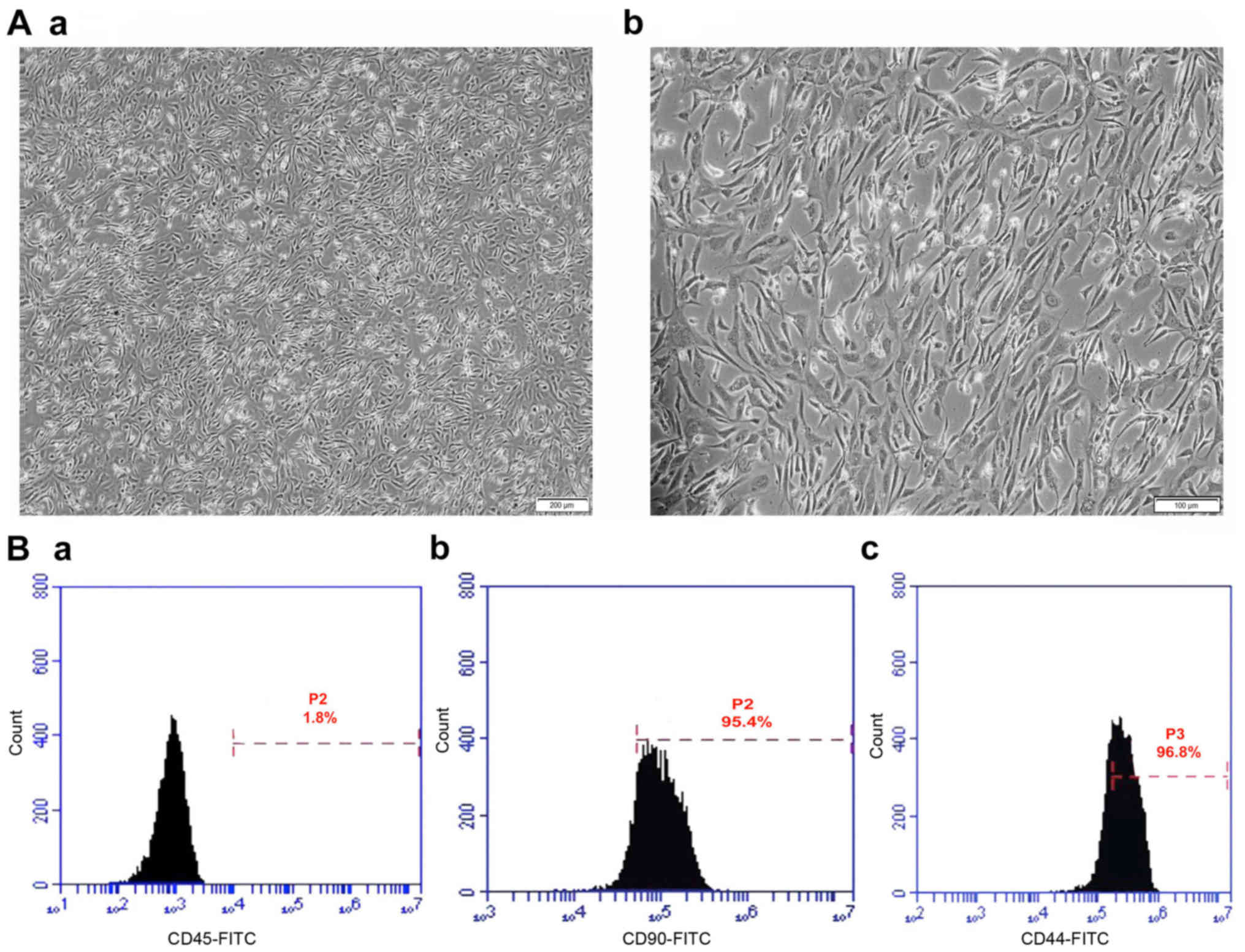
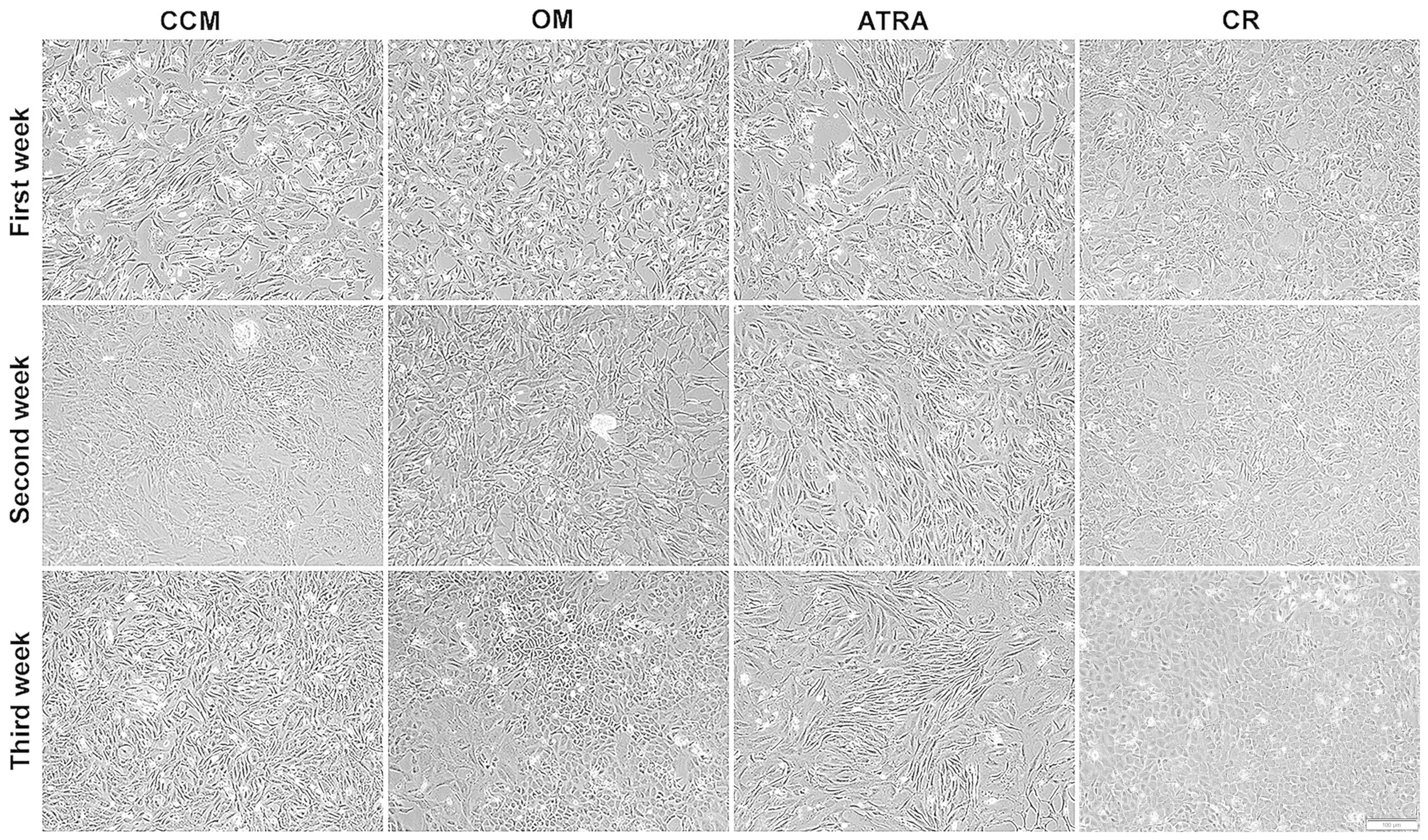
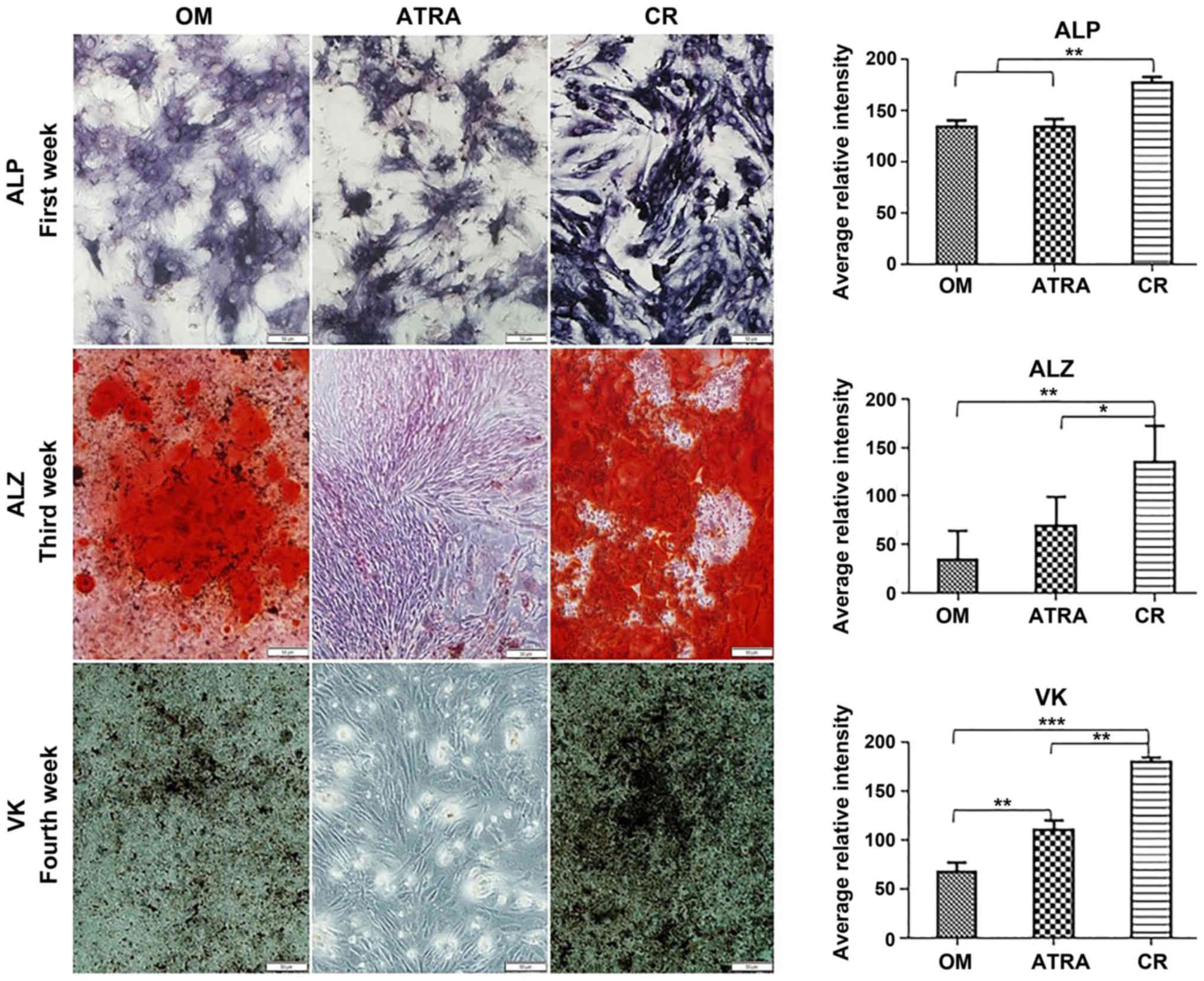
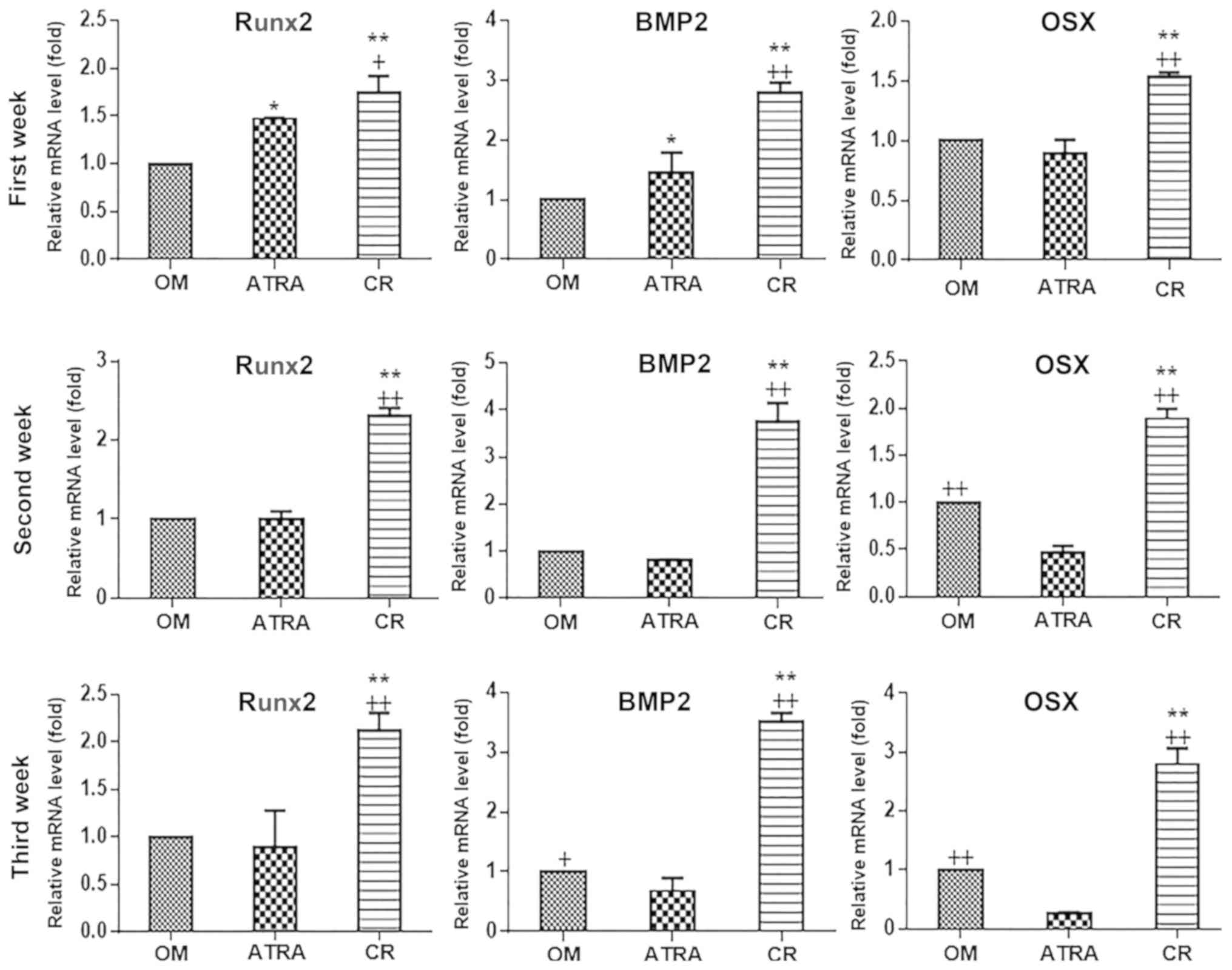
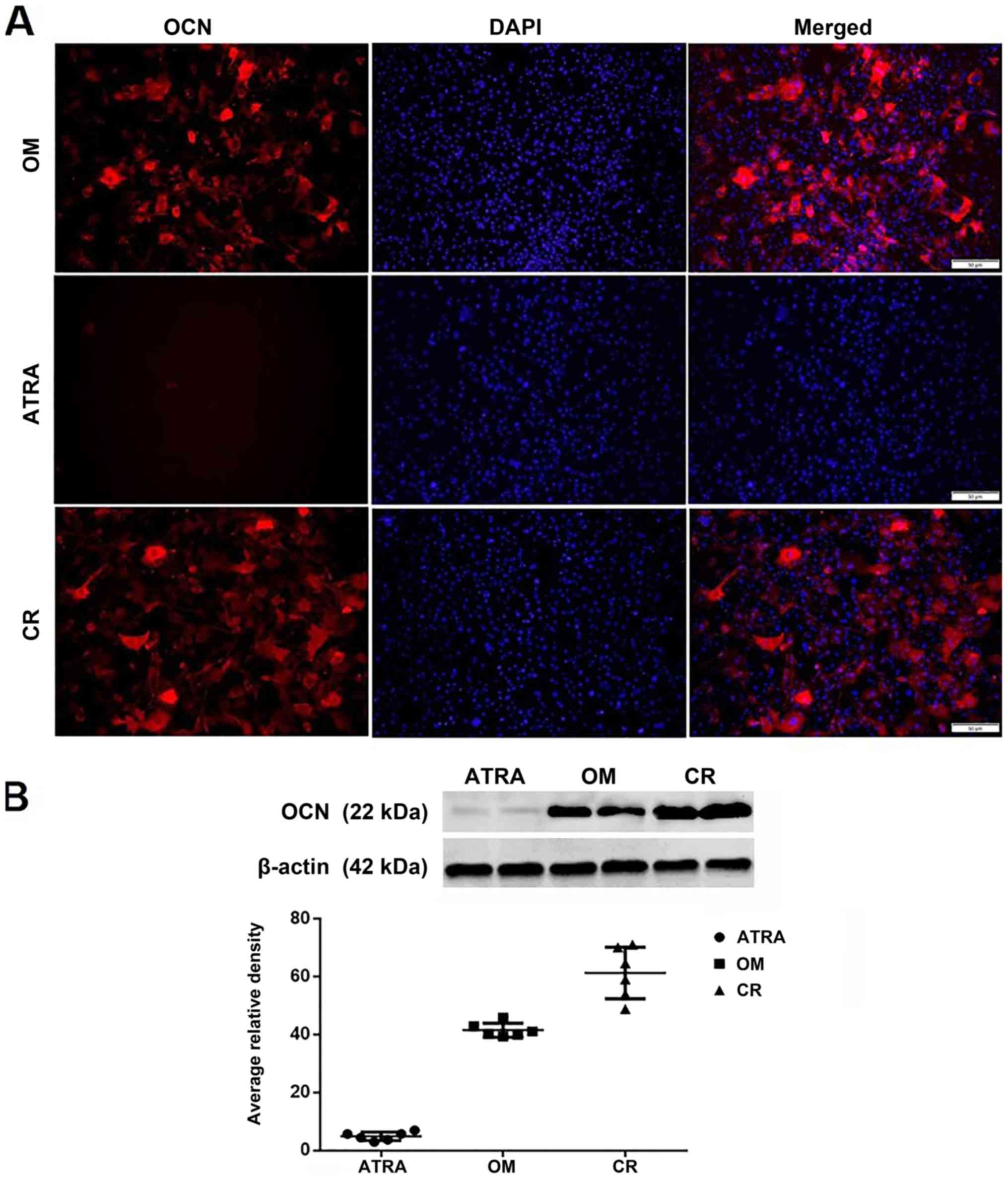
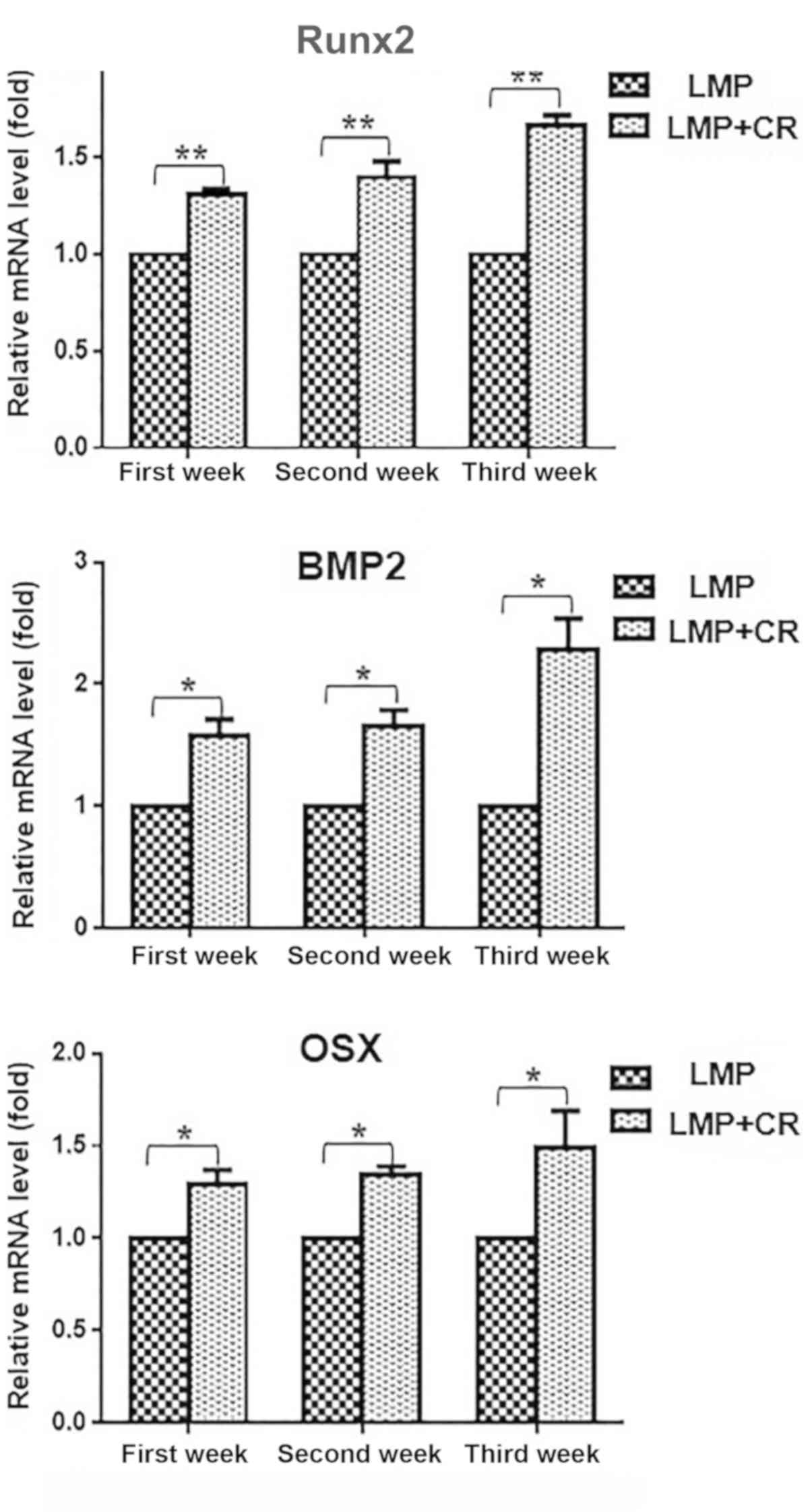
|
1
|
Wrobel E, Leszczynska J and Brzoska E: The
characteristics of human bone-derived cells (HBDCS) during
osteogenesis in vitro. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 21:262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bianco P, Riminucci M, Gronthos S and
Robey PG: Bone marrow stromal stem cells: Nature, biology, and
potential applications. Stem Cells. 19:180–192. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kon E, Muraglia A, Corsi A, Bianco P,
Marcacci M, Martin I, Boyde A, Ruspantini I, Chistolini P, Rocca M,
et al: Autologous bone marrow stromal cells loaded onto porous
hydroxyapatite ceramic accelerate bone repair in critical-size
defects of sheep long bones. J Biomed Mater Res. 49:328–337. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Petite H, Viateau V, Bensaïd W, Meunier A,
de Pollak C, Bourguignon M, Oudina K, Sedel L and Guillemin G:
Tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Nat Biotechnol. 18:959–963.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Quarto R, Mastrogiacomo M, Cancedda R,
Kutepov SM, Mukhachev V, Lavroukov A, Kon E and Marcacci M: Repair
of large bone defects with the use of autologous bone marrow
stromal cells. N Engl J Med. 344:385–386. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Beresford JN, Bennett JH, Devlin C, Leboy
PS and Owen ME: Evidence for an inverse relationship between the
differentiation of adipocytic and osteogenic cells in rat marrow
stromal cell cultures. J Cell Sci. 102:341–351. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Caplan AI: Adult mesenchymal stem cells
for tissue engineering versus regenerative medicine. J Cell
Physiol. 213:341–347. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jaiswal N, Haynesworth SE, Caplan AI and
Bruder SP: Osteogenic differentiation of purified, culture-expanded
human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 64:295–312.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu L, Chaudhary SC, Atigadda VR, Belyaeva
OV, Harville SR, Elmets CA, Muccio DD, Athar M and Kedishvili NY:
Retinoid X receptor agonists upregulate genes responsible for the
biosynthesis of all-trans-retinoic acid in human epidermis. PLoS
One. 11:e01535562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jacobson A, Johansson S, Branting M and
Melhus H: Vitamin A differentially regulates RANKL and OPG
expression in human osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
322:162–167. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Michaëlsson K, Lithell H, Vessby B and
Melhus H: Serum retinol levels and the risk of fracture. N Engl J
Med. 348:287–294. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Skillington J, Choy L and Derynck R: Bone
morphogenetic protein and retinoic acid signaling cooperate to
induce osteoblast differentiation of preadipocytes. J Cell Biol.
159:135–146. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hisada K, Hata K, Ichida F, Matsubara T,
Orimo H, Nakano T, Yatani H, Nishimura R and Yoneda T: Retinoic
acid regulates commitment of undifferentiated mesenchymal stem
cells into osteoblasts and adipocytes. J Bone Miner Metab.
31:53–63. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Malladi P, Xu Y, Yang GP and Longaker MT:
Functions of vitamin D, retinoic acid, and dexamethasone in mouse
adipose-derived mesenchymal cells. Tissue Eng. 12:2031–2040. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mirsaidi A, Kleinhans KN, Rimann M, Tiaden
AN, Stauber M, Rudolph KL and Richards PJ: Telomere length,
telomerase activity and osteogenic differentiation are maintained
in adipose-derived stromal cells from senile osteoporotic SAMP6
mice. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 6:378–390. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song HM, Nacamuli RP, Xia W, Bari AS, Shi
YY, Fang TD and Longaker MT: High-dose retinoic acid modulates rat
calvarial osteoblast biology. J Cell Physiol. 202:255–262. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tiaden AN, Breiden M, Mirsaidi A, Weber
FA, Bahrenberg G, Glanz S, Cinelli P, Ehrmann M and Richards PJ:
Human serine protease HTRA1 positively regulates osteogenesis of
human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and mineralization
of differentiating bone-forming cells through the modulation of
extracellular matrix protein. Stem Cells. 30:2271–2282. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wan DC, Shi YY, Nacamuli RP, Quarto N,
Lyons KM and Longaker MT: Osteogenic differentiation of mouse
adipose-derived adult stromal cells requires retinoic acid and bone
morphogenetic protein receptor type IB signaling. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:12335–12340. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wan DC, Siedhoff MT, Kwan MD, Nacamuli RP,
Wu BM and Longaker MT: Refining retinoic acid stimulation for
osteogenic differentiation of murine adipose-derived adult stromal
cells. Tissue Eng. 13:1623–1631. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choong PF, Martin TJ and Ng KW: Effects of
ascorbic acid, calcitriol, and retinoic acid on the differentiation
of preosteoblasts. J Orthop Res. 11:638–647. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Descalzi Cancedda F, Gentili C, Manduca P
and Cancedda R: Hypertrophic chondrocytes undergo further
differentiation in culture. J Cell Biol. 117:427–435. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leboy PS, Beresford JN, Devlin C and Owen
ME: Dexamethasone induction of osteoblast mRNAs in rat marrow
stromal cell cultures. J Cell Physiol. 146:370–378. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Iba K, Chiba H, Yamashita T, Ishii S and
Sawada N: Phase-independent inhibition by retinoic acid of
mineralization correlated with loss of tetranectin expression in a
human osteoblastic cell line. Cell Struct Funct. 26:227–233. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lind T, Sundqvist A, Hu L, Pejler G,
Andersson G, Jacobson A and Melhus H: Vitamin a is a negative
regulator of osteoblast mineralization. PLoS One. 8:e823882013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ohishi K, Nishikawa S, Nagata T, Yamauchi
N, Shinohara H, Kido J and Ishida H: Physiological concentrations
of retinoic acid suppress the osteoblastic differentiation of fetal
rat calvaria cells in vitro. Eur J Endocrinol. 133:335–341. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nallamshetty S, Wang H, Rhee EJ, Kiefer
FW, Brown JD, Lotinun S, Le P, Baron R, Rosen CJ and Plutzky J:
Deficiency of retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 1 induces BMP2 and
increases bone mass in vivo. PLoS One. 8:e713072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen M, Huang HZ, Wang M and Wang AX:
Retinoic acid inhibits osteogenic differentiation of mouse
embryonic palate mesenchymal cells. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol
Teratol. 88:965–970. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xin M, Yang Y, Zhang D, Wang J, Chen S and
Zhou D: Attenuation of hind-limb suspension-induced bone loss by
curcumin is associated with reduced oxidative stress and increased
vitamin D receptor expression. Osteoporos Int. 26:2665–2676. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aggarwal BB, Sundaram C, Malani N and
Ichikawa H: Curcumin: The Indian solid gold. Adv Exp Med Biol.
595:1–75. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shishodia S, Sethi G and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin: Getting back to the roots. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1056:206–217. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Riva A, Togni S, Giacomelli L, Franceschi
F, Eggenhoffner R, Feragalli B, Belcaro G, Cacchio M, Shu H and
Dugall M: Effects of a curcumin-based supplementation in
asymptomatic subjects with low bone density: A preliminary 24-week
supplement study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:1684–1689.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lone J, Choi JH, Kim SW and Yun JW:
Curcumin induces brown fat-like phenotype in 3T3-L1 and primary
white adipocytes. J Nutr Biochem. 27:193–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rohanizadeh R, Deng Y and Verron E:
Therapeutic actions of curcumin in bone disorders. Bonekey Rep.
5:7932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yun JW: Possible anti-obesity therapeutics
from nature-a review. Phytochemistry. 71:1625–1641. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cho DC, Jung HS, Kim KT, Jeon Y, Sung JK
and Hwang JH: Therapeutic advantages of treatment of high-dose
curcumin in the ovariectomized rat. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
54:461–466. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Folwarczna J, Zych M and Trzeciak HI:
Effects of curcumin on the skeletal system in rats. Pharmacol Rep.
62:900–909. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hussan F, Ibraheem NG, Kamarudin TA, Shuid
AN, Soelaiman IN and Othman F: Curcumin protects against
ovariectomy-induced bone changes in rat model. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:1749162012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim WK, Ke K, Sul OJ, Kim HJ, Kim SH, Lee
MH, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Chung HT and Choi HS: Curcumin protects against
ovariectomy-induced bone loss and decreases osteoclastogenesis. J
Cell Biochem. 112:3159–3166. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang MW, Wang TH, Yan PP, Chu LW, Yu J,
Gao ZD, Li YZ and Guo BL: Curcumin improves bone microarchitecture
and enhances mineral density in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.
Phytomedicine. 18:205–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
French DL, Muir JM and Webber CE: The
ovariectomized, mature rat model of postmenopausal osteoporosis: An
assessment of the bone sparing effects of curcumin. Phytomedicine.
15:1069–1078. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kuncha M, Naidu VG, Sahu BD, Gadepalli SG
and Sistla R: Curcumin potentiates the anti-arthritic effect of
prednisolone in Freund's complete adjuvant-induced arthritic rats.
J Pharm Pharmacol. 66:133–144. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jain S, Meka SRK and Chatterjee K:
Curcumin eluting nanofibers augment osteogenesis toward
phytochemical based bone tissue engineering. Biomed Mater.
11:0550072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Aggarwal BB, Kumar A and Bharti AC:
Anticancer potential of curcumin: Preclinical and clinical studies.
Anticancer Res. 23:363–398. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Biswas S and Rahman I: Modulation of
steroid activity in chronic inflammation: A novel anti-inflammatory
role for curcumin. Mol Nutr Food Res. 52:987–994. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Goel A, Jhurani S and Aggarwal BB:
Multi-targeted therapy by curcumin: how spicy is it? Mol Nutr Food
Res. 52:1010–1030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
López-Lázaro M: Anticancer and
carcinogenic properties of curcumin: Considerations for its
clinical development as a cancer chemopreventive and
chemotherapeutic agent. Mol Nutr Food Res. 52 Suppl 1:S103–S127.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bharti AC, Takada Y and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) inhibits receptor activator of
NF-kappa B ligand-induced NF-kappa B activation in osteoclast
precursors and suppresses osteoclastogenesis. J Immunol.
172:5940–5947. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chan WH, Wu HY and Chang WH: Dosage
effects of curcumin on cell death types in a human osteoblast cell
line. Food Chem Toxicol. 44:1362–1371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Notoya M, Nishimura H, Woo JT, Nagai K,
Ishihara Y and Hagiwara H: Curcumin inhibits the proliferation and
mineralization of cultured osteoblasts. Eur J Pharmacol. 534:55–62.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ozaki K, Kawata Y, Amano S and Hanazawa S:
Stimulatory effect of curcumin on osteoclast apoptosis. Biochem
Pharmacol. 59:1577–1581. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Von Metzler I, Krebbel H, Kuckelkorn U,
Heider U, Jakob C, Kaiser M, Fleissner C, Terpos E and Sezer O:
Curcumin diminishes human osteoclastogenesis by inhibition of the
signalosome-associated I kappaB kinase. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
135:173–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yamaguchi M, Hamamoto R, Uchiyama S and
Ishiyama K: Effects of flavonoid on calcium content in femoral
tissue culture and parathyroid hormone-stimulated
osteoclastogenesis in bone marrow culture in vitro. Mol Cell
Biochem. 303:83–88. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gu Q, Cai Y, Huang C, Shi Q and Yang H:
Curcumin increases rat mesenchymal stem cell osteoblast
differentiation but inhibits adipocyte differentiation. Pharmacogn
Mag. 8:202–208. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hou M, Song Y, Li Z, Luo C, Ou JS, Yu H,
Yan J and Lu L: Curcumin attenuates osteogenic differentiation and
calcification of rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 420:151–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen F, Wang H, Xiang X, Yuan J, Chu W,
Xue X, Zhu H, Ge H, Zou M, Feng H and Lin J: Curcumin increased the
differentiation rate of neurons in neural stem cells via wnt
signaling in vitro study. J Surg Res. 192:298–304. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tiwari SK, Agarwal S, Seth B, Yadav A,
Nair S, Bhatnagar P, Karmakar M, Kumari M, Chauhan LK, Patel DK, et
al: Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles potently induce adult
neurogenesis and reverse cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease
model via canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway. ACS Nano. 8:76–103.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Tiwari SK, Agarwal S, Tripathi A and
Chaturvedi RK: Bisphenol-A mediated inhibition of hippocampal
neurogenesis attenuated by curcumin via canonical Wnt pathway. Mol
Neurobiol. 53:3010–3029. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cui L, Jia X, Zhou Q, Zhai X, Zhou Y and
Zhu H: Curcumin affects β-catenin pathway in hepatic stellate cell
in vitro and in vivo. J Pharm Pharmacol. 66:1615–1622. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
He M, Li Y, Zhang L, Li L, Shen Y, Lin L,
Zheng W, Chen L, Bian X, Ng HK and Tang L: Curcumin suppresses cell
proliferation through inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in medulloblastoma. Oncol Rep. 32:173–180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Moran JM, Roncero-Martin R,
Rodriguez-Velasco FJ, Calderon-Garcia JF, Rey-Sanchez P, Vera V,
Canal-Macias ML and Pedrera-Zamorano JD: Effects of curcumin on the
proliferation and mineralization of human osteoblast-like cells:
Implications of nitric oxide. Int J Mol Sci. 13:16104–16118. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Oh S, Kyung TW and Choi HS: Curcumin
inhibits osteoclastogenesis by decreasing receptor activator of
nuclear factor-kappaB ligand (RANKL) in bone marrow stromal cells.
Mol Cells. 26:486–489. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Vierbuchen T, Ostermeier A, Pang ZP,
Kokubu Y, Südhof TC and Wernig M: Direct conversion of fibroblasts
to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature. 463:1035–1041.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ieda M, Fu JD, Delgado-Olguin P, Vedantham
V, Hayashi Y, Bruneau BG and Srivastava D: Direct reprogramming of
fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes by defined factors.
Cell. 142:375–386. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sekiya S and Suzuki A: Direct conversion
of mouse fibroblasts to hepatocyte-like cells by defined factors.
Nature. 475:390–393. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li Y, Wang Y, Yu J, Ma Z, Bai Q, Wu X, Bao
P, Li L, Ma D..Liu J, et al: Direct conversion of human fibroblasts
into osteoblasts and osteocytes with small molecules and a single
factor, Runx2. bioRxiv. 1274802017.
|
|
66
|
Wang Y, Wu MH, Cheung MPL, Sham MH,
Akiyama H, Chan D, Cheah KSE and Cheung M: Reprogramming of dermal
fibroblasts into osteo-chondrogenic cells with elevated osteogenic
potency by defined transcription factors. Stem Cell Reports.
8:1587–1599. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Nam YJ, Song K, Luo X, Daniel E, Lambeth
K, West K, Hill JA, DiMaio JM, Baker LA, Bassel-Duby R and Olson
EN: Reprogramming of human fibroblasts toward a cardiac fate. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:5588–5593. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Qian L, Huang Y, Spencer CI, Foley A,
Vedantham V, Liu L, Conway SJ, Fu JD and Srivastava D: In vivo
reprogramming of murine cardiac fibroblasts into induced
cardiomyocytes. Nature. 485:593–598. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Minamide A, Boden SD, Viggeswarapu M, Hair
GA, Oliver C and Titus L: Mechanism of bone formation with gene
transfer of the cDNA encoding for the intracellular protein LMP-1.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 85-A:1030–1039. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Salgia R, Li JL, Lo SH, Brunkhorst B,
Kansas GS, Sobhany ES, Sun Y, Pisick E, Hallek M, Ernst T, et al:
Molecular cloning of human paxillin, a focal adhesion protein
phosphorylated by P210BCR/ABL. J Biol Chem. 270:5039–5047. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lattanzi W, Barba M, Novegno F, Massimi L,
Tesori V, Tamburrini G, Galgano S, Bernardini C, Caldarelli M,
Michetti F and Di Rocco C: Lim mineralization protein is involved
in the premature calvarial ossification in sporadic
craniosynostoses. Bone. 52:474–484. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lattanzi W, Parrilla C, Fetoni A,
Logroscino G, Straface G, Pecorini G, Stigliano E, Tampieri A,
Bedini R, Pecci R, et al: Ex vivo-transduced autologous skin
fibroblasts expressing human Lim mineralization protein-3
efficiently form new bone in animal models. Gene Ther.
15:1330–1343. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yoon ST and Boden SD: Spine fusion by gene
therapy. Gene Ther. 11:360–367. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Soleimani M and Nadri S: A protocol for
isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone
marrow. Nat Protoc. 4:102–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Pola E, Gao W, Zhou Y, Pola R, Lattanzi W,
Sfeir C, Gambotto A and Robbins PD: Efficient bone formation by
gene transfer of human LIM mineralization protein-3. Gene Ther.
11:683–693. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Huang S, Xu L, Sun Y, Wu T, Wang K and Li
G: An improved protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal
stem cells from mouse bone marrow. J Orthop Translat. 3:26–33.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Zhang T, Lee YW, Rui YF, Cheng TY, Jiang
XH and Li G: Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote
growth and angiogenesis of breast and prostate tumors. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 4:702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Chang R, Sun L and Webster TJ: Short
communication: Selective cytotoxicity of curcumin on osteosarcoma
cells compared to healthy osteoblasts. Int J Nanomedicine.
9:461–465. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wang N, Wang F, Gao Y, Yin P, Pan C, Liu
W, Zhou Z and Wang J: Curcumin protects human adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells against oxidative stress-induced inhibition
of osteogenesis. J Pharmacol Sci. 132:192–200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bi W, Gu Z, Zheng Y, Wang L, Guo J and Wu
G: Antagonistic and synergistic effects of bone morphogenetic
protein 2/7 and all-trans retinoic acid on the osteogenic
differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Dev Growth
Differ. 55:744–754. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Sheng N, Xie Z, Wang C, Bai G, Zhang K,
Zhu Q, Song J, Guillemot F, Chen YG, Lin A and Jing N: Retinoic
acid regulates bone morphogenic protein signal duration by
promoting the degradation of phosphorylated Smad1. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:18886–18891. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang A, Ding X, Sheng S and Yao Z:
Retinoic acid inhibits osteogenic differentiation of rat bone
marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 375:435–439.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Yamamoto K, Kishida T, Sato Y, Nishioka K,
Ejima A, Fujiwara H, Kubo T, Yamamoto T, Kanamura N and Mazda O:
Direct conversion of human fibroblasts into functional osteoblasts
by defined factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:6152–6157. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Schindelin J, Arganda-Carreras I, Frise E,
Kaynig V, Longair M, Pietzsch T, Preibisch S, Rueden C, Saalfeld S,
Schmid B, et al: Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image
analysis. Nat Methods. 9:676–682. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ahmed MF, El-Sayed AK, Chen H, Zhao R, Jin
K, Zuo Q, Zhang Y and Li B: Direct conversion of mouse embryonic
fibroblast to osteoblast cells using hLMP-3 with Yamanaka factors.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 106:84–95. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
James AW, Levi B, Xu Y, Carre AL and
Longaker MT: Retinoic acid enhances osteogenesis in cranial
suture-derived mesenchymal cells: Potential mechanisms of
retinoid-induced craniosynostosis. Plast Reconstr Surg.
125:1352–1361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Green AC, Kocovski P, Jovic T, Walia MK,
Chandraratna RAS, Martin TJ, Baker EK and Purton LE: Retinoic acid
receptor signalling directly regulates osteoblast and adipocyte
differentiation from mesenchymal progenitor cells. Exp Cell Res.
350:284–297. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhang S, Chen X, Hu Y, Wu J, Cao Q, Chen S
and Gao Y: All-trans retinoic acid modulates Wnt3A-induced
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via activating
the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signalling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
422:243–253. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ding J, Woo JT and Nagai K: The effects of
retinoic acid on reversing the adipocyte differentiation into an
osteoblastic tendency in ST2 cells, a murine bone marrow-derived
stromal cell line. Cytotechnology. 36:125–136. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Cohen-Tanugi A and Forest N: Retinoic acid
suppresses the osteogenic differentiation capacity of murine
osteoblast-like 3/A/1D-1M cell cultures. Differentiation.
63:115–123. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Son HE, Kim EJ and Jang WG: Curcumin
induces osteoblast differentiation through mild-endoplasmic
reticulum stress-mediated such as BMP2 on osteoblast cells. Life
Sci. 193:34–39. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Eghbali-Fatourechi G, Khosla S, Sanyal A,
Boyle WJ, Lacey DL and Riggs BL: Role of RANK ligand in mediating
increased bone resorption in early postmenopausal women. J Clin
Invest. 111:1221–1230. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Li Y, Li A, Strait K, Zhang H, Nanes MS
and Weitzmann MN: Endogenous TNFalpha lowers maximum peak bone mass
and inhibits osteoblastic Smad activation through NF-kappaB. J Bone
Miner Res. 22:646–655. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Chang J, Wang Z, Tang E, Fan Z, McCauley
L, Franceschi R, Gaun K, Krebsbach PH and Wang CY: Inhibition of
osteoblast functions by IKK/NF-κB in osteoporosis. Nat Med.
15:682–689. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Zhang X, Yin WK, Shi XD and Li Y: Curcumin
activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through inhibiting the
activity of GSK-3β in APPswe transfected SY5Y cells. Eur J Pharm
Sci. 42:540–546. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Thacker PC and Karunagaran D: Curcumin and
emodin down-regulate TGF-β signaling pathway in human cervical
cancer cells. PLoS One. 10:e01200452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|