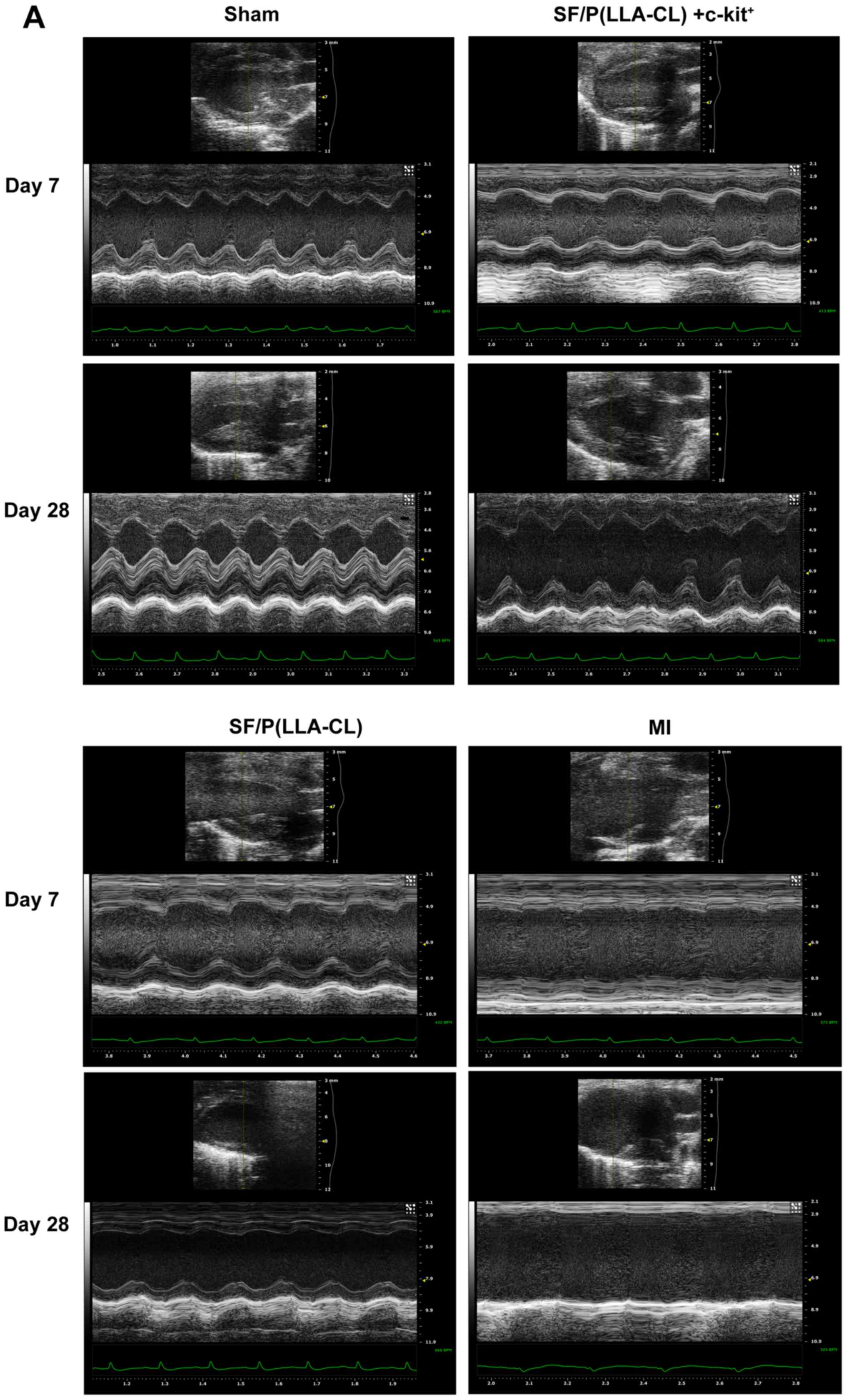
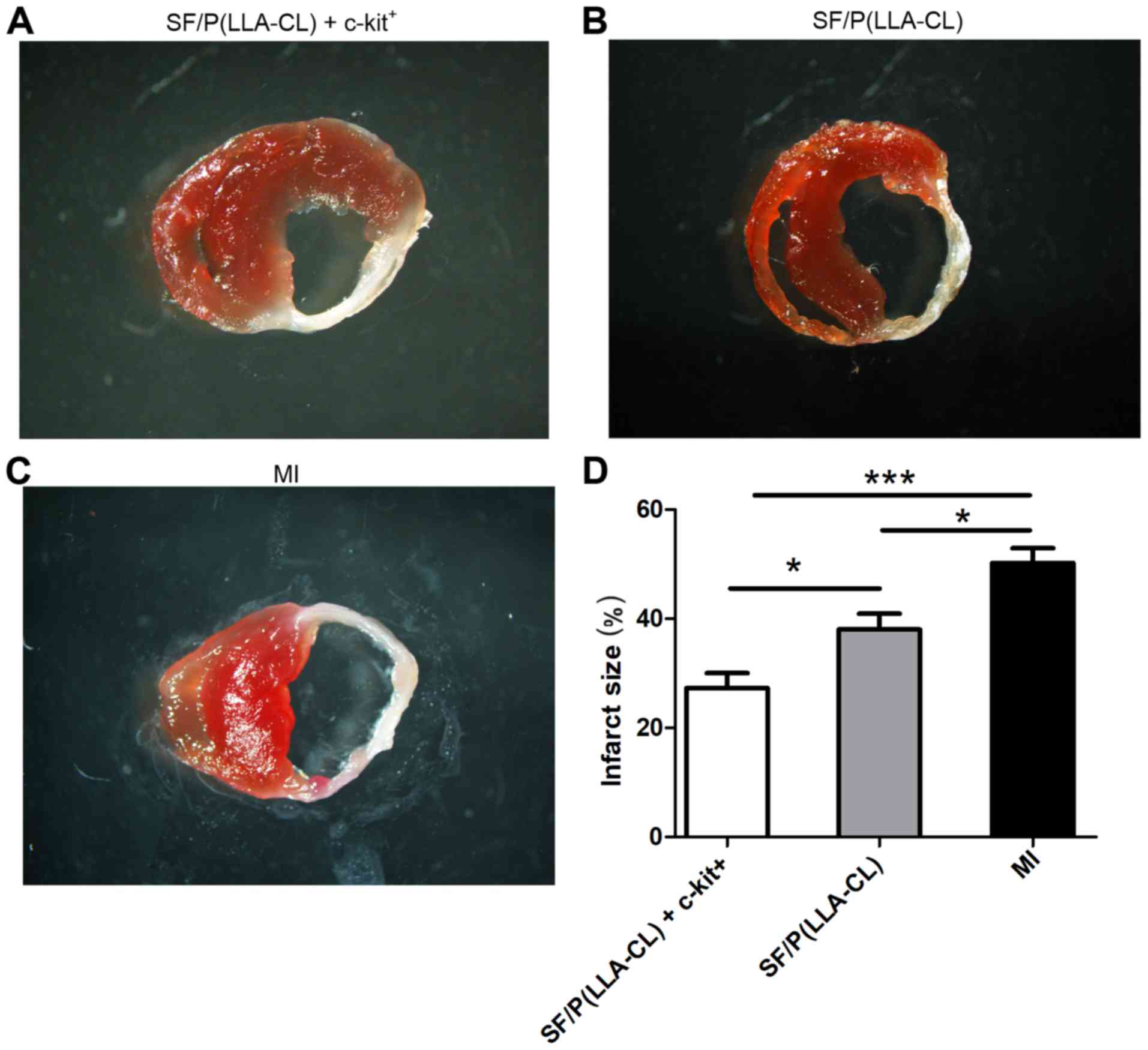
|
1
|
Du M, Schmull S, Zhang W, Wang C, Lian F,
Chen Y and Xue S: c-kit(+)AT2R(+) bone marrow mononuclear cell
subset is a superior subset for cardiac protection after myocardial
infarction. Stem Cells Int. 2016:49135152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duran JM, Makarewich CA, Sharp TE,
Starosta T, Zhu F, Hoffman NE, Chiba Y, Madesh M, Berretta RM, Kubo
H and Houser SR: Bone-derived stem cells repair the heart after
myocardial infarction through transdifferentiation and paracrine
signaling mechanisms. Circ Res. 113:539–552. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jessup M and Brozena S: Heart failure. N
Engl J Med. 348:2007–2018. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lehtinen M, Pätilä T, Kankuri E, Lauerma
K, Sinisalo J, Laine M, Kupari M, Vento A and Harjula A; Helsinki
BMMC Collaboration, : Intramyocardial bone marrow mononuclear cell
transplantation in ischemic heart failure: Long-term follow-up. J
Heart Lung Transplant. 34:899–905. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gude NA and Sussman MA: Chasing c-Kit
through the heart: Taking a broader view. Pharmacol Res.
127:110–115. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lagostena L, Avitabile D, De Falco E,
Orlandi A, Grassi F, Iachininoto MG, Ragone G, Fucile S, Pompilio
G, Eusebi F, et al: Electrophysiological properties of mouse bone
marrow c-kit+ cells co-cultured onto neonatal cardiac myocytes.
Cardiovasc Res. 66:482–492. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu J, Wu P, Wang H, Wang Y, Du Y, Cheng
W, Xu Z, Zhou N, Wang L and Yang Z: Necroptosis induced by Ad-HGF
activates endogenous C-Kit+ cardiac stem cells and promotes
cardiomyocyte proliferation and angiogenesis in the infarcted aged
heart. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:847–860. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Awada HK, Long DW, Wang Z, Hwang MP, Kim K
and Wang Y: A single injection of protein-loaded coacervate-gel
significantly improves cardiac function post infarction.
Biomaterials. 125:65–80. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kai D, Prabhakaran MP, Jin G and
Ramakrishna S: Polypyrrole-contained electrospun conductive
nanofibrous membranes for cardiac tissue engineering. J Biomed
Mater Res A. 99:376–385. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Godier-Furnemont AF, Martens TP, Koeckert
MS, Wan L, Parks J, Arai K, Zhang G, Hudson B, Homma S and
Vunjak-Novakovic G: Composite scaffold provides a cell delivery
platform for cardiovascular repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:7974–7979. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dhand C, Ong ST, Dwivedi N, Diaz SM,
Venugopal JR, Navaneethan B, Fazil MH, Liu S, Seitz V, Wintermantel
E, et al: Bio-inspired in situ crosslinking and
mineralization of electrospun collagen scaffolds for bone tissue
engineering. Biomaterials. 104:323–338. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mo Y, Guo R, Zhang Y, Xue W and Cheng B:
Controlled dual delivery of angiogenin and curcumin by electrospun
nanofibers for skin regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 27:2017.
|
|
13
|
Prabhakaran MP, Kai D, Ghasemi-Mobarakeh L
and Ramakrishna S: Electrospun biocomposite nanofibrous patch for
cardiac tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 6:1748–6041. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kai D, Prabhakaran MP, Jin G and
Ramakrishna S: Guided orientation of cardiomyocytes on electrospun
aligned nanofibers for cardiac tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater
Res B Appl Biomater. 98:379–386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Lin M, Xie Q, Sun H, Huang Y,
Zhang D, Yu Z, Bi X, Chen J, Wang J, et al: Electrospun silk
fibroin/poly(lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone) nanofibrous scaffolds
for bone regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 11:1483–1500.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang D, Ni N, Chen J, Yao Q, Shen B,
Zhang Y, Zhu M, Wang Z, Ruan J, Wang J, et al: Electrospun SF/PLCL
nanofibrous membrane: A potential scaffold for retinal progenitor
cell proliferation and differentiation. Sci Rep. 5:143262015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang CY, Zhang KH, Fan CY, Mo XM, Ruan HJ
and Li FF: Aligned natural-synthetic polyblend nanofibers for
peripheral nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater. 7:634–643. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen J, Yan C, Zhu M, Yao Q, Shao C, Lu W,
Wang J, Mo X, Gu P, Fu Y and Fan X: Electrospun nanofibrous
SF/P(LLA-CL) membrane: A potential substratum for endothelial
keratoplasty. Int J Nanomedicine. 10:3337–3350. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xiang P, Wu KC, Zhu Y, Xiang L, Li C, Chen
DL, Chen F, Xu G, Wang A, Li M and Jin ZB: A novel Bruch's
membrane-mimetic electrospun substrate scaffold for human retinal
pigment epithelium cells. Biomaterials. 35:9777–9788. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang K, Mo X, Huang C, He C and Wang H:
Electrospun scaffolds from silk fibroin and their cellular
compatibility. J Biomed Mater Res A. 93:976–983. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kuihua Z, Chunyang W, Cunyi F and Xiumei
M: Aligned SF/P(LLA-CL)-blended nanofibers encapsulating nerve
growth factor for peripheral nerve regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res
A. 102:2680–2691. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang K, Wang H, Huang C, Su Y, Mo X and
Ikada Y: Fabrication of silk fibroin blended P(LLA-CL) nanofibrous
scaffolds for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 93:984–993.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aznar-Cervantes S, Pagán A, Martínez JG,
Bernabeu-Esclapez A, Otero TF, Meseguer-Olmo L, Paredes JI and
Cenis JL: Electrospun silk fibroin scaffolds coated with reduced
graphene promote neurite outgrowth of PC-12 cells under electrical
stimulation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 79:315–325. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Du J, Zhang L, Wang Z, Yano N, Zhao YT,
Wei L, Dubielecka-Szczerba P, Liu PY, Zhuang S, Qin G and Zhao TC:
Exendin-4 induces myocardial protection through MKK3 and Akt-1 in
infarcted hearts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 310:C270–C283. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brooks AC, DeMartino AM, Brainard RE,
Brittian KR, Bhatnagar A and Jones SP: Induction of activating
transcription factor 3 limits survival following infarct-induced
heart failure in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
309:H1326–H1335. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nishikido T, Oyama J, Shiraki A, Komoda H
and Node K: Deletion of apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage
(AIM)/CD5L attenuates the inflammatory response and infarct size in
acute myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 5:0028632016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hu X, Huang X, Yang Q, Wang L, Sun J, Zhan
H, Lin J, Pu Z, Jiang J, Sun Y, et al: Safety and efficacy of
intracoronary hypoxia-preconditioned bone marrow mononuclear cell
administration for acute myocardial infarction patients: The
CHINA-AMI randomized controlled trial. Int J Cardiol. 184:446–451.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bao L, Meng Q, Li Y, Deng S, Yu Z, Liu Z,
Zhang L and Fan H: C-Kit positive cardiac stem cells and bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells synergistically enhance
angiogenesis and improve cardiac function after myocardial
infarction in a paracrine manner. J Card Fail. 23:403–415. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fazel S, Cimini M, Chen L, Li S,
Angoulvant D, Fedak P, Verma S, Weisel RD, Keating A and Li RK:
Cardioprotective c-kit+ cells are from the bone marrow and regulate
the myocardial balance of angiogenic cytokines. J Clin Invest.
116:1865–1877. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yao Q, Cosme JG, Xu T, Miszuk JM, Picciani
PH, Fong H and Sun H: Three dimensional electrospun PCL/PLA blend
nanofibrous scaffolds with significantly improved stem cells
osteogenic differentiation and cranial bone formation.
Biomaterials. 115:115–127. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li H, Wu T, Zheng Y, El-Hamshary H,
Al-Deyab SS and Mo X: Fabrication and characterization of
Mg/P(LLA-CL)-blended nanofiber scaffold. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.
25:1013–1027. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang K, Fu Q, Yoo J, Chen X, Chandra P,
Mo X, Song L, Atala A and Zhao W: 3D bioprinting of urethra with
PCL/PLCL blend and dual autologous cells in fibrin hydrogel: An in
vitro evaluation of biomimetic mechanical property and cell growth
environment. Acta Biomater. 50:154–164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fluke LM, Restrepo RD, Patel S, Hoagland
BD, Krevetski LM and Stephenson JT: Strength and histology of a
nanofiber scaffold in rats. J Surg Res. 205:432–439. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Johari N, Madaah Hosseini HR and
Samadikuchaksaraei A: Optimized composition of nanocomposite
scaffolds formed from silk fibroin and nano-TiO2 for bone tissue
engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 79:783–792. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Naskar D, Ghosh AK, Mandal M, Das P, Nandi
SK and Kundu SC: Dual growth factor loaded nonmulberry silk
fibroin/carbon nanofiber composite 3D scaffolds for in vitro and in
vivo bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 136:67–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yin A, Luo R, Li J, Mo X, Wang Y and Zhang
X: Coaxial electrospinning multicomponent functional
controlled-release vascular graft: Optimization of graft
properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 152:432–439. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Y, Xu Y, Wang Z, Wen D, Zhang W,
Schmull S, Li H, Chen Y and Xue S: Electrospun nanofibrous sheets
of collagen/elastin/polycaprolactone improve cardiac repair after
myocardial infarction. Am J Transl Res. 8:1678–1694.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kai D, Wang QL, Wang HJ, Prabhakaran MP,
Zhang Y, Tan YZ and Ramakrishna S: Stem cell-loaded nanofibrous
patch promotes the regeneration of infarcted myocardium with
functional improvement in rat model. Acta Biomater. 10:2727–2738.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stevens KR, Kreutziger KL, Dupras SK,
Korte FS, Regnier M, Muskheli V, Nourse MB, Bendixen K, Reinecke H
and Murry CE: Physiological function and transplantation of
scaffold-free and vascularized human cardiac muscle tissue. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:16568–16573. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Beltrami AP, Barlucchi L, Torella D, Baker
M, Limana F, Chimenti S, Kasahara H, Rota M, Musso E, Urbanek K, et
al: Adult cardiac stem cells are multipotent and support myocardial
regeneration. Cell. 114:763–776. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hao H, Hu S, Chen H, Bu D, Zhu L, Xu C,
Chu F, Huo X, Tang Y, Sun X, et al: Loss of endothelial CXCR7
impairs vascular homeostasis and cardiac remodeling after
myocardial infarction: Implications for cardiovascular drug
discovery. Circulation. 135:1253–1264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pinet F, Cuvelliez M, Kelder T, Amouyel P,
Radonjic M and Bauters C: Integrative network analysis reveals
time-dependent molecular events underlying left ventricular
remodeling in post-myocardial infarction patients. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:1445–1453. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Olivier A, Girerd N, Michel JB,
Ketelslegers JM, Fay R, Vincent J, Bramlage P, Pitt B, Zannad F and
Rossignol P; EPHESUS Investigators, : Combined baseline and
one-month changes in big endothelin-1 and brain natriuretic peptide
plasma concentrations predict clinical outcomes in patients with
left ventricular dysfunction after acute myocardial infarction:
Insights from the Eplerenone Post-Acute Myocardial Infarction Heart
Failure Efficacy and Survival Study (EPHESUS) study. Int J Cardiol.
241:344–350. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Frey A, Saxon VM, Popp S, Lehmann M,
Mathes D, Pachel C, Hofmann U, Ertl G, Lesch KP and Frantz S: Early
citalopram treatment increases mortality due to left ventricular
rupture in mice after myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
98:28–36. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|