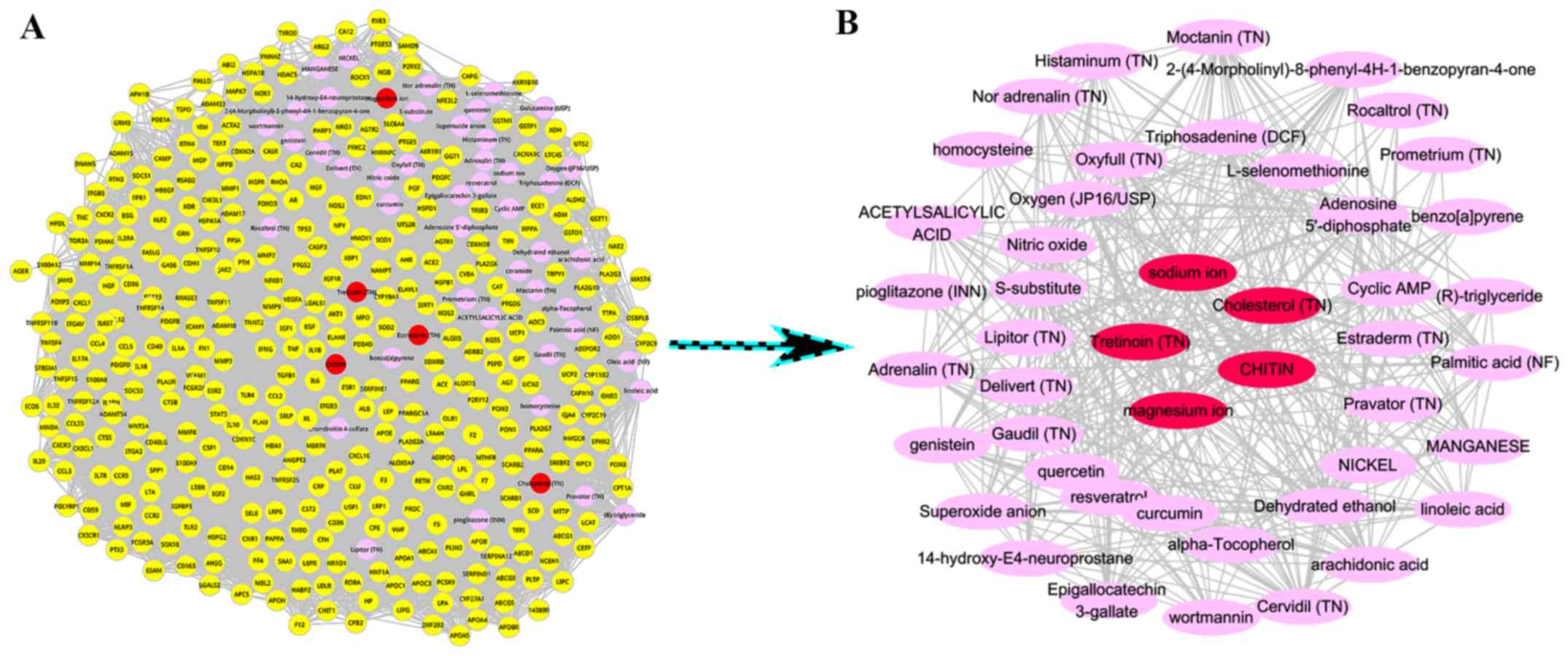
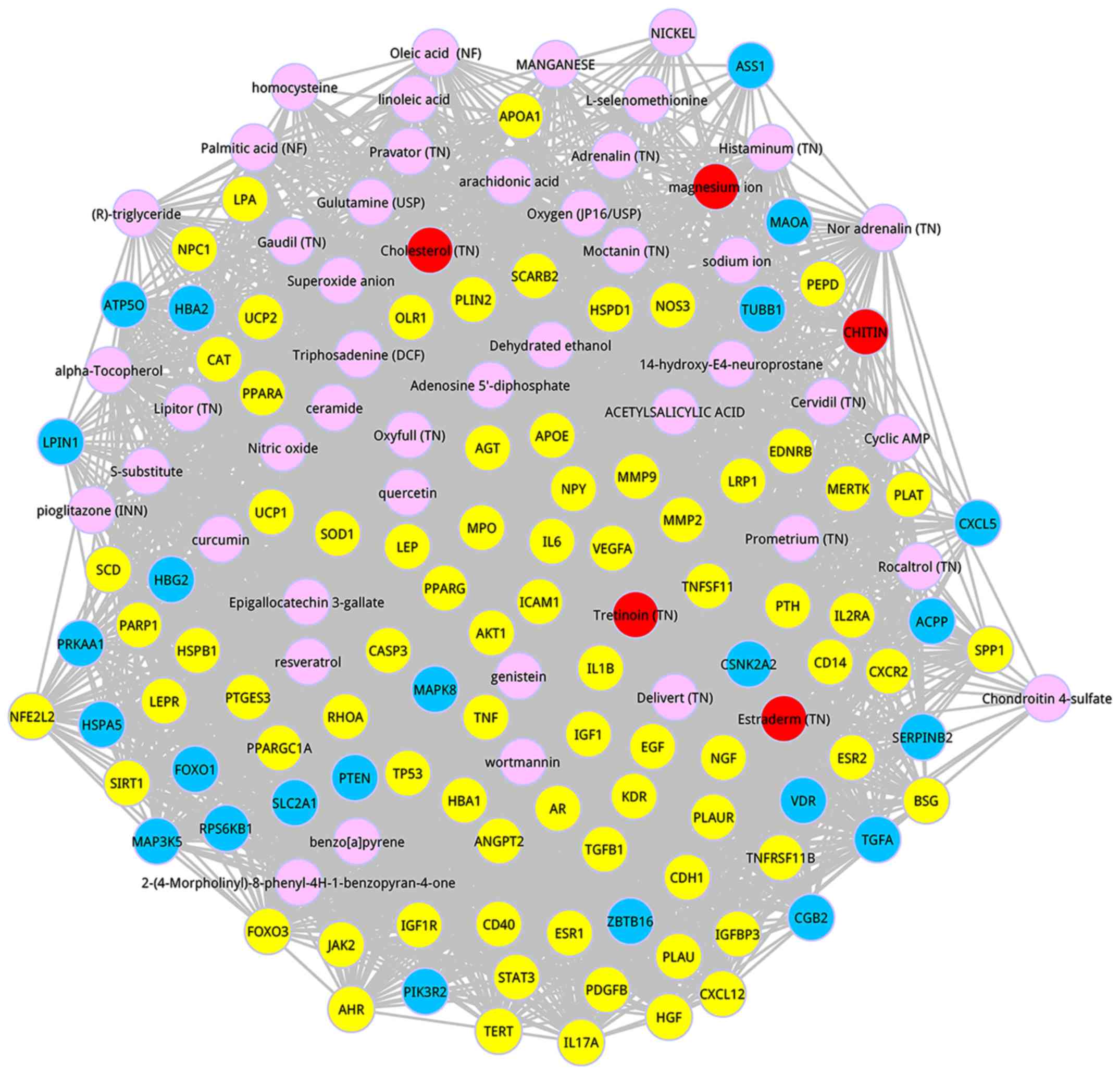
|
1
|
Lusis AJ: Atherosclerosis. Nature.
407:233–241. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akerele OA and Cheema SK: Fatty acyl
composition of lysophosphatidylcholine is important in
atherosclerosis. Med Hypotheses. 85:754–760. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tabas I, García-Cardeña G and Owens GK:
Recent insights into the cellular biology of atherosclerosis. J
Cell Biol. 209:13–22. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holmes E, Wilson ID and Nicholson JK:
Metabolic phenotyping in health and disease. Cell. 134:714–717.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Iqbal O, Ottman A, Gaynes J, De Alba F,
Gaynes BI, Fareed J and Bouchard CS: The effects of aspirin and its
metabolites on peripheral blood mononuclear cells and human retinal
pigment epithelial cells - implications in the pathophysiology of
age-related macular degeneration. IOVS. 55:6342014.
|
|
6
|
Kell DB: Metabolomics and systems biology:
Making sense of the soup. Curr Opin Microbiol. 7:296–307. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nicholson JK and Lindon JC: Systems
biology: Metabonomics. Nature. 455:1054–1056. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moco S, Bino RJ, De Vos RCH and Vervoort
J: Metabolomics technologies and metabolite identification. Trends
Analyt Chem. 26:855–866. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee DS, Park J, Kay KA, Christakis NA,
Oltvai ZN and Barabási AL: The implications of human metabolic
network topology for disease comorbidity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:9880–9885. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yao Q, Xu Y, Yang H, Shang D, Zhang C,
Zhang Y, Sun Z, Shi X, Feng L, Han J, et al: Global prioritization
of disease candidate metabolites based on a multi-omics composite
network. Sci Rep. 5:172012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt
S, Bork P and Snel B: STRING: A database of predicted functional
associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:258–261. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Eisner R,
Young N, Gautam B, Hau DD, Psychogios N, Dong E, Bouatra S, et al:
HMDB: A knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:D603–D610. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D109–D114.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
D'Eustachio P: Reactome knowledgebase of
human biological pathways and processes. Methods Mol Biol.
694:49–61. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xia J and Wishart DS: MSEA: a web-based
tool to identify biologically meaningful patterns in quantitative
metabolomic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 38 (Suppl 2):W71–W77. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jewison T, Su Y, Disfany FM, Liang Y, Knox
C, Maciejewski A, Poelzer J, Huynh J, Zhou Y, Arndt D, et al: SMPDB
2.0: Big improvements to the Small Molecule Pathway Database.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:D478–D484. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuhn M, Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A,
Campillos M, von Mering C, Jensen LJ, Beyer A and Bork P: STITCH 2:
An interaction network database for small molecules and proteins.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38 (Suppl 1):D552–D556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
van Driel MA, Bruggeman J, Vriend G,
Brunner HG and Leunissen JA: A text-mining analysis of the human
phenome. Eur J Hum Genet. 14:535–542. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Åstrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope
LM, Hobbs B and Speed TP: Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe
level data. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:e152003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Belitskaya-Lévy I, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A,
Russo J, Russo IH, Bordás P, Ahman J, Afanasyeva Y, Johansson R,
Lenner P, Li X, et al: Characterization of a genomic signature of
pregnancy identified in the breast. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
4:1457–1464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reiner A, Yekutieli D and Benjamini Y:
Identifying differentially expressed genes using false discovery
rate controlling procedures. Bioinformatics. 19:368–375. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Datta S, Satten GA, Benos DJ, Xia J,
Heslin MJ and Datta S: An empirical bayes adjustment to increase
the sensitivity of detecting differentially expressed genes in
microarray experiments. Bioinformatics. 20:235–242. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu X, Jiang R, Zhang MQ and Li S:
Network-based global inference of human disease genes. Mol Syst
Biol. 4:1892008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Amini N, Boyle JJ, Moers B, Warboys CM,
Malik TH, Zakkar M, Francis SE, Mason JC, Haskard DO and Evans PC:
Requirement of JNK1 for endothelial cell injury in atherogenesis.
Atherosclerosis. 235:613–618. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kedenko L, Lamina C, Kedenko I, Kollerits
B, Kiesslich T, Iglseder B, Kronenberg F and Paulweber B: Genetic
polymorphisms at SIRT1 and FOXO1 are associated with carotid
atherosclerosis in the SAPHIR cohort. BMC Med Genet. 15:1122014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hadi NR: Effect of vildagliptin on
atherosclerosis progression in high cholesterol - fed male rabbits.
J Clin Exp Cardiolog. 04:150252016.
|
|
29
|
Gey KF and Puska P: Plasma vitamins E and
A inversely correlated to mortality from ischemic heart disease in
cross-cultural epidemiology. Ann NY Acad Sci. 570:268–282. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hornig B: Vitamins, antioxidants and
endothelial function in coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Drugs
Ther. 16:401–409. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Környei Z, Gócza E, Rühl R, Orsolits B,
Vörös E, Szabó B, Vágovits B and Madarász E: Astroglia-derived
retinoic acid is a key factor in glia-induced neurogenesis. FASEB
J. 21:2496–2509. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bowles J, Secker G, Nguyen C, Kazenwadel
J, Truong V, Frampton E, Curtis C, Skoczylas R, Davidson TL, Miura
N, et al: Control of retinoid levels by CYP26B1 is important for
lymphatic vascular development in the mouse embryo. Dev Biol.
386:25–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim YM, Kim JH, Park SW, Kim HJ and Chang
KC: Retinoic acid inhibits tissue factor and HMGB1 via modulation
of AMPK activity in TNF-α activated endothelial cells and
LPS-injected mice. Atherosclerosis. 241:615–623. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang SJ, Campbell LA, Berry MW, Rosenfeld
ME and Kuo CC: Retinoic acid prevents Chlamydia pneumoniae-induced
foam cell development in a mouse model of atherosclerosis. Microbes
Infect. 10:1393–1397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li H, Mani S, Wu L, Fu M, Shuang T, Xu C
and Wang R: The interaction of estrogen and CSE/H2S pathway in the
development of atherosclerosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
312:H406–H414. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dai W, Ming W, Li Y, Zheng HY, Wei CD, Rui
Z and Yan C: Synergistic effect of a physiological ratio of
estradiol and testosterone in the treatment of early-stage
atherosclerosis. Arch Med Res. 46:619–629. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee CS, Kwon SJ, Na SY, Lim SP and Lee JH:
Genistein supplementation inhibits atherosclerosis with
stabilization of the lesions in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J
Korean Med Sci. 19:656–661. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Voloshyna I, Hussaini SM and Reiss AB:
Resveratrol in cholesterol metabolism and atherosclerosis. J Med
Food. 15:763–773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tin A, Grams ME, Maruthur NM, Astor BC,
Couper D, Mosley TH, Selvin E, Coresh J and Kao WH: Results from
the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study suggest that low
serum magnesium is associated with incident kidney disease. Kidney
Int. 87:820–827. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Förstermann U, Xia N and Li H: Roles of
vascular oxidative stress and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 120:713–735. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Babaev VR, Yeung M, Erbay E, Ding L, Zhang
Y, May JM, Fazio S, Hotamisligil GS and Linton MF: Jnk1 deficiency
in hematopoietic cells suppresses macrophage apoptosis and
increases atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor null
mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 36:1122–1131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yuan M, Wang X, Zhan Q, Duan X, Yang Q and
Xia J: Association of PTEN genetic polymorphisms with
atherosclerotic cerebral infarction in the Han Chinese population.
J Clin Neurosci. 19:1641–1645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Accili D and Arden KC: FoxOs at the
crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and
transformation. Cell. 117:421–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sengupta A, Molkentin JD and Yutzey KE:
FoxO transcription factors promote autophagy in cardiomyocytes. J
Biol Chem. 284:28319–28331. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Qiang L, Tsuchiya K, Kim-Muller JY, Lin
HV, Welch C and Accili D: Increased atherosclerosis and endothelial
dysfunction in mice bearing constitutively deacetylated alleles of
Foxo1 gene. J Biol Chem. 287:13944–13951. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhao J, Forsberg CW, Goldberg J, Smith NL
and Vaccarino V: MAOA promoter methylation and susceptibility to
carotid atherosclerosis: Role of familial factors in a monozygotic
twin sample. BMC Med Genet. 13:1002012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rousselle A, Qadri F, Leukel L, Yilmaz R,
Fontaine JF, Sihn G, Bader M, Ahluwalia A and Duchene J: CXCL5
limits macrophage foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. J Clin
Invest. 123:1343–1347. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Orešič M, Clish CB, Davidov EJ, Verheij E,
Vogels J, Havekes LM, Neumann E, Adourian A, Naylor S, van der
Greef J and Plasterer T: Phenotype characterisation using
integrated gene transcript, protein and metabolite profiling.
Applied Bioinformatics. 3:205–217. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|