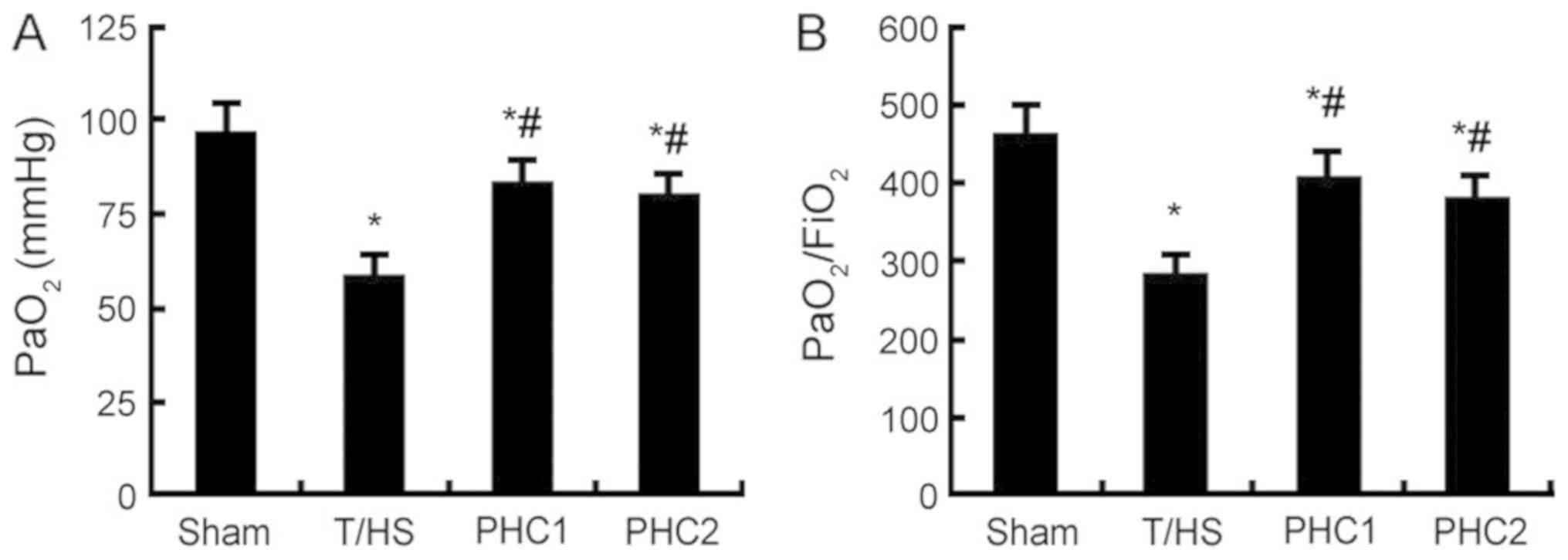
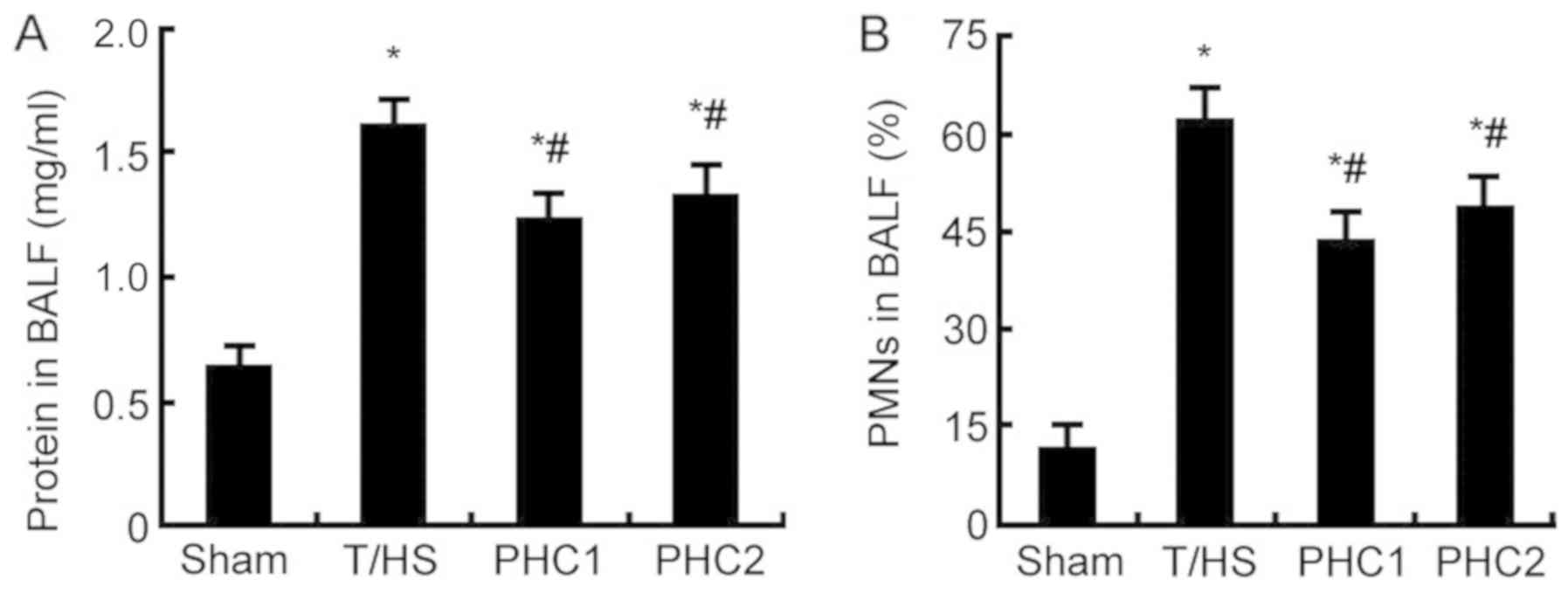
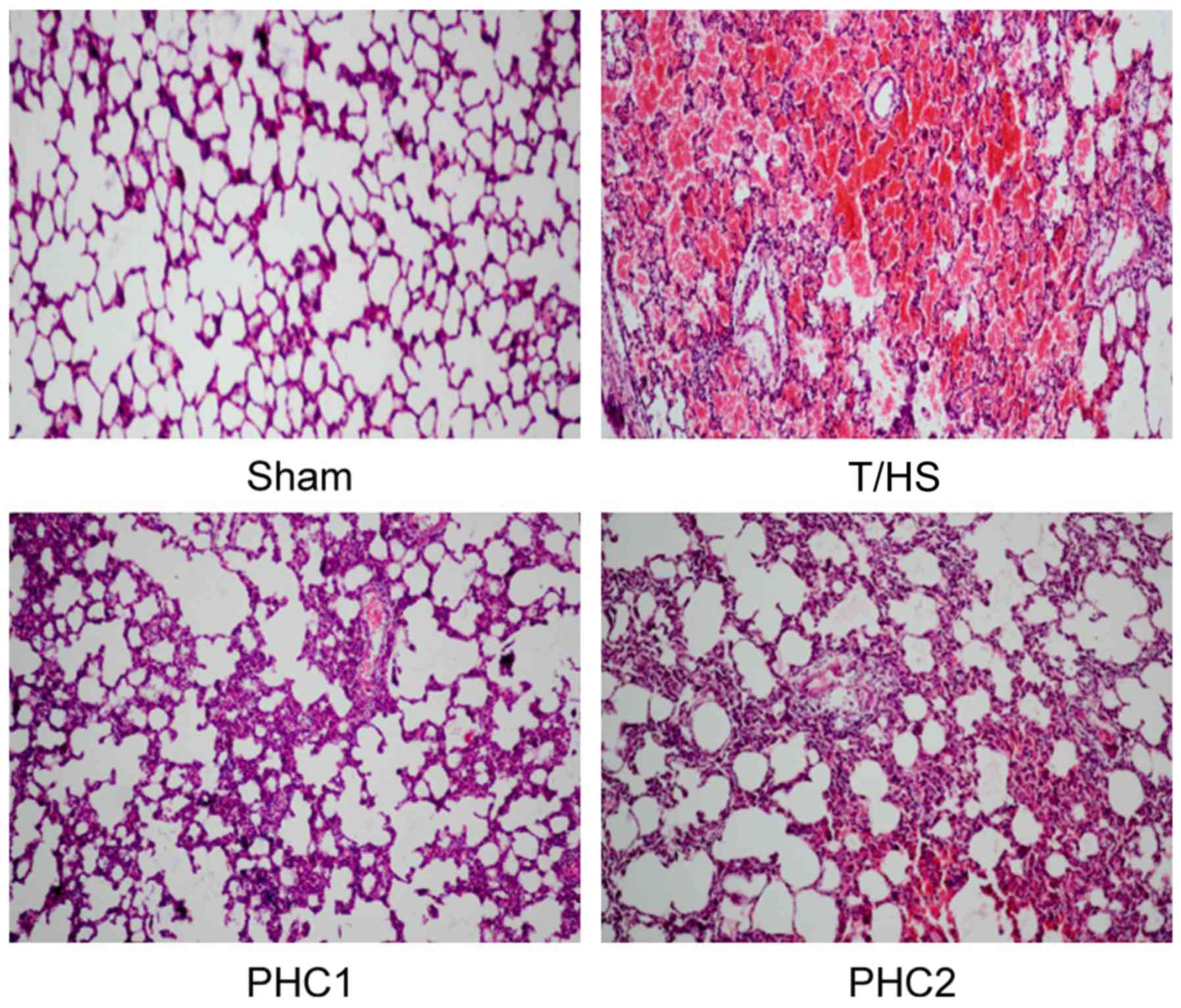
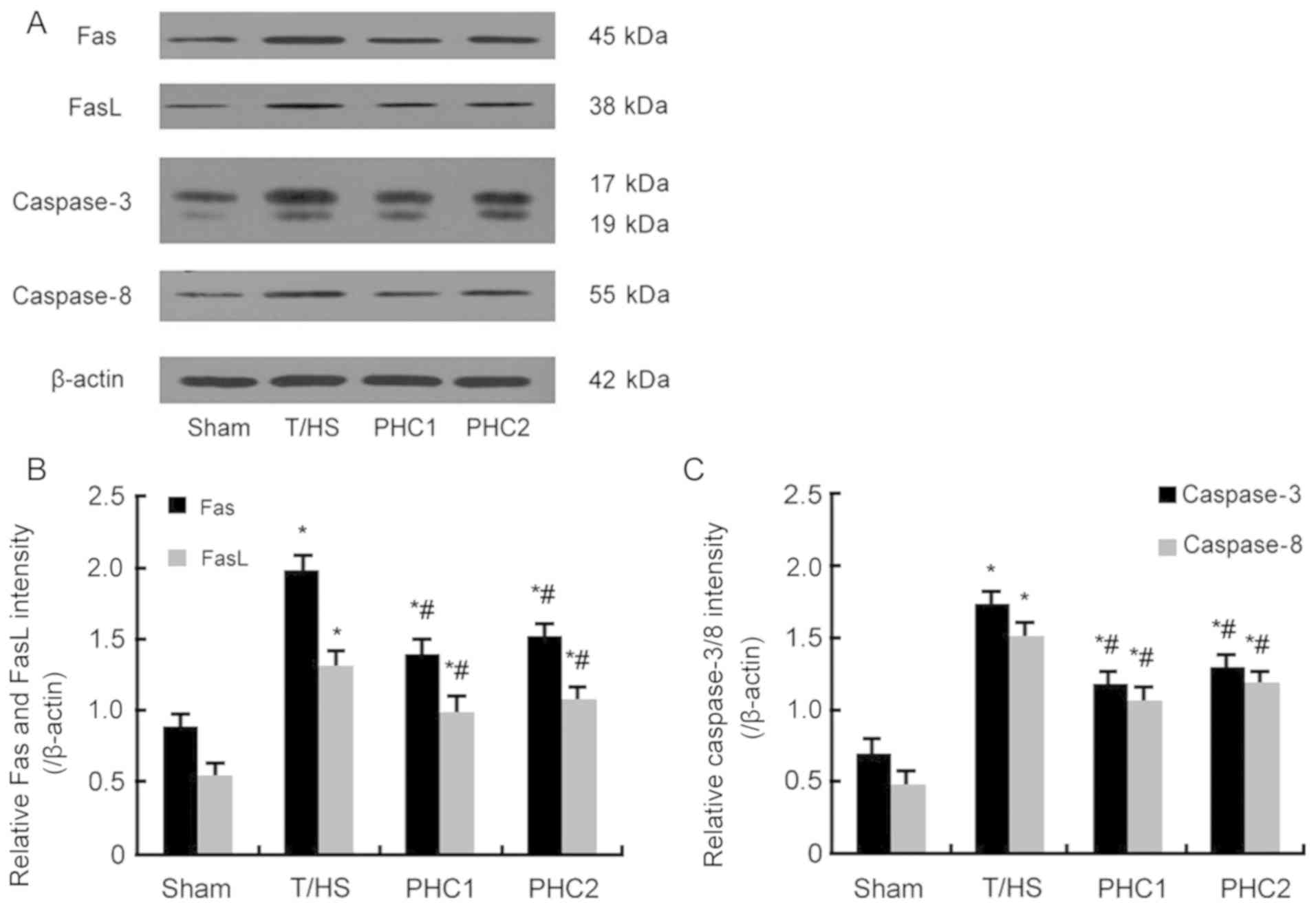
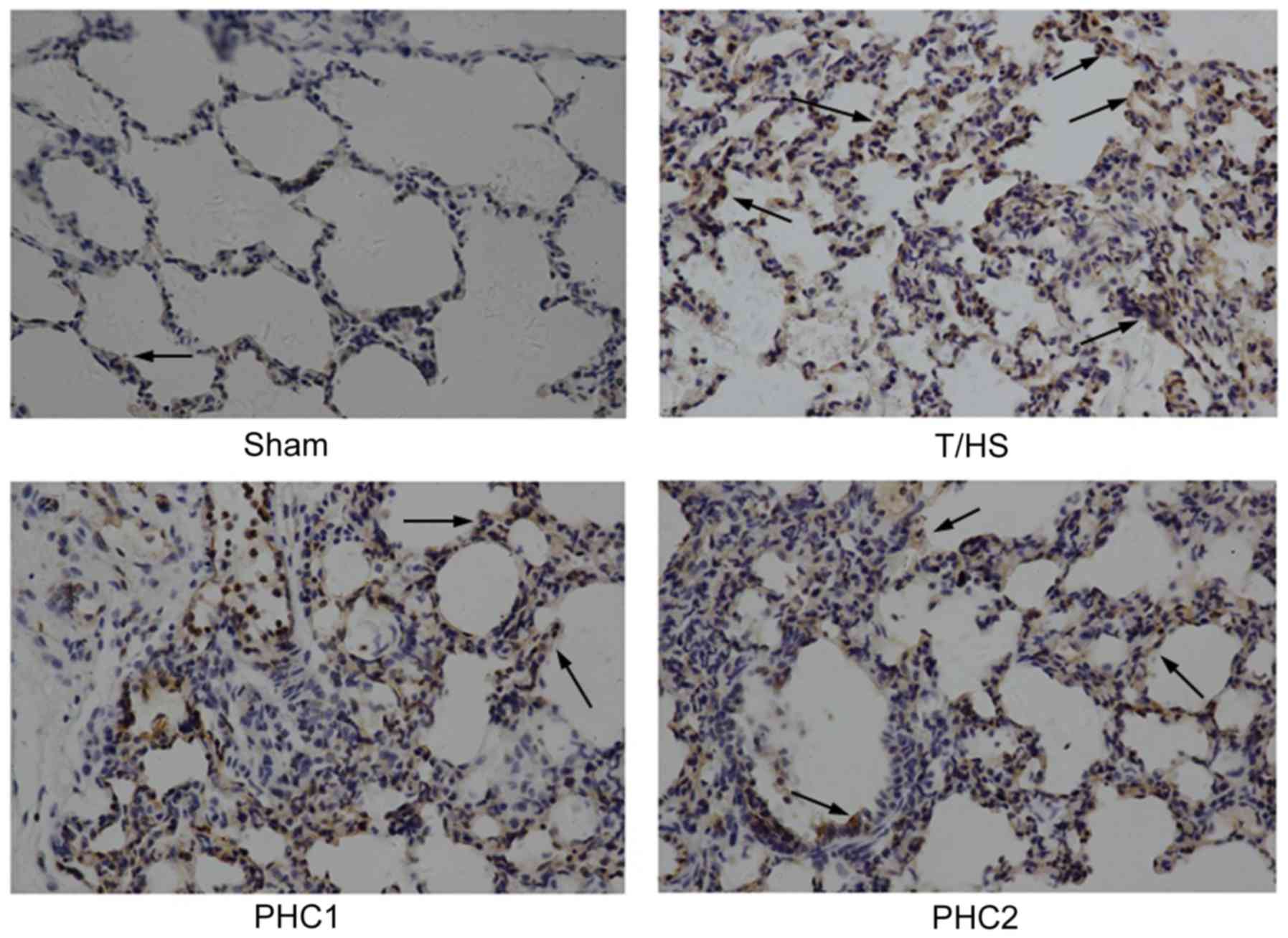
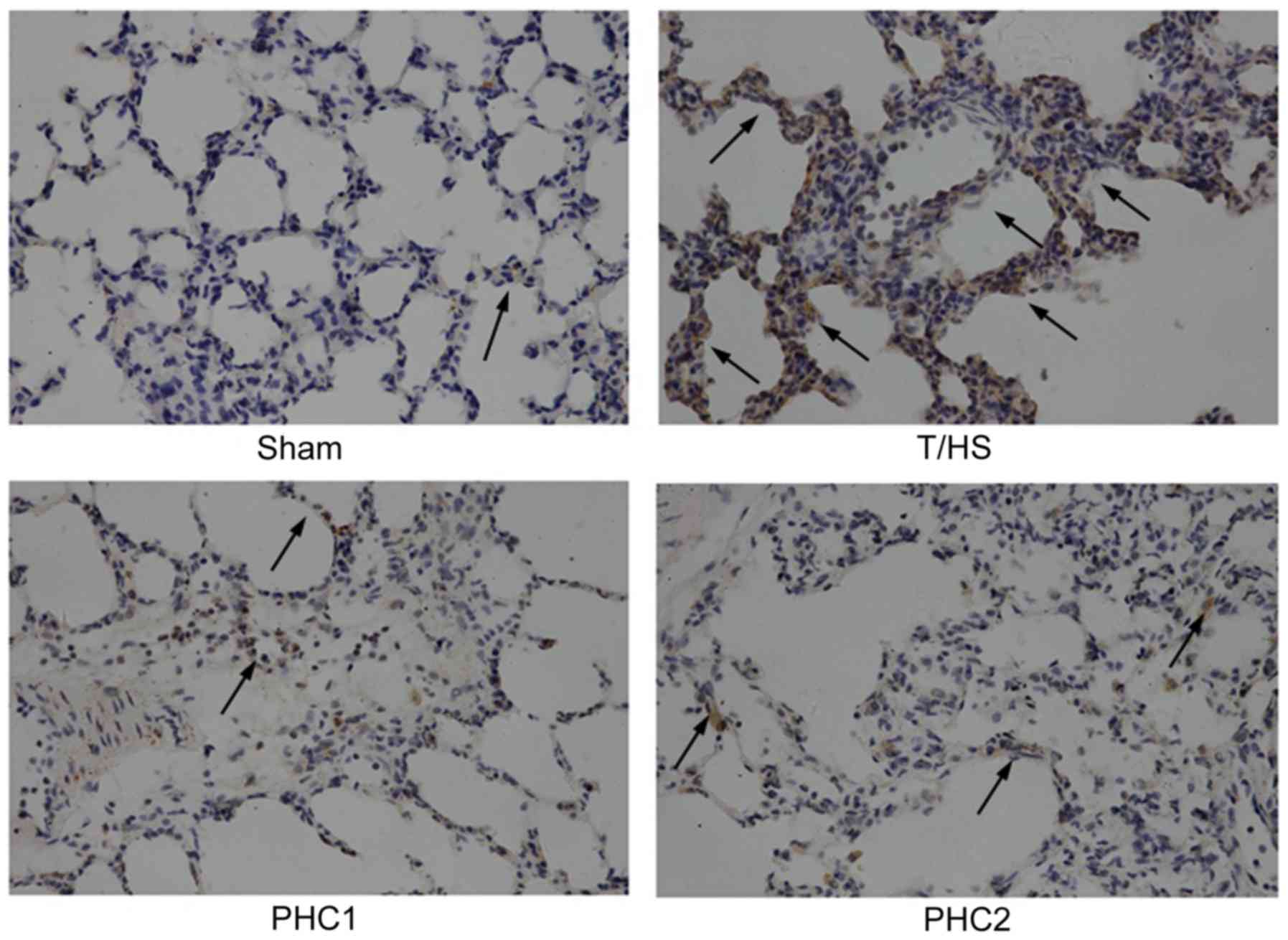
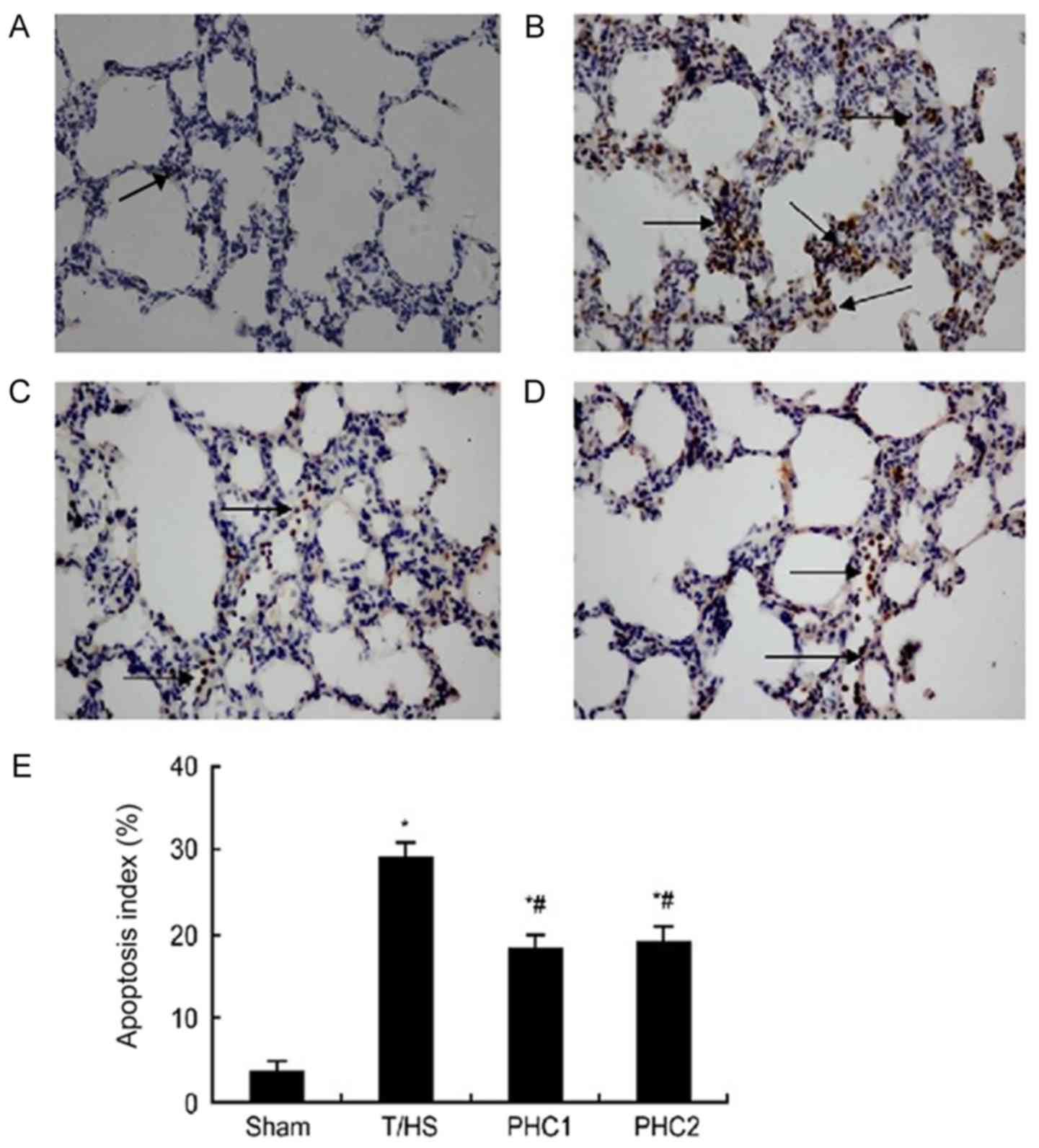
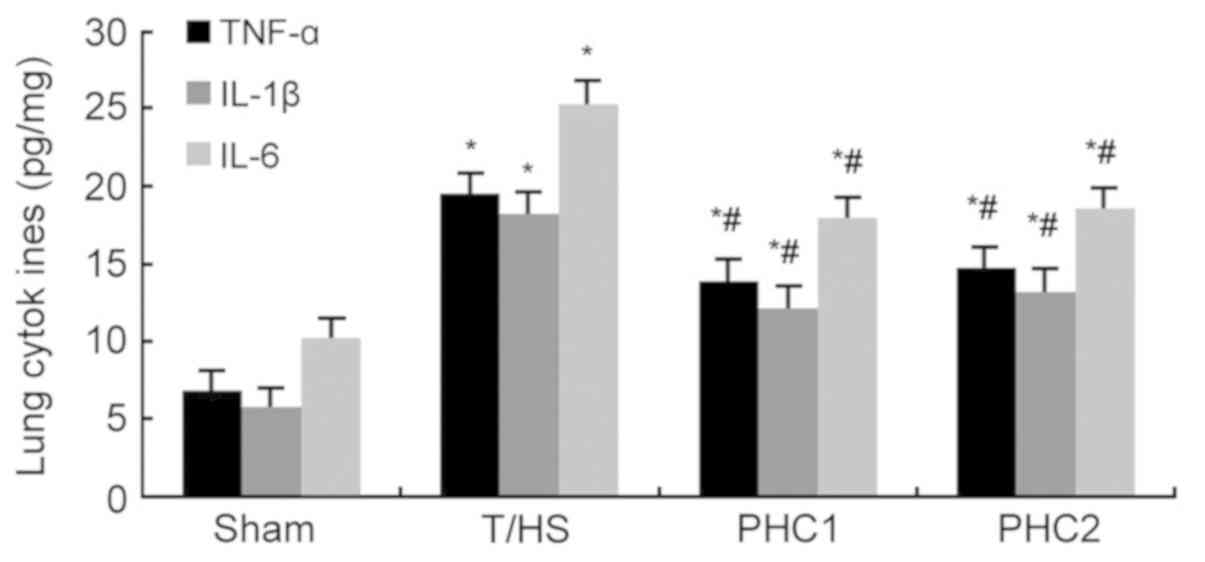
|
1
|
Liu Y, Du DY, Hu X, Xia DK, Xiang XY,
Huang C, Zhou JH and Jiang JX: Prevalence and mortality of severe
chest trauma in three gorges area of China. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue
Yuan Xue Bao. 34:567–572. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Erickson SE, Martin GS, Davis JL, Matthay
MA and Eisner MD; NIH NHLBI ARDS Network, : Recent trends in acute
lung injury mortality: 1996–2005. Crit Care Med. 37:1574–1579.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gallagher JJ: Management of blunt
pulmonary injury. AACN Adv Crit Care. 25:375–386. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown LM, Kallet RH, Matthay MA and Dicker
RA: The influence of race on the development of acute lung injury
in trauma patients. Am J Surg. 201:486–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Messer MP, Kellermann P, Weber SJ, Hohmann
C, Denk S, Klohs B, Schultze A, Braumüller S, Huber-Lang MS and
Perl M: Silencing of fas, fas-associated via death domain, or
caspase 3 differentially affects lung inflammation, apoptosis, and
development of trauma-induced septic acute lung injury. Shock.
39:19–27. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thakkar RK, Chung CS, Chen Y, Monaghan SF,
Lomas-Neira J, Heffernan DS, Cioffi WG and Ayala A: Local tissue
expression of the cell death ligand, fas ligand, plays a central
role in the development of extrapulmonary acute lung injury. Shock.
36:138–143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Glavan BJ, Holden TD, Goss CH, Black RA,
Neff MJ, Nathens AB, Martin TR and Wurfel MM; ARDSnet
Investigators, : Genetic variation in the FAS gene and associations
with acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 183:356–363.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Herrero R, Tanino M, Smith LS, Kajikawa O,
Wong VA, Mongovin S, Matute-Bello G and Martin TR: The Fas/FasL
pathway impairs the alveolar fluid clearance in mouse lungs. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 305:L377–L388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Lin D, Zhang L, Liu W, Tan H and
Ma J: Penehyclidine hydrochloride prevents anoxia/reoxygenation
injury and induces H9c2 cardiomyocyte apoptosis via a mitochondrial
pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 797:115–123. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang Y, Zhao L and Ma J: Penehyclidine
hydrochloride preconditioning provides cardiac protection in a rat
model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via the mechanism
of mitochondrial dynamics mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol. 813:130–139.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu R, Zhao Y, Li X, Bai T, Wang S, Wang W
and Sun Y: Effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on severe acute
pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury in rats. Biomed
Pharmacother. 97:1689–1693. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu XJ, Liu HM, Song XM, Zhao B, Leng Y,
Wang EY, Zhan LY, Meng QT and Xia ZY: Penehyclidine hydrochloride
inhibits TLR4 signaling and inflammation, and attenuates blunt
chest trauma and hemorrhagic shock-induced acute lung injury in
rats. Mol Med Rep. 17:6327–6336. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng F, Xiao F, Yuan QH, Liu QS, Zhang
ZZ, Wang YL and Zhan J: Penehyclidine hydrochloride decreases
pulmonary microvascular endothelial inflammatory injury through a
beta-arrestin-1-dependent mechanism. Inflammation. 41:1610–1620.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang LL, Zhan LY, Wu XJ and Xia ZY:
Effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on apoptosis of lung tissues
in rats with traumatic acute lung injury. Chin J Traumatol.
13:15–19. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cui J, Li CS, He XH and Song YG:
Protective effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on acute lung
injury caused by severe dichlorvos poisoning in swine. Chin Med J
(Engl). 126:4764–4770. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu XJ, Xia ZY, Wang LL, Luo T, Zhan LY,
Meng QT and Song XM: Effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on
pulmonary contusion from blunt chest trauma in rats. Injury.
43:232–236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Raghavendran K, Davidson BA, Helinski JD,
Marschke CJ, Manderscheid P, Woytash JA, Notter RH and Knight PR: A
rat model for isolated bilateral lung contusion from blunt chest
trauma. Anesth Analg. 101:1482–1489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu X, Song X, Li N, Zhan L, Meng Q and Xia
Z: Protective effects of dexmedetomidine on blunt chest
trauma-induced pulmonary contusion in rats. J Trauma Acute Care
Surg. 74:524–530. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kellner M, Noonepalle S, Lu Q, Srivastava
A, Zemskov E and Black SM: ROS signaling in the pathogenesis of
Acute Lung Injury (ALI) and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
(ARDS). Adv Exp Med Biol. 967:105–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu DQ, Wu HB, Zhang M and Wang JA: Effects
of zinc finger protein A20 on Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced
pulmonary inflammation/anti-inflammatory mediators in an acute lung
injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome rat model. Med Sci
Monit. 23:3536–3545. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Agarwal R, Handa A, Aggarwal AN, Gupta D
and Behera D: Outcomes of noninvasive ventilation in acute
hypoxemic respiratory failure in a respiratory intensive care unit
in north India. Respir Care. 54:1679–1887. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han F, Luo Y, Li Y, Liu Z, Xu D, Jin F and
Li Z: Seawater induces apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells via
the Fas/FasL-mediated pathway. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 182:71–80.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seitz DH, Palmer A, Niesler U, Braumüller
ST, Bauknecht S, Gebhard F and Knöferl MW: Altered expression of
Fas receptor on alveolar macrophages and inflammatory effects of
soluble Fas ligand following blunt chest trauma. Shock. 35:610–617.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kobata T, Takasaki K, Asahara H, Hong NM,
Masuko-Hongo K, Kato T, Hirose S, Shirai T, Kayagaki N, Yagita H,
et al: Apoptosis with FasL+ cell infiltration in the periphery and
thymus of corrected autoimmune mice. Immunology. 92:206–213. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gil S, Farnand AW, Altemeier WA, Gill SE,
Kurdowska A, Krupa A, Florence JM and Matute-Bello G: Fas-deficient
mice have impaired alveolar neutrophil recruitment and decreased
expression of anti-KC autoantibody: KC complexes in a model of
acute lung injury. Respir Res. 13:912012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weckbach S, Hohmann C, Braumueller S, Denk
S, Klohs B, Stahel PF, Gebhard F, Huber-Lang MS and Perl M:
Inflammatory and apoptotic alterations in serum and injured tissue
after experimental polytrauma in mice: Distinct early response
compared with single trauma or ‘double-hit’ injury. J Trauma Acute
Care Surg. 74:489–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Serrao KL, Fortenberry JD, Owens ML,
Harris FL and Brown LA: Neutrophils induce apoptosis of lung
epithelial cells via release of soluble Fas ligand. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 280:L298–L305. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Perl M, Hohmann C, Denk S, Kellermann P,
Lu D, Braumüller S, Bachem MG, Thomas J, Knöferl MW, Ayala A, et
al: Role of activated neutrophils in chest trauma-induced septic
acute lung injury. Shock. 38:98–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li H, Qian Z, Li J, Han X and Liu M:
Effects of early administration of a novel anticholinergic drug on
acute respiratory distress syndrome induced by sepsis. Med Sci
Monit. 11:BR319–BR325. 2011.
|
|
30
|
Shen W, Gan J, Xu S, Jiang G and Wu H:
Penehyclidine hydrochloride attenuates LPS-induced acute lung
injury involvement of NF-kappaB pathway. Pharmacol Res. 60:296–302.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han XY, Liu H, Liu CH, Wu B, Chen LF,
Zhong BH and Liu KL: Synthesis of the optical isomers of a new
anticholinergic drug, penehyclidine hydrochloride (8018). Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 15:1979–1982. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tan H, Chen L and Ma J: Penehyclidine
hydrochloride post-conditioning reduces
ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats. Exp
Ther Med. 14:4272–4278. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang D, Jiang Q and Du X: Protective
effects of scopolamine and penehyclidine hydrochloride on acute
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury after cardiopulmonary
resuscitation and effects on cytokines. Exp Ther Med. 15:2027–2031.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu GM, Mou M, Mo LQ, Liu L, Ren CH, Chen Y
and Zhou J: Penehyclidine hydrochloride postconditioning on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibition of
inflammatory factors in a rodent model. J Surg Res. 195:219–227.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cao HJ, Sun YJ, Zhang TZ, Zhou J and Diao
YG: Penehyclidine hydrochloride attenuates the cerebral injury in a
rat model of cardiopulmonary bypass. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
91:521–527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang YP, Li G, Ma LL, Zheng Y, Zhang SD,
Zhang HX, Qiu M and Ma X: Penehyclidine hydrochloride ameliorates
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Surg Res. 186:390–397.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|