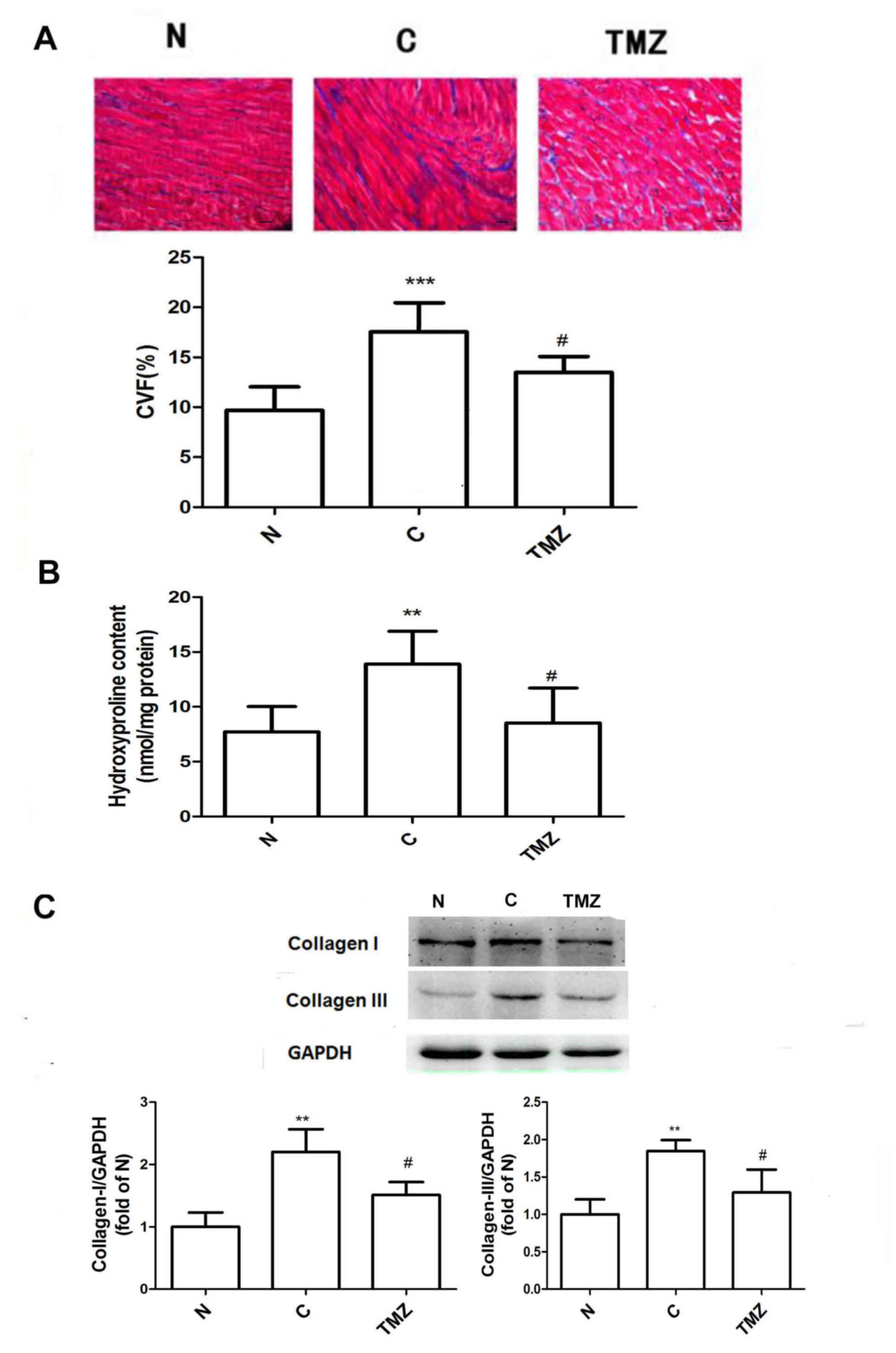
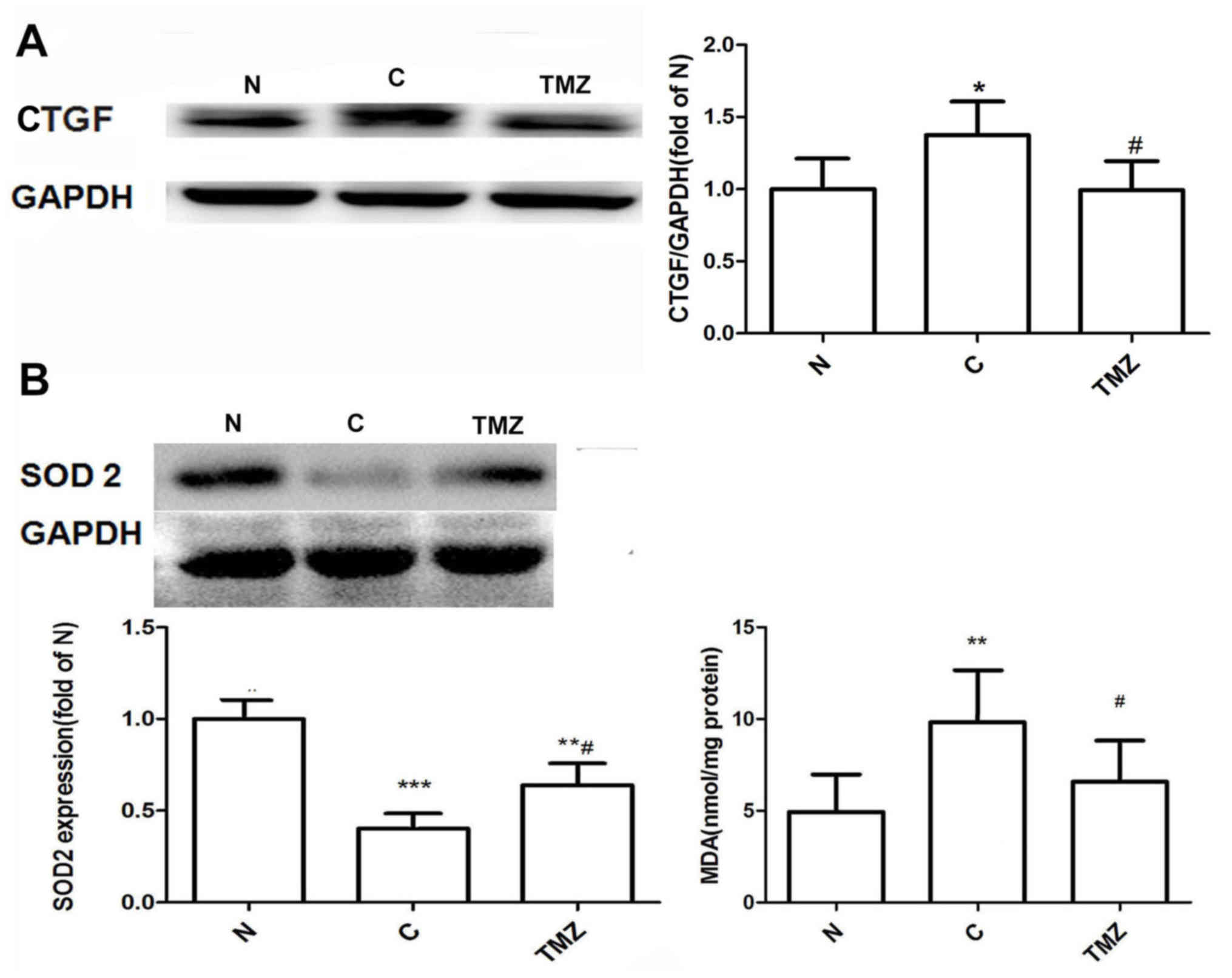
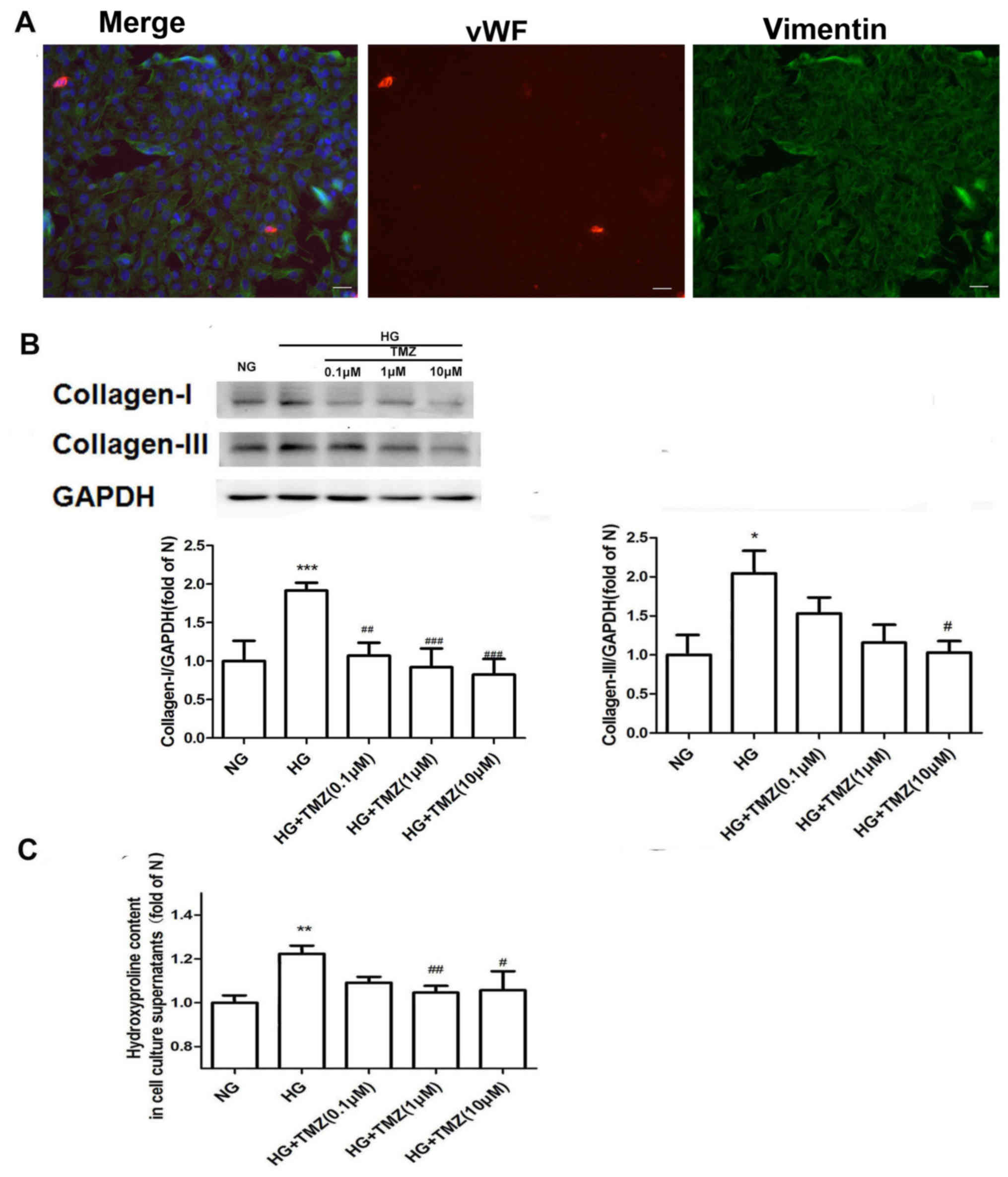
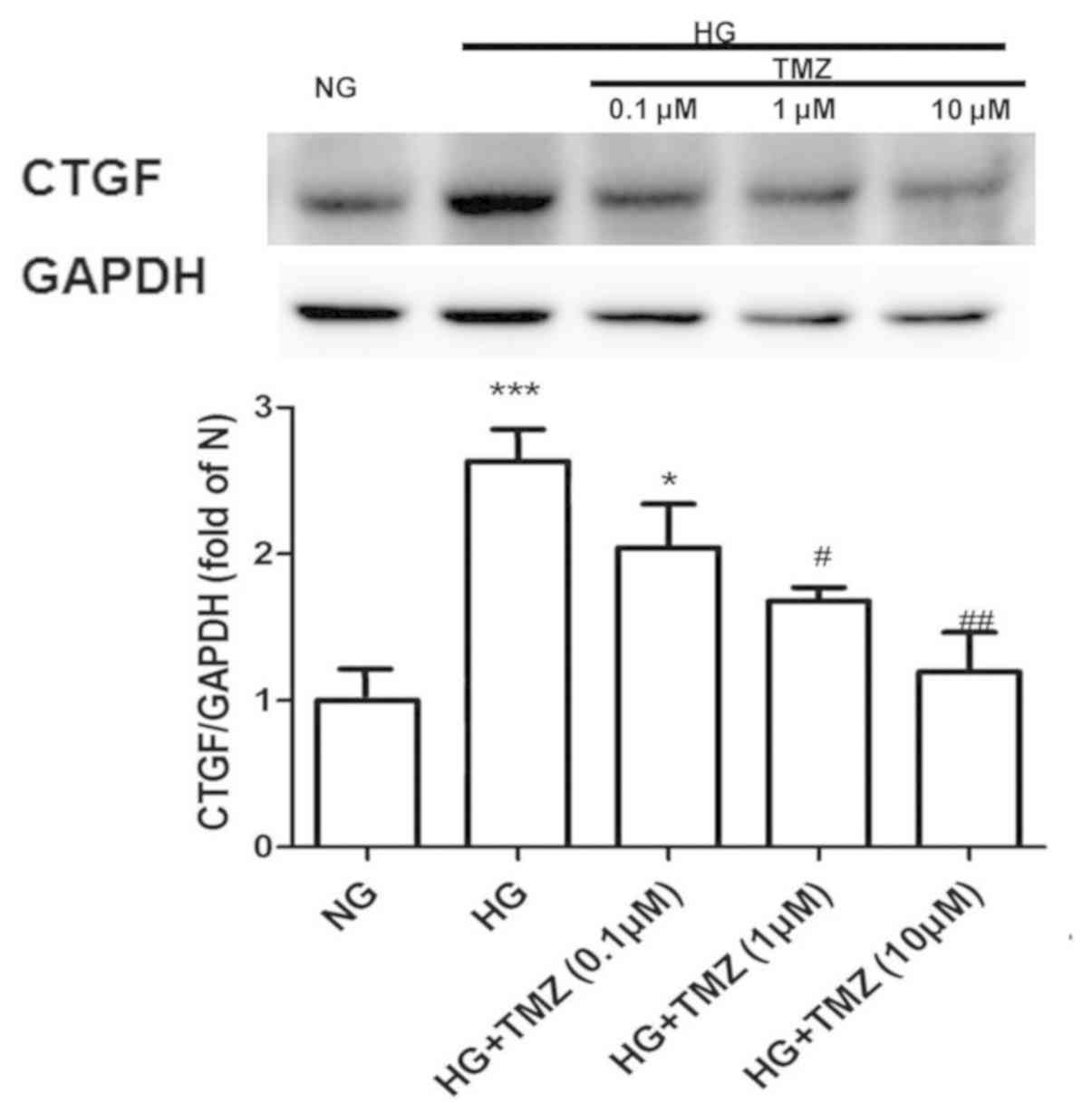
|
1
|
Shamhart PE, Luther DJ, Hodson BR, Koshy
JC, Ohanyan V and Meszaros JG: Impact of type 1 diabetes on cardiac
fibroblast activation: Enhanced cell cycle progression and reduced
myofibroblast content in diabetic myocardium. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 297:E1147–E1153. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
van Heerebeek L, Hamdani N, Handoko ML,
Falcao-Pires I, Musters RJ, Kupreishvili K, Ijsselmuiden AJ,
Schalkwijk CG, Bronzwaer JG, Diamant M, et al: Diastolic stiffness
of the failing diabetic heart: Importance of fibrosis, advanced
glycation end products, and myocyte resting tension. Circulation.
117:43–51. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krenning G, Zeisberg EM and Kalluri R: The
origin of fibroblasts and mechanism of cardiac fibrosis. J Cell
Physiol. 225:631–637. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bugyei-Twum A, Advani A, Advani SL, Zhang
Y, Thai K, Kelly DJ and Connelly KA: High glucose induces Smad
activation via the transcriptional coregulator p300 and contributes
to cardiac fibrosis and hypertrophy. Cardiovas Diabetol. 13:892014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dai B, Cui M, Zhu M, Su WL, Qiu MC and
Zhang H: STAT1/3 and ERK1/2 synergistically regulate cardiac
fibrosis induced by high glucose. Cell Physiol Biochem. 32:960–971.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wahab NA, Weston BS and Mason RM:
Connective tissue growth factor CCN2 interacts with and activates
the tyrosine kinase receptor TrkA. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:340–351.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang J, Li PH, Yang L, Du QS, Guo TT and
Tang X: Connective tissue growth factor mediates high
glucose-induced down-regulation of podocalyxin expression in mouse
podocytes. Nan Fang Yi ke Da Xue Xue Bao (Chinese). 31:839–843.
2011.
|
|
8
|
Kobayashi T, Inoue T, Okada H, Kikuta T,
Kanno Y, Nishida T, Takigawa M, Sugaya T and Suzuki H: Connective
tissue growth factor mediates the profibrotic effects of
transforming growth factor-beta produced by tubular epithelial
cells in response to high glucose. Clin Exp Nephrol. 9:114–121.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McLennan SV, Wang XY, Moreno V, Yue DK and
Twigg SM: Connective tissue growth factor mediates high glucose
effects on matrix degradation through tissue inhibitor of matrix
metalloproteinase type 1: Implications for diabetic nephropathy.
Endocrinology. 145:5646–5655. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Matsuda S, Gomi F, Katayama T, Koyama Y,
Tohyama M and Tano Y: Induction of connective tissue growth factor
in retinal pigment epithelium cells by oxidative stress. Jpn J
Ophthalmol. 50:229–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matsuda S, Gomi F, Oshima Y, Tohyama M and
Tano Y: Vascular endothelial growth factor reduced and connective
tissue growth factor induced by triamcinolone in ARPE19 cells under
oxidative stress. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:1062–1068. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu X, Gai Y, Liu F, Gao W, Zhang Y, Xu M
and Li Z: Trimetazidine inhibits pressure overload-induced cardiac
fibrosis through NADPH oxidase-ROS-CTGF pathway. Cardiovas Res.
88:150–158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kantor PF, Lucien A, Kozak R and Lopaschuk
GD: The antianginal drug trimetazidine shifts cardiac energy
metabolism from fatty acid oxidation to glucose oxidation by
inhibiting mitochondrial long-chain 3-ketoacyl coenzyme A thiolase.
Circ Res. 86:580–588. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Williams FM, Tanda K, Kus M and Williams
TJ: Trimetazidine inhibits neutrophil accumulation after myocardial
ischaemia and reperfusion in rabbits. J Cardiovas Pharmacol.
22:828–833. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ruixing Y, Wenwu L and Al-Ghazali R:
Trimetazidine inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a rabbit model of
ischemia-reperfusion. Transl Res. 149:152–160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Di Napoli P, Chierchia S, Taccardi AA,
Grilli A, Felaco M, De Caterina R and Barsotti A: Trimetazidine
improves post-ischemic recovery by preserving endothelial nitric
oxide synthase expression in isolated working rat hearts. Nitric
Oxide. 16:228–236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gajdosík A, Gajdosíkova A, Stefek M,
Navarová J and Hozová R: Streptozotocin-induced experimental
diabetes in male wistar rats. Gen Physiol Biophys 18 Spec No.
54–62. 1999.
|
|
18
|
Rennison JH, McElfresh TA, Okere IC,
Vazquez EJ, Patel HV, Foster AB, Patel KK, Chen Q, Hoit BD, Tserng
KY, et al: High-fat diet postinfarction enhances mitochondrial
function and does not exacerbate left ventricular dysfunction. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 292:H1498–H506. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo J, Gao X, Peng L, Sun H and Dai G:
Effects of hydrochlorothiazide on cardiac remodeling in a rat model
of myocardial infarction-induced congestive heart failure. Eur J
Pharmacol. 667:314–321. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsumoto K, Ishihara K, Tanaka K, Inoue K
and Fushiki T: An adjustable-current swimming pool for the
evaluation of endurance capacity of mice. J Appl Physiol (1985).
81:1843–1849. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fan YH, Dong H, Pan Q, Cao YJ, Li H and
Wang HC: Notch signaling may negatively regulate neonatal rat
cardiac fibroblast-myofibroblast transformation. Physiol Res.
60:739–748. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morici ML, Di Marco A, Sestito D, Candore
R, Cangemi C, Accardo F, Donatelli M, Cataldo MG and Lombardo A:
The impact of coexistent diabetes on the prevalence of coronary
heart disease. J Diabetes Complications. 11:268–273. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Isfort M, Stevens SC, Schaffer S, Jong CJ
and Wold LE: Metabolic dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Heart Fail Rev. 19:35–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kumar D, Lou H and Singal PK: Oxidative
stress and apoptosis in heart dysfunction. Herz. 27:662–668. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yeung EH, Pankow JS, Astor BC, Powe NR,
Saudek CD and Kao WH: Increased risk of type 2 diabetes from a
family history of coronary heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Care. 30:154–156. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fragasso G, Salerno A, Lattuada G, Cuko A,
Calori G, Scollo A, Ragogna F, Arioli F, Bassanelli G, Spoladore R,
et al: Effect of partial inhibition of fatty acid oxidation by
trimetazidine on whole body energy metabolism in patients with
chronic heart failure. Heart. 97:1495–500. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fragasso G, Perseghin G, De Cobelli F,
Esposito A, Palloshi A, Lattuada G, Scifo P, Calori G, Del Maschio
A and Margonato A: Effects of metabolic modulation by trimetazidine
on left ventricular function and phosphocreatine/adenosine
triphosphate ratio in patients with heart failure. Eur Heart J.
27:942–948. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Belardinelli R, Cianci G, Gigli M,
Mazzanti M and Lacalaprice F: Effects of trimetazidine on
myocardial perfusion and left ventricular systolic function in type
2 diabetic patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 51:611–615. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Belardinelli R, Lacalaprice F, Faccenda E
and Volpe L: Trimetazidine potentiates the effects of exercise
training in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy referred for
cardiac rehabilitation. Eur J Cardiovas Prev Rehabili. 15:533–540.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
El-Kady T, El-Sabban K, Gabaly M, Sabry A
and Abdel-Hady S: Effects of trimetazidine on myocardial perfusion
and the contractile response of chronically dysfunctional
myocardium in ischemic cardiomyopathy: A 24-month study. Am J
Cardiovasc Drugs. 5:271–278. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fragasso G, Palloshi A, Puccetti P,
Silipigni C, Rossodivita A, Pala M, Calori G, Alfieri O and
Margonato A: A randomized clinical trial of trimetazidine, a
partial free fatty acid oxidation inhibitor, in patients with heart
failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 48:992–998. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fragasso G, Piatti Md PM, Monti L,
Palloshi A, Setola E, Puccetti P, Calori G, Lopaschuk GD and
Margonato A: Short- and long-term beneficial effects of
trimetazidine in patients with diabetes and ischemic
cardiomyopathy. Am Heart J. 146:E182003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao P, Zhang J, Yin XG, Maharaj P,
Narraindoo S, Cui LQ and Tang YS: The effect of trimetazidine on
cardiac function in diabetic patients with idiopathic dilated
cardiomyopathy. Life Sci. 92:633–638. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Belardinelli R, Solenghi M, Volpe L and
Purcaro A: Trimetazidine improves endothelial dysfunction in
chronic heart failure: An antioxidant effect. Eur Heart J.
28:1102–1108. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang L, Ding WY, Wang ZH, Tang MX, Wang
F, Li Y, Zhong M, Zhang Y and Zhang W: Early administration of
trimetazidine attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats by
alleviating fibrosis, reducing apoptosis and enhancing autophagy. J
Transl Med. 14:1092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Aragno M, Mastrocola R, Alloatti G,
Vercellinatto I, Bardini P, Geuna S, Catalano MG, Danni O and
Boccuzzi G: Oxidative stress triggers cardiac fibrosis in the heart
of diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 149:380–388. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Aragno M, Meineri G, Vercellinatto I,
Bardini P, Raimondo S, Peiretti PG, Vercelli A, Alloatti G,
Tomasinelli CE, Danni O and Boccuzzi G: Cardiac impairment in
rabbits fed a high-fat diet is counteracted by
dehydroepiandrosterone supplementation. Life Sci. 85:77–84. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang X, McLennan SV, Allen TJ, Tsoutsman
T, Semsarian C and Twigg SM: Adverse effects of high glucose and
free fatty acid on cardiomyocytes are mediated by connective tissue
growth factor. Am J Physiol Cell physiol. 297:C1490–500. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|