|
1
|
Villanueva-Romero R, Gutiérrez-Cañas I,
Carrión M, Pérez García S, Seoane IV, Martínez C, Gomariz RP and
Juarranz Y: The anti-inflammatory mediator, vasoactive intestinal
peptide, modulates the differentiation and function of Th subsets
in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Res. 2018:60437102018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kalaiselvi P, Rajashree K, Bharathi Priya
L and Padma VV: Cytoprotective effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate
against deoxynivalenol-induced toxicity through anti-oxidative and
anti-inflammatory mechanisms in HT-29 cells. Food Chem Toxicol.
56:110–118. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Morrison M, van der Heijden R, Heeringa P,
Kaijzel E, Verschuren L, Blomhoff R, Kooistra T and Kleemann R:
Epicatechin attenuates atherosclerosis and exerts anti-inflammatory
effects on diet-induced human-CRP and NFκB in vivo.
Atherosclerosis. 233:149–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qian Y, Chen Y, Wang L and Tou J: Effects
of baicalin on inflammatory reaction, oxidative stress and PKDl and
NF-kB protein expressions in rats with severe acute pancreatitis1.
Acta Cir Bras. 33:556–564. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bitto A, Squadrito F, Irrera N, Pizzino G,
Pallio G, Mecchio A, Galfo F and Altavilla D: Flavocoxid, a
nutraceutical approach to blunt inflammatory conditions. Mediators
Inflamm. 2014:7908512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma C, Al Kaabi JM, Nurulain SM, Goyal
SN, Kamal MA and Ojha S: Polypharmacological properties and
therapeutic potential of β-caryophyllene: a dietary
phytocannabinoid of pharmaceutical promise. Curr Pharm Des.
22:3237–3264. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Klauke AL, Racz I, Pradier B, Markert A,
Zimmer AM, Gertsch J and Zimmer A: The cannabinoid CB2
receptor-selective phytocannabinoid beta-caryophyllene exerts
analgesic effects in mouse models of inflammatory and neuropathic
pain. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 24:608–620. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gertsch J, Leonti M, Raduner S, Racz I,
Chen JZ, Xie XQ, Altmann KH, Karsak M and Zimmer A and Zimmer A:
Beta-caryophyllene is a dietary cannabinoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:9099–9104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ormeño E, Baldy V, Ballini C and Fernandez
C: Production and diversity of volatile terpenes from plants on
calcareous and siliceous soils: effect of soil nutrients. J Chem
Ecol. 34:1219–1229. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Katsuyama S, Mizoguchi H, Kuwahata H,
Komatsu T, Nagaoka K, Nakamura H, Bagetta G, Sakurada T and
Sakurada S: Involvement of peripheral cannabinoid and opioid
receptors in β-caryophyllene-induced antinociception. Eur J Pain.
17:664–675. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Paula-Freire LI, Andersen ML, Gama VS,
Molska GR and Carlini EL: The oral administration of
trans-caryophyllene attenuates acute and chronic pain in mice.
Phytomedicine. 21:356–362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chavan MJ, Wakte PS and Shinde DB:
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of Caryophyllene oxide
from Annona squamosa L. bark. Phytomedicine. 17:149–151. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ghelardini C, Galeotti N, Di Cesare
Mannelli L, Mazzanti G and Bartolini A: Local anaesthetic activity
of beta-caryophyllene. Farmaco. 56:387–389. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Martinez RM, Zarpelon AC, Cardoso RD,
Vicentini FT, Georgetti SR, Baracat MM, Andrei CC, Moreira IC,
Verri WA Jr and Casagrande R: Tephrosia sinapou ethyl acetate
extract inhibits inflammatory pain in mice: Opioid receptor
dependent inhibition of TNFα and IL-1β production. Pharm Biol.
51:1262–1271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
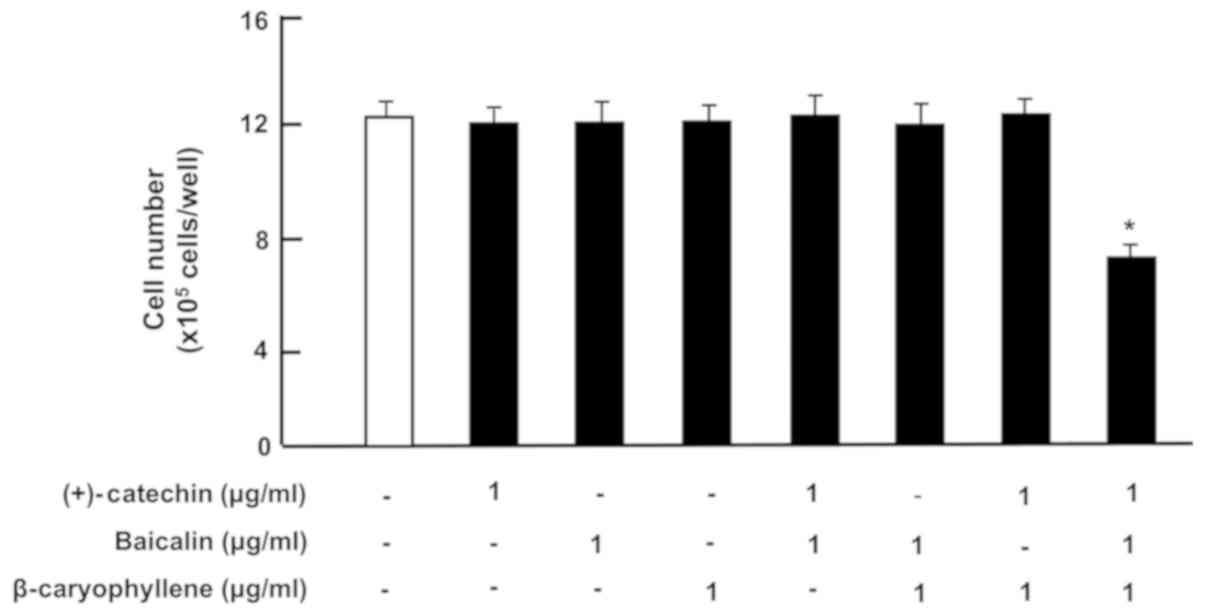
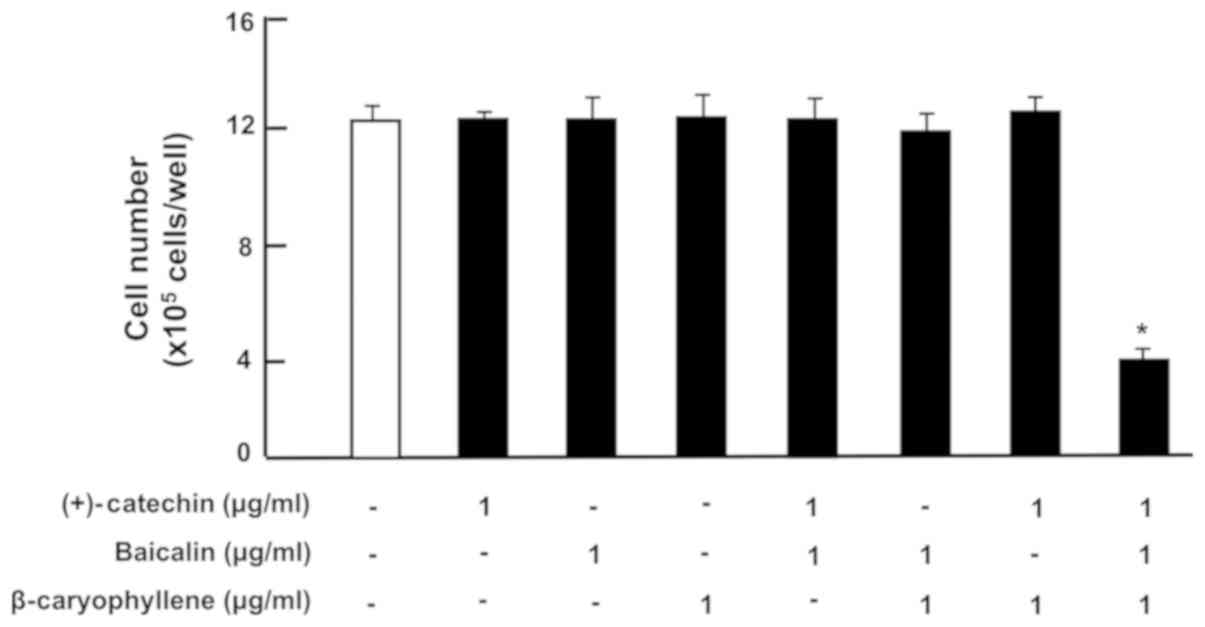
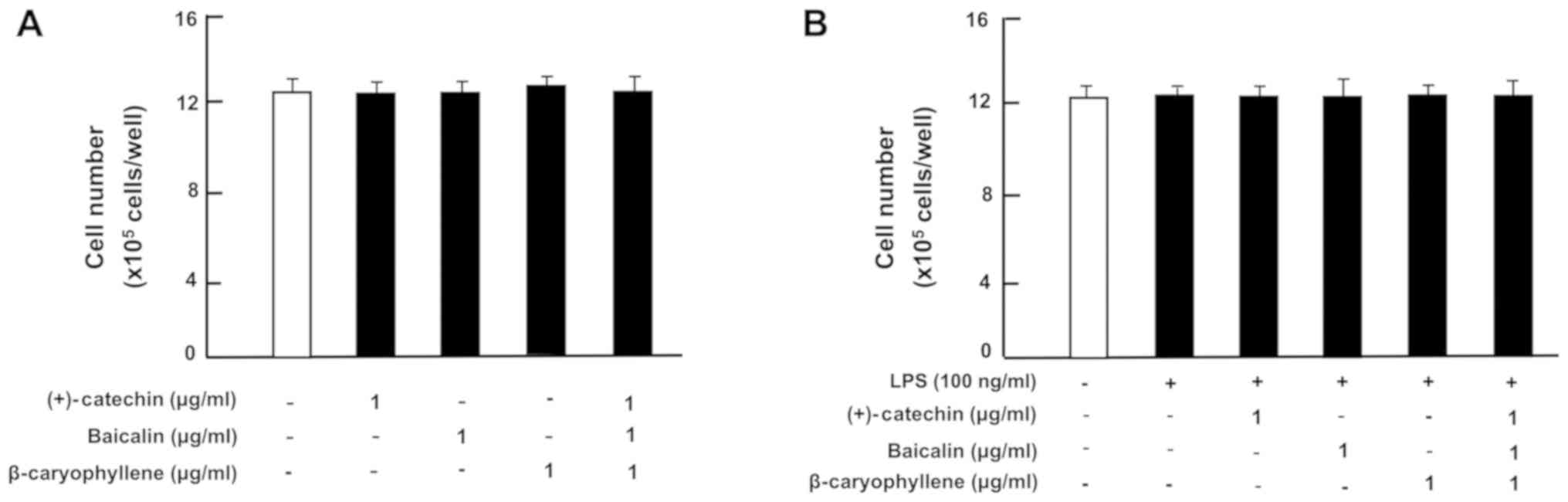
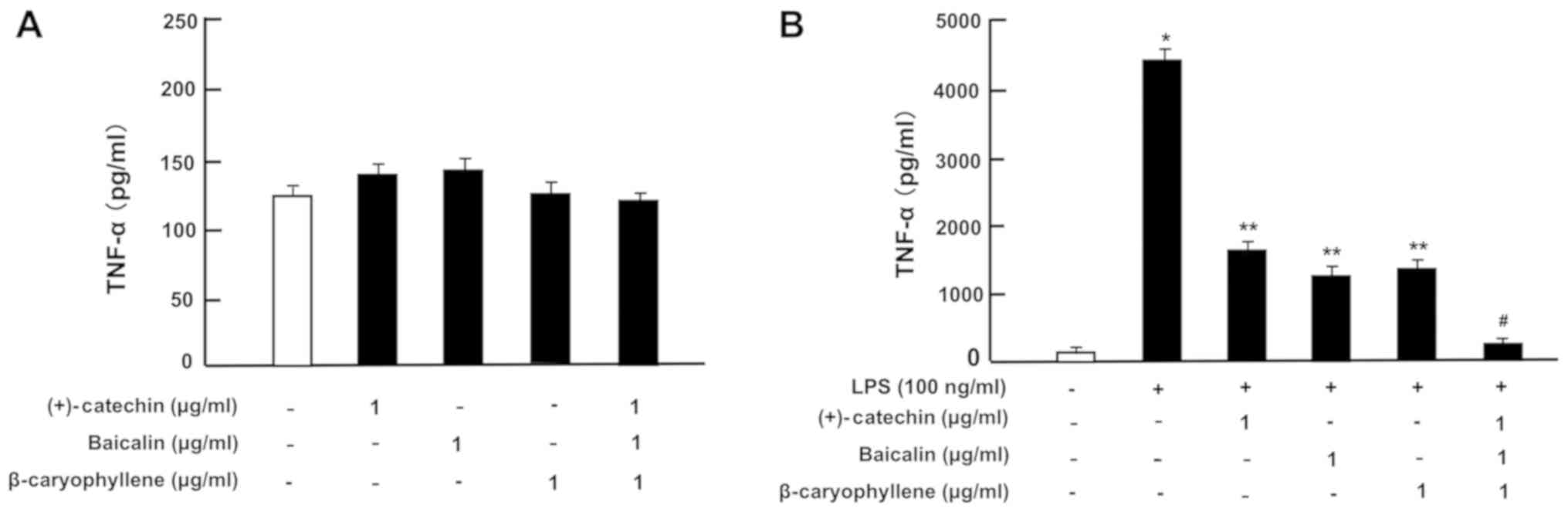
Yamaguchi M and Levy RM: The combination
of β-caryophyllene, baicalin and catechin synergistically
suppresses the proliferation and promotes the death of RAW267.4
macrophages in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 38:1940–1946. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pomari E, Stefanon B and Colitti M: Effect
of plant extracts on H2O2-induced inflammatory gene expression in
macrophages. J Inflamm Res. 7:103–112. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamaguchi M, Vikulina T, Arbiser JL and
Weitzmann MN: Suppression of NF-κB activation by gentian violet
promotes osteoblastogenesis and suppresses osteoclastogenesis. Curr
Mol Med. 14:783–792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamaguchi M and Weitzmann MN: The bone
anabolic carotenoid p-hydroxycinnamic acid promotes osteoblast
mineralization and suppresses osteoclast differentiation by
antagonizing NF-κB activation. Int J Mol Med. 30:708–712. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamaguchi M and Daimon Y: Overexpression
of regucalcin suppresses cell proliferation in cloned rat hepatoma
H4-II-E cells: involvement of intracellular signaling factors and
cell cycle-related genes. J Cell Biochem. 95:1169–1177. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Izumi T and Yamaguchi M: Overexpression of
regucalcin suppresses cell death in cloned rat hepatoma H4-II-E
cells induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha or thapsigargin. J
Cell Biochem. 92:296–306. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Okuno T, Gijón MA, Zarini S, Martin SA,
Barkley RM, Johnson CA, Ohba M, Yokomizo T and Murphy RC: Altered
eicosanoid production and phospholipid remodeling during cell
culture. J Lipid Res. 59:542–549. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meijer L, Borgne A, Mulner O, Chong JP,
Blow JJ, Inagaki N, Inagaki M, Delcros JG and Moulinoux JP:
Biochemical and cellular effects of roscovitine, a potent and
selective inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinases cdc2, cdk2 and
cdk5. Eur J Biochem. 243:527–536. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh SV, Herman-Antosiewicz A, Singh AV,
Lew KL, Srivastava SK, Kamath R, Brown KD, Zhang L and Baskaran R:
Sulforaphane-induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest involves
checkpoint kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of cell division cycle
25C. J Biol Chem. 279:25813–25822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Serrano-Nascimento C, da Silva Teixeira S,
Nicola JP, Nachbar RT, Masini-Repiso AM and Nunes MT: The acute
inhibitory effect of iodide excess on sodium/iodide symporter
expression and activity involves the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Endocrinology. 155:1145–1156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen S, Wang Y, Ruan W, Wang X and Pan C:
Reversing multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
inhibiting extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated
protein kinase signaling pathway activity. Oncol Lett. 8:2333–2339.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao Y, Jing Z, Li Y and Mao W: Berberine
in combination with cisplatin suppresses breast cancer cell growth
through induction of DNA breaks and caspase-3-dependent apoptosis.
Oncol Rep. 36:567–572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Echizen K, Hirose O, Maeda Y and Oshima M:
Inflammation in gastric cancer: interplay of the
COX-2/prostaglandin E2 and Toll-like receptor/MyD88 pathways.
Cancer Sci. 107:391–397. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin CC, Chan CM, Huang YP, Hsu SH, Huang
CL and Tsai SJ: Methylglyoxal activates NF-κB nuclear translocation
and induces COX-2 expression via a p38-dependent pathway in
synovial cells. Life Sci. 149:25–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li N, Liu BW, Ren WZ, Liu JX, Li SN, Fu
SP, Zeng YL, Xu SY, Yan X, Gao YJ, et al: GLP-2 attenuates
LPS-induced inflammation in BV-2 cells by inhibiting ERK1/2, JNK1/2
and NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 17:1902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cha SM, Cha JD, Jang EJ, Kim GU and Lee
KY: Sophoraflavanone G prevents Streptococcus mutans surface
antigen I/II-induced production of NO and PGE2 by inhibiting
MAPK-mediated pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Arch Oral Biol.
68:97–104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu X, Yin P, Wan C, Chong X, Liu M, Cheng
P, Chen J, Liu F and Xu J: Punicalagin inhibits inflammation in
LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages via the suppression of
TLR4-mediated MAPKs and NF-κB activation. Inflammation. 37:956–965.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cho BO, So Y, Jin CH, Nam BM, Yee ST and
Jeong IY: 3-deoxysilybin exerts anti-inflammatory effects by
suppressing NF-κB activation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
RAW264.7 macrophages. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 78:2051–2058.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao G, Zhang T, Ma X, Jiang K, Wu H, Qiu
C, Guo M and Deng G: Oridonin attenuates the release of
pro-inflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7
cells and acute lung injury. Oncotarget. 8:68153–68164.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|