Introduction
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a serious
complication of diabetes, which increases the mortality of patients
(1). DCM is defined as left
ventricular dysfunction that occurs independently of hypertension
and coronary artery atherosclerosis and is a cause of heart failure
in patients with diabetes (2).
Increased oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis have been
implicated in the development of DCM (3,4).
Therefore, inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis is a key step in the
prevention of DCM. Glucose-lowering agents that decrease the risk
of major cardiovascular events would thus be considered important
(5). Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)
is a 30-amino acid gut hormone that is secreted from intestinal
endocrine L cells, which stimulates insulin secretion, inhibits
glucagon secretion and inhibits gastric emptying, causing
postprandial euglycemia and body weight reduction (6). Multiple GLP-1 analogs have been
developed and one such agent, liraglutide, was approved for the
treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity (7). Growing evidence has indicated that
GLP-1 analogs have the potential to reduce cardiac inflammation,
limit infarct size and mitigate ischemic-reperfusion injury in
animals with experimental myocardial infarction (MI) (8–10).
Recently, several cardiovascular studies have documented the
reduction of major adverse cardiovascular events and cardiovascular
mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes or preexisting
cardiovascular disease, via treatment with liraglutide and
semaglutide (11,12). The beneficial effects exhibited by
liraglutide and semaglutide may be associated with reductions in
hemoglobin A1c, body weight, systolic blood pressure and
lipoproteins (11–13). However, traditional atherogenic risk
factor modifications alone cannot explain the overall benefits
observed, indicating that additional mechanisms may occur (11–13). The
favorable effects of liraglutide on oxidative stress and carotid
atherosclerosis in patients with diabetes has been previously
reported (14,15). Various studies have also revealed
that liraglutide exhibits protective myocardial actions in diabetic
animal models in vivo (16,17).
However, the results of in vivo studies may have been
influenced by many factors, including metabolic and environmental
factors as well as the anti-atherosclerotic effect of liraglutide
(15,17,18).
Furthermore, few in vitro reports detail the role of
liraglutide on cardiomyocytes in a high glucose (HG) state.
Therefore, to assess the possible mechanism of liraglutide on
myocardial protection in diabetes, the present study determined the
effects of liraglutide on HG-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis
in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes in vitro.
Materials and methods
Primary culture of rat myocytes
The animal protocol was reviewed and approved by the
Laboratory Animal Ethical and Welfare Committee of Hebei Medical
University (Shijiazhuang, China; approval no.
IACUC-Hebmu-20160027). A total of 160 Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats
(age, 3 days; weight, 8–10 g; 80 males and 80 females) were
obtained from the Laboratory Animal Center of Hebei Medical
University and used in the experiment immediately. Rat myocytes
were prepared as previously described (19). Neonatal SD rats were euthanized using
carbon dioxide (CO2) and the flow rate displaced 20% of
the chamber volume/minute. Rats were exposed to 50% CO2
until they were euthanized, at which point they were decapitated.
Rat ventricles were subsequently removed, minced and digested in
PBS (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA)
containing 0.1% trypsin (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA, Darmstadt,
Germany) and 0.04% type II collagenase (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) eight to 10 times. Samples were centrifuged (320
× g, 37°C, 5 min) and suspended in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's
medium (DMEM; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) containing 10% fetal
bovine serum (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and 5.5 mmol/l
D-glucose. The suspension was maintained in DMEM for 2 h in a
humidified atmosphere of 95% air and 5% CO2 at 37°C,
which was used to further increase the ratio of rat myocytes to
non-cardiomyocytes. Unattached myocytes were plated at
1×106 cells/cm2 in the aforementioned medium
supplemented with 0.1 mM bromodeoxyuridine (Invitrogen; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at 37°C for 48 h. Myocytes were then
placed in Lonza 12-725F UltraCULTURE serum-free medium (Lonza
Walkersville, Inc., Walkersville, MD, USA) at 37°C for 24 h prior
to experimentation. Rat myocytes were confirmed via morphological
examination on a light microscope at a magnification of ×400 and
staining with an anti-α-sarcomeric actin (α-SMA) antibodies (cat.
no. LM-10196R-FITC; dilution, 1:200; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA)
overnight at 4°C. The α-SMA-positive cells were verified to be
myocytes, ~95% of cells were identified as rat myocytes.
Drug treatments
Liraglutide, a GLP-1 analog, was obtained from Novo
Nordisk Ltd. (Gatwick, UK). Liraglutide at a concentration of 10
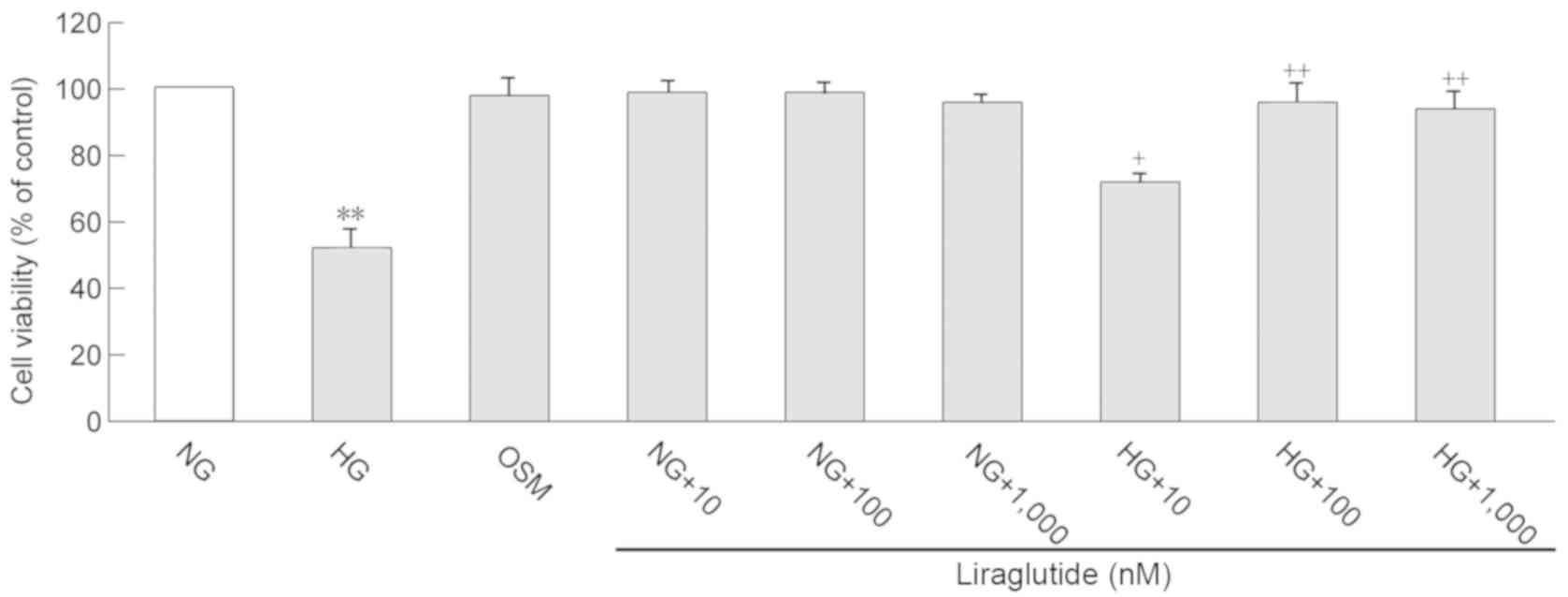
and 100 nmol/l was selected according to previous studies (9,18) and
cardiomyocyte viability determined in the present study (Fig. 1). When cardiomyocytes reached a
confluence of 80%, cells were pre-incubated at 37°C in the presence
or absence of 10 or 100 nmol/l liraglutide for 30 min. DMEM was
then replaced with DMEM containing 5.5 mmol/l D-glucose [normal
glucose (NG) group], 25 mmol/l D-glucose (HG group) or mannitol
containing 5.5 mmol/l D-glucose and 19.5 mmol/l mannitol [osmotic
control (OSM) group]. Myocytes of the HG group were further
incubated at 37°C for 24 h in the presence of liraglutide (10 and
100 nmol/l; named the HG + 10 nM liraglutide and HG + 100 nM
liraglutide groups, respectively).
Cell survival assay
Cell viability was assessed via an MTT assay
(Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA). Myocytes were plated at
1×104 cells/well in 96-well plates and 20 µl of 5 mg/ml
MTT was added to each well and incubated for 4 h at 37°C. Samples
were then were solubilized with 150 µl dimethyl sulfoxide.
Absorbance was read at 490 nm. Each experiment was repeated three
times and three independent experiments were performed.
Flow cytometry
A fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) Annexin-V
apoptosis detection kit (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) was
used to detect apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes following
various treatments. Cardiomyocytes were washed in PBS three times
and resuspended in 400 µl of binding buffer with FITC Annexin V and
propidium iodide (PI, 5 µl of each). Cell suspensions were
incubated for 15 min at room temperature in the dark and analyzed
via flow cytometry within 1 h. FlowJo software (version 7.6; FlowJo
LLC, Ashland, OR, USA) was used for data acquisition. Positive
Annexin V-FITC and negative PI cells were identified as early
apoptotic cells. Apoptosis rate was calculated as the number of
early apoptotic cells relative to the total number of cells. Each
experiment was repeated three times and three independent
experiments were performed.
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity
and malondialdehyde (MDA) content
Following cell treatments, the supernatant was
collected to measure SOD activity and MDA content. Measurements
were obtained using commercial kits (SOD, cat. no. A001-1-1; MDA,
cat. no. A003-1; Nanjing Jiancheng Biological Engineering
Institute, Nanjing, China) in accordance with the manufacturer's
protocol. Each experiment was repeated three times and three
independent experiments were performed.
Western blotting
Myocytes were grown at 1×106
cells/cm2 in culture dishes as aforementioned. Following
rinsing with cold D-Hanks buffer, cells were collected and lysed.
Protein was extracted using radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysis
buffer (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Haimen, China) and
measured using a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kit
(Pierce; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Protein (~50 µg/lane) was
separated on 10% SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to polyvinylidene
fluoride membranes. Membranes were then blocked with 5% fat-free
milk in TBST buffer [20 mmol/l Tris-HCl (pH 7.5); 150 mmol/l NaCl
and 0.05% Tween 20] and subsequently incubated with the following
primary antibodies at 4°C overnight: Anti-cleaved caspase-3 (cat.
no. 9661S; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA),
anti-Bcl2-associated X (Bax; cat. no. BS90120; Bioworld Technology,
Inc., St Louis Park, MN, USA), anti-B cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2; cat.
no. BS1511; Bioworld Technology, Inc., St Louis Park, MN, USA),
anti-full length caspase-3 (cat. no. sc-56053) and polyclonal
anti-β-actin (cat. no. sc-47778; both Santa Cruz Biotechnology,
Inc., Dallas, TX, USA) antibodies. Each primary antibody was
diluted in Tris-buffered saline with Tween 20 to 1:1,000. The
mixture was washed and then incubated at room temperature for 1 h
with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated immunoglobulin G secondary
antibody (dilution 1:500; cat. no. 074-1506; KPL Inc.,
Gaithersburg, MD, USA). Membranes were developed using an ECL kit
(Pierce; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and band quantification
was performed via densitometry using a gel image analysis system
(GelDoc-It; UVP, LLC, Upland, CA, USA) and GeneSnap software
(version 7.8; SynGene, Cambridge, UK). β-actin served as the
loading control. Each experiment was repeated three times and three
independent experiments were performed.
Statistical analysis
Data were presented as the mean ± standard
deviation. One-way analysis of variance was used to assess multiple
differences, followed by a Tukey's post-hoc test with SPSS 19.0
software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). P<0.05 was considered to
indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Effect of HG and liraglutide on
cardiomyocyte viability
Cardiomyocyte viability was assessed using an MTT
assay, the results of which are presented in Fig. 1. Compared with the NG group, cell
viability was significantly decreased in the HG group (P<0.01).
Liraglutide treatment (10, 100 and 1,000 nmol/l) significantly
improved cell viability following exposure to HG (P<0.05 and
P<0.01). However, no significant differences in cell viability
were determined between the concentrations of 100 and 1,000 nmol/l
liraglutide. Therefore, the current study selected 10 and 100
nmol/l liraglutide for the following experiments. All
concentrations of liraglutide (10, 100 and 1,000 nmol/l) did not
affect cell viability when exposed to NG, which indicates that
liraglutide treatment is not cytotoxic to cardiomyocytes.
Effect of HG and liraglutide on
cardiomyocyte apoptosis
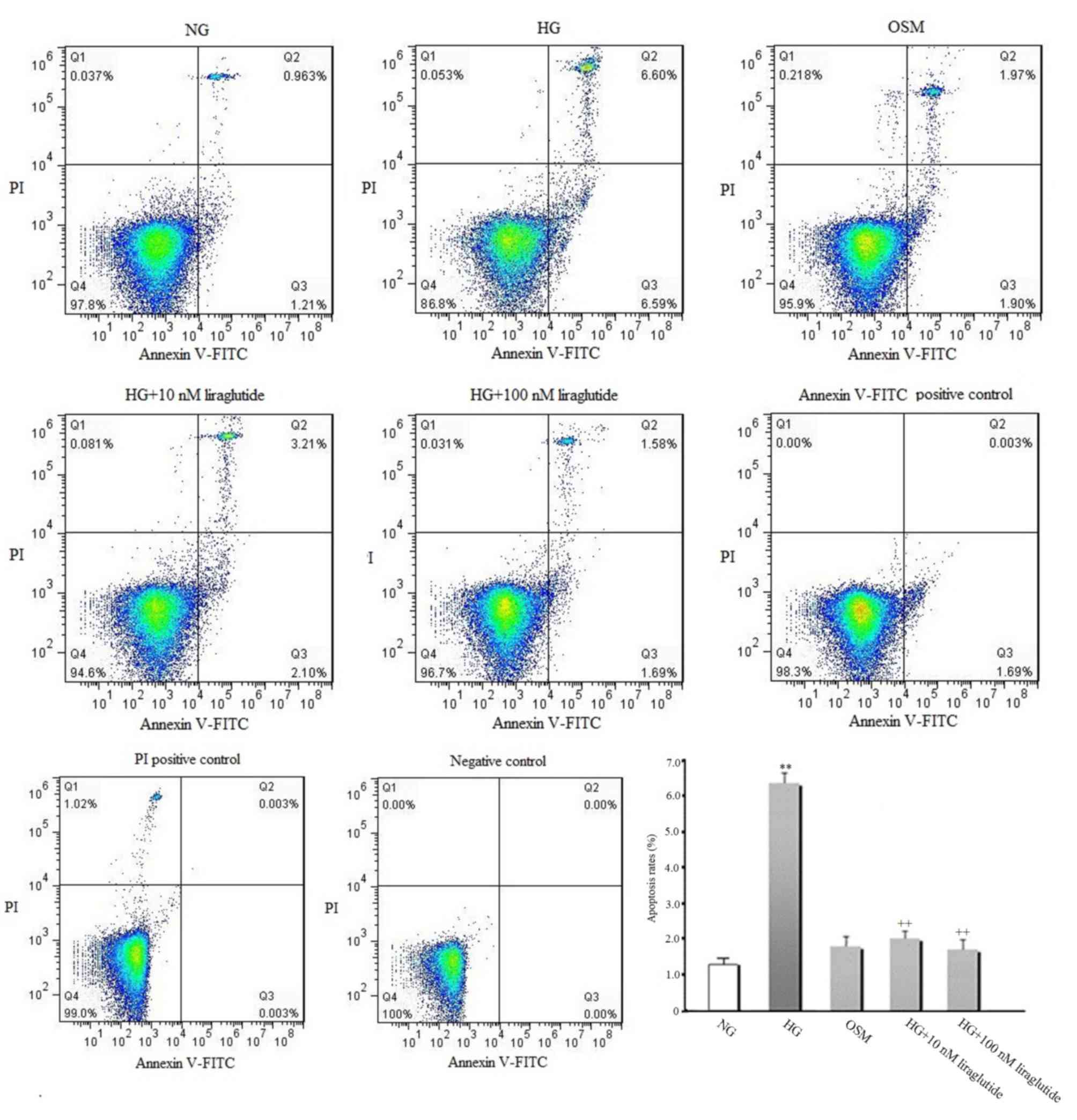
The early apoptosis rate of cardiomyocytes was
measured (Fig. 2). Compared with the
NG group, increased early apoptosis was observed in the presence of
HG (P<0.01). However, liraglutide treatment (10 and 100 nmol/l)
significantly suppressed the HG-induced increase of early apoptosis
(P<0.01). No significant difference in early apoptosis between
the OSM and NG groups was identified, indicating that the effect of
HG on myocyte apoptosis is independent of high osmotic
pressure.
Effect of HG and liraglutide on
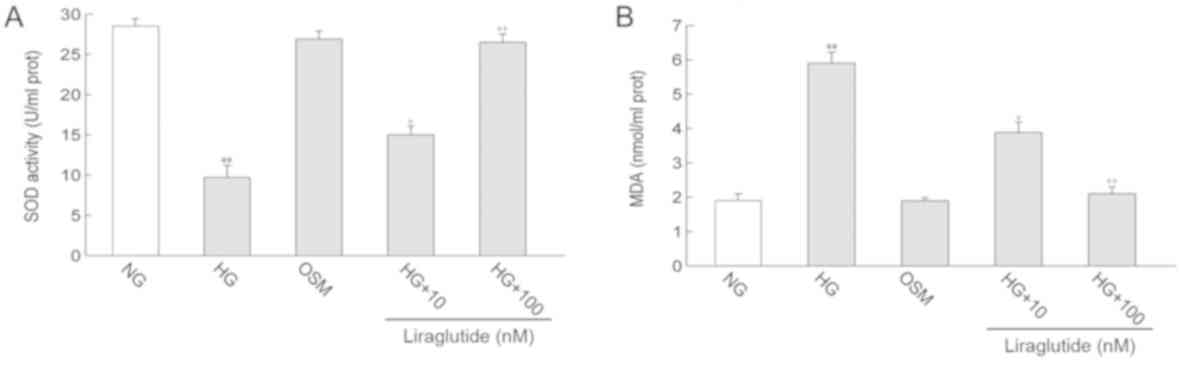
oxidative stress
MDA content, a classic marker of oxidative damage
and SOD activity, a marker of anti-oxidants, were measured.
Compared with the NG group, MDA content in the HG group was
significantly increased (P<0.01). In contrast, SOD activity was
decreased in the HG group compared with the NG group (P<0.01).
Treatment with liraglutide markedly decreased the HG-induced
increase in MDA content and enhanced SOD activity (P<0.05 and
P<0.01). No significant differences in MDA level and SOD
activity were identified between the OSM and NG groups (Fig. 3).
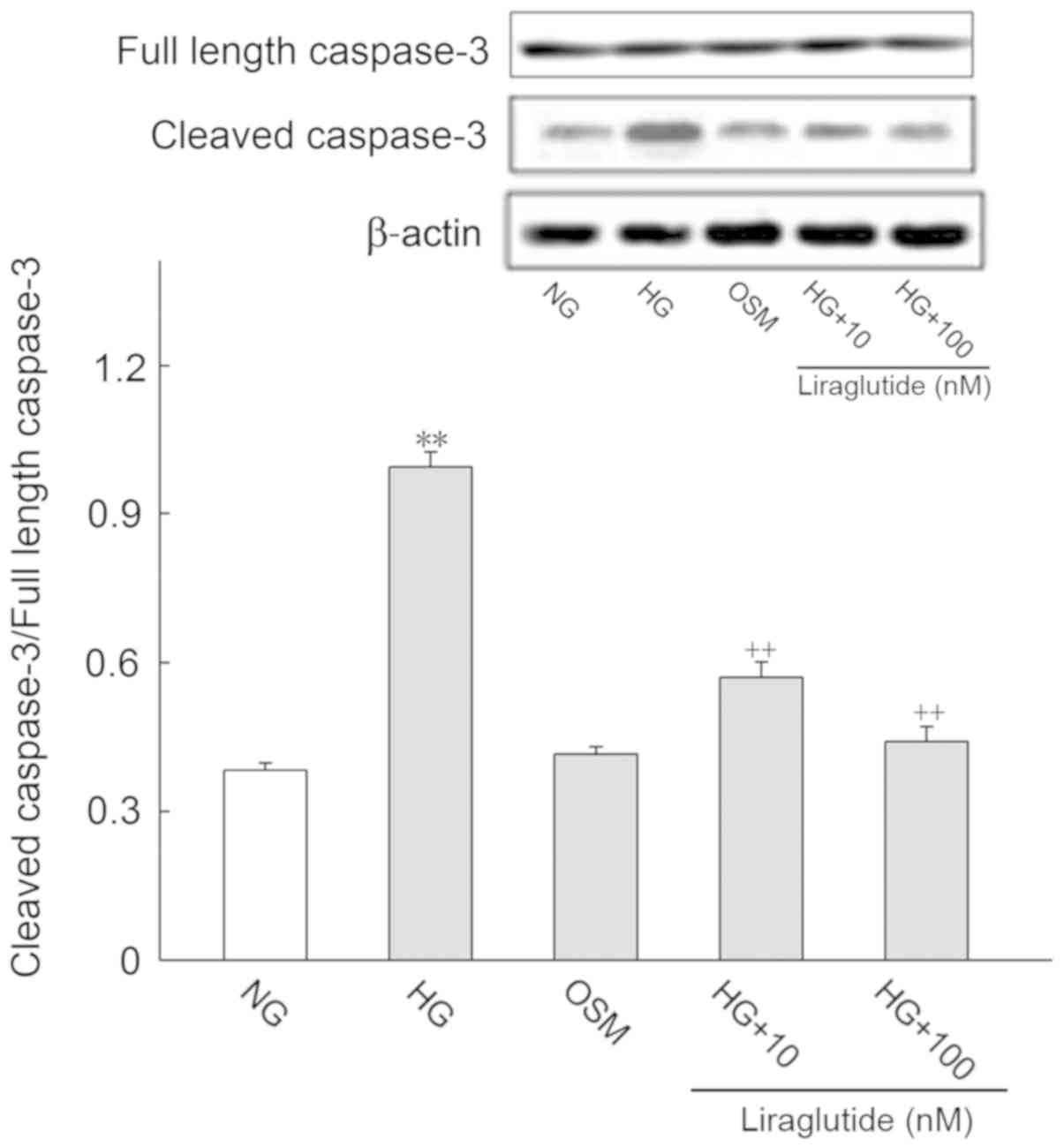
Effect of HG and liraglutide on
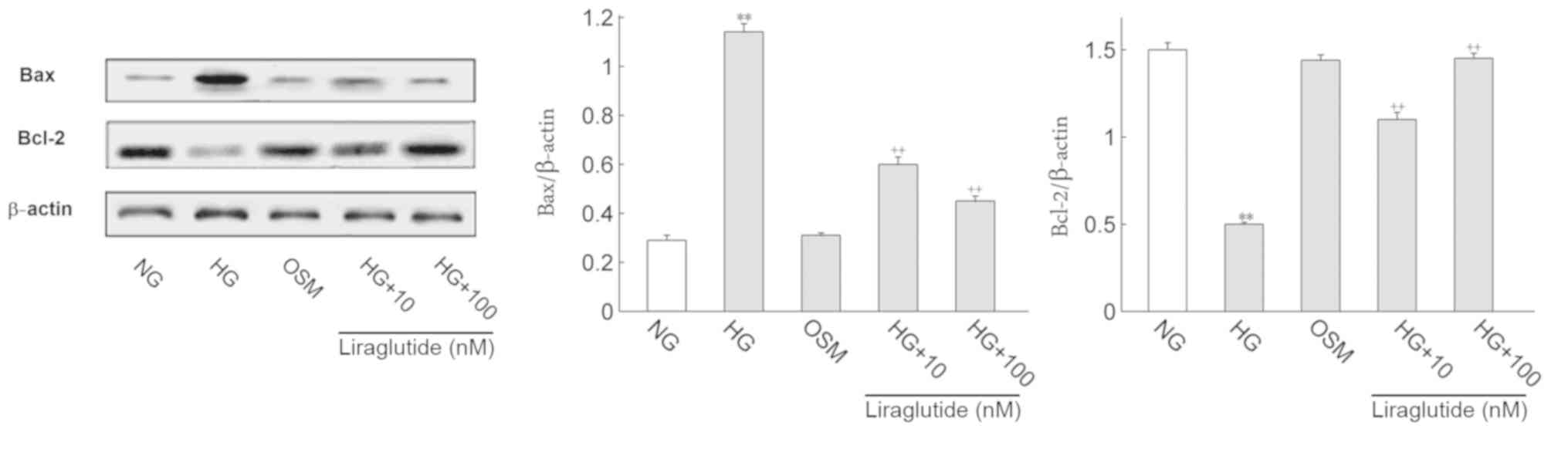
apoptosis-associated proteins
It is well known that apoptosis-associated proteins
regulate the progression of apoptosis. Thus, the protein expression
of Bax, Bcl-2, cleaved caspase-3 and full length caspase-3 were
determined (Figs. 4 and 5, respectively). Cleaved caspase-3/full
length caspase-3 was deemed to represent active caspase-3 levels.
Compared with the NG group, Bax and active caspase-3 expression
were significantly increased and Bcl-2 was markedly decreased in
the HG group (P<0.01). Following treatment with liraglutide, Bax
and active caspase-3 protein levels were significantly decreased
and Bcl-2 was significantly increased when compared with the HG
group (P<0.01). No significant differences in the OSM and NG
groups were identified.
Discussion
In addition to its glucose-lowering effect, GLP-1
analogs exhibit potential clinical and cardioprotective effects.
Arturi et al (20) revealed
that treatment with liraglutide improved left ventricular function
in patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of post-ischemic
chronic heart failure. The Liraglutide Effect and Action in
Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results-A Long Term
Evaluation clinical trial also demonstrated that, among patients
with type 2 diabetes who were at high risk for cardiovascular
events and were receiving standard therapy, those in the
liraglutide group exhibited lower rates of cardiovascular events
and mortality from any cause compared with those in the placebo
group (11). Furthermore, Okada
et al (21) demonstrated that
treatment with liraglutide induced a reduction in reactive oxygen
markers in patients with type 2 diabetes, hypothesizing that the
cardioprotective action of liraglutide may be associated with the
alleviation of oxidative stress. It has also been revealed that
liraglutide increases the activity of nitric oxide synthase in
human endothelial cells, improving their vascular endothelial
function (22,23). These cardioprotective actions may be
associated with the pleiotropic effects that liraglutide exerts on
the heart.
Accumulating evidence has revealed that long-term
exposure to HG results in oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte
apoptosis, which serve important roles in the pathogenesis of DCM
(24–26). Consistent with these observations,
the results of the present study demonstrated that HG augmented
oxidative stress and concurrently triggered the apoptosis signaling
pathway, leading to the upregulation of the pro-apoptotic protein
Bax and the downregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. It
has been previously reported that the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R)
agonist, exenatide, attenuates extracellular matrix remodeling,
cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis in experimental models of
type 1 and type 2 diabetes via various mechanisms, including the
suppression of oxidative stress and myocardial inflammation, as
well as the regulation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and
microvascular barrier function (27–29).
Noyan-Ashraf et al (9)
revealed that treatment with liraglutide reduced infarct
development and improved cardiac output in murine models of type 2
diabetes with myocardial infarction (MI) compared with mice treated
with metformin, and that the effects of liraglutide on enhanced
survival following MI in diabetic mice were independent of glycemic
control and weight loss. Their further experiment revealed that
liraglutide activated cytoprotective pathways, upregulated the
expression of cardioprotective genes (including protein kinase B,
glycogen synthase kinase 3β and nuclear factor erythroid factor
2-related factor 2) and inhibited the activation of caspase-3 in
diabetic murine hearts, which was an effect that was superior to
that of metformin (18).
Additionally, Liu et al (16)
revealed that liraglutide protects against DCM by inhibiting the ER
stress pathway in rat models of type 2 diabetes and that the
improvement of cardiac function by liraglutide was independent of
glucose control. Inoue et al (17) also demonstrated that liraglutide
prevents cardiac oxidative stress and apoptosis by activating the
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) pathway in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats in vivo. These previous
studies confirm that liraglutide inhibits cardiac oxidative stress
and protects against DCM in diabetic animals in vivo. To
further elucidate the protective mechanism of liraglutide against
cardiomyocytes, it is necessary to perform an in vitro
study. The present study demonstrated that liraglutide alleviates
HG-induced oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, which may
be attributable, in part, to the inhibition of Bax expression, the
inhibition of caspase-3 activation and the upregulation of Bcl-2
expression. These results are congruent with those of diabetic
in vivo models utilized in previous studies. Inoue et
al (17) hypothesized that the
beneficial effect of liraglutide on diabetic hearts may be
associated with the improvement of myocardial fatty acid metabolism
in vivo by activating the AMPK-Sirt1 pathway. The results of
the current study revealed that liraglutide exhibited a direct
preventive effect on cardiomyocyte apoptosis in vitro.
However, elucidating the mechanisms by which liraglutide exerts
cardioprotection is challenging, as GLP-1R is largely expressed in
atrial and not ventricular cardiomyocytes (30,31).
Noyan-Ashraf et al (9)
determined that liraglutide increased cyclic AMP formation and
reduced cardiomyocyte caspase-3 activation in a GLP-1R-dependent
manner. The previous study revealed that liraglutide provides
cardioprotection and increased survival in GLP-1R CM−/−
mice, that liraglutide improved cardiac function in a
GLP-1R-independent manner and that atrial GLP-1R is not required
for GLP-1R agonist-mediated cardioprotection (32). Therefore, the cardioprotective
effects of liraglutide may be mediated through GLP-1R-dependent and
GLP-1R-independent pathways (33).
Younce et al (34) determined
that exendin-4 attenuates HG-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in
neonatal rat ventricular myocytes in vitro, and that the
protective effect is dependent on the inhibition of ER stress,
which is downstream of oxidative stress but independent of reduced
oxidative stress. However, these differences among previous studies
on the cardioprotective actions of GLP-1 analogs may be associated
with the different types of GLP-1 analogs used (17,34).
Clinical trials have confirmed that liraglutide
exerts anti-oxidative, anti-atherosclerotic and beneficial
cardiovascular effects in patients with diabetes (5–7,13–15).
Consistent with these data, the present study indicated that
liraglutide exerts a cardioprotective effect. The results may
reveal one of the mechanisms that underlie the cardiovascular
benefit of diabetic patients treated with liraglutide. The present
study has certain limitations. There is an absence of data on the
effect of liraglutide on myocardial apoptosis in an in vivo
rat model of type 2 diabetes. However, a previous study has
demonstrated that liraglutide inhibits cardiac myocyte apoptosis by
decreasing ER stress in DCM rats (16). Furthermore, although early apoptosis
rates and cell viabilities were determined via reliable methods
(flow cytometry and cell viability, respectively) (35,36),
terminal deoxynucleotidyl-tranferase-mediated dUTP nick end
labeling or DNA laddering would have provided stronger evidence to
support conclusions. Additionally, the association between
oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis was not assessed in
the present study. Thus, further experimental confirmation is
required.
In conclusion, the current study revealed that HG
augments oxidative stress and apoptosis in neonatal rat
cardiomyocytes. It also demonstrated that liraglutide suppresses
HG-induced oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, indicating
that the anti-apoptotic actions of liraglutide may be, in part, due
to the inhibition of Bax, the inhibition of caspase-3 activation
and the upregualtion of Bcl-2.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr Wenjian Li
(Department of immunology, School of Basic Medicine, Hebei Medical
University) for providing technical assistance.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Author contributions
ZL and LC cultured cardiomyocytes and wrote the
manuscript. ZQ and LN performed the superoxide dismutase and
malondialdehyde measurements, and western blotting. ZH designed the
current study and performed statistical analysis. All authors read
and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethical approval and consent to
participate
The animal protocol was reviewed and approved by the
Laboratory Animal Ethical and Welfare Committee of Hebei Medical
University (Shijiazhuang, China).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Jia G, Whaley-Connell A and Sowers JR:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: A hyperglycaemia-and
insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia. 61:21–28.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aneja A, Tang WH, Bansilal S, Garcia MJ
and Farkouh ME: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Insights into
pathogenesis, diagnostic challenges, and therapeutic options. Am J
Med. 121:748–757. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang Y, Sun W, Du B, Miao X, Bai Y, Xin Y,
Tan Y, Cui W, Liu B, Cui T, et al: Therapeutic effect of MG-132 on
diabetic cardiomyopathy is associated with its suppression of
proteasomal activities: Roles of Nrf2 and NF-κB. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 304:H567–H578. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guan SJ, Ma ZH, Wu YL, Zhang JP, Liang F,
Weiss JW, Guo QY, Wang JY, Ji ES and Chu L: Long-term
administration of fasudil improves cardiomyopathy in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
50:1874–1882. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Scheen AJ: Cardiovascular effects of new
oral glucose-lowering agents: DPP-4 and SGLT-2 inhibitors. Circ
Res. 122:1439–1459. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Drucker DJ: The biology of incretin
hormones. Cell Metab. 3:153–165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Drucker DJ, Habener JF and Holst JJ:
Discovery, characterization, and clinical development of the
glucagon-like peptides. J Clin Invest. 127:4217–4227. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Drucker DJ: The cardiovascular biology of
glucagon-like peptide-1. Cell Metab. 24:15–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Noyan-Ashraf MH, Momen MA, Ban K, Sadi AM,
Zhou YQ, Riazi AM, Baggio LL, Henkelman RM, Husain M and Drucker
DJ: GLP-1R agonist liraglutide activates cytoprotective pathways
and improves outcomes after experimental myocardial infarction in
mice. Diabetes. 58:975–983. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dokken BB, La Bonte LR, Davis-Gorman G,
Teachey MK, Seaver N and McDonagh PF: Glucagon-like peptide-1
(GLP-1), immediately prior to reperfusion, decreases neutrophil
activation and reduces myocardial infarct size in rodents. Horm
Metab Res. 43:300–305. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K,
Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, Nissen SE, Pocock S, Poulter NR,
Ravn LS, et al: Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2
diabetes. N Engl J Med. 375:311–322. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz
FG, Jódar E, Leiter LA, Lingvay I, Rosenstock J, Seufert J, Warren
ML, et al: Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with
type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 375:1834–1844. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nauck MA, Meier JJ, Cavender MA, Abd El
Aziz M and Drucker DJ: Cardiovascular actions and clinical outcomes
with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl
peptidase-4 inhibitors. Circulation. 136:849–870. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rizzo M, Abate N, Chandalia M, Rizvi AA,
Giglio RV, Nikolic D, Marino Gammazza A, Barbagallo I, Isenovic ER,
Banach M, et al: Liraglutide reduces oxidative stress and restores
heme oxygenase-1 and ghrelin levels in patients with type 2
diabetes: A prospective pilot study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
100:603–606. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rizzo M, Rizvi AA, Patti AM, Nikolic D,
Giglio RV, Castellino G, Li Volti G, Caprio M, Montalto G,
Provenzano V, et al: Liraglutide improves metabolic parameters and
carotid intima-media thickness in diabetic patients with the
metabolic syndrome: An 18-month prospective study. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 15:1622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu J, Liu Y, Chen L, Wang Y and Li J:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 analog liraglutide protects against
diabetic cardiomyopathy by the inhibition of the endoplasmic
reticulum stress pathway. J Diabetes Res. 2013:6305372013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Inoue T, Inoguchi T, Sonoda N, Hendarto H,
Makimura H, Sasaki S, Yokomizo H, Fujimura Y, Miura D and
Takayanagi R: GLP-1 analog liraglutide protects against cardiac
steatosis, oxidative stress and apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Atherosclerosis. 240:250–259. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Noyan-Ashraf MH, Shikatani EA, Schuiki I,
Mukovozov I, Wu J, Li RK, Volchuk A, Robinson LA, Billia F, Drucker
DJ and Husain M: A glucagon-like peptide-1 analog reverses the
molecular pathology and cardiac dysfunction of a mouse model of
obesity. Circulation. 127:74–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu C, Xue R, Wu D, Wu L, Chen C, Tan W,
Chen Y and Dong Y: REDD1 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via
enhancing autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 454:215–220. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Arturi F, Succurro E, Miceli S, Cloro C,
Ruffo M, Maio R, Perticone M, Sesti G and Perticone F: Liraglutide
improves cardiac function in patients with type 2 diabetes and
chronic heart failure. Endocrin. 57:464–473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Okada K, Kotani K, Yaqyu H, Ando A, Osuqa
J and Ishibashi S: Effects of treatment with liraglutide on
oxidative strss and cardiac natriuretic peptide levels in patients
with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine. 47:962–964. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai Y, Mehta JL and Chen M: Glucagon-like
peptide-1 receptor agonist liraglutide inhibits endothelin-1 in
endothelial cell by repressing nuclear factor-kappa B activation.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 27:371–380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nandy D, Johnson C, Basu R, Joyner M,
Brett J, Svendsen CB and Basu A: The effect of liraglutide on
endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diab Vasc
Dis Res. 11:419–430. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo S, Yao Q, Ke Z, Chen H, Wu J and Liu
C: Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced oxidative stress and
cardiomyocyte apoptosis through AMPK. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
412:85–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang F, Lin X, Yu L, Li W, Qian D, Cheng
P, He L, Yang H and Zhang C: Low-dose radiation prevents type 1
diabetes-induced cardiomyopathy via activation of AKT mediated
anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidant effects. J Cell Mol Med.
20:1352–1366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Despa S, Margulies KB, Chen L, Knowlton
AA, Havel PJ, Taegtmeyer H, Bers DM and Despa F: Hyperamylinemia
contributes to cardiac dysfunction in obesity and diabetes: A study
in humans and rats. Circ Res. 110:598–608. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Monji A, Mitsui T, Bando YK, Aoyama M,
Shigeta T and Murohara T: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
activation reverses cardiac remodeling via normalizing cardiac
steatosis and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 305:H295–H304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang D, Luo P, Wang Y, Li W, Wang C, Sun
D, Zhang R, Su T, Ma X, Zeng C, et al: Glucagon-like peptide-1
protects against cardiac microvascular injury in diabetes via a
cAMP/PKA/Rho-dependent mechanism. Diabetes. 62:1697–1708. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
XiaoTian L, QiNan W, XiaGuang G, WuQuan D,
Bing C and ZiWen L: Exenatide activates the APPL1-AMPK-PPARα axis
to prevent diabetic cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Diabetes Res.
2016:42197352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim M, Platt MJ, Shibasaki T, Quaggin SE,
Backx PH, Seino S, Simpson JA and Drucker DJ: GLP-1 receptor
activation and Epac2 link atrial natriuretic peptide secretion to
control of blood pressure. Nat Med. 19:567–575. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Richards P, Parker HE, Adriaenssens AE,
Hodgson JM, Cork SC, Trapp S, Gribble FM and Reimann F:
Identification and characterisation of glucagon-like peptide-1
receptor expressing cells using a new transgenic mouse model.
Diabetes. 63:1224–1233. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ussher JR, Baggio LL, Campbell JE,
Mulvihill EE, Kim M, Kabir MG, Cao X, Baranek BM, Stoffers DA,
Seeley RJ and Drucker DJ: Inactivation of the cardiomyocyte
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) unmasks
cardiomyocyte-independent GLP-1R-mediated cardioprotection. Mol
Metab. 3:507–517. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ban K, Noyan-Ashraf MH, Hoefer J, Bolz SS,
Drucker DJ and Husain M: Cardioprotective and vasodilatory actions
of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor are mediated through both
glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-dependent and -independent
pathways. Circulation. 117:2340–2350. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Younce CW, Burmeister MA and Ayala JE:
Exendin-4 attenuates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis
via inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress and activation of
SERCA2a. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 304:C508–C518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu H, Chen X, Han Y, Li C, Chen P, Su S,
Zhang Y and Pan Z: Rho kinase inhibition by fasudil suppresses
lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of rat pulmonary microvascular
endothelial cells via JNK and p38 MAPK pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 68:267–275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gao H, Hou F, Dong R, Wang Z, Zhao C, Tang
W and Wu Y: Rho-Kinase inhibitor fasudil suppresses high
glucose-induced H9c2 cell apoptosis through activation of
autophagy. Cardiovasc Ther. 34:352–359. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|