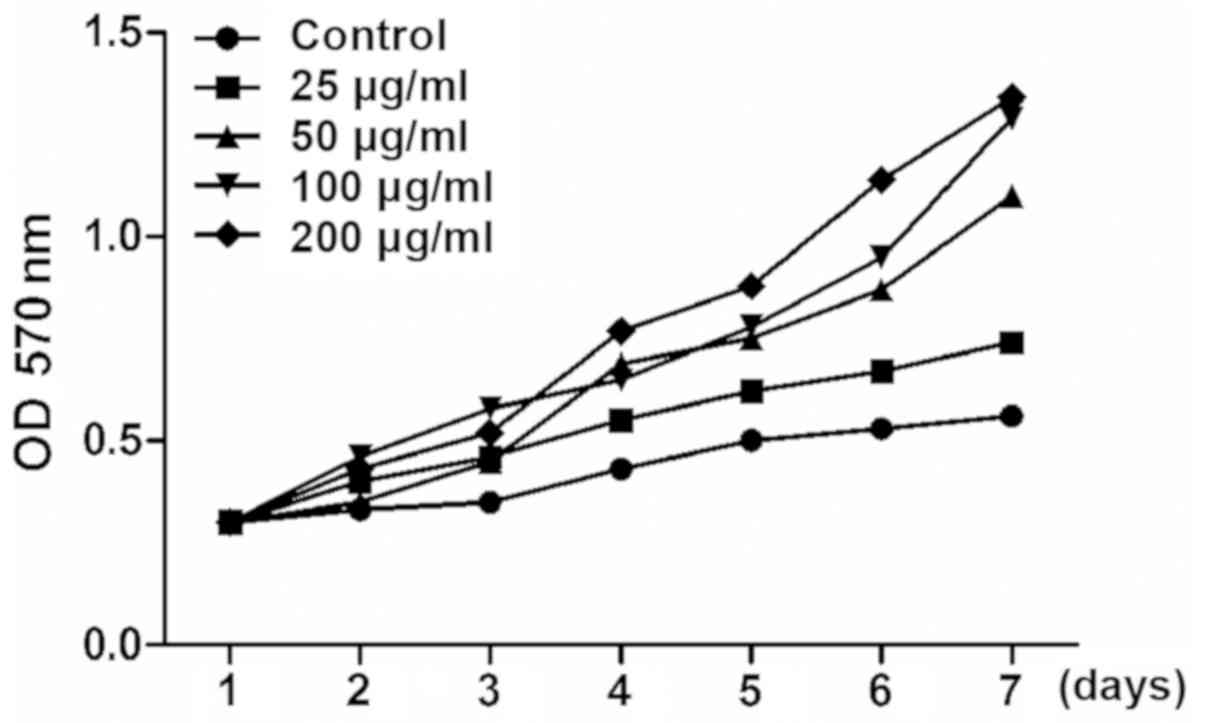
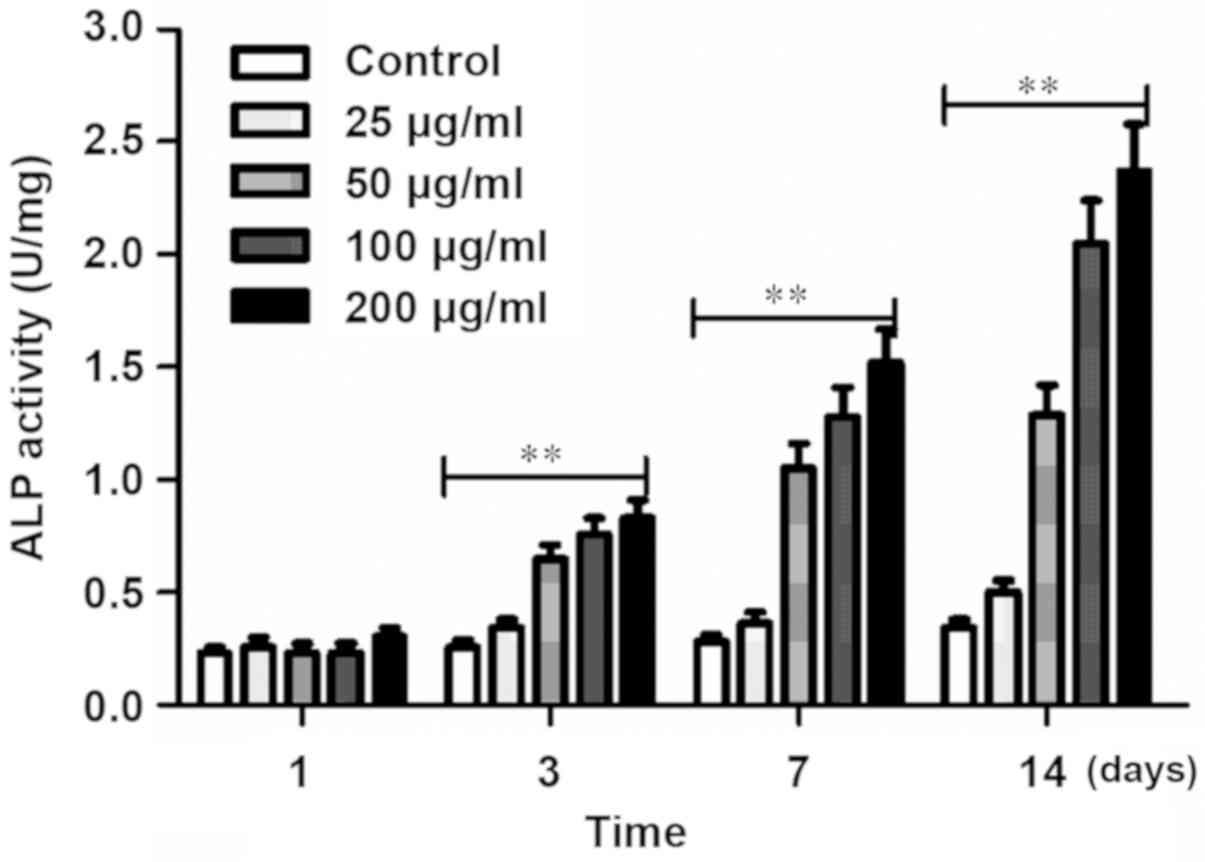
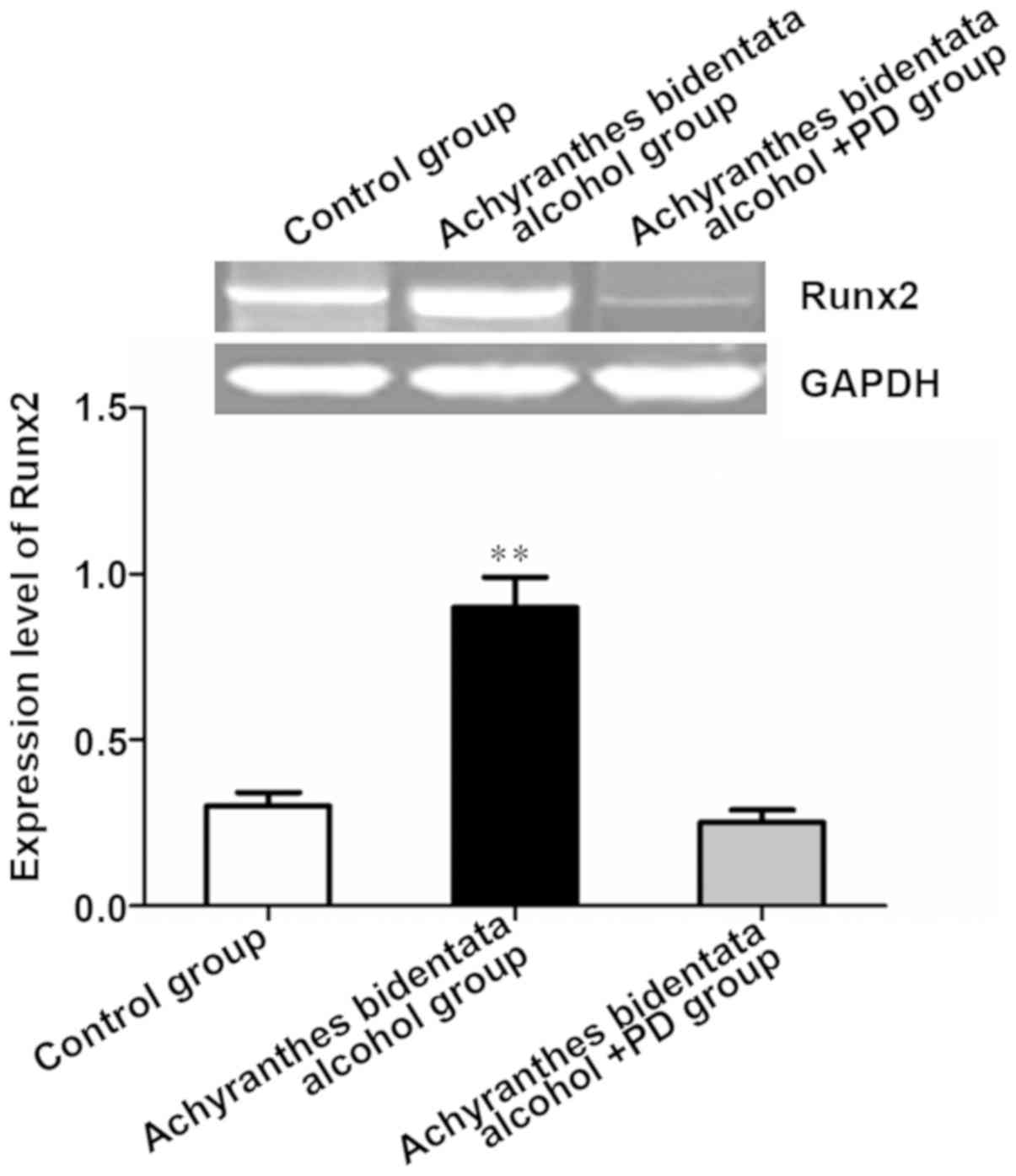
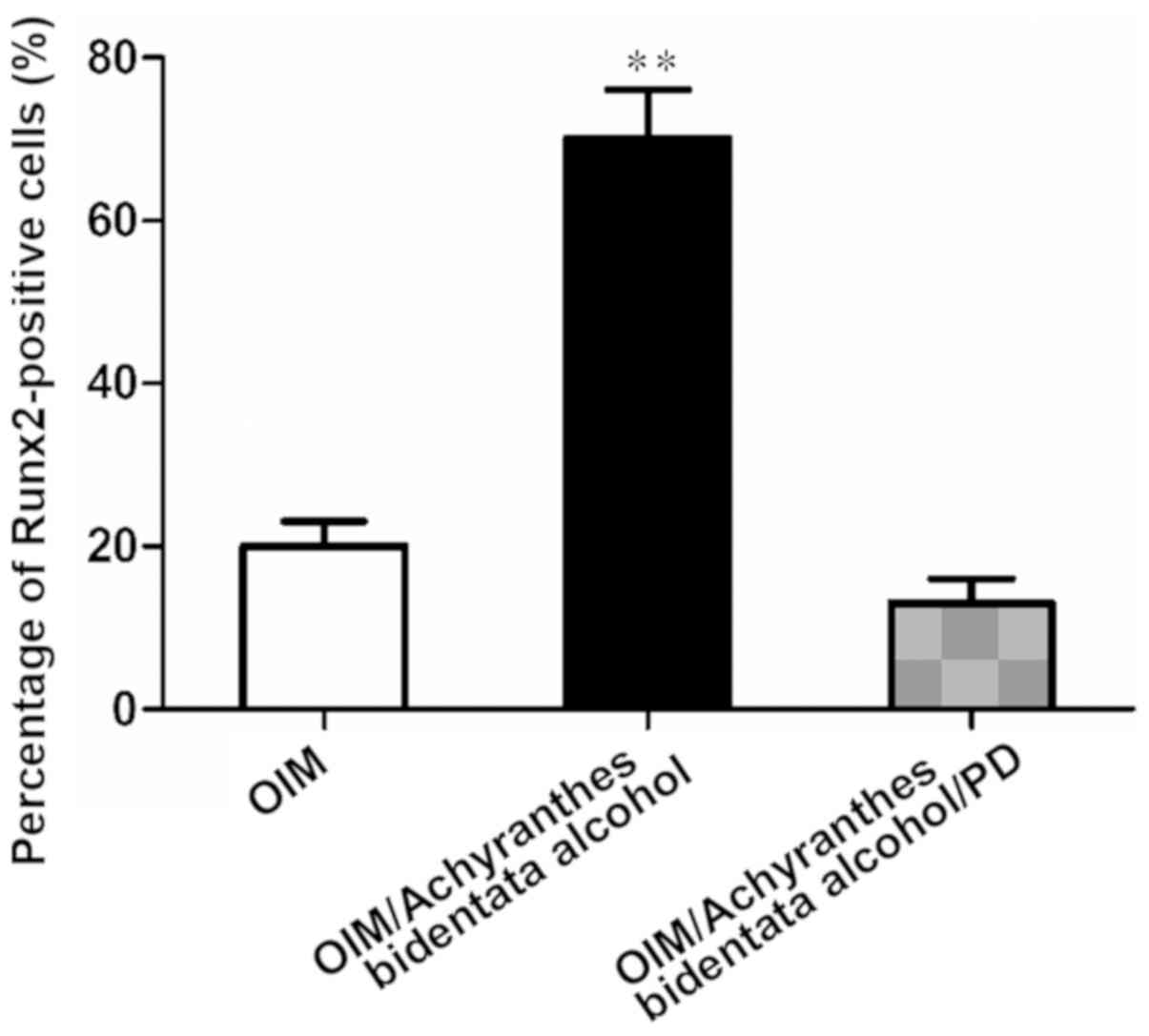
|
1
|
Niu Y, Li Y, Huang H, Kong X, Zhang R, Liu
L, Sun Y, Wang T and Mei Q: Asperosaponin VI, a saponin component
from Dipsacus asper wall, induces osteoblast differentiation
through bone morphogenetic protein-2/p38 and extracellular
signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Phytother Res. 25:1700–1706.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Licata AA: Discovery, clinical
development, and therapeutic uses of bisphosphonates. Ann
Pharmacother. 39:668–677. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang P, Dai KR, Yan SG, Yan WQ, Zhang C,
Chen DQ, Xu B and Xu ZW: Effects of naringin on the proliferation
and osteogenic differentiation of human bone mesenchymal stem cell.
Eur J Pharmacol. 607:1–5. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Berger I, Piecha G, Rabkin R, Kaya N,
Geldyyev A, Sun D, Chen Y, Koleganova N and Gross ML: Growth
hormone treatment prevents osteoporosis in uremic rats. Histol
Histopathol. 22:1231–1239. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lühe A, Künkele KP, Haiker M, Schad K,
Zihlmann C, Bauss F, Suter L and Pfister T: Preclinical evidence
for nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate inhibition of farnesyl
diphosphate (FPP) synthase in the kidney: Implications for renal
safety. Toxicol In Vitro. 22:899–909. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deng HB, Cui DP, Jiang JM, Feng YC, Cai NS
and Li DD: Inhibiting effects of Achyranthes bidentata
polysaccharide and Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on
nonenzyme glycation in D-galactose induced mouse aging model.
Biomed Environ Sci. 16:267–275. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen H, Yuan Y, Ding F, Liu J and Gu X:
The protective effects of Achyranthes bidentata polypeptides
against NMDA-induced cell apoptosis in cultured hippocampal neurons
through differential modulation of NR2A- and NR2B-containing NMDA
receptors. Brain Res Bull. 77:274–281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jin LQ, Zheng ZJ, Peng Y, Li WX, Chen XM
and Lu JX: Opposite effects on tumor growth depending on dose of
Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides in C57BL/6 mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 7:568–577. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li JX, Hareyama T, Tezuka Y, Zhang Y,
Miyahara T and Kadota S: Five new oleanolic acid glycosides from
Achyranthes bidentata with inhibitory activity on osteoclast
formation. Planta Med. 71:673–679. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wattel A, Kamel S, Prouillet C, Petit JP,
Lorget F, Offord E and Brazier M: Flavonoid quercetin decreases
osteoclastic differentiation induced by RANKL via a mechanism
involving NF kappa B and AP-1. J Cell Biochem. 92:285–295. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shibeshi W, Makonnen E, Zerihun L and
Debella A: Effect of Achyranthes aspera L. on fetal
abortion, uterine and pituitary weights, serum lipids and hormones.
Afr Health Sci. 6:108–112. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen XM, Xu YJ and Tian GY:
Physical-chemical properties and structure elucidation of abPS
isolated from the root of Achyranthes bidentata. Yao Xue Xue
Bao. 40:32–35. 2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han SB, Lee CW, Yoon YD, Lee JH, Kang JS,
Lee KH, Yoon WK, Lee K, Park SK and Kim HM: Prevention of arthritic
inflammation using an oriental herbal combination BDX-1 isolated
from Achyranthes bidentata and Atractylodes japonica.
Arch Pharm Res. 28:902–908. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou ZD and Xia DJ: Effect of
Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides stimulated dendritic
cells co-cultured with cytokine induced killer cells against SW480
cells. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 38:1056–1060. 2013.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang M, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Wang C, Zhang D,
Wan JB and Yan C: UPLC/Q-TOF-MS-based metabolomics study of the
anti-osteoporosis effects of Achyranthes bidentata
polysaccharides in ovariectomized rats. Int J Biol Macromol.
112:433–441. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang R, Hu SJ, Li C, Zhang F, Gan HQ and
Mei QB: Achyranthes bidentata root extract prevent
OVX-induced osteoporosis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 139:12–18.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu
BE, Karandikar M, Berman K and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated protein
(MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions.
Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jaiswal RK, Jaiswal N, Bruder SP,
Mbalaviele G, Marshak DR and Pittenger MF: Adult human mesenchymal
stem cell differentiation to the osteogenic or adipogenic lineage
is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem.
275:9645–9652. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sale EM, Atkinson PG and Sale GJ:
Requirement of MAP kinase for differentiation of fibroblasts to
adipocytes, for insulin activation of p90 S6 kinase and for insulin
or serum stimulation of DNA synthesis. EMBO J. 14:674–684. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alanay Y, Avaygan H, Camacho N, Utine GE,
Boduroglu K, Aktas D, Alikasifoglu M, Tuncbilek E, Orhan D, Bakar
FT, et al: Mutations in the gene encoding the RER protein FKBP65
cause autosomal-recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. Am J Hum Genet.
86:551–559. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei J, Shimazu J, Makinistoglu MP, Maurizi
A, Kajimura D, Zong H, Takarada T, Lezaki T, Pessin JE, Hinoi E, et
al: Glucose uptake and Runx2 synergize to orchestrate osteoblast
differentiation and bone formation. Cell. 161:1576–1591. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nishio Y, Dong Y, Paris M, O'Keefe RJ,
Schwarz EM and Drissi H: Runx2-mediated regulation of the zinc
finger Osterix/Sp7 gene. Gene. 372:62–70. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, Yamaguchi A,
Sasaki K, Deguchi K, Shimizu Y, Bronson RT, Gao YH, Inada M, et al:
Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone
formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell.
89:755–764. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, Zhang Z,
Deng JM, Behringer RR and de Crombrugghe B: The novel zinc
finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for
osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell. 108:17–29.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee MH, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Park HD, Kang AR,
Kyung HM, Sung JH, Wozney JM, Kim HJ and Ryoo HM: BMP-2-induced
Runx2 expression is mediated by Dlx5, and TGF-beta 1 opposes the
BMP-2-induced osteoblast differentiation by suppression of Dlx5
expression. J Biol Chem. 278:34387–34394. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Turjanski AG, Vaqué JP and Gutkind JS: MAP
kinases and the control of nuclear events. Oncogene. 26:3240–3253.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|