 2.84 (1.71–4.72),
<0.001 | 2.00 (1.19–3.37),
0.009 | 3.02 (1.25–7.31),
0.014 | 2.91 (1.20–7.08),
0.019 | 2.77 (1.49–5.16),
0.001 | 1.66 (0.86–3.19),
0.132 |
| Histologic subtype
(clear cell carcinoma vs. non-clear cell carcinoma) | 1.61 (0.82–3.18),
0.170 |
| 2.78 (0.97–7.95),
0.057 |
| 1.06 (0.41–2.71),
0.905 |
|
| NLR (≥3.2 vs.
<3.2) | 2.32 (1.38–3.90),
0.001 | 1.77 (1.04–3.01),
0.037 | 1.84 (0.73–4.66),
0.192 |
| 2.55 (1.35–4.81),
0.003 | 2.03 (1.05–3.93),
0.036 |
| Diabetes mellitus
(Positive vs. negative) | 1.12 (0.65–1.90),
0.712 |
|
|
|
|
|
Factors affecting MFS in total
subjects
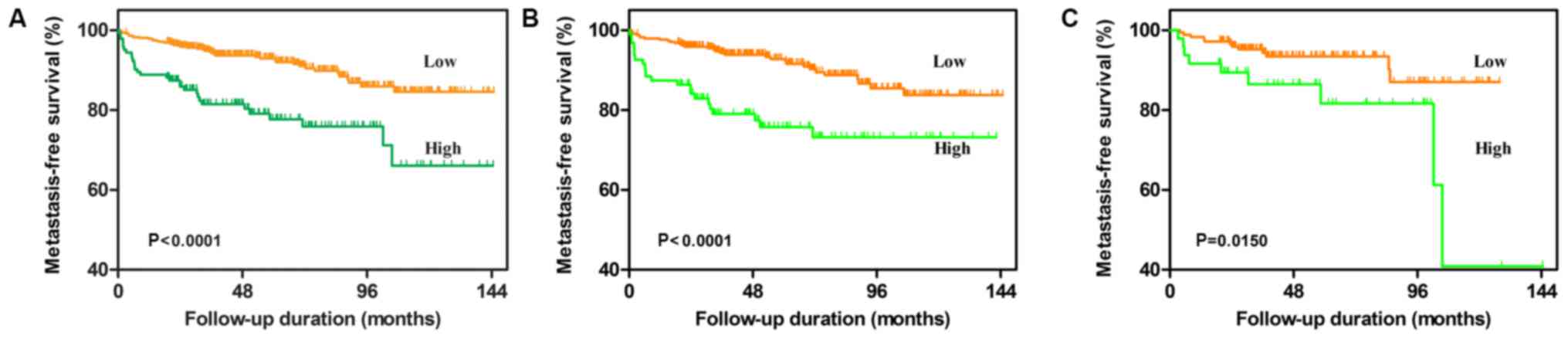
According to the univariate analysis, an NLR of
≥3.2, a higher age (≥65 years), a higher ASA grade (≥III), a higher
BMI (≥25 kg/m2), a larger mean tumor size (≥7 cm), a
higher pathological T stage (≥3) and a higher Fuhrman grade (≥3)
were significantly associated with poor MFS (All P<0.05;
Table III and Fig. 3A). Multivariate analysis revealed
that an NLR of ≥3.2, a higher age (≥65 years), a higher BMI (≥25
kg/m2), a larger mean tumor size (≥7 cm), a higher
pathological T stage (≥3) and a higher Fuhrman grade (≥3) were
independent prognostic factors associated with poor MFS.
 | Table III.Univariate and multivariate analysis
of clinicopathological parameters for the prediction of
metastatic-free survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma. |
Table III.
Univariate and multivariate analysis
of clinicopathological parameters for the prediction of
metastatic-free survival in patients with renal cell carcinoma.
|
| Total | With diabetes
mellitus | Without diabetes
mellitus |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Factor | Univariate analysis
HR (95% CI), P-value | Multivariate
analysis HR (95% CI), P-value | Univariate analysis
HR (95% CI), P-value | Multivariate
analysis HR (95% CI), P-value | Univariate analysis
HR (95% CI), P-value | Multivariate
analysis HR (95% CI), P-value |
|---|
| Sex (male vs.
female) | 1.65 (0.99–2.76),
0.055 |
| 2.42 (0.81–7.21),
0.112 |
| 1.46 (0.81–2.63),
0.203 |
|
| Age (≥65 vs. <65
years) | 2.67 (1.64–4.35),
<0.001 | 2.24 (1.36–3.69),
0.002 | 3.55 (1.29–9.73),
0.014 | 3.35 (1.17–9.56),
0.024 | 2.45 (1.39–4.29),
0.002 | 1.94 (1.08–3.50),
0.028 |
| ASA grade (≥III vs.
<III) | 2.14 (1.10–4.18),
0.025 | 1.37 (0.69–2.73),
0.363 | 0.89 (0.20–3.86),
0.873 |
| 3.05 (1.44–6.48),
0.004 | 2.74 (1.20–6.27),
0.017 |
| BMI (≥25 vs. <25
kg/m2) | 0.32 (0.15–0.69),
0.004 | 0.32 (0.14–0.69),
0.004 | 0.46 (0.16–1.39),
0.169 |
| 0.22 (0.07–0.71),
0.011 | 0.22 (0.07–0.72),
0.012 |
| Type of surgery
(partial nephrectomy vs. radical nephrectomy) | 0.50 (0.24–1.05),
0.068 |
| 0.77 (0.23–2.61),
0.670 |
| 0.41 (0.16–1.03),
0.058 |
|
| Mean tumor size (≥7
vs. <7 cm) | 2.80 (1.74–4.52),
<0.001 | 2.07 (1.27–3.38),
0.004 | 1.84 (0.71–4.77),
0.210 |
| 3.24 (1.86–5.66),
<0.001 | 3.17 (1.73–5.78),
<0.001 |
| Pathological T
stage (≥3 vs. <3) | 3.26 (1.89–5.61),
<0.001 | 2.49 (1.42–4.36),
0.001 | 3.28 (0.93–11.63),
0.005 | 3.24 (0.54–3.68),
0.009 | 3.21 (1.74–5.91),
<0.001 | 2.06 (1.08–3.94),
0.028 |
| Fuhrman grade (≥3
vs. <3) | 2.60 (1.65–4.11),
<0.001 | 1.90 (1.19–3.03),
0.007 | 2.28 (0.96–5.42),
0.013 | 2.02 (1.54–3.68),
0.011 | 2.71 (1.58–4.66),
<0.001 | 1.88 (1.08–3.28),
0.026 |
| Histologic subtype
(clear cell carcinoma vs. non-clear cell carcinoma) | 1.40 (0.74–2.67),
0.302 |
| 3.60 (1.28–10.12),
0.015 | 2.75 (0.87–8.67),
0.085 | 0.93 (0.40–2.17),
0.860 |
|
| NLR (≥3.2 vs.
<3.2) | 2.82 (1.78–4.48),
<0.001 | 2.31 (1.45–3.70),
<0.001 | 2.80 (1.18–6.66),
0.015 | 2.03 (0.82–5.04),
0.128 | 2.84 (1.64–4.90),
<0.001 | 2.57 (1.47–4.49),
0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus
(positive vs. negative) | 0.85 (0.51–1.42),
0.536 |
|
|
|
|
|
Subgroup analysis
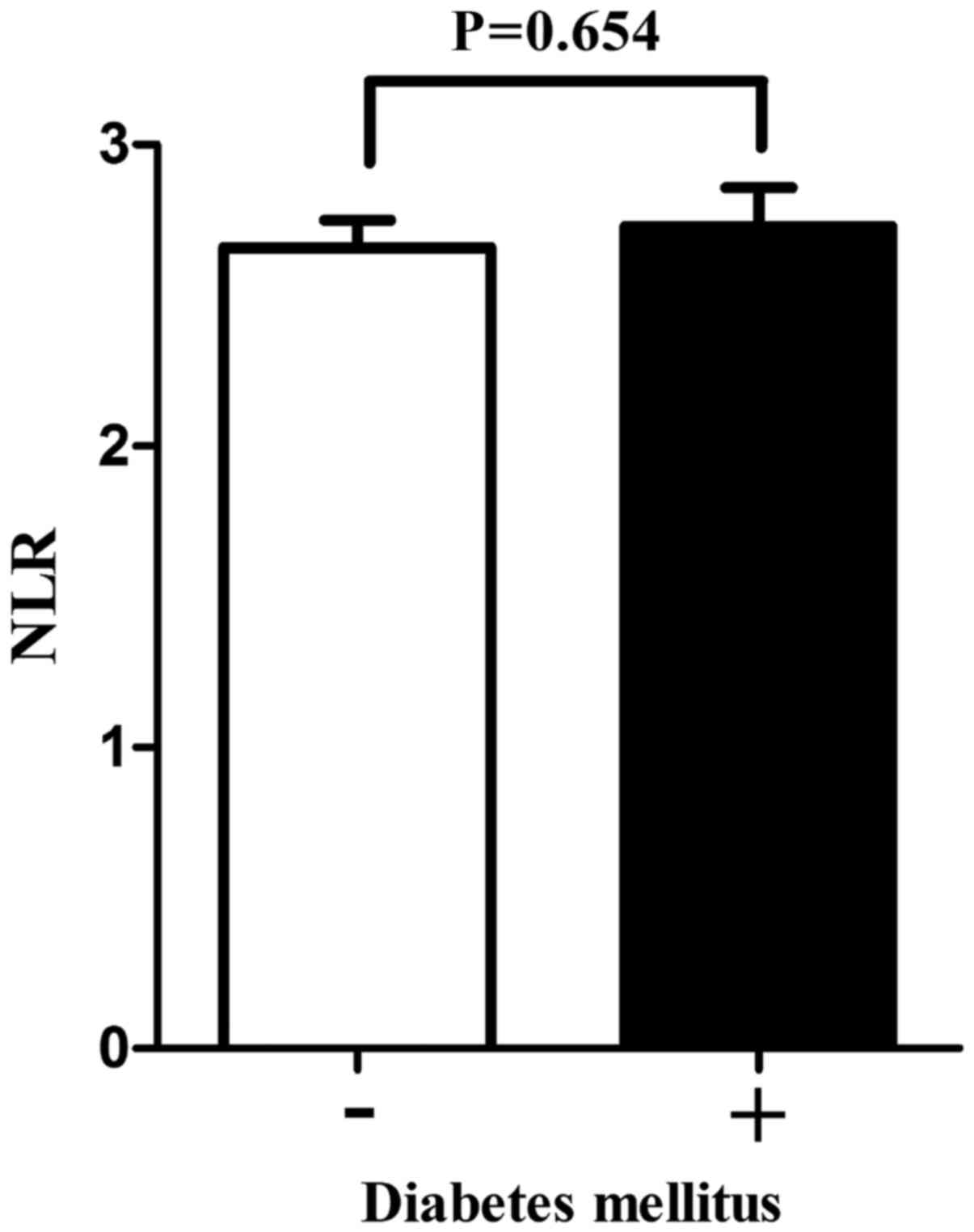
The patients were then divided into two subgroups
according to the absence or presence of DM. There was no
significant difference in NLR values between the two groups as
indicated by the t-test (P=0.654; Fig.
4). Furthermore, according to univariate analysis, DM did not
significantly affect OS or MFS (P=0.712 or 0.536, respectively), so
that no subsequent multivariate analysis was performed for this
factor. Kaplan-Meier analysis indicated that in the non-DM group, a
high pre-operative NLR (≥3.2) was significantly associated with a
worse OS and MFS (Fig. 2C and
3C). While a high NLR was still
associated with MFS in the DM group, it was no longer associated
with OS (Fig. 2C and 3C). Uni- and multivariate analysis of
factors affecting survival was then performed for the DM and non-DM
subgroups individually, as summarized in Tables II and III. In the non-DM group, the results
demonstrated that a high NLR was still an independent predictive
factor of poor OS and MFS in patients with RCC. However, in the DM
group, an NLR of ≥3.2 was not a significant independent prognostic
factor.
Discussion
According to previous studies, an elevated NLR is
associated with poor prognosis for patients with RCC (7–10). In
the present study, a retrospective review was performed to
investigate the correlation between the pre-operative NLR and the
post-surgical outcomes for patients with RCC. In line with the
results of previous studies (1,7–10), it was demonstrated that a high NLR
has a prognostic value in patients with RCC. A high NLR was
associated with old age, high neutrophil and lymphocyte counts, as
well as an advanced pathologic T stage and tumor grade. In
addition, multivariate analysis identified that an NLR of ≥3.2 is
an independent adverse prognostic factor for RCC patients. The
present study therefore confirmed that NLR is a significant
prognostic factor for RCC and may be useful for tailoring therapies
for patients with RCC. However, unlike other systemic inflammatory
indicators, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and the
platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, NLR has still not been incorporated
in any clinical evaluation system for RCC. Therefore, the primary
aim of the present study was to identify the possible reasons.
Various studies have emphasized the importance of
inflammation in carcinogenesis (19–21).
According to them, one potential mechanism is that the response of
systemic inflammation to various physiological challenges is
characterized by increased neutrophil and decreased lymphocyte
counts, largely favoring tumor development by preventing or
suppressing the activation of anti-tumor cells in the immune
system. Of note, cancer cells themselves are able to recruit and
activate various types of leukocytes, particularly neutrophils and
monocytes (22). Therefore, an
increased NLR is thought to provide a favorable microenvironment
for tumor development and metastasis. The NLR has also been
associated with poor prognosis in conditions other than cancer,
including cardiovascular diseases (23,24),
respiratory diseases (25) and
hypertension (26). Therefore, NLR
is a non-specific parameter, which may be affected by concurrent
conditions, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and
coronary chronic total occlusion.
Previous meta-analyses indicated that DM may
increase the risk of RCC (17,18). Of
note, an increased NLR was also reported to be associated with DM,
and a high NLR value may be a significant predictive marker of DM
(15). In the present study, a high
NLR was identified as an independent risk factor for RCC regarding
OS and MFS. No significant difference in NLR values was identified
between the patient groups with and without DM, and DM was not a
significant influencing factor of OS and MFS according to the
multivariate regression analysis. However, in the multivariate
analysis for the subgroup of patients with DM, an elevated NLR was
no longer identified as an independent predictive factor of OS and
MFS, but it was still a significant independent predictor in the
subgroup of patients without DM. The HR value of NLR for OS and MFS
increased from 1.77 in the total subject group to 2.03 in the
non-DM group. A further increase was identified from 2.31 in the
total subject group to 2.57 in the non-DM group. Furthermore, the
results of multivariate analysis demonstrate that an elevated NLR
is no longer identified as the independent factor of OS and MFS in
the DM group, but may still serve as an independent predictor in
patients without DM. All of the above indicates that DM is a
disturbance factor in the evaluation of prognosis of RCC using NLR.
The link between DM and RCC-associated mortality has been evaluated
in several previous studies. In 2013, Ha et al (27) published a multi-institutional
analysis including a total of 2,597 patients, revealing that DM is
an independent prognostic factor for recurrence-free survival
(RFS), CSS and OS. Another meta-analysis published in 2015
including a total of 20,199 patients, also revealed a significant
negative impact of DM on OS, CSS and RFS in patients with RCC
(28). Therefore, more attention
should be paid when evaluating the prognosis of patients with RCC
based on the NLR and DM.
All of the factors included in the pTNM
classification are able to provide reliable prognostic information.
In addition, these factors, e.g. the pathological T stage, are
confirmed from pathological specimens and are stable predictors
that are not influenced by any physiological factors. However, the
most widely used prognostic nomograms and risk scores for RCC,
which are based on the pTNM stage, are established
post-operatively. These conventional prognostic factors have
limited accuracy. Furthermore, it is also important for clinical
surgeons to identify prognostic factors prior to the surgery in
order to conceive patient-specific therapeutic strategies. In
recent years, the prognostic value of biomarkers of inflammation,
including the NLR and CRP, has been evidenced in patients with
cancer. Hu et al (7) reported
that the NLR is superior to CRP as a predictor of RCC. However, the
NLR is easily affected by numerous physiological factors, but its
application still has potential value in patients with no
underlying conditions (e.g. DM or cardiopulmonary diseases), as it
is easily measured, inexpensive and repeatable.
Of note, the present study has several limitations.
First, it was a retrospective single-center study. It may be argued
that the size of the study population was insufficient; however,
the results were representative and reliable, as our department is
the largest urologic cancer center in the South of Zhejiang
Province and provides access to a wide variety of patients with RCC
Furthermore, the cutoff value of NLR was different in other studies
(29). However, a threshold of NLR=3
is considered reasonable for RCC (29), which is close to the cutoff value of
NLR=3.2 used in the present study. Finally, the measurement of NLR
may be complicated by concurrent conditions, including infections
and inflammation, as well as by certain medications. In the present
study, all of the blood specimens were obtained prior to surgery.
In addition, surgeons commonly delay procedures for patients with
active infections. Therefore, it is unlikely that the NLR was
influenced by any infections. However, the complicating effect of
concurrent inflammatory conditions was not completely excluded.
In conclusion, the present study indicated that the
prognostic value of NLR for patients with RCC was impaired by
concurrent DM, as indicated by a subgroup analysis of patients with
and without DM. It is therefore suggested that DM should be
considered when evaluating the prognostic value of NLR in patients
with RCC.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Editage for English language
editing.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
XG conceived and designed the study, YZ, BL, and YJ
acquired the data, YP and QW analyzed and interpreted the data, and
XG drafted the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the ethics
committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical
University (Wenzhou, China). The study protocol is in accordance
with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
RCC
|
renal cell carcinoma
|
|
NLR
|
neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio
|
|
DM
|
diabetes mellitus
|
|
OS
|
overall survival
|
|
MFS
|
metastasis-free survival
|
|
CSS
|
cancer-specific survival
|
|
SSIGN
|
Stage, Size, Grade and Necrosis
Score
|
References
|
1
|
Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Šeruga B,
Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocaña A, Leibowitz-Amit R, Sonpavde G,
Knox JJ, Tran B, et al: Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 106:dju1242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xue TC, Zhang L, Xie XY, Ge NL, Li LX,
Zhang BH, Ye SL and Ren ZG: Prognostic significance of the
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in primary liver cancer: A
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e960722014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walsh SR, Cook EJ, Goulder F, Justin TA
and Keeling NJ: Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor
in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 91:181–184. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kang MH, Go SI, Song HN, Lee A, Kim SH,
Kang JH, Jeong BK, Kang KM, Ling H and Lee GW: The prognostic
impact of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with
small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 111:452–460. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lieto E, Galizia G, Auricchio A, Cardella
F, Mabilia A, Basile N, Del Sorbo G, Castellano P, Romano C,
Orditura M and Napolitano V: Preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte
ratio and lymphocyte to monocyte ratio are prognostic factors in
gastric cancers undergoing surgery. J Gastrointest Surg.
21:1764–1774. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cho H, Hur HW, Kim SW, Kim SH, Kim JH, Kim
YT and Lee K: Pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is
elevated in epithelial ovarian cancer and predicts survival after
treatment. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 58:15–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu H, Yao X, Xie X, Wu X, Zheng C, Xia W
and Ma S: Prognostic value of preoperative NLR, dNLR, PLR and CRP
in surgical renal cell carcinoma patients. World J Urol.
35:261–270. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohno Y, Nakashima J, Ohori M, Hatano T and
Tachibana M: Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an
independent predictor of recurrence in patients with nonmetastatic
renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 184:873–878. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cetin B, Berk V, Kaplan MA, Afsar B, Tufan
G, Ozkan M, Isikdogan A, Benekli M, Coskun U and Buyukberber S: Is
the pretreatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio an important
prognostic parameter in patients with metastatic renal cell
carcinoma? Clin Genitourin Cancer. 11:141–148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fox P, Hudson M, Brown C, Lord S, Gebski
V, De Souza P and Lee CK: Markers of systemic inflammation predict
survival in patients with advanced renal cell cancer. Br J Cancer.
109:147–153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Frank I, Blute ML, Cheville JC, Lohse CM,
Weaver AL and Zincke H: An outcome prediction model for patients
with clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with radical
nephrectomy based on tumor stage, size, grade and necrosis: The
SSIGN score. J Urol. 168:2395–2400. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Leibovich BC, Blute ML, Cheville JC, Lohse
CM, Frank I, Kwon ED, Weaver AL, Parker AS and Zincke H: Prediction
of progression after radical nephrectomy for patients with clear
cell renal cell carcinoma: A stratification tool for prospective
clinical trials. Cancer. 97:1663–1671. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Patard JJ, Kim HL, Lam JS, Dorey FJ,
Pantuck AJ, Zisman A, Ficarra V, Han KR, Cindolo L, De La Taille A,
et al: Use of the University of California Los Angeles integrated
staging system to predict survival in renal cell carcinoma: An
international multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 22:3316–3322. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karakiewicz PI, Suardi N, Capitanio U,
Jeldres C, Ficarra V, Cindolo L, de la Taille A, Tostain J, Mulders
PF, Bensalah K, et al: A preoperative prognostic model for patients
treated with nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol.
55:287–295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lou M, Luo P, Tang R, Peng Y, Yu S, Huang
W and He L: Relationship between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and
insulin resistance in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus
patients. BMC Endocr Disord. 15:92015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shiny A, Bibin YS, Shanthirani CS, Regin
BS, Anjana RM, Balasubramanyam M, Jebarani S and Mohan V:
Association of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio with glucose
intolerance: An indicator of systemic inflammation in patients with
type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 16:524–530. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Larsson SC and Wolk A: Diabetes mellitus
and incidence of kidney cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies.
Diabetologia. 54:1013–1018. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bao C, Yang X, Xu W, Luo H, Xu Z, Su C and
Qi X: Diabetes mellitus and incidence and mortality of kidney
cancer: A meta-analysis. J Diabetes Complications. 27:357–364.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Balkwill FR and Mantovani A:
Cancer-related inflammation: Common themes and therapeutic
opportunities. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:33–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chan AT, Ogino S and Fuchs CS: Aspirin and
the risk of colorectal cancer in relation to the expression of
COX-2. N Eng J Med. 356:2131–2142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sparmann A and Bar-Sagi D: Ras-induced
interleukin-8 expression plays a critical role in tumor growth and
angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 6:447–458. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stoppacciaro A, Melani C, Parenza M,
Mastracchio A, Bassi C, Baroni C, Parmiani G and Colombo MP:
Regression of an established tumor genetically modified to release
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor requires granulocyte-T cell
cooperation and T cell-produced interferon gamma. J Exp Med.
178:151–161. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Avci A, Elnur A, Göksel A, Serdar F,
Servet I, Atilla K, Mustafa TM, Cuneyt T, Yeliz G, Mustafa B and
Metin EA: The relationship between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and
calcific aortic stenosis. Echocardiography. 31:1031–1035. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Balta S, Demirkol S, Kucuk U, Celik T,
Ozturk C and Iyisoy A: The relationship between
neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and coronary collateral circulation.
Perfusion. 29:367–368. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yao C, Liu X and Tang Z: Prognostic role
of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio for
hospital mortality in patients with AECOPD. Int J Chron Obstruct
Pulmon Dis. 12:2285–2290. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Demir M: The relationship between
neutrophil lymphocyte ratio and non-dipper hypertension. Clin Exp
Hypertens. 35:570–573. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ha YS, Kim WT, Yun SJ, Lee SC, Kim WJ,
Park YH, Kang SH, Hong SH, Byun SS and Kim YJ: Multi-institutional
analysis of localized renal cell carcinoma that demonstrates the
impact of diabetic status on prognosis after nephrectomy. Ann Surg
Oncol. 20:3662–3668. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen L, Li H, Gu L, Ma X, Li X, Gao Y,
Zhang Y, Shen D, Fan Y, Wang B, et al: The impact of diabetes
mellitus on renal cell carcinoma prognosis: A meta-analysis of
cohort studies. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e10552015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Boissier R, Campagna J, Branger N,
Karsenty G and Lechevallier E: The prognostic value of the
neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in renal oncology: A review. Urol
Oncol. 35:135–141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|