Introduction
Bladder cancer (BCa) is the second most common
malignancy of the genitourinary tract (1), with ~76,960 new diagnoses and 16,390
BCa associated deaths reported in the USA in 2016 (2). Since 1984, the number of BCa diagnoses
has increased by~36% per year (2).
Urothelial carcinoma (transitional cell carcinoma) is the most
common BCa (>90%) and is generally classified as non-muscle
invasive BCa (NMIBC) or muscle invasive BCa (MIBC), according to
the nature of the tumor (3). Among
NMIBC cases, 50–70% recur after treatment and an estimated 10–15%
develop into MIBC, which possesses the characteristics of
metastatic malignant tumors, exhibiting a 5-year survival rate of
50–60% (4,5). When MIBC progresses to metastatic BCa,
the 5-year survival rate decreases to 5% (4). Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy
is widely used in MIBC treatment and increases survival (6). However, the response rate to
chemotherapy is only ~50% and resistance to cisplatin is considered
to be the principal cause of this poor response (7). An in-depth study of possible factors
affecting cisplatin sensitivity is therefore required to identify
potential novel therapeutic targets for BCa and subsequently
improve clinical treatment outcomes.
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3), one of
the four highly conserved FGFRs, is a receptor tyrosine kinase
involved in cancer cell proliferation and migration (8). A total of 11 different FGFR3-activating
missense mutations have been reported in ~70% of NMIBC and 15% of
MIBC cases (8,9). An analysis of the latest mutation data
of BCa tissue from The Cancer Genome Atlas database (http://www.cbioportal.org/index.do) revealed that
14% of patients with BCa exhibited FGFR3-activating point mutations
(10,11). Among the FGFR3 mutations, S249C
accounted for 53.4% and was the most frequent mutation in BCa
(10,11). S249C, located on exon 7, induces a
substitution of serine with cysteine at codon 249. This
substitution leads to a ligand-independent dimerization and the
auto-phosphorylation of FGFR3, which results in the continued
activation of downstream proliferative pathways (12). A study has demonstrated that FGFR3
may be an oncogenic driver of BCa and hence targeting FGFR3 may be
a beneficial therapeutic approach (13). However, whether FGFR3 mutations,
particularly the major mutation S249C, are involved in
chemoresistance of BCa remains unknown.
The current study aimed to elucidate the function
and underlying mechanism of the FGFR3S249C mutation in
the development of chemoresistance in BCa cells, to identify
potential therapeutic targets for patients with BCa and for those
who carry this mutation.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
The BCa cell line 97-7 expressing endogenous mutant
FGFR3S249C (12,14) was provided by Professor Margaret
Knowles at the Leeds Institute of Cancer and Pathology, Cancer
Research UK Clinical Centre, St. James's University Hospital
(Leeds, UK). The FGFR3 wild-type (FGFR3WT) BCa cell line
5637 and T24 were obtained from the Cell Bank of the Chinese
Academy of Sciences. 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells were
cultured in Hams F12 medium (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.)
containing 10% (v/v) FBS (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.),
1× Insulin-Transferrin-Selenium (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA), 1×
non-essential amino acids (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.)
and 1 µg/ml hydrocortisone (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA). 5637
(FGFR3WT) and T24 (FGFR3WT) cells were
cultured in RPMI 1640 and McCoy's 5A medium (all Gibco; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.), supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS. All cell
lines were cultured in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5%
CO2.
Chemosensitivity assay
5637 (FGFR3WT), T24 (FGFR3WT)
and 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells were seeded in 96-well
plates at a density of 6,000 cells/well in RPMI 1640 medium,
McCoy's 5A medium and Hams F12 medium, respectively, containing 10%
FBS. Following overnight attachment in a humidified incubator at
37°C with 5% CO2, the medium was discarded and 5637
(FGFR3WT) and T24 (FGFR3WT) cells were
incubated at 37°C with various concentrations of cisplatin (0,
0.15625, 0.3125, 0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40 and 80 µg/ml;
MedChemExpress LLC) for 48 h. For the 97-7 (FGFR3S249C)
cells, medium was discarded following overnight attachment at 37°C
and cells were treated with different concentrations of cisplatin
(0, 0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 100, 200 and 400 µg/ml
with or without the pan-Akt inhibitor GDC-0068 (10 µM;
MedChemExpress LLC), or a broad-spectrum PI3K inhibitor LY294002
(20 µM; MedChemExpress LLC) were used for 48 h. After incubation at
37°C, cell viability was detected in all cells using a Cell
Counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay kit (Dojindo Molecular Technologies,
Inc.) in accordance with the manufacturer's protocol. Optical
density (OD) values were recorded using a microplate reader
(Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) at 450 nm. The ratio of cisplatin
inhibition, GDC-0068, LY294002 or a combination treatment at each
concentration was calculated as follows: (the OD value of
experimental groups - the OD value of blank groups)/(the OD value
of control groups - the OD value of blank groups).
Concentration-viability curves were presented using Graph Pad Prism
7.0 software (GraphPad Software, Inc.). Half maximal inhibitory
concentration (IC50) values were subsequently
determined.
Western blot analysis
5637 (FGFR3WT), T24 (FGFR3WT)
and 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells were lysed in cell lysis
buffer (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) supplemented with protease
inhibitors (Roche Diagnostics). Protein concentration was
determined with a Pierce™ BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.). Protein (30 µg) underwent 12% SDS-PAGE and was
transferred to PVDF membranes (EMD Millipore). After blocking with
5% skimmed milk at room temperature for 1 h membranes were
overnight incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies
against phosphorylated-Akt (P-Akt; 1:600; cat. no. 9271; Cell
Signaling Technology, Inc.), total-Akt (T-Akt; 1:1,000; cat. no.
9272; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.), FGFR3 (1:500; cat. no.
AP14841c-400; Abgent Biotech Co., Ltd.) and β-actin (1:2,500; cat.
no. A5441; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA). Secondary anti-mouse IgG
(H+L), HRP conjugated (1:5,000; cat. no. SA00001-1; Proteintech
Group, Inc.) or anti-rabbit IgG (H+L), HRP conjugated (1:5,000;
cat. no. SA00001-2; Proteintech Group, Inc.) antibodies were
incubated at room temperature for 2 h and blots were developed
using the SuperSignal™ West Dura Extended Duration Substrate
reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) with an Amersham Imager
600 (GE Healthcare). Band intensity was determined by ImageJ 2X
software (National Institutes of Health) and normalized to β-actin.
The activation of the Akt signaling pathway was determined using
the ratio of P-Akt/T-Akt.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
(RT-q) PCR
Total RNA was extracted from 97-7 cells using TRIzol
(Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and was
reverse-transcribed using a PrimeScript RT reagent kit with a gDNA
Eraser (Takara Bio, Inc.) for cDNA synthesis and genomic DNA
removal. RT-qPCR was performed using a QuantiNova™ SYBR Green PCR
mix kit (Qiagen GmbH) and performed using Applied Biosystems Prism
7500 (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
Amplification was performed according to the reaction conditions of
95°C for 10 min; 95°C for 10 sec, 60°C for 30 sec, for 40 cycles.
The relative expression of FGFR3 was compared with that of β-actin
and fold changes were calculated using the 2−∆∆Ct method
(15). The primers used were as
follows: FGFR3 forward, 5′-TGCGTCGTGGAGAACAAGTTT-3′ and reverse,
5′-GCACGGTAACGTAGGGTGTG-3′; β-actin forward,
5′-CTGGAACGGTGAAGGTGACA-3′ and reverse,
5′-AAGGGACTTCCTGTAACAATGCA-3′.
RNA interference assay
RNA interference was used to knockdown the
expression of FGFR3 in 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells. Small
interfering RNA (siRNA) for FGFR3 (siRNA-FGFR3) and scrambled
negative control (NC) siRNA (siRNA-NC) were obtained from Shanghai
GenePharma Co., Ltd. 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells were
transfected with 30 nM siRNA using lipofectamine RNAiMAX
(Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at 37°C in six-well
plates. After 48 h, cells were collected and used for RNA and
protein extraction. The siRNA sequences were as follows: siRNA-NC
forward, 5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3′ and reverse, ACG UGA CAC GUU
CGG AGA ATT; siRNA-FGFR3 forward, 5′-GCUGAAAGACGAUGCCACUTT-3′ and
reverse, 5′-AGUGGCAUCGUCUUUCAGCTT-3′.
Cell proliferation assay
A CCK-8 assay was performed to determine cell
proliferation as described in a previous study (16). 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells
were seeded into 96-well plates at a density of 5,000 cells per
well and incubated at 37°C with 5 µg/ml cisplatin with or without
10 µM GDC0068 and 10 µg/ml cisplatin with or without 20 µM
LY294002. These concentrations were selected based on the
IC50 values of treatments. Following incubation for 1,
2, 3, and 4 days, the cell morphology was assessed using a light
microscope (Nikon Corporation), and cell proliferation was detected
using a CCK-8 assay kit (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, Inc.) in
accordance with the manufacturer's protocol. OD values at 450 nm
were measured using a microplate reader.
Cell apoptosis analysis
Cell apoptosis analysis was performed using an
Annexin V-FITC/propidium Iodide (PI) Cell Apoptosis Analysis kit
according to manufacturer's protocol (Absin Bioscience, Inc.).
Cells were treated with 5 µg/ml cisplatin with or without 10 µM
GDC0068 and 10 µg/ml cisplatin with or without 20 µM LY294002 at
37°C for 72 h. 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells were harvested
and washed twice in ice-cold PBS, resuspended in 300 µl binding
buffer (Absin Bioscience, Inc.) and incubated with 5 µl Annexin
V-FITC and 10 µl PI in the dark for 15 min at room temperature.
After adding 200 µl PBS to each sample, cell apoptosis was detected
within 1 h using a flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Inc.). The
results were analysed using FlowJo v10 software (FlowJo LLC).
Statistical analysis
Analyses were performed using SPSS 23.0 software
(IBM Corp.). Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed
Student's t-test or one-way ANOVA, followed by a Newman-Keuls or a
Dunnett's multiple comparison test. All data were presented as the
mean ± SEM. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
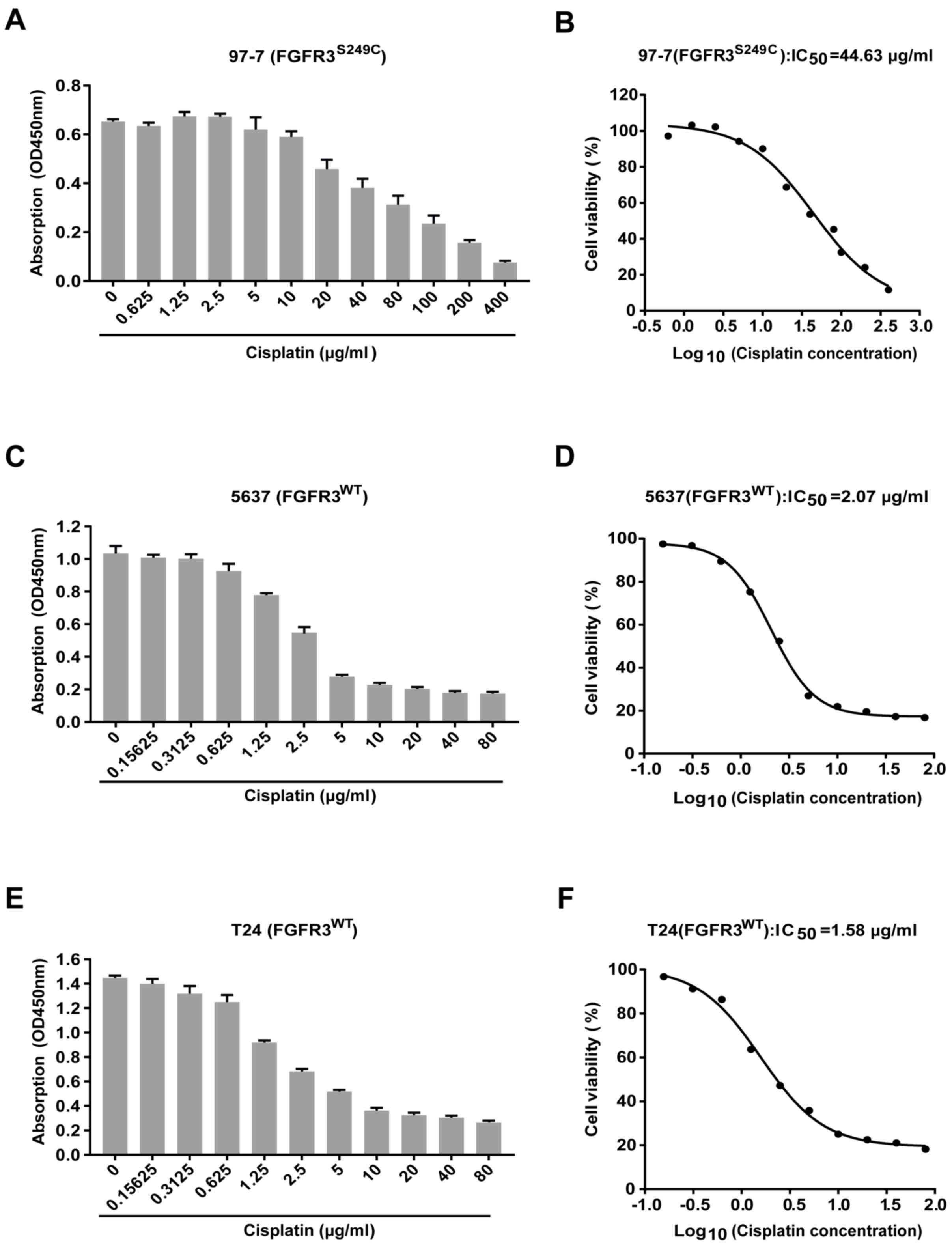
97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells are
more resistant to cisplatin treatment compared with 5637
(FGFR3WT) and T24 (FGFR3WT) cells
Cell viability was assessed using a CCK-8 assay
after treatment with different concentrations of cisplatin for 48
h, to determine whether cisplatin sensitivity was significantly
different between the BCa cells carrying the S249C mutant FGFR3
(97–7) and wild type FGFR3 (5637 and T24). The results revealed
that cell viability was reduced following cisplatin treatment in
all three cell lines (Fig. 1A, C and
E). Concentration-viability curves revealed that the
IC50 of cisplatin was ~21 and ~28 fold higher in 97-7
cells (FGFR3S249C), compared with 5637
(FGFR3WT) and T24 (FGFR3WT) cells (44.63
µg/ml vs. 2.07 µg/ml and 1.58 µg/ml, respectively; Fig. 1B, D and F). 97-7
(FGFR3S249C) cells were therefore more resistant to
cisplatin treatment compared with 5637 (FGFR3WT) and T24
(FGFR3WT) cells.
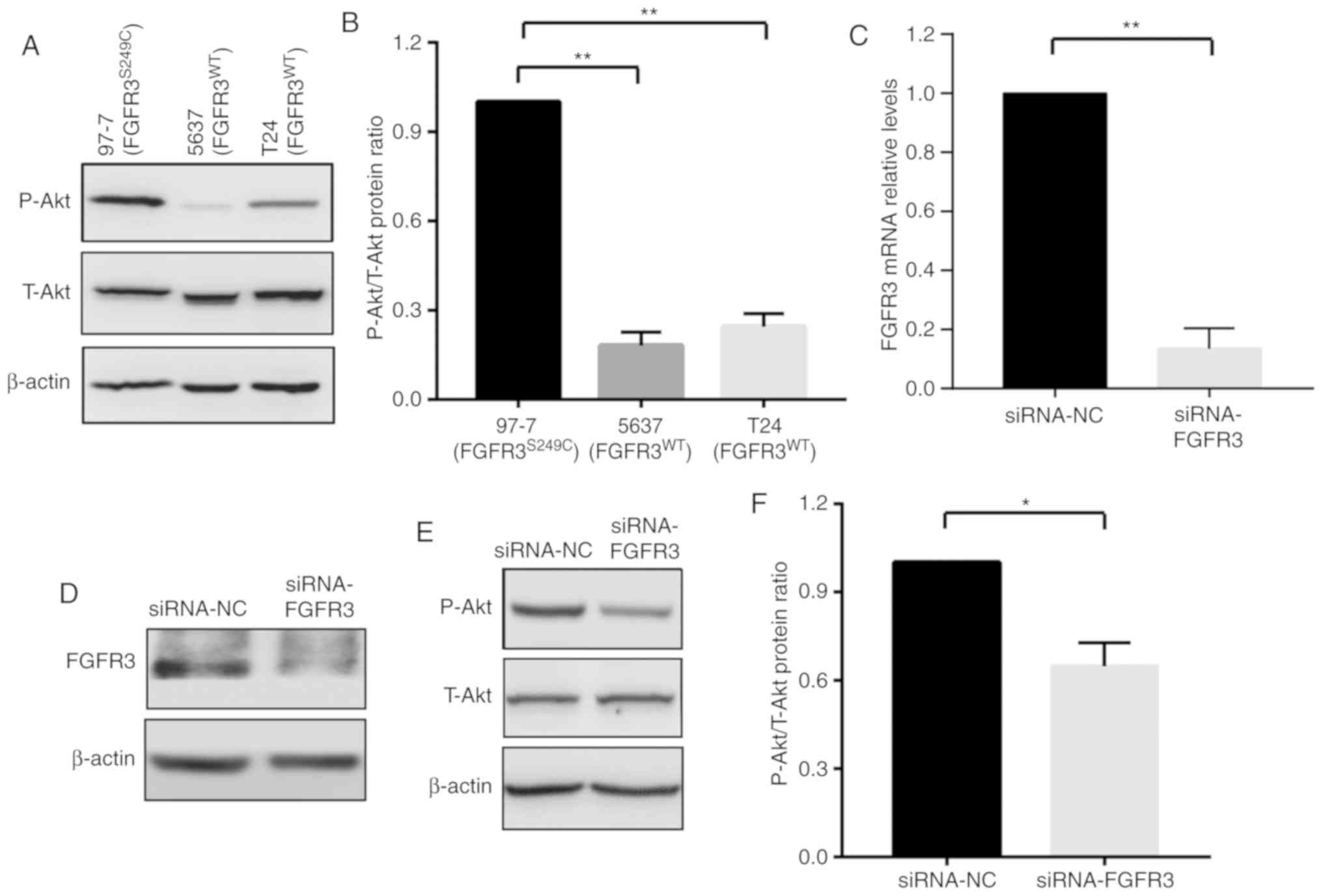
Akt signaling pathway is activated in
97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells
Previous studies have demonstrated that the
activation of Akt signaling serves an important role in cancer cell
chemoresistance (17,18). It has also been revealed that the
phosphorylation of FGFR3 leads to the activation of several
downstream signaling cascades, including PI3K-Akt-mTOR and
Ras-Raf-mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) (13,19).
These data revealed that FGFR3S249C mutations in BCa
cells may induce chemoresistance by activating Akt signaling.
Therefore, levels of T-Akt and P-Akt were detected in the present
study using western blot analysis in 97-7 (FGFR3S249C),
5637 (FGFR3WT) and T24 (FGFR3WT) cells. The
activation of the Akt signaling pathway was determined using the
ratio of P-Akt/T-Akt. As presented in Fig. 2A-C, 97-7 (FGFR3S249C)
cells exhibited increased P-Akt levels compared with 5637
(FGFR3WT) and T24 (FGFR3WT) cells, although
no marked change in T-Akt levels were observed (Fig. 2A). The elevated P-Akt/T-Akt ratio in
97-7(FGFR3S249C) cells indicated the activation of Akt
signaling (Fig. 2B).
To further verify the regulatory effect of FGFR3 on
Akt signaling, the P-Akt/T-Akt ratio was assessed in 97-7
(FGFR3S249C) cells after FGFR3 knockdown using siRNA for
48 h. Consistent with a previous study (19), the knockdown of FGFR3, which
decreased FGFR3 mRNA and protein expression levels (Fig. 2C and D), resulted in a ~30% decrease
in the ratio of P-Akt/T-Akt (Fig. 2E and
F). The results indicated that the FGFR3S249C
mutation, which leads to the auto-phosphorylation of FGFR3 in 97-7
(FGFR3S249C) cells, augments Akt signaling.
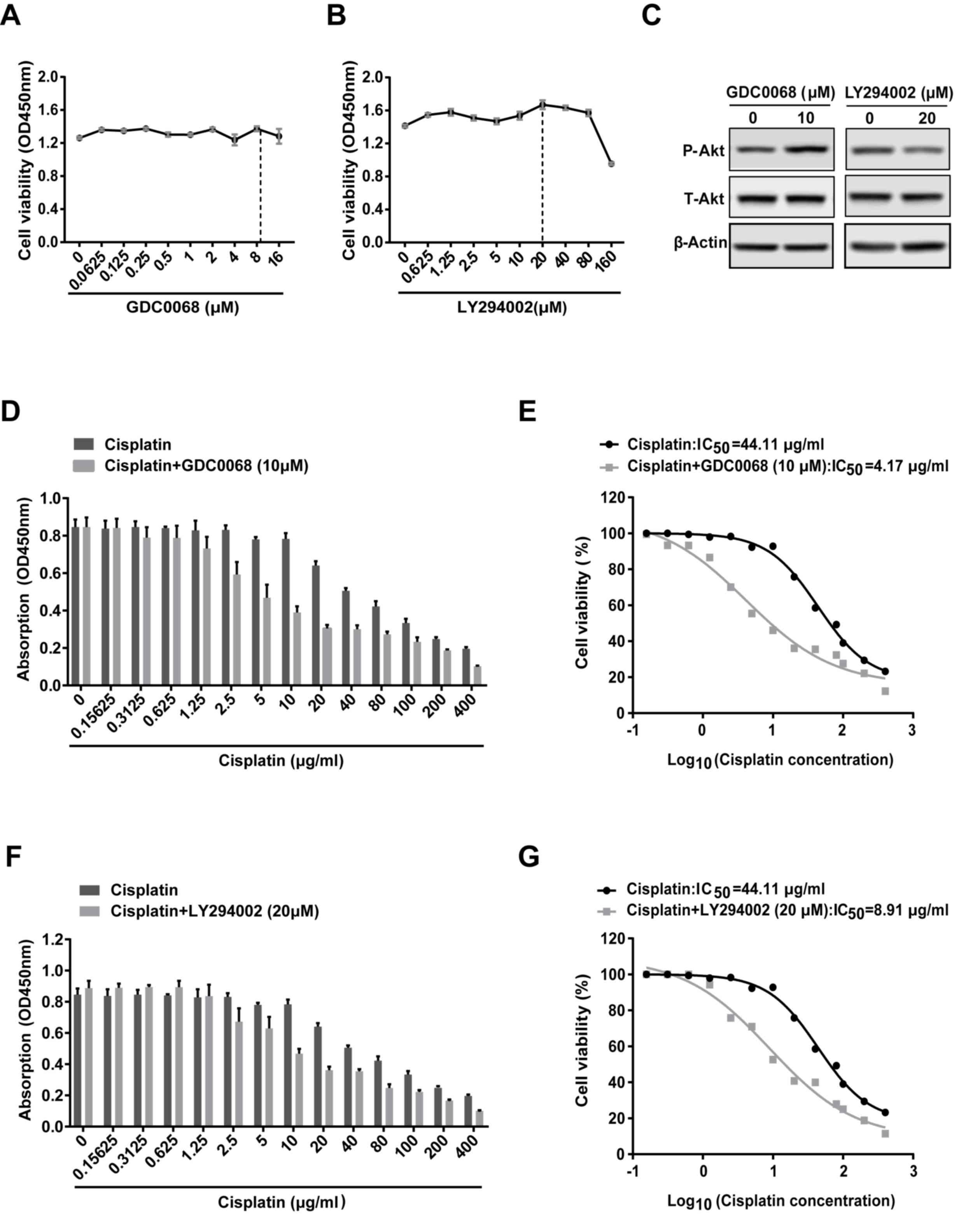
Inhibition of the Akt signaling
pathway sensitizes 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells to
cisplatin
To determine the role of Akt signaling in cisplatin
resistance, 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells treated with
cisplatin were subsequently treated with or without the Akt
inhibitor (GDC0068) or the PI3K inhibitor (LY294002) for 48 h,
following which cell viability was assessed. GDC0068 <16 µM and
LY294002 <80 µM did not affect cell viability in 97-7
(FGFR3S249C) cells (Fig. 3A
and B). Western blot analysis revealed that 20 µM LY294002
decreased the level of P-Akt and inhibited the activation of Akt
signaling (Fig. 3C). GDC0068, is an
ATP-competitive Akt inhibitor (20),
which occupies the ATP binding pocket of Akt kinases and
facilitates intramolecular interactions of phosphorylated T308/S473
with two residues in the catalytic cleft (R273, H194), results in
restricting phosphatase access and sustaining Akt phosphorylation
(21). Therefore, as other previous
studies (20,22,23),
although GDC0068 inhibits the activity of Akt signaling, a high
level of P-Akt can be detected after GDC0068 treatment (Fig. 3C). Based on these data, 10 µM GDC0068
and 20 µM LY294002 were utilized in subsequent combined treatment
studies. GDC0068 and LY294002 increased the sensitivity of 97-7
(FGFR3S249C) cells to cisplatin (Fig. D and F). The
IC50 value was reduced from 44.11 µg/ml for treatment
with cisplatin alone to 4.17 and 8.91 µg/ml when administered in
combination with GDC0068 and LY294002, respectively (Fig. 3E and G). The results revealed that
the Akt signaling pathway may be involved in the chemoresistance of
97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells.
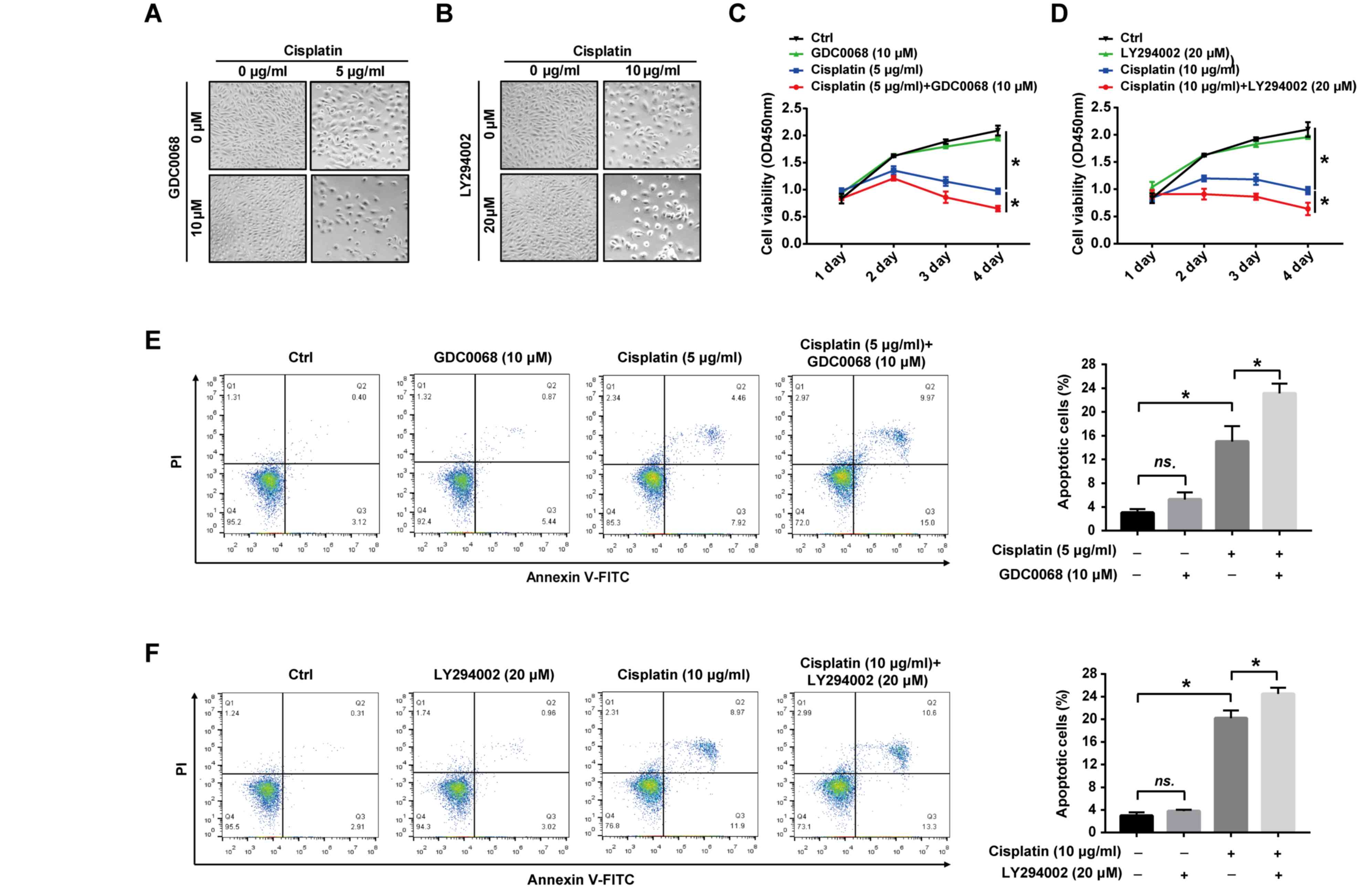
Inhibition of the Akt signaling
pathway augments the effects of cisplatin on 97-7
(FGFR3S249C) cell proliferation and apoptosis
To assess the potential role of the Akt signaling
pathway in cisplatin-induced apoptosis, the effect of Akt
inhibitors on the proliferation and apoptosis of 97-7
(FGFR3S249C) cells was determined following treatment
with cisplatin. The results revealed that cisplatin treatment
altered the cell from fusiform to round, and reduced cell numbers,
which were more pronounced after combinational treatment with
GDC0068 or LY294002 (Fig. 4A and B).
The suppression of cell proliferation by cisplatin was more
apparent with prolonged treatments and the combined treatment of
cisplatin with GDC0068 or LY294002 significantly increased the
effect of cisplatin on the proliferation of 97-7 cells
(FGFR3S249C; Fig. 4C and
D). After 72 h of treatment, 5 and 10 µg/ml cisplatin
significantly increased apoptosis compared with untreated cells
(Fig. 4E and F). Furthermore,
GDC0068 and LY294002 in combination with cisplatin significantly
increased apoptosis by 53.3% and 25%, respectively, compared with
cisplatin treatment alone (the numbers of apoptotic cells were 23%
vs. 15% and 25% vs. 20%, respectively; Fig. 4E and F). The results of the current
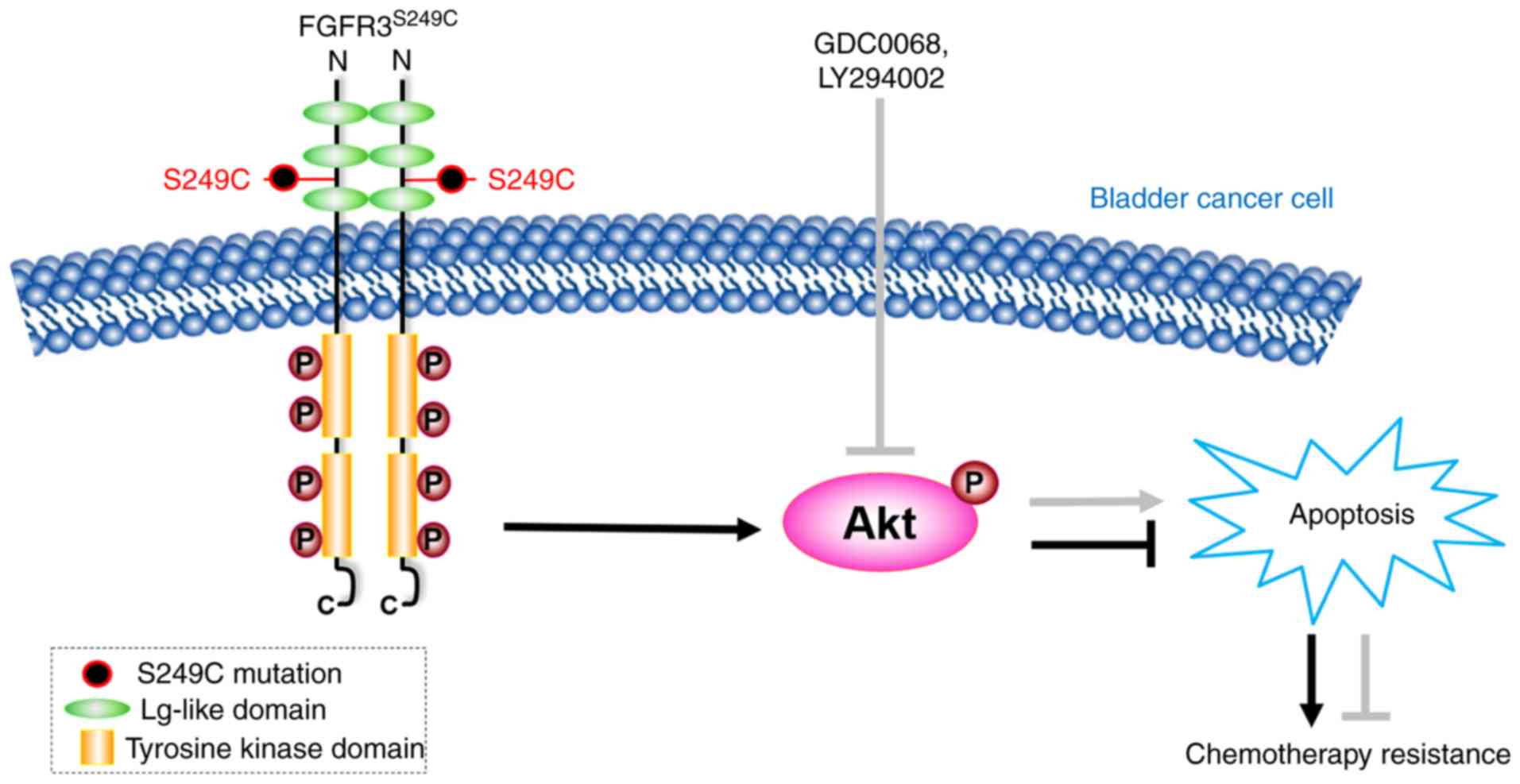
study indicate that the Akt signaling pathway is activated in
FGFR3S249C mutant BCa cells, resulting in the promotion
of cisplatin resistance, and the chemical inhibition of the Akt
signaling pathway in 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells indicated
improved chemosensitivity (Fig.
5).
Discussion
BCa is the most common malignant carcinoma of the
urinary system (1). Despite initial
sensitivity to standard first-line combination cisplatin-based
chemotherapy, the overall prognosis of MIBC is poor (8,24). Since
chemoresistance is a critical factor that effects clinical
treatment outcomes (7), studies that
assess and develop efficient chemosensitizers have become an urgent
requirement. FGFR3, a high-frequency mutant gene in BCa with known
regulatory roles in tumor progression, has become a promising
therapeutic target (8,25,26). In
the present study, the role of S249C mutant FGFR3 was elucidated in
the development of BCa cell chemoresistance. The results revealed
that BCa cells carrying FGFR3S249C exhibited a lower
sensitivity to cisplatin. The FGFR3S249C mutation in BCa
cells also activated Akt signaling and the chemical inhibition of
the Akt signaling pathway in 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells
improved chemosensitivity and enhanced the cisplatin-induced
suppression of cell proliferation and apoptosis induction.
Conventional chemotherapeutic drugs, including
platinum and fluorouracil induce an anti-tumor effect by damaging
DNA and promoting tumor cell apoptosis (27). As cisplatin-based combination
chemotherapy is the most important therapeutic strategy for MIBC
(6), cisplatin resistance in BCa
cells was assessed in the current study. S249C accounts for >50%
of all FGFR3 point mutations in BCa (10,11) and
therefore the effect of FGFR3S249C on BCa cell
chemosensitivity was also assessed in the present study. The cell
line 97-7 was utilized as it carried the FGFR3S249C
mutation without additional mutations in Ras, Akt or PIK3CA
(Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase, catalytic subunit
alpha) (12,14). The 97-7 cell line was established
from a primary tumor with invasive transitional cell carcinoma
(Grade II/III Stage I) and was demonstrated to express similar
FGFR3 levels as low-stage and low-grade tumors (28). In the present study, it was
demonstrated that 97-7 cells carrying S249C mutant FGFR3 exhibited
a higher IC50 value for cisplatin, indicating that the
FGFR3S249C mutation reduced BCa cell sensitivity to
cisplatin. This result indicated that the FGFR3S249C
mutation may be developed as a predictor of chemosensitivity in
patients with BCa.
The mechanisms underlying the development of
chemoresistance are complex and include increased drug efflux,
alterations in chemotherapy drug targets and the abnormal
activation of key signaling pathways such as PI3K/Akt and signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 (17,18).
Evidence from previous studies has demonstrated that FGFR3
phosphorylation activates several signaling pathways, including the
PI3K-Akt-mTOR and Ras-Raf-MAPK pathway (13,19). The
Akt signaling pathway may therefore be involved in the
FGFR3S249C mutation-induced chemoresistance of BCa
cells. In the current study, the ratio of P-Akt/T-Akt increased in
97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells compared with 5637
(FGFR3WT) and T24 (FGFR3WT; Fig. 2A and B). Furthermore, as reported
previously (19), the P-Akt/T-Akt
ratio in 97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells was reversed by FGFR3
knockdown. The results demonstrated that the FGFR3S249C
mutation in BCa cells may activate the Akt signaling pathway.
Previous studies have reported that high
concentrations of Akt inhibitor (GDC0068) and PI3K inhibitor
(LY294002) promotes tumor cell apoptosis and inhibits proliferation
(29) (30,31). To
avoid these effects, the current study utilized low concentrations
of GDC0068 (10 µM) and LY294002 (20 µM). Consistent with previous
studies (30,32), 20 µM LY294002 inhibited the Akt
signaling pathway and reduced P-Akt levels. GDC0068, is an
ATP-competitive Akt inhibitor that occupies the ATP binding pocket
of Akt kinases and facilitates intramolecular interactions,
resulting restricts phosphatase access and sustains Akt
phosphorylation (15,21). This may explain the high P-Akt level
detected after treatment with 10 µM GDC0068 in the current study
and other previous studies (20,22,23). The
inhibition of Akt signaling with GDC0068 or LY294002 sharply
decreased the IC50 of cisplatin and improved the
chemosensitivity of BCa cells carrying S249C mutant FGFR3,
enhancing the cisplatin-mediated reduction of proliferation and the
induction of apoptosis. The results verified the hypothesis that
the Akt signaling pathway may be involved in the
FGFR3S249C mutation-induced chemoresistance of BCa
cells.
Currently, several Akt inhibitors including GDC0068,
MK2206, GSK2110183 and AZD5363 have entered phase II of clinical
trials, but the efficacy of therapies with Akt inhibitors as single
agents is limited (33). A previous
study therefore combine Akt inhibitors with other compounds to
increase efficacy (30). For
example, a recent study combining cisplatin with MK2206 showed
synergistic activity in vivo and in vitro in lung
cancer (34). Furthermore, MK2206
also increased the sensitivity to paclitaxel and carboplatin in
melanoma cell lines (35). The
results of the current study demonstrated that the use of Akt
inhibitors combined with cisplatin-based chemotherapy may be used
as a potential treatment strategy for patients with BCa carrying
the FGFR3S249C mutation.
97-7 (FGFR3S249C) cells have not been
demonstrated to produce tumors in subcutaneous xenografts in nude
mice, which may be due to the dependence of tumor cells on
tissue-specific microenvironmental factors (12). However, the current study was not
able to verify the effects of the FGFR3S249C mutation on
BCa chemosensitivity in vivo. It is therefore important to
develop a FGFR3 mutant BCa in vivo model and in particular,
an in-situ model, for studying the effects of the FGFR3
mutation on chemoresistance and determining associated underlying
mechanisms.
In summary, the in vitro analysis used in the
current study demonstrated that the FGFR3S249C mutation
in BCa cells promoted chemoresistance, at least in part, via the
activation of the Akt signaling pathway. The results also indicated
that the FGFR3S249C mutation may be developed as a
biomarker for the detection of chemosensitivity and that targeting
Akt signaling may be a promising treatment strategy for improving
chemosensitivity in patients with BCa carrying the
FGFR3S249C mutation.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Margaret
A. Knowles for providing the bladder transitional cell carcinoma
cell line, 97-7.
Funding
The present study was supported by the China
Postdoctoral Foundation (grant no. 2018M633250), the High Level
University's Medical Discipline Construction (grant no.
2016031638), Shenzhen Science and Technology Project (grant no.
JSGG20160301162913683) and Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen
(grant no. SZSM201612031).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during the present
study are included in this published article.
Authors' contributions
XX, JL and AT designed the current study. XX, YZ and
MF performed the experiments. XX analyzed the data and XX and JL
wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final
manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Babjuk M, Bohle A, Burger M, Capoun O,
Cohen D, Comperat EM, Hernandez V, Kaasinen E, Palou J, Roupret M,
et al: EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma
of the bladder: Update 2016. Eur Urol. 71:447–461. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Metts MC, Metts JC, Milito SJ and Thomas
CR Jr: Bladder cancer: A review of diagnosis and management. J Natl
Med Assoc. 92:285–294. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Babjuk M: Trends in bladder cancer
incidence and mortality: Success or Disappointment? Eur Urol.
71:109–110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun M and Trinh QD: Diagnosis and staging
of bladder cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 29205–218.
(vii)2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
von der Maase H, Sengelov L, Roberts JT,
Ricci S, Dogliotti L, Oliver T, Moore MJ, Zimmermann A and Arning
M: Long-term survival results of a randomized trial comparing
gemcitabine plus cisplatin, with methotrexate, vinblastine,
doxorubicin, plus cisplatin in patients with bladder cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 23:4602–4608. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vaishampayan U: Systemic therapy of
advanced urothelial cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 10:256–266.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iyer G and Milowsky MI: Fibroblast growth
factor receptor-3 in urothelial tumorigenesis. Urol Oncol.
31:303–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Billerey C, Chopin D, Aubriot-Lorton MH,
Ricol D, Gil Diez de Medina S, Van Rhijn B, Bralet MP,
Lefrere-Belda MA, Lahaye JB, Abbou CC, et al: Frequent FGFR3
mutations in papillary non-invasive bladder (pTa) tumors. Am J
Pathol. 158:1955–1959. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tomlinson DC, Hurst CD and Knowles MA:
Knockdown by shRNA identifies S249C mutant FGFR3 as a potential
therapeutic target in bladder cancer. Oncogene. 26:5889–5899. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Du X, Lin BC, Wang QR, Li H, Ingalla E,
Tien J, Rooney I, Ashkenazi A, Penuel E and Qing J: MMP-1 and
Pro-MMP-10 as potential urinary pharmacodynamic biomarkers of
FGFR3-targeted therapy in patients with bladder cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 20:6324–6335. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jebar AH, Hurst CD, Tomlinson DC, Johnston
C, Taylor CF and Knowles MA: FGFR3 and Ras gene mutations are
mutually exclusive genetic events in urothelial cell carcinoma.
Oncogene. 24:5218–5225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang C, Li A, Yang S, Qiao R, Zhu X and
Zhang J: CXCL5 promotes mitomycin C resistance in non-muscle
invasive bladder cancer by activating EMT and NF-κB pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 498:862–868. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lei ZJ, Wang J, Xiao HL, Guo Y, Wang T, Li
Q, Liu L, Luo X, Fan LL, Lin L, et al: Lysine-specific demethylase
1 promotes the stemness and chemoresistance of Lgr5+ liver cancer
initiating cells by suppressing negative regulators of β-catenin
signaling. Oncogene. 34:32142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao J: Cancer stem cells and
chemoresistance: The smartest survives the raid. Pharmacol Ther.
160:145–158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Johnson MD, O'Connell MJ, Pilcher W and
Reeder JE: Fibroblast growth factor receptor-3 expression in
meningiomas with stimulation of proliferation by the
phosphoinositide 3 kinase-Akt pathway. J Neurosurg. 112:934–939.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan Y, Serra V, Prudkin L, Scaltriti M,
Murli S, Rodriguez O, Guzman M, Sampath D, Nannini M, Xiao Y, et
al: Evaluation and clinical analyses of downstream targets of the
Akt inhibitor GDC-0068. Clin Cancer Res. 19:6976–6986. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chan TO, Zhang J, Rodeck U, Pascal JM,
Armen RS, Spring M, Dumitru CD, Myers V, Li X, Cheung JY, et al:
Resistance of Akt kinases to dephosphorylation through
ATP-dependent conformational plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:E1120–E1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kajitani N, Glahder J, Wu C, Yu H, Nilsson
K and Schwartz S: hnRNP L controls HPV16 RNA polyadenylation and
splicing in an Akt kinase-dependent manner. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:9654–9678. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin J, Sampath D, Nannini MA, Lee BB,
Degtyarev M, Oeh J, Savage H, Guan Z, Hong R, Kassees R, et al:
Targeting activated Akt with GDC-0068, a novel selective Akt
inhibitor that is efficacious in multiple tumor models. Clin Cancer
Res. 19:1760–1772. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Clark PE, Agarwal N, Biagioli MC,
Eisenberger MA, Greenberg RE, Herr HW, Inman BA, Kuban DA, Kuzel
TM, Lele SM, et al: Bladder cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
11:446–475. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo G, Sun X, Chen C, Wu S, Huang P, Li Z,
Dean M, Huang Y, Jia W, Zhou Q, et al: Whole-genome and whole-exome
sequencing of bladder cancer identifies frequent alterations in
genes involved in sister chromatid cohesion and segregation. Nat
Genet. 45:1459–1463. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guancial EA, Werner L, Bellmunt J, Bamias
A, Choueiri TK, Ross R, Schutz FA, Park RS, O'Brien RJ, Hirsch MS,
et al: FGFR3 expression in primary and metastatic urothelial
carcinoma of the bladder. Cancer Med. 3:835–844. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tian H, Gao Z, Li H, Zhang B, Wang G,
Zhang Q, Pei D and Zheng J: DNA damage response-a double-edged
sword in cancer prevention and cancer therapy. Cancer Lett.
358:8–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sarkar S, Julicher KP, Burger MS, Della
Valle V, Larsen CJ, Yeager TR, Grossman TB, Nickells RW, Protzel C,
Jarrard DF and Reznikoff CA: Different combinations of
genetic/epigenetic alterations inactivate the p53 and pRb pathways
in invasive human bladder cancers. Cancer Res. 60:3862–3871.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ren W, Joshi R and Mathew P: Synthetic
Lethality in PTEN-Mutant Prostate Cancer Is Induced by
Combinatorial PI3K/Akt and BCL-XL Inhibition. Mol Cancer Res.
14:1176–1181. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li A, Gu Y, Li X, Sun H, Zha H, Xie J,
Zhao J, Huang M, Chen L, Peng Q, et al: S100A6 promotes the
proliferation and migration of cervical cancer cells via the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 15:5685–5693.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu D, Tao J, Xu B, Qing W, Li P, Lu Q and
Zhang W: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002
suppresses proliferation and sensitizes doxorubicin chemotherapy in
bladder cancer cells. Urol Int. 87:105–113. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng LP, Hu ZM, Li K and Xia K: miR-222
attenuates cisplatin-induced cell death by targeting the
PPP2R2A/Akt/mTOR Axis in bladder cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med.
20:559–567. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pretre V and Wicki A: Inhibition of Akt
and other AGC kinases: A target for clinical cancer therapy? Semin
Cancer Biol. 48:70–77. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Galvez-Peralta M, Flatten KS, Loegering
DA, Peterson KL, Schneider PA, Erlichman C and Kaufmann SH:
Context-dependent antagonism between Akt inhibitors and
topoisomerase poisons. Mol Pharmacol. 85:723–734. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rebecca VW, Massaro RR, Fedorenko IV,
Sondak VK, Anderson AR, Kim E, Amaravadi RK, Maria-Engler SS,
Messina JL, Gibney GT, et al: Inhibition of autophagy enhances the
effects of the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 when combined with paclitaxel
and carboplatin in BRAF wild-type melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma
Res. 27:465–478. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|