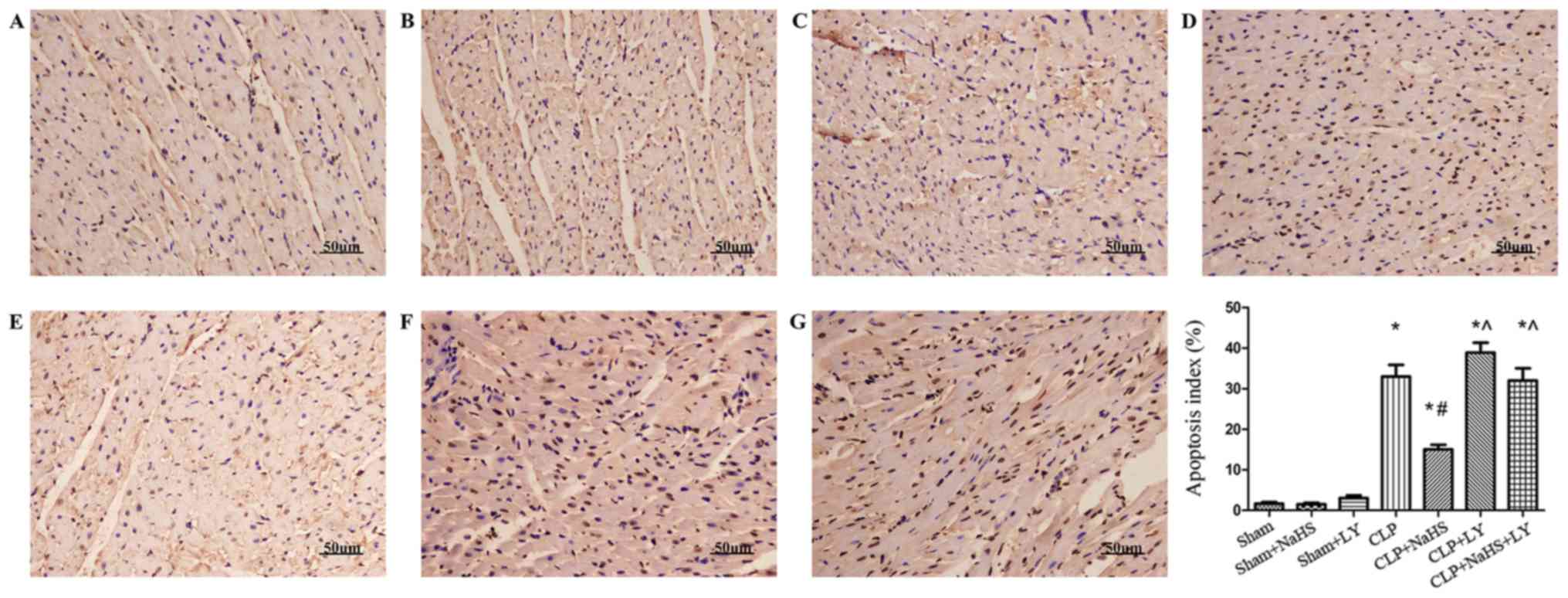
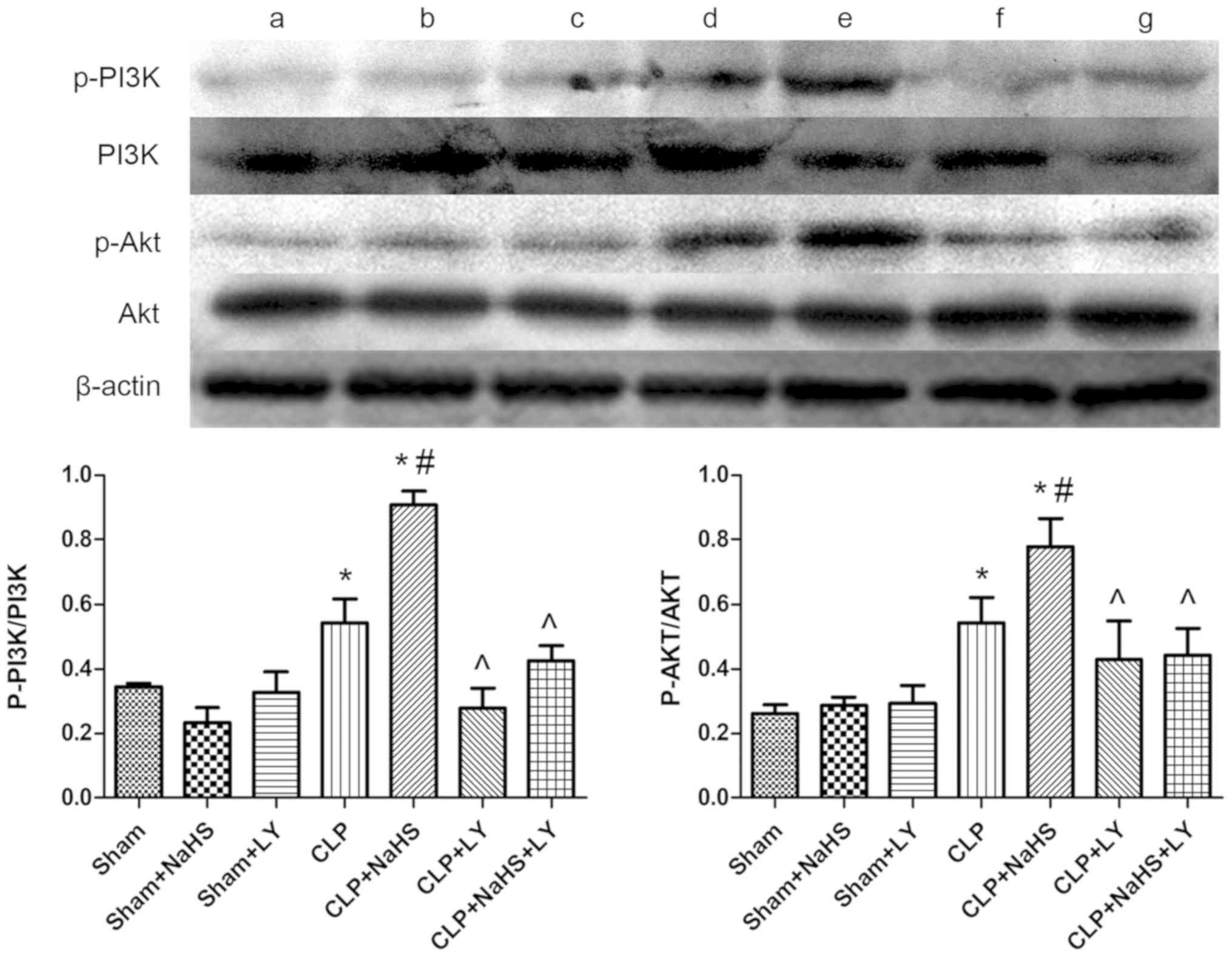
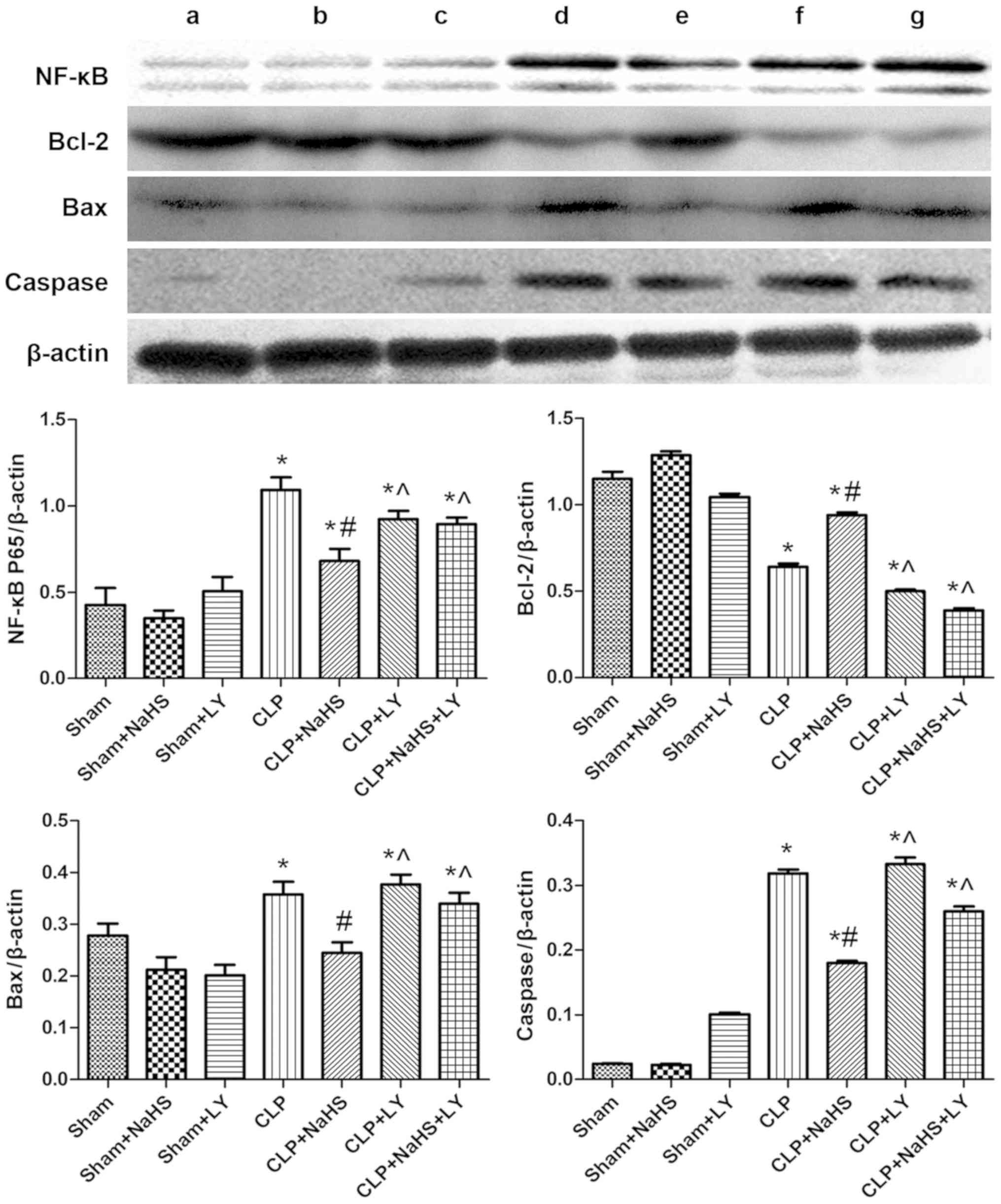
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The Third International Consensus
Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK,
Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC and Reinhart K;
International Forum of Acute Care Trialists, : Assessment of Global
incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current
estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:259–272.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vincent JL, Marshall JC, Namendys-Silva
SA, VinFrancois B, Martin-Loeches I, Lipman J, Reinhart K,
Antonelli M, Pickkers P, Njimi H, et al: Assessment of the
worldwide burden of critical illness: The intensive care over
nations (ICON) audit. Lancet Respir Med. 2:380–386. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zaky A, Deem S, Bendjelid K and Treggiari
MM: Characterization of cardiac dysfunction in sepsis: An ongoing
challenge. Shock. 41:12–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
An R, Zhao L, Xi C, Li H, Shen G, Liu H,
Zhang S and Sun L: Melatonin attenuates sepsis-induced cardiac
dysfunction via a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Basic Res Cardiol.
111:82016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stein A and Bailey SM: Redox Biology of
Hydrogen Sulfide: Implications for Physiology, Pathophysiology and
Pharmacology. Redox Biol. 1:32–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen Y, Shen Z, Luo S, Guo W and Zhu YZ:
The cardioprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide in heart diseases:
From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic potential. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2015:9251672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu Y, Chen X, Pan TT, Neo KL, Lee SW, Khin
ES, Moore PK and Bian JS: Cardioprotection induced by hydrogen
sulfide preconditioning involves activation of ERK and PI3K/Akt
pathways. Pflugers Arch. 455:607–616. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Donnarumma E, Trivedi RK and Lefer DJ:
Protective Actions of H2S in acute myocardial infarction and heart
failure. Compre Physiol. 7:583–602. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Patel VB, McLean BA, Chen X and Oudit GY:
Hydrogen sulfide: An old gas with new cardioprotective effects.
Clin Sci (Lond. 128:321–323. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calvert JW, Coetzee WA and Lefer DJ: Novel
insights into hydrogen sulfide-mediated cytoprotection. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 12:1203–1217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Cheng Q, Li J, He Y, Tian P and Xu
C: Significance of hydrogen sulfide in sepsis-induced myocardial
injury in rats. Exp Ther Med. 14:2153–2161. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhai J and Guo Y: Paeoniflorin attenuates
cardiac dysfunction in endotoxemic mice via the inhibition of
nuclear factor-κB. Biomed Pharmacother. 80:200–206. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao P, Wang Y, Zeng S, Lu J, Jiang TM and
Li YM: Protective effect of astragaloside IV on
lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction via downregulation
of inflammatory signaling in mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
37:428–433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luo K, Long H, Xu B and Luo Y: Apelin
attenuates postburn sepsis via a phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/protein kinase B dependent mechanism: A randomized animal
study. Int J Surg. 21:22–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Williams DL, Li C, Ha T, Ozment-Skelton T,
Kalbfleisc JH, Preiszner J, Brooks L, Breuel K and Schweitzer JB:
Modulation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway alters innate
resistance to polymicrobial sepsis. J Immunol. 172:449–456. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun N, Wang H, Ma L, Lei P and Zhang Q:
Ghrelin attenuates brain injury in septic mice via PI3K/Akt
signaling activation. Brain Res Bull. 124:278–285. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shao M, Zhuo C, Jiang R, Chen G, Shan J,
Ping J, Tian H, Wang L, Lin C and Hu L: Protective effect of
hydrogen sulphide against myocardial hypertrophy in mice.
Oncotarget. 8:22344–22352. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tamizhselvi R, Moore PK and Bhatia M:
Hydrogen sulfide acts as a mediator of inflammation in acute
pancreatitis: In vitro studies using isolated mouse pancreatic
acinar cells. J Cell Mol Med. 11:315–326. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Liao R, Qiang Z and Zhang C:
Pro-inflammatory cytokine-driven PI3K/Akt/Sp1 signalling and H2S
production facilitates the pathogenesis of severe acute
pancreatitis. Biosci Rep. 37(pii): BSR201604832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rittirsch D, Huber-Lang MS, Flierl MA and
Ward PA: Immunodesign of experimental sepsis by cecal ligation and
puncture. Nat Protoc. 4:31–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM,
Antonelli M, Ferrer R, Kumar A, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Nunnally
ME, et al: Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for
Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med.
43:304–377. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cohen J: The immunopathogenesis of sepsis.
Nature. 420:885–891. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kosir M and Podbregar M: Advances in the
diagnosis of sepsis: Hydrogen sulfide as a prognostic marker of
septic shock severity. Ejifcc. 28:134–141. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lavu M, Bhushan S and Lefer DJ: Hydrogen
sulfide-mediated cardioprotection: Mechanisms and therapeutic
potential. Clin Sci (Lond). 120:219–229. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Shan H, Wang T, Liu W, Wang Y,
Wang L, Zhang L, Chang P, Dong W, Chen X and Tao L: Dynamic change
of hydrogen sulfide after traumatic brain injury and its effect in
mice. Neurochem Res. 38:714–725. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li L, Xiao T, Li F, Li Y, Zeng O, Liu M,
Liang B, Li Z, Chu C and Yang J: Hydrogen sulfide reduced renal
tissue fibrosis by regulating autophagy in diabetic rats. Mol Med
Rep. 16:1715–1722. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bhatia M, Wong FL, Fu D, Lau HY, Moochhala
SM and Moore PK: Role of hydrogen sulfide in acute pancreatitis and
associated lung injury. FASEB J. 19:623–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Abdelrahman RS, El-Awady MS, Nader MA and
Ammar EM: Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates cardiovascular dysfunction
induced by cecal ligation and puncture in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol.
34:953–964. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Y, Jin S, Teng X, Hu Z, Zhang Z, Qiu
X, Tian D and Wu Y: Hydrogen Sulfide Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute
Kidney Injury by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2018:67172122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ahmad A, Druzhyna N and Szabo C: Delayed
treatment with sodium hydrosulfide improves regional blood flow and
alleviates cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-Induced Septic Shock.
Shock. 46:183–193. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang H, Moochhala SM and Bhatia M:
Endogenous hydrogen sulfide regulates inflammatory response by
activating the ERK pathway in polymicrobial sepsis. J Immunol.
181:4320–4331. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang H, Zhi L, Moochhala S, Moore PK and
Bhatia M: Hydrogen sulfide acts as an inflammatory mediator in
cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis in mice by upregulating
the production of cytokines and chemokines via NF-kappaB. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L960–971. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bee N, White R and Petros AJ: Hydrogen
sulfide in exhaled gases from ventilated septic neonates and
children: A Preliminary Report. Pediatr Crit Care Med.
18:e327–e332. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Coletta C and Szabo C: Potential role of
hydrogen sulfide in the pathogenesis of vascular dysfunction in
septic shock. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 11:208–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dahlin LG, Kagedal B, Nylander E, Olin C,
Rutberg H and Svedjeholm R: Early identification of permanent
myocardial damage after coronary surgery is aided by repeated
measurements of CK-MB. Scand Cardiovasc J. 36:35–40. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y and Chen M: Fentanyl ameliorates
severe acute pancreatitis-induced myocardial injury in rats by
regulating NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Med Sci Monit. 23:3276–3283.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mair J: Cardiac troponin I and troponin T:
Are enzymes still relevant as cardiac markers? Clin Chim Acta.
257:99–115. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang B, Liu Y, Zhang JS, Zhang XH, Chen
WJ, Yin XH and Qi YF: Cortistatin protects myocardium from
endoplasmic reticulum stress induced apoptosis during sepsis. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 406:40–48. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Comstock KL, Krown KA, Page MT, Martin D,
Ho P, Pedraza M, Castro EN, Nakajima N, Glembotski CC, Quintana PJ
and Sabbadini RA: LPS-induced TNF-alpha release from and apoptosis
in rat cardiomyocytes: Obligatory role for CD14 in mediating the
LPS response. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 30:2761–2775. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu
J, Yankner BA and Yuan J: Caspase-12 mediates
endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by
amyloid-beta. Nature. 403:98–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Abraham E, Wunderink R, Silverman H, Perl
TM, Nasraway S, Levy H, Bone R, Wenzel RP, Balk R, Allred R, et al:
Efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis
factor alpha in patients with sepsis syndrome. A randomized,
controlled, double-blind, multicenter clinical trial. TNF-alpha MAb
Sepsis Study Group. JAMA. 273:934–941. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Williams DL, Ha T, Li C, Kalbfleisch JH
and Ferguson DA Jr: Early activation of hepatic NFkappaB and NF-IL6
in polymicrobial sepsis correlates with bacteremia, cytokine
expression, and mortality. Ann Sur. 230:95–104. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Preiser JC, Zhang H, Vray B, Hrabak A and
Vincent JL: Time course of inducible nitric oxide synthase activity
following endotoxin administration in dogs. Nitric Oxide.
5:208–211. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim TH, Kim SJ and Lee SM: Stimulation of
the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor protects against sepsis
by inhibiting Toll-like receptor via phosphoinositide 3-kinase
activation. J Infect Dis. 209:1668–1677. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gao M, Ha T, Zhang X, Wang X, Liu L,
Kalbfleisch J, Singh K, Williams D and Li C: The Toll-like receptor
9 ligand, CpG oligodeoxynucleotide, attenuates cardiac dysfunction
in polymicrobial sepsis, involving activation of both
phosphoinositide 3 kinase/Akt and extracellular-signal-related
kinase signaling. J Infect Dis. 207:1471–1479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhou H, Qian J, Li C, Li J, Zhang X, Ding
Z, Gao X, Han Z, Cheng Y and Liu L: Attenuation of cardiac
dysfunction by HSPA12B in endotoxin-induced sepsis in mice through
a PI3K-dependent mechanism. Cardiovasc Res. 89:109–118. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
You W, Min X, Zhang X, Qian B, Pang S,
Ding Z, Li C, Gao X, Di R, Cheng Y and Liu L: Cardiac-specific
expression of heat shock protein 27 attenuated endotoxin-induced
cardiac dysfunction and mortality in mice through a
PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Shock. 32:108–117. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tamizhselvi R, Sun J, Koh YH and Bhatia M:
Effect of hydrogen sulfide on the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-protein kinase B pathway and on caerulein-induced cytokine
production in isolated mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 329:1166–1177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hackfort BT and Mishra PK: Emerging role
of hydrogen sulfide-microRNA crosstalk in cardiovascular diseases.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 310:H802–H812. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chatzianastasiou A, Bibli SI, Andreadou I,
Efentakis P, Kaludercic N, Wood ME, Whiteman M, Di Lisa F, Daiber
A, Manolopoulos VG, et al: Cardioprotection by H2S Donors: Nitric
oxide-dependent and independent mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
358:431–440. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|