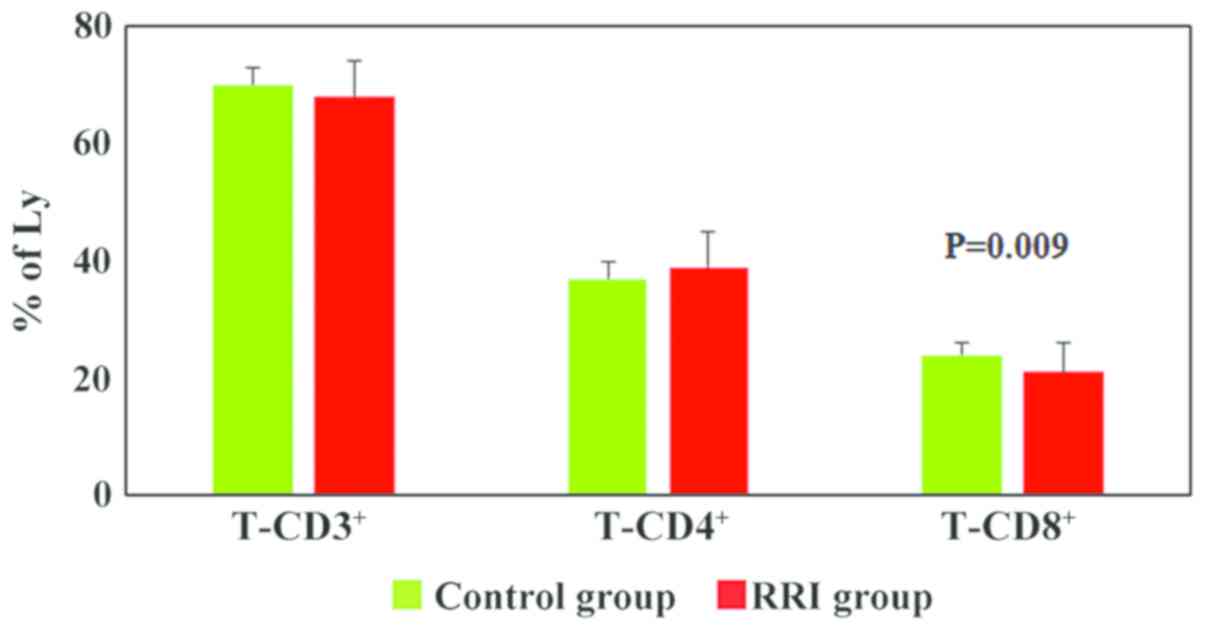
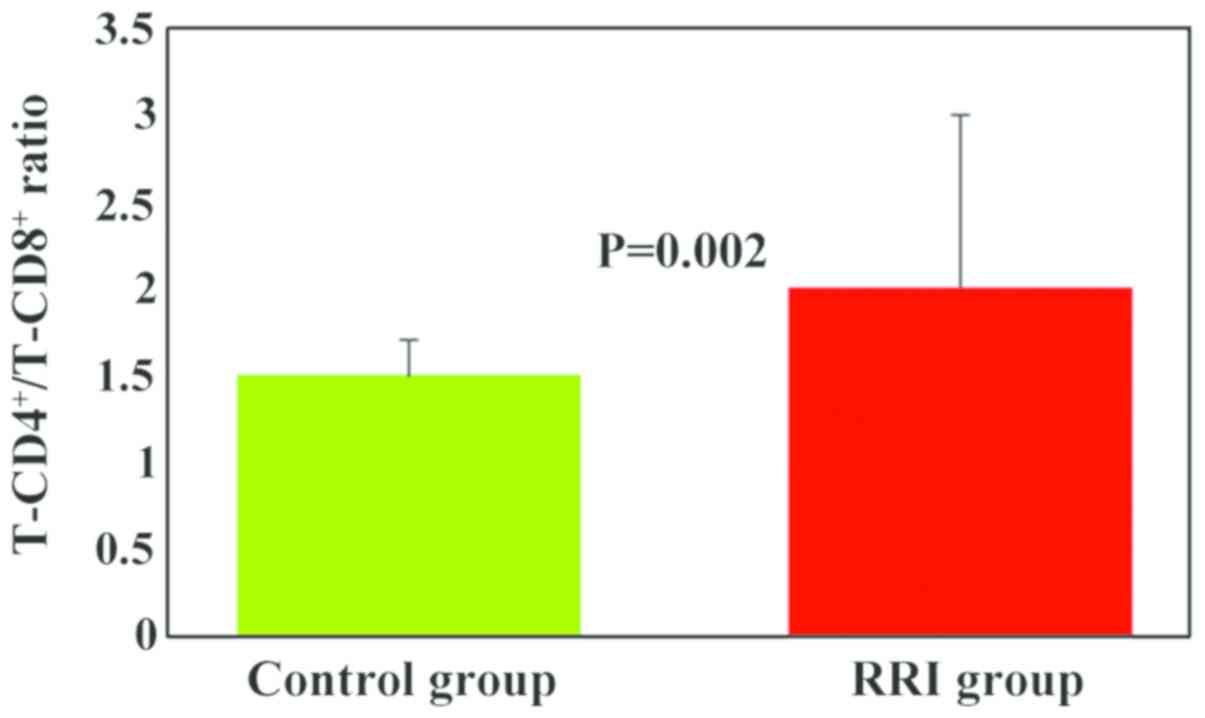
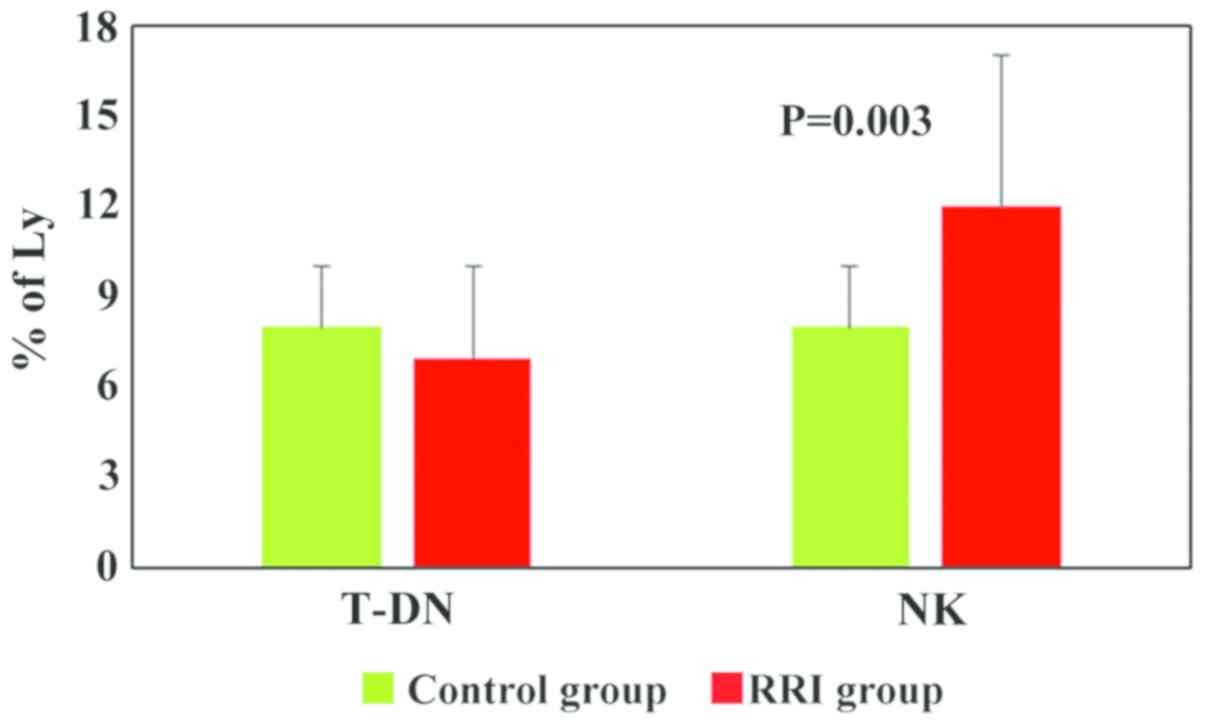
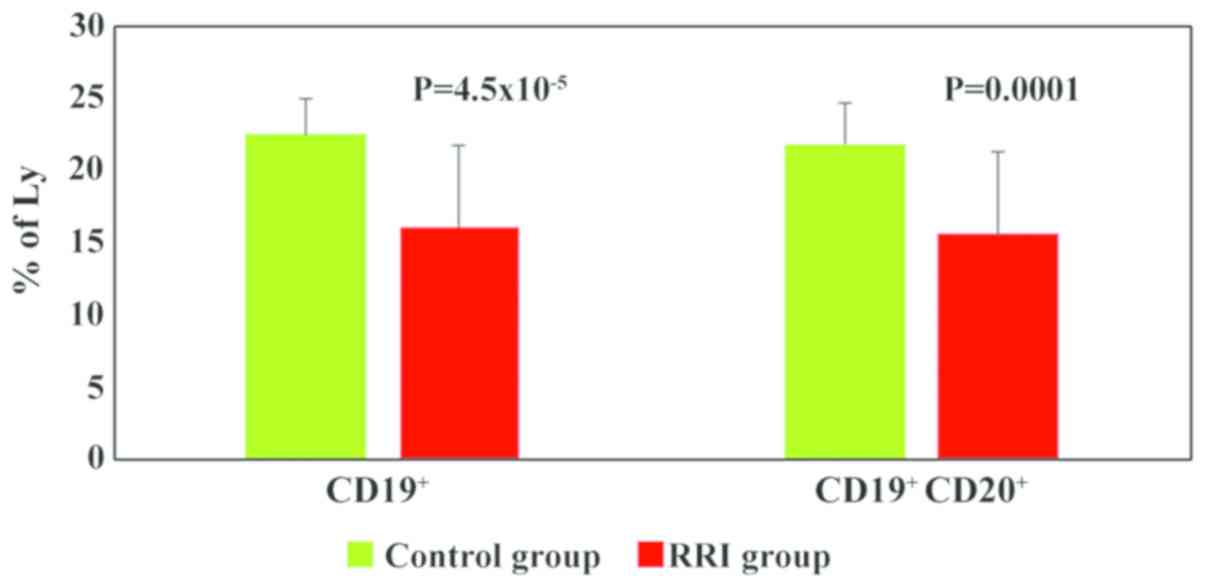
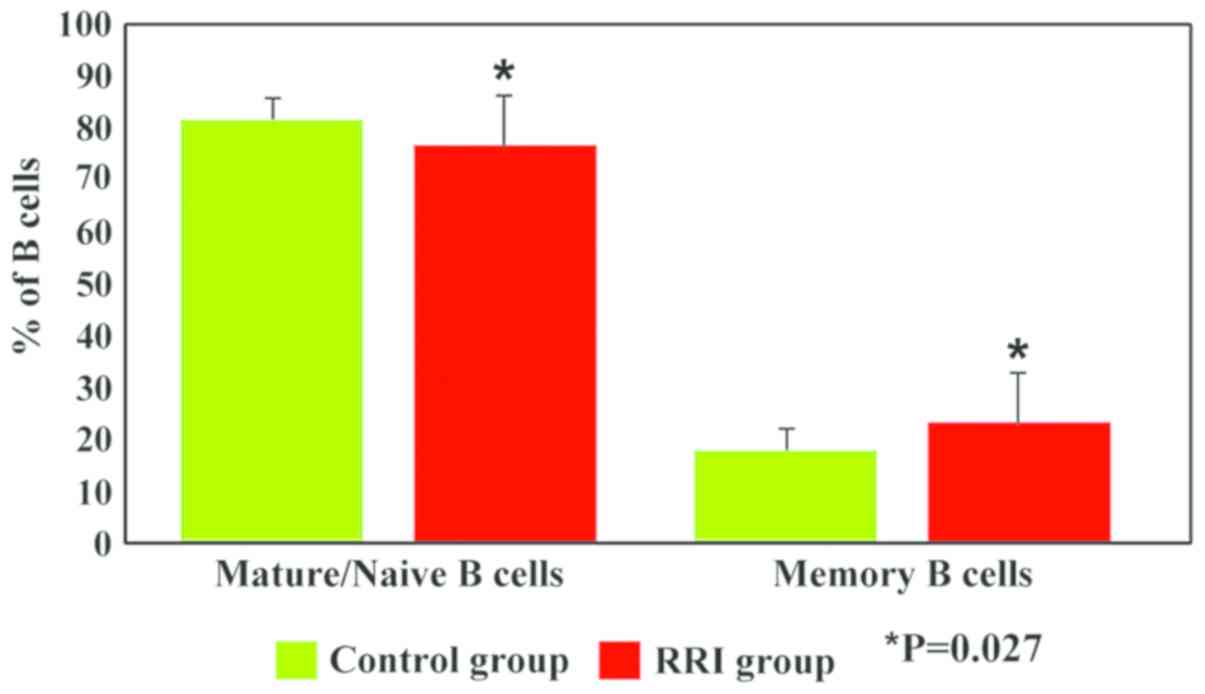
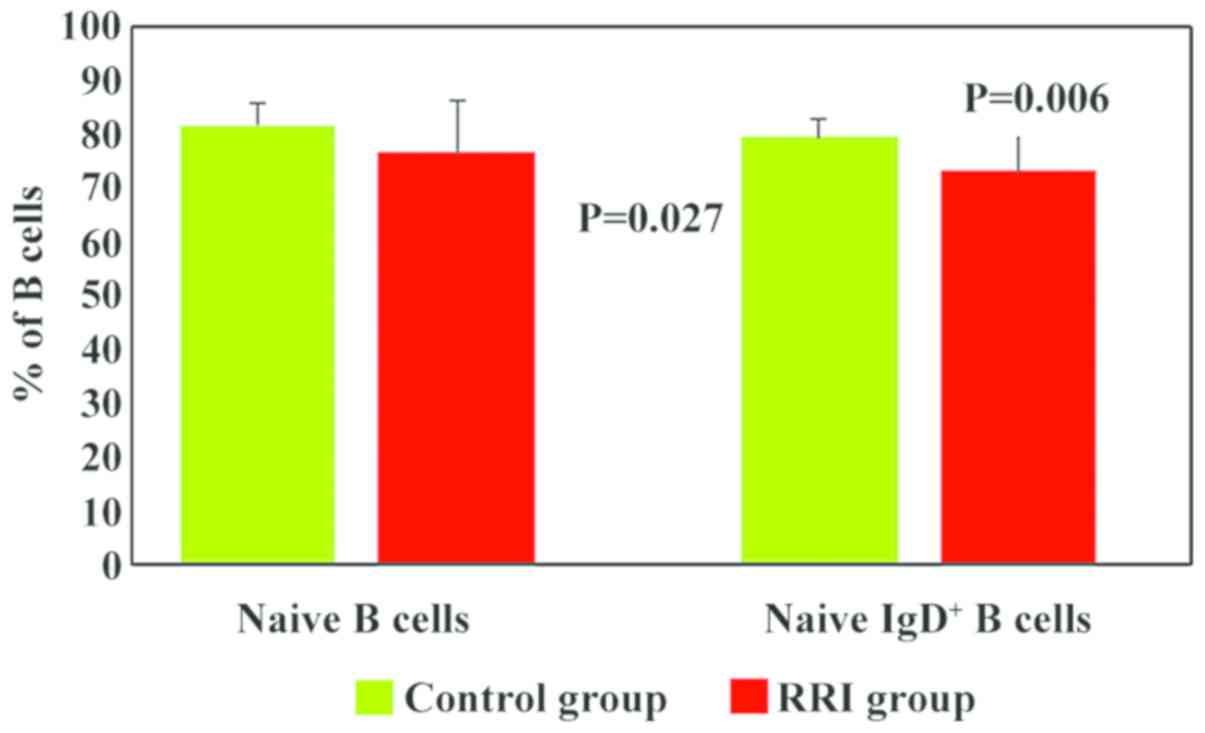
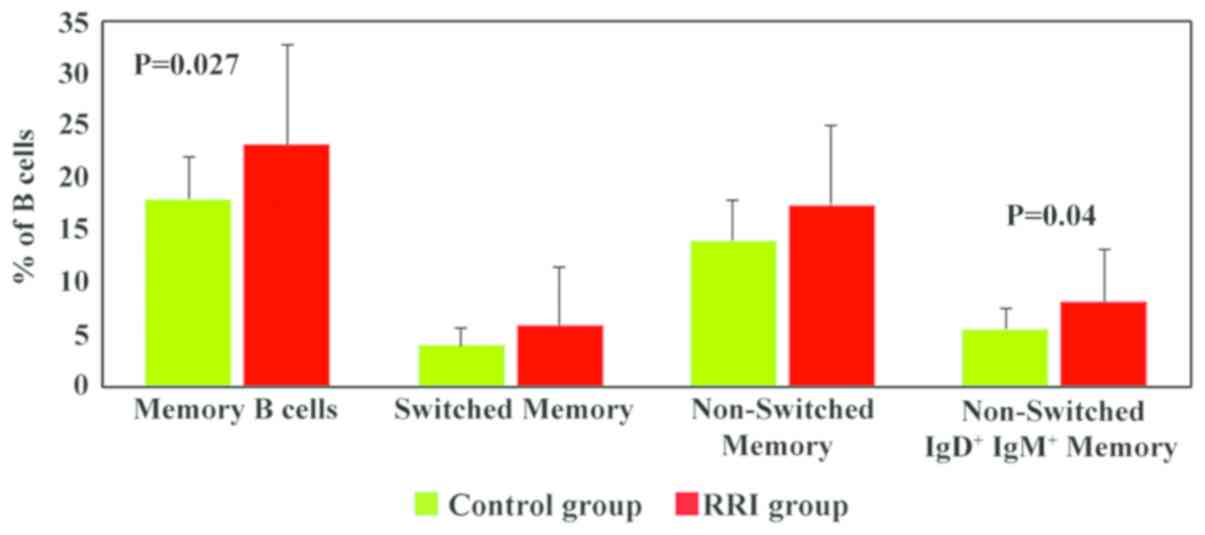
|
1
|
Gervassi AL and Horton H: Is infant
immunity actively suppressed or immature? Virology (Auckl).
2014:1–9. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maddux AB and Douglas IS: Is the
developmentally immature immune response in paediatric sepsis a
recapitulation of immune tolerance? Immunology. 145:1–10. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Feleszko W, Ruszczyński M and Zalewski BM:
Non-specific immune stimulation in respiratory tract infections.
Separating the wheat from the chaff. Paediatr Respir Rev.
15:200–206. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McCusker C and Warrington R: Primary
immunodeficiency. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 7 (Suppl 1):S112011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alkhater SA: Approach to the child with
recurrent infections. J Family Community Med. 16:77–82.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
El-Azami-El-Idrissi M, Lakhdar-Idrissi M,
Chaouki S, Atmani S, Bouharrou A and Hida M: Pediatric recurrent
respiratory tract infections: When and how to explore the immune
system? (About 53 cases). Pan Afr Med J. 24:532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mammas IN, Koutsaftiki C, Nika E, Vagia F,
Zaravinos A, Priftis KN, Voyatzi A, Theodoridou M, Myriokefalitakis
N and Spandidos DA: Detection of human metapneumovirus in infants
with acute respiratory tract infection. Mol Med Rep. 4:267–271.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee
on Environmental Health, . Environmental tobacco smoke: A hazard to
children. Pediatrics. 99:639–642. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grüber C, Keil T, Kulig M, Roll S, Wahn U
and Wahn V; MAS-90 Study Group, : History of respiratory infections
in the first 12 yr among children from a birth cohort. Pediatr
Allergy Immunol. 19:505–512. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Erkeller-Yuksel FM, Deneys V, Yuksel B,
Hannet I, Hulstaert F, Hamilton C, Mackinnon H, Stokes LT,
Munhyeshuli V, Vanlangendonck F, et al: Age-related changes in
human blood lymphocyte subpopulations. J Pediatr. 120:216–222.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Johnson JE, Gonzales RA, Olson SJ, Wright
PF and Graham BS: The histopathology of fatal untreated human
respiratory syncytial virus infection. Mod Pathol. 20:108–119.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hillhouse EE and Lesage S: A comprehensive
review of the phenotype and function of antigen-specific
immunoregulatory double negative T cells. J Autoimmun. 40:58–65.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sundaravaradan V, Mir KD and Sodora DL:
Double-negative T cells during HIV/SIV infections: Potential pinch
hitters in the T-cell lineup. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 7:164–171. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hassan MA, Eldin AME and Ahmed MM:
T-helper2 /T-helper1 imbalance in respiratory syncytial virus
bronchiolitis in relation to disease severity and outcome. Egypt J
Immunol. 15:153–160. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qin L, Peng D, Hu C, Xiang Y, Zhou Y, Tan
Y and Qin X: Differentiation of Th subsets inhibited by
nonstructural proteins of respiratory syncytial virus is mediated
by ubiquitination. PLoS One. 9:e1014692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dulek DE, Newcomb DC, Toki S, Goliniewska
K, Cephus J, Reiss S, Bates JT, Crowe JE Jr, Boyd KL, Moore ML, et
al: STAT4 deficiency fails to induce lung Th2 or Th17 immunity
following primary or secondary respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
challenge but enhances the lung RSV-specific CD8+ T cell immune
response to secondary challenge. J Virol. 88:9655–9672. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Legg JP, Hussain IR, Warner JA, Johnston
SL and Warner JO: Type 1 and type 2 cytokine imbalance in acute
respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 168:633–639. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pinto RA, Arredondo SM, Bono MR, Gaggero
AA and Díaz PV: T helper 1/T helper 2 cytokine imbalance in
respiratory syncytial virus infection is associated with increased
endogenous plasma cortisol. Pediatrics. 117:e878–e886. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
van Benten IJ, van Drunen CM, Koopman LP,
KleinJan A, van Middelkoop BC, de Waal L, Osterhaus AD, Neijens HJ
and Fokkens WJ: RSV-induced bronchiolitis but not upper respiratory
tract infection is accompanied by an increased nasal IL-18
response. J Med Virol. 71:290–297. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mangodt TC, Van Herck MA, Nullens S, Ramet
J, De Dooy JJ, Jorens PG and De Winter BY: The role of Th17 and
Treg responses in the pathogenesis of RSV infection. Pediatr Res.
78:483–491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bueno SM, González PA, Pacheco R, Leiva
ED, Cautivo KM, Tobar HE, Mora JE, Prado CE, Zúñiga JP, Jiménez J,
et al: Host immunity during RSV pathogenesis. Int Immunopharmacol.
8:1320–1329. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McNamara PS and Smyth RL: The pathogenesis
of respiratory syncytial virus disease in childhood. Br Med Bull.
61:13–28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hervás D, Reina J, Yañez A, del Valle JM,
Figuerola J and Hervás JA: Epidemiology of hospitalization for
acute bronchiolitis in children: Differences between RSV and
non-RSV bronchiolitis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis.
31:1975–1981. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mammas IN, Greenough A, Theodoridou M,
Kramvis A, Rusan M, Melidou A, Korovessi P, Papaioannou G,
Papatheodoropoulou A, Koutsaftiki C, et al: Paediatric Virology and
its interaction between basic science and clinical practice
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 41:1165–1176. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Munteanu A, Surcel M, Constantin C and
Neagu M: Respiratory infection with syncitial virus in children -
immunologicalhighlights. Rev Biol Biomed Sci. (In Press).
|