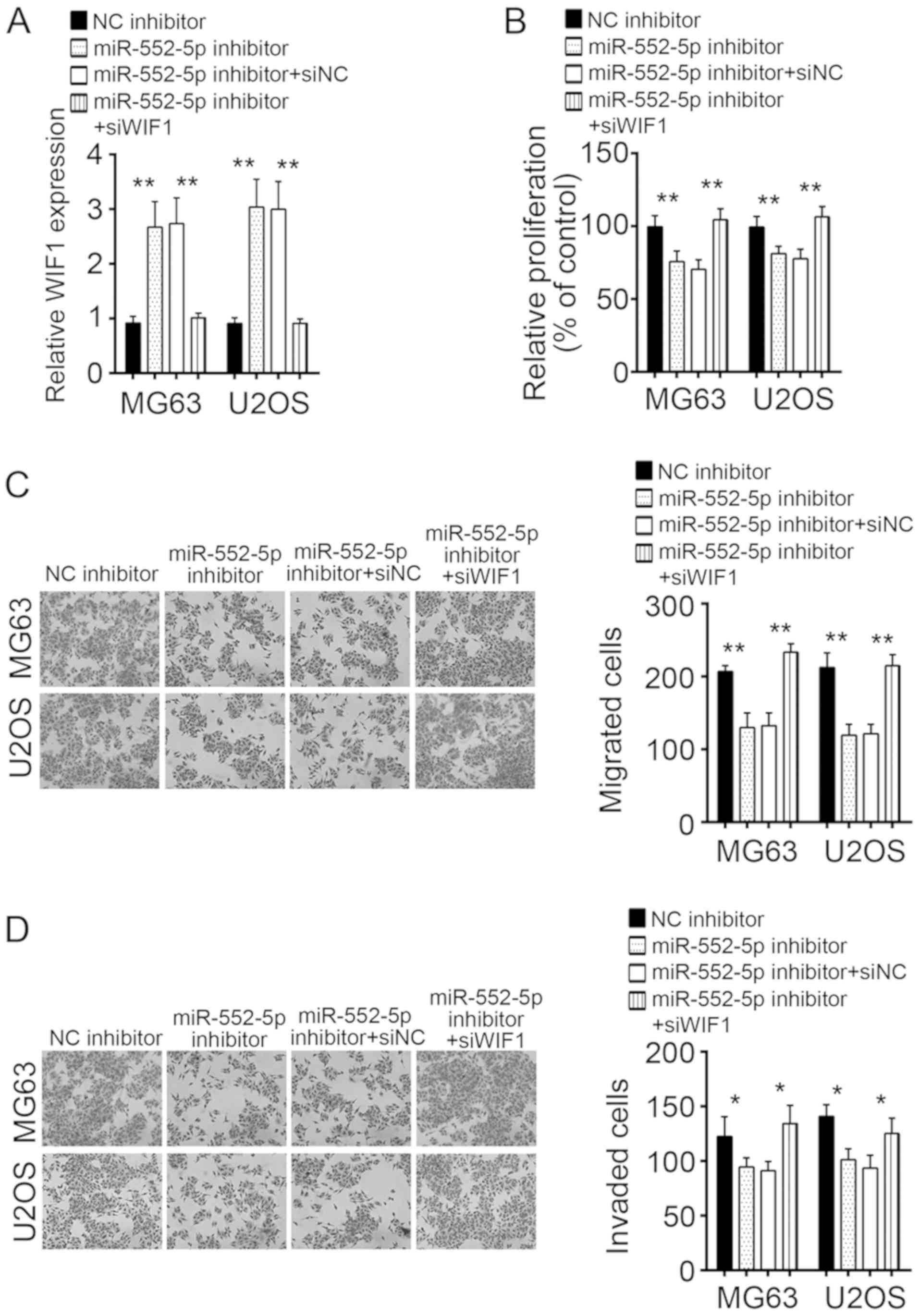
|
1
|
Yu JJ, Pi WS, Cao Y, Peng AF, Cao ZY, Liu
JM, Huang SH, Liu ZL and Zhang W: Let-7a inhibits osteosarcoma cell
growth and lung metastasis by targeting Aurora-B. Cancer Manag Res.
10:6305–6315. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zheng WP, Huang YP, Chen HY, Wang N, Xiao
W, Liang Y, Jiang X, Su W and Wen S: Nomogram application to
predict overall and cancer-specific survival in osteosarcoma.
Cancer Manag Res. 10:5439–5450. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pan R, He Z, Ruan W, Li S, Chen H, Chen Z,
Liu F, Tian X and Nie Y: lncRNA FBXL19-AS1 regulates osteosarcoma
cell proliferation, migration and invasion by sponging miR-346.
Onco Targets Ther. 11:8409–8420. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu M, Lang N, Qiu M, Xu F, Li Q, Tang Q,
Chen J, Chen X, Zhang S, Liu Z, et al: miR-137 targets Cdc42
expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in
colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 128:1269–1279. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mei Q, Li X, Guo MZ, Fu XB and Han WD: The
miRNA network: micro-regulator of cell signaling in cancer. Expert
Rev Anticancer Ther. 14:1515–1527. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kushlinskii NE, Fridman MV and Braga EA:
Molecular mechanisms and microRNAs in osteosarcoma pathogenesis.
Biochemistry (Mosc). 81:315–328. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nature Reviews Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: Microrna expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–8. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim KJ and Cho SB: Exploring features and
classifiers to classify microrna expression profiles of human
cancer. Neural Inf Process Models Appl. 6444:234–241. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Bai X, Meng L, Sun H, Li Z, Zhang X and
Hua S: MicroRNA-196b inhibits cell growth and metastasis of lung
cancer cells by targeting Runx2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:757–767.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang J, Zeng H, Li H, Chen T, Wang L,
Zhang K, Chen J, Wang R, Li Q and Wang S: MicroRNA-101 inhibits
growth, proliferation and migration and induces apoptosis of breast
cancer cells by targeting sex-determining region Y-Box 2. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 43:717–732. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang W, Liu J, Xu T and Yu X: MiR-329
suppresses osteosarcoma development by downregulating Rab10. FEBS
Lett. 590:2973–2981. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yao J, Qin L, Miao S, Wang X and Wu X:
Overexpression of miR-506 suppresses proliferation and promotes
apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by targeting astrocyte elevated
gene-1. Oncol Lett. 12:1840–1848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao J, Yan XR, Liu T, Han XB, Yu JJ, Liu
SH and Wang LB: MicroRNA-552 promotes tumor cell proliferation and
migration by directly targeting DACH1 via the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:3795–3802.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Li H, Wang Y, Wang L, Yan X, Zhang
D, Ma X, Du Y, Liu X and Yang Y: MicroRNA-552 enhances metastatic
capacity of colorectal cancer cells by targeting a disintegrin and
metalloprotease 28. Oncotarget. 7:70194–70210. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo X, Ye S, Jiang Q, Gong Y, Yuan Y, Hu
X, Su X and Zhu W: Wnt inhibitory factor-1-mediated autophagy
inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling by downregulating dishevelled-2
expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
53:904–914. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hou Z, Guo K, Sun X, Hu F, Chen Q, Luo X,
Wang G, Hu J and Sun L: TRIB2 functions as novel oncogene in
colorectal cancer by blocking cellular senescence through AP4/p21
signaling. Mol Cancer. 17:1722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng ZY, Xu XH, Cen DZ, Luo CY and Wu SB:
miR-590-3p promotes colon cancer cell proliferation via
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by inhibiting WIF1 and DKK1. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:4844–4852. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Zhang L, Zhang G, Li S, Duan J,
Cheng J, Ding G, Zhou C, Zhang J, Luo P, et al: Osteosarcoma
metastasis: Prospective role of ezrin. Tumour Biol. 35:5055–5059.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li SL, Gao HL, Lv XK, Hei YR, Li PZ, Zhang
JX and Lu N: MicroRNA-124 inhibits cell invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by directly repressing Snail2 in
gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3389–3396.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Song YX, Sun JX, Zhao JH, Yang YC, Shi JX,
Wu ZH, Chen XW, Gao P, Miao ZF and Wang ZN: Non-coding RNAs
participate in the regulatory network of CLDN4 via ceRNA mediated
miRNA evasion. Nat Commun. 8:2892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang L, Hao ZP, Deng Y, Zhang P, Fu XN and
Zhang N: MiR-29a-3p suppresses the proliferation, migration and
invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting IGF-1.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:1293–1302. 2017.
|
|
26
|
Liu C, Liu Z, Li X, Tang X, He J and Lu S:
MicroRNA-1297 contributes to tumor growth of human breast cancer by
targeting PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling. Oncol Rep. 38:2435–2443. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ring A, Kim YM and Kahn M: Wnt/catenin
signaling in adult stem cell physiology and disease. Stem Cell Rev.
10:512–525. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stewart DJ, Chang DW, Ye Y, Spitz M, Lu C,
Shu X, Wampfler JA, Marks RS, Garces YI, Yang P and Wu X: Wnt
signaling pathway pharmacogenetics in non-small cell lung cancer.
Pharmacogenom J. 14:509–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dai G, Zheng D, Wang Q, Yang J, Liu G,
Song Q, Sun X, Tao C, Hu Q, Gao T, et al: Baicalein inhibits
progression of osteosarcoma cells through inactivation of the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 8:86098–86116. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang H, Hu B, Wang Z, Zhang F, Wei H and
Li L: miR-181c contributes to cisplatin resistance in non-small
cell lung cancer cells by targeting Wnt inhibition factor 1. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 80:973–984. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Deng X, Hou C, Wang H, Liang T and Zhu L:
Hypermethylation of WIF1 and its inhibitory role in the tumor
growth of endometrial adenocarcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 16:7497–7503.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rubin EM, Guo Y, Tu K, Xie J, Zi X and
Hoang BH: Wnt inhibitory factor 1 decreases tumorigenesis and
metastasis in osteosarcoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:731–741. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|