|
1
|
Poli-Neto OB, Campos Martins Chamochumbi
C, Toscano P, Pitanguy Julio M, Marques W Jr, Rosa-E-Silva JC,
Candido-Dos-Reis FJ and Nogueira AA: Electromyographic
characterization of abdominal wall trigger points developed after
caesarean section and response to local anaesthesia: An
observational study. BJOG. 125:1313–1318. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Feng XL, Xu L, Guo Y and Ronsmans C:
Factors influencing rising caesarean section rates in China between
1988 and 2008. Bull World Health Organ. 90:30–39, 39A. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singal S, Bharti R, Dewan R, Divya, Dabral
A, Batra A, Sharma M and Mittal P: Clinical outcome of
postplacental copper T 380A insertion in women delivering by
caesarean section. J Clin Diagn Res. 8:OC01–OC04. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ozkan Seyhan T, Orhan-Sungur M, Basaran B,
Savran Karadeniz M, Demircan F, Xu Z and Sessler DI: The effect of
intra-abdominal pressure on sensory block level of single-shot
spinal anesthesia for cesarean section: An observational study. Int
J Obstet Anesth. 24:35–40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Menacker F, Declercq E and Macdorman MF:
Cesarean delivery: Background, trends and epidemiology. Semin
Perinatol. 30:235–241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
El-Agwany AS: Considerable observations in
cesarean section surgical technique and proposed steps. Arch
Gynecol Obstet. 297:1075–1077. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu C, Sun W, Wang C, Liu F and Zhou M:
Delivery during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support
of pregnant woman with severe respiratory distress syndrome caused
by influenza: A case report and review of the literature. J Matern
Fetal Neonatal Med. 32:2570–2574. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shi YC, Guo H, Chen J, Sun G, Ren RR, Guo
MZ, Peng LH and Yang YS: Initial meconium microbiome in Chinese
neonates delivered naturally or by cesarean section. Sci Rep.
8:32552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carness JM and Lenart MJ: Spinal
anaesthesia for cesarean section in a patient with vascular type
ehlers-danlos syndrome. Case Rep Anesthesiol.
2018:19247252018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yamashita A and Irikoma S: Comparison of
inflationary non-invasive blood pressure (iNIBP) monitoring
technology and conventional deflationary non-invasive blood
pressure (dNIBP) measurement in detecting hypotension during
cesarean section. JA Clin Rep. 4:52018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nishio Y, Hiraki T, Taniguchi H and
Ushijima K: Anesthetic management during a cesarean section in a
patient with cleidocranial dysplasia: A case report. JA Clin Rep.
4:22018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bard M, Bersot Y, Legros V, Raimond E and
Malinovsky JM: Hemodynamic monitoring by the aortic velocity-time
integral in supra sternal Doppler echocardiography and total
cavo-pulmonary derivation in cesarean delivery. J Clin Anesth.
46:99–100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eskandr AM, Metwally AA, Ahmed AA, Elfeky
EM, Eldesoky IM, Obada MA and Abd-Elmegid OA: Dexmedetomidine as a
part of general anaesthesia for caesarean delivery in patients with
pre-eclampsia: A randomised double-blinded trial. Eur J
Anaesthesiol. 35:372–378. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan L, Zhang J, Lv Z, Guo H and Zhao Y:
Clinical research on the dexmedetomidine applied for
patient-controlled sedation during the lower limbs operation under
combined spinal-epidural anesthesia. Pak J Pharm Sci. 29:1095–2100.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sayed E and Yassen KA: Intraoperative
effect of dexmedetomidine infusion during living donor liver
transplantation: A randomized control trial. Saudi J Anaesth.
10:288–294. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Das A, Chhaule S, Bhattacharya S, Basunia
SR, Mitra T, Halder PS, Chattopadhyay S and Mandal SK: Controlled
hypotension in day care functional endoscopic sinus surgery: A
comparison between esmolol and dexmedetomidine: A prospective,
double-blind and randomized study. Saudi J Anaesth. 10:276–282.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Conti G, Ranieri VM, Costa R, Garratt C,
Wighton A, Spinazzola G, Urbino R, Mascia L, Ferrone G, Pohjanjousi
P, et al: Effects of dexmedetomidine and propofol on
patient-ventilator interaction in difficult-to-wean, mechanically
ventilated patients: A prospective, open-label, randomised,
multicentre study. Crit Care. 20:2062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li B, Li Y, Tian S, Wang H, Wu H, Zhang A
and Gao C: Anti-inflammatory effects of perioperative
dexmedetomidine administered as an adjunct to general anesthesia: A
Meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 5:123422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Doyle DJ and Garmon EH: American Society
of Anesthesiologists Classification (ASA Class). StatPearls
[Internet] Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2019 Jan
19
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yuan F, Fu H, Yang P, Sun K, Wu S, Lv M,
Dong Z and Dong T: Dexmedetomidine-fentanyl versus
propofol-fentanyl in flexible bronchoscopy: A randomized study. Exp
Ther Med. 12:506–512. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nair AS and Sriprakash K: Dexmedetomidine
in pregnancy: Review of literature and possible use. J Obstetric
Anaesthesia Critical Care. 3:3–6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang L, Zhang A, Liu W, Liu H, Su F and Qi
L: Effects of dexmedetomidine on perioperative stress response,
inflammation and immune function in patients with different degrees
of liver cirrhosis. Exp Ther Med. 16:3869–3874. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bawdane KD, Magar JS and Tendolkar BA:
Double blind comparison of combination of 0.1% ropivacaine and
fentanyl to combination of 0.1% bupivacaine and fentanyl for
extradural analgesia in labour. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol.
32:38–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kundra TS, Nagaraja PS, Singh NG,
Dhananjaya M, Sathish N and Manjunatha N: Effect of dexmedetomidine
on diseased coronary vessel diameter and myocardial protection in
percutaneous coronary interventional patients. Ann Card Anaesth.
19:394–398. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jeong SI, Shin JA, Cho S, Kim HW, Lee JY,
Kang JL and Park EM: Resveratrol attenuates peripheral and brain
inflammation and reduces ischemic brain injury in aged female mice.
Neurobiol Aging. 44:74–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elmoutaz Mahmoud H and Rashwan DAE:
Efficacy of dexmedetomidine versus ketofol for sedation of
postoperative mechanically ventilated patients with obstructive
sleep apnea. Crit Care Res Pract. 2018:10150542018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee CH, Park JH, Ahn JH and Won MH:
Effects of melatonin on cognitive impairment and hippocampal
neuronal damage in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
Exp Ther Med. 11:2240–2246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
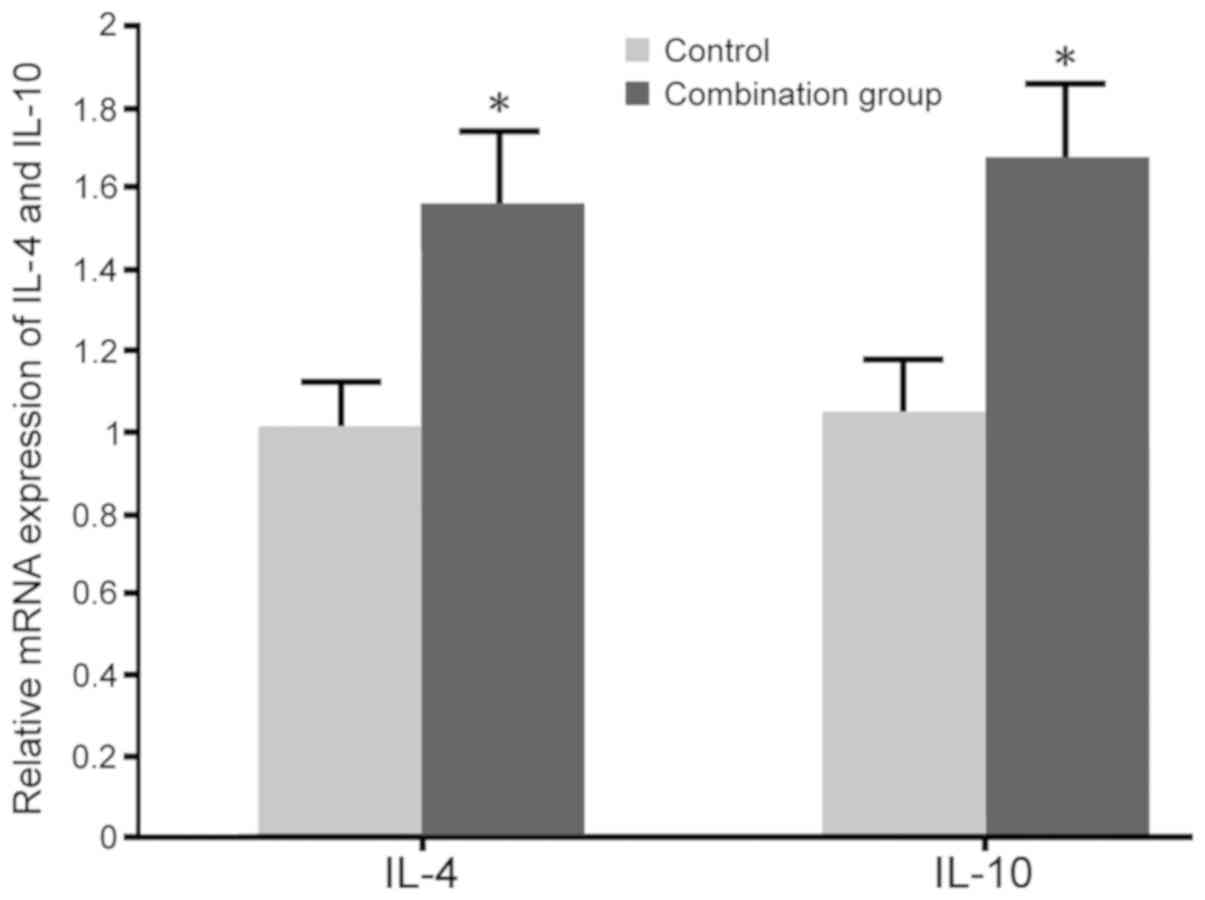
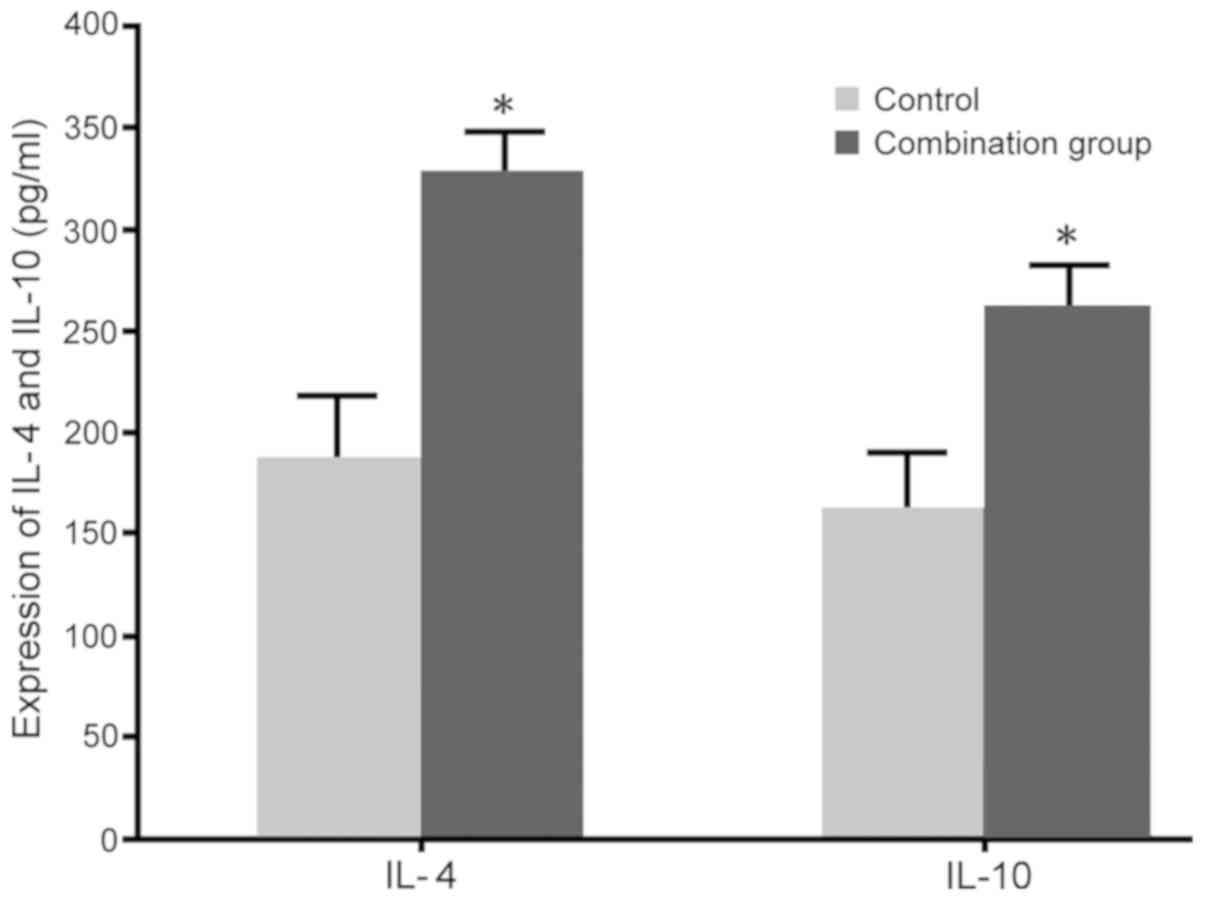
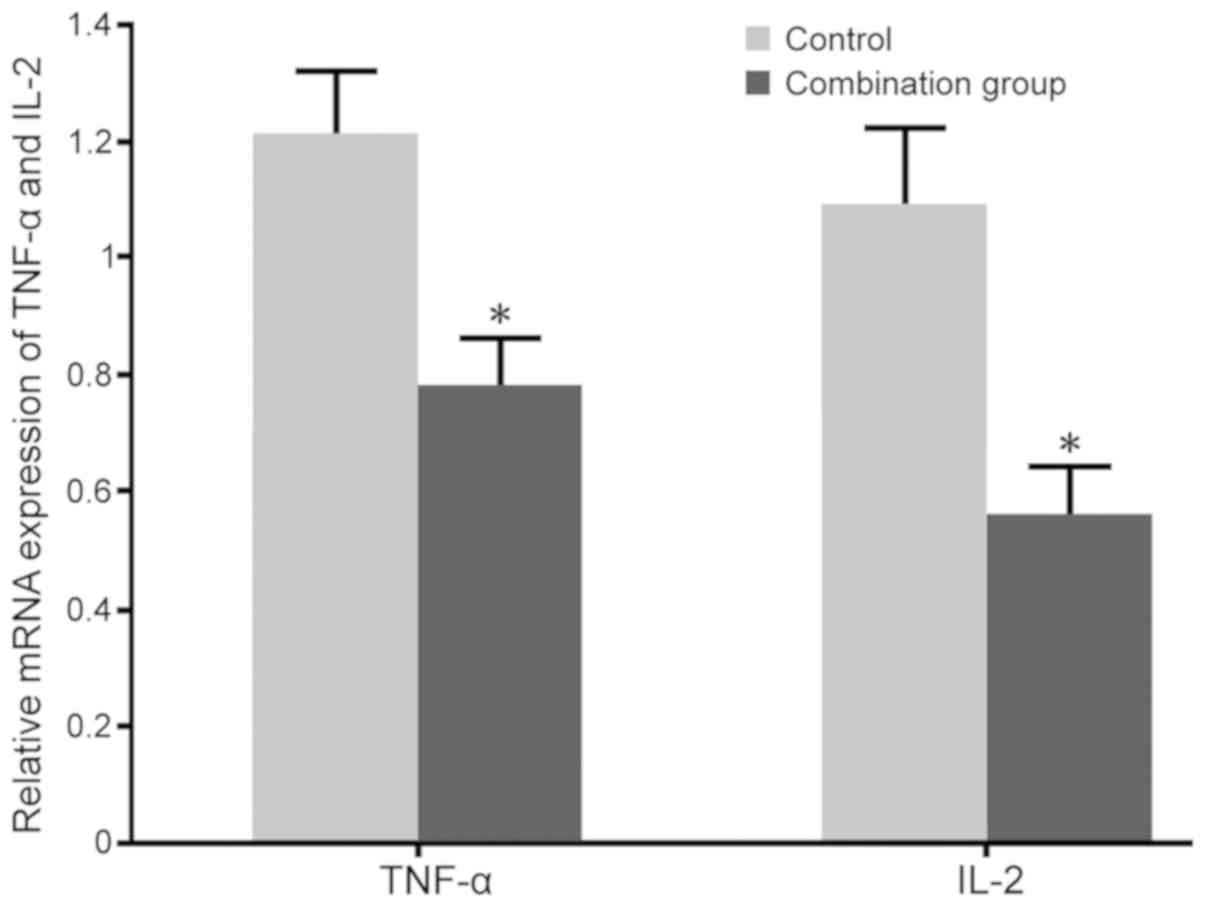
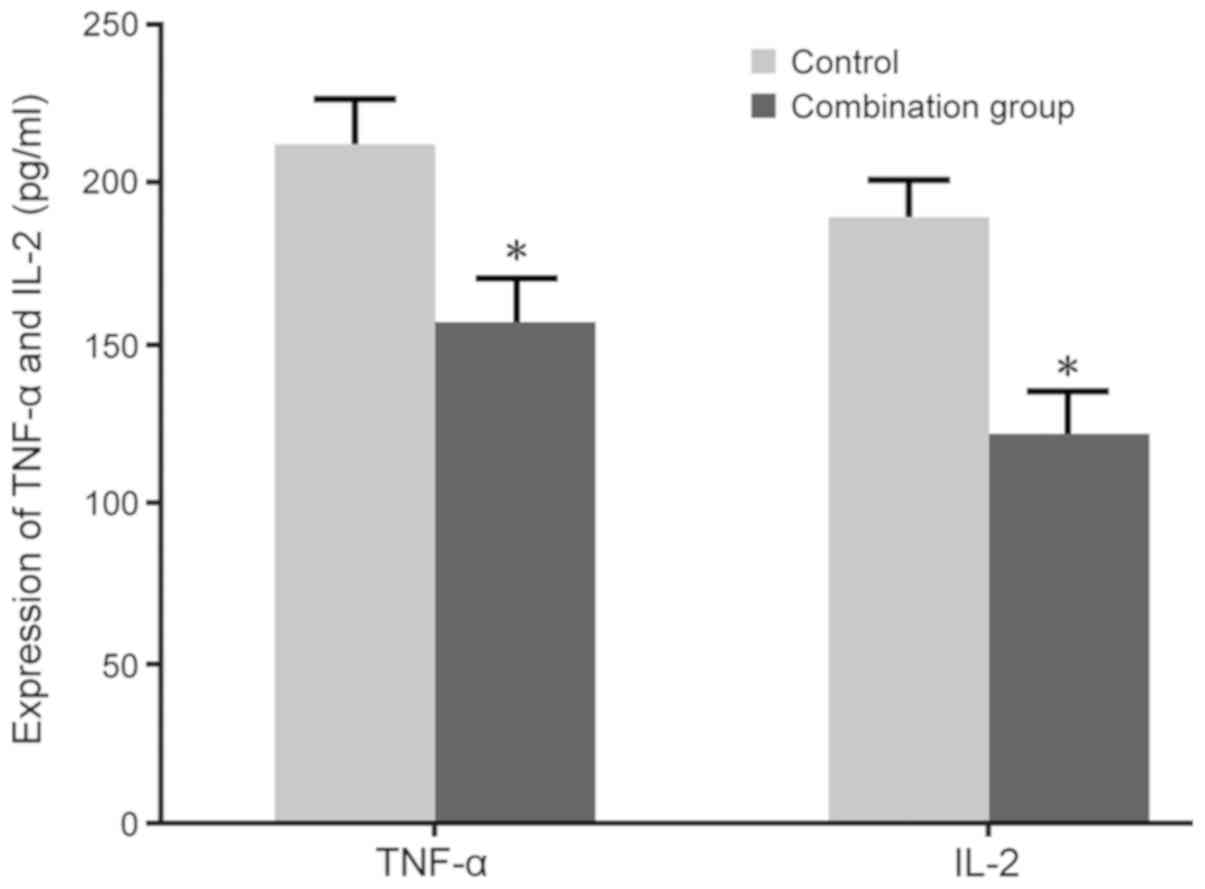
Wegmann TG, Lin H, Guilbert L and Mosmann
TR: Bidirectional cytokine interactions in the maternal-fetal
relationship: Is successful pregnancy a TH2 phenomenon? Immunol
Today. 14:353–356. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Druckmann R and Druckmann MA: Progesterone
and the immunology of pregnancy. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
97:389–396. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin H, Mosmann TR, Guilbert L,
Tuntipopipat S and Wegmann TG: Synthesis of T helper 2-type
cytokines at the maternal-fetal interface. J Immunol.
151:4562–4573. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Werlang ICR, Mueller NT, Pizoni A,
Wisintainer H, Matte U, Costa SHAM, Ramos JGL, Goldani MZ,
Dominguez-Bello MG and Goldani HAS: Associations of birth mode with
cord blood cytokines, white blood cells and newborn intestinal
bifidobacteria. PLoS One. 13:e02059622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|