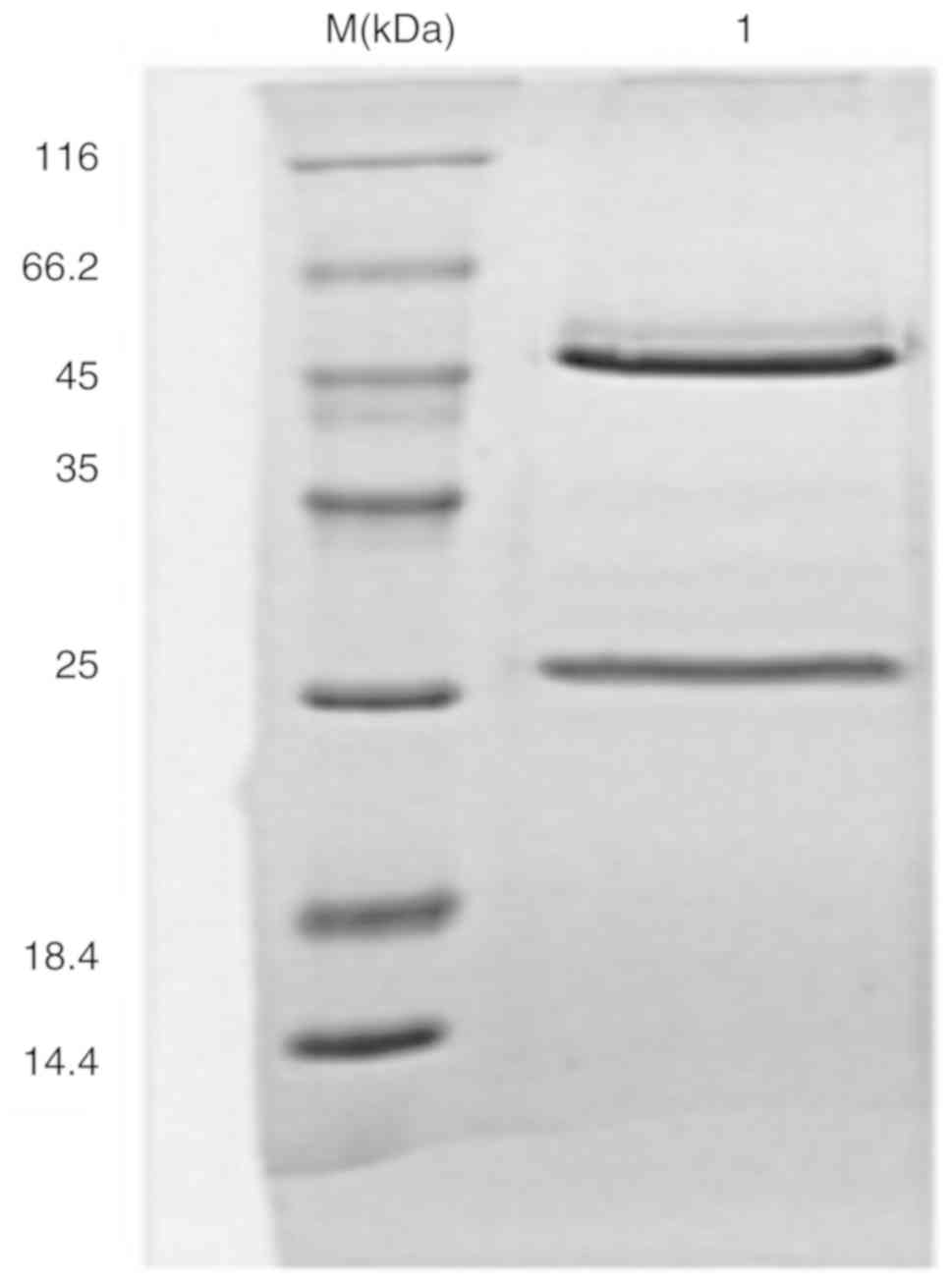
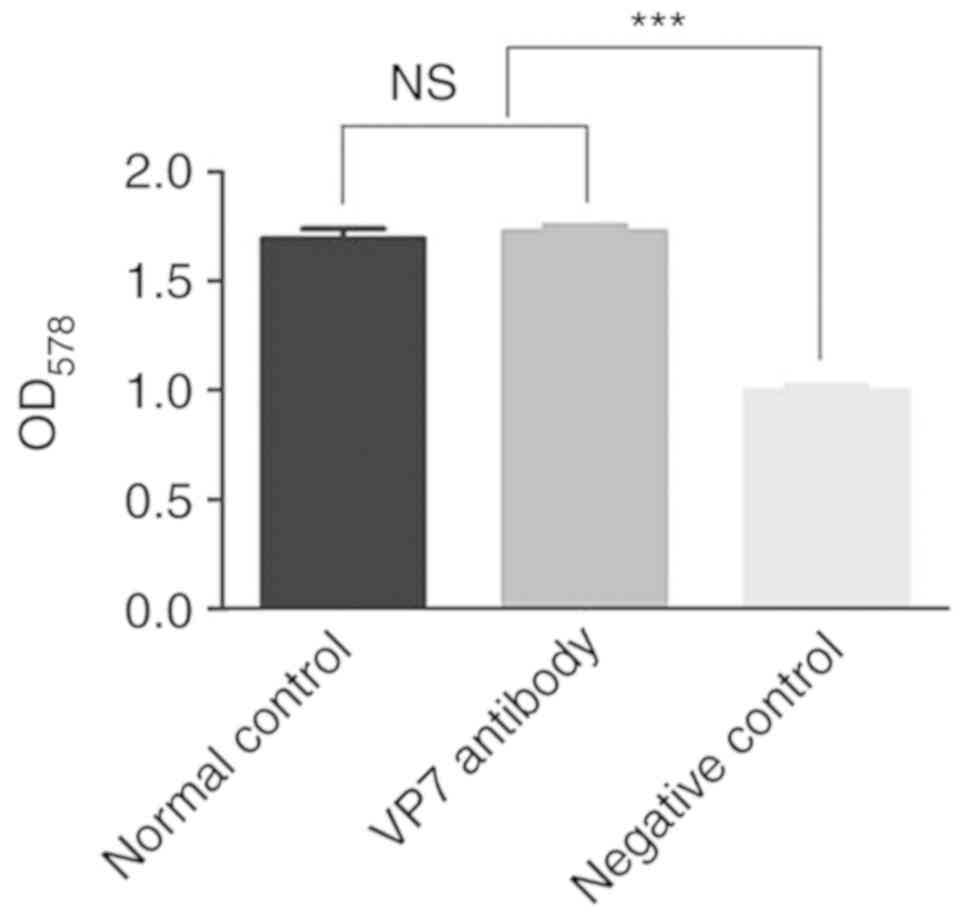
|
1
|
Yin N, Yang FM, Qiao HT, Zhou Y, Duan SQ,
Lin XC, Wu JY, Xie YP, He ZL, Sun MS and Li HJ: Neonatal rhesus
monkeys as an animal model for rotavirus infection. World J
Gastroenterol. 24:5109–5119. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Layton JB, Butler AM, Panozzo CA and
Brookhart MA: Rotavirus vaccination and short-term risk of adverse
events in US infants. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 32:448–457. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vannie P, Capua I, Le Potier MF, Mackay
DK, Muylkens B, Parida S, Paton DJ and Thiry E: Marker vaccines and
the impact of their use on diagnosis and prophylactic measures. Rev
Sci Tech. 26:351–372. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Teng Y, Zhao B, Pan X, Wen Y and Chen Y: A
new rotavirus VP6-based foreign epitope presenting vector and
immunoreactivity of VP4 epitope chimeric proteins. Viral Immunol.
27:96–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Perez CA, Eichwald C, Burrone O and
Mendoza D: Rotavirus vp7 antigen produced by Lactococcus lactis
induces neutralizing antibodies in mice. J Appl Microbiol.
99:1158–1164. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Morozova OV, Sashina TA, Fomina SG and
Novikova NA: Comparative characteristics of the VP7 and VP4
antigenic epitopes of the rotaviruses circulating in Russia (Nizhny
Novgorod) and the Rotarix and RotaTeq vaccines. Arch Virol.
160:1693–1703. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang SH: Research on genetic engineering
subunit vaccine of A group bovine rotavirus. Chin J Zoonoses.
27:506–510. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Jalilvand S, Afchangi A, Mohajel N,
Roohvand F and Shoja Z: Diversity of VP7 genes of G1 rotaviruses
isolated in Iran, 2009–2013. Infect Genet Evol. 37:275–279. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Macek C: Monoclonal antibodies: Key to a
revolution in clinical medicine. JAMA. 247:2463–2470. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peterson NC and Peavey JE: Comparison of
in vitro monoclonal antibody production methods with an in vivo
ascites production technique. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci. 37:61–66.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kairemo KJ, Lappalainen AK, Kääpä E,
Laitinen OM, Hyytinen T, Karonen SL and Grönblad M: In vivo
detection of intervertebral disk injury using a radiolabeled
monoclonal antibody against keratan sulfate. J Nucl Med.
42:476–482. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ogawa M, Regino CA, Choyke PL and
Kobayashi H: In vivo target-specific activatable near-infrared
optical labeling of humanized monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cancer
Ther. 8:232–239. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fernández D, Valle I, Llamos R, Guerra M,
Sorell L and Gavilondo J: Rapid detection of rotavirus in faeces
using a dipstick system with monoclonal antibodies and colloidal
gold as marker. J Virol Methods. 48:315–323. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang GM and Yao GH: Investigation on
genetic background of Kunming mice (KM mice) in China. Chin J Lab
Anim Sci. 7:246–251, (In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Shang H, Wei H, Yue B, Xu P and Huang H:
Microsatellite analysis in two populations of Kunming mice. Lab
Anim. 43:34–40. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma P, Wu Y, Zeng Q, Gan Y, Chen J, Ye X
and Yang X: Oxidative damage induced by chlorpyrifos in the hepatic
and renal tissue of Kunming mice and the antioxidant role of
vitamin E. Food Chem Toxicol. 58:177–183. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Weng J, Yang L, Lei C, Li T, Peng G, Fu C,
Han X, Li H, Jiang Z, Zhang Z, et al: Elimination of mycoplasma
contamination from infected human hepatocyte C3A cells by
intraperitoneal injection in BALB/c mice. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 7:4402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tammer R, Evensen O, Lutz H and Reinacher
M: Immunohistological demonstration of feline infectious
peritonitis virus antigen in paraffin-embedded tissues using feline
ascites or murine monoclonal antibodies. Vet Immunol Immunopathol.
49:177–82. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zheng J, Zhang H, Bao K, Gao W, Xu C and
Xia C: Preparation of monoclonal antibodies against bovine
progesterone. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 34:275–277.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ezzatifar F, Majidi J, Baradaran B,
Aghebati Maleki L, Abdolalizadeh J and Yousefi M: Large scale
generation and characterization of anti-human IgA monoclonal
antibody in ascitic fluid of BALB/c mice. Adv Pharm Bull. 5:97–102.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Velez D, Miller L and Macmillan JD: Use of
tangential flow filtration in perfusion propagation of hybridoma
cells for production of monoclonal antibodies. Biotechnol Bioeng.
33:938–940. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rokni M, Razavi AR, Shokri F, Ahmadi Kia
K, Solaymani-Mohammadi F, Chahardoli R and Saboor-Yaraghi AA:
Enhancement of monoclonal antibody production after single and
combination treatment of the hybridoma cells with all-trans
retinoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid: An in vitro and in vivo
study. Int Immunopharmacol,. 59:295–300. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hnasko R, Lin AV, Stanker L and McGarvey
J: A bioassay for optimization of macrophage-conditioned medium as
a culture supplement to promote hybridoma cell survival and growth.
Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 37:126–133. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu YC, Huang YC and Lee TY: Purification
of antibodies from protein mixtures and mouse ascites fluid using
Zeolite X. Biotechnol Prog. 14:332–337. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ohkawa K, Tsukada Y and Hirai H: Effect of
antibody to rat alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) on protein and DNA
synthesis of rat ascites hepatoma AH66 cells. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho.
11:227–234. 1984.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Johnson E, Miribel L, Arnaud P and Tsang
KY: Purification of IgM monoclonal antibody from murine ascitic
fluid by a two-step column chromatography procedure. Immunol Lett.
14:159–165. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jermy A, Beeson D and Vincent A:
Pathogenic autoimmunity to affinity-purified mouse acetylcholine
receptor induced without adjuvant in BALB/c mice. Eur J Immunol.
23:973–976. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yavuz H, Bereli N, Yılmaz F, Armutcu C and
Denizli A: Antibody purification from human plasma by
metal-chelated affinity membranes. Methods Mol Biol. 1286:43–46.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Graczyk TK and Cranfield MR: Detection of
Cryptosporidium- specific serum immunoglobulins in captive snakes
by a polyclonal antibody in the indirect ELISA. Vet Res.
28:131–142. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pringels L, Broeckx V, Boonen K, Landuyt B
and Schoofs L: Abundant plasma protein depletion using ammonium
sulfate precipitation and protein A affinity chromatography. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1089:43–59. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Grodzki AC and Berenstein E: Antibody
purification: Ammonium sulfate fractionation or gel filtration.
Methods Mol Biol. 588:15–26. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kent UM: Purification of antibodies using
ammonium sulfate fractionation or gel filtration. Methods Mol Biol.
34:13–21. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ahlstedt S, Holmgren J and Hanson LA: The
validity of the ammonium sulphate precipitation technique of
estimation of antibody amount and avidity. Immunology. 25:917–922.
1973.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Surin AM, Sharipov RR, Krasil'nikova IA,
Boyarkin DP, Lisina OY, Gorbacheva LR, Avetisyan AV and Pinelis VG:
Disruption of functional activity of mitochondria during MTT assay
of viability of cultured neurons. Biochemistry (Mosc). 82:737–749.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nguyen VS, Shi L, Luan FQ and Wang QA:
Synthesis of kaempferide Mannich base derivatives and their
antiproliferative activity on three human cancer cell lines. Acta
Biochim Pol. 62:547–552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shetty AK, Gans HA, So S, Millan MT, Arvin
AM and Gutierrez KM: Intravenous ribavirin therapy for adenovirus
pneumonia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 29:69–73. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gross AE and Bryson ML: Oral ribavirin for
the treatment of noninfluenza respiratory viral infections: A
systematic review. Ann Pharmacother. 49:1125–1135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Satoh S, Mori K, Onomura D, Ueda Y,
Dansako H, Honda M, Kaneko S, Ikeda M and Kato N: Ribavirin
suppresses hepatic lipogenesis through inosine monophosphate
dehydrogenase inhibition: Involvement of adenosine
monophosphate-activated protein kinase-related kinases and retinoid
X receptor α. Hepatol Commun. 1:550–563. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Musser JMB, Heatley JJ, Koinis AV,
Suchodolskin PF, Guo J, Escandon P and Tizard IR: Ribavirin
inhibits parrot bornavirus 4 replication in cell culture. PLoS One.
10:e01340802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|