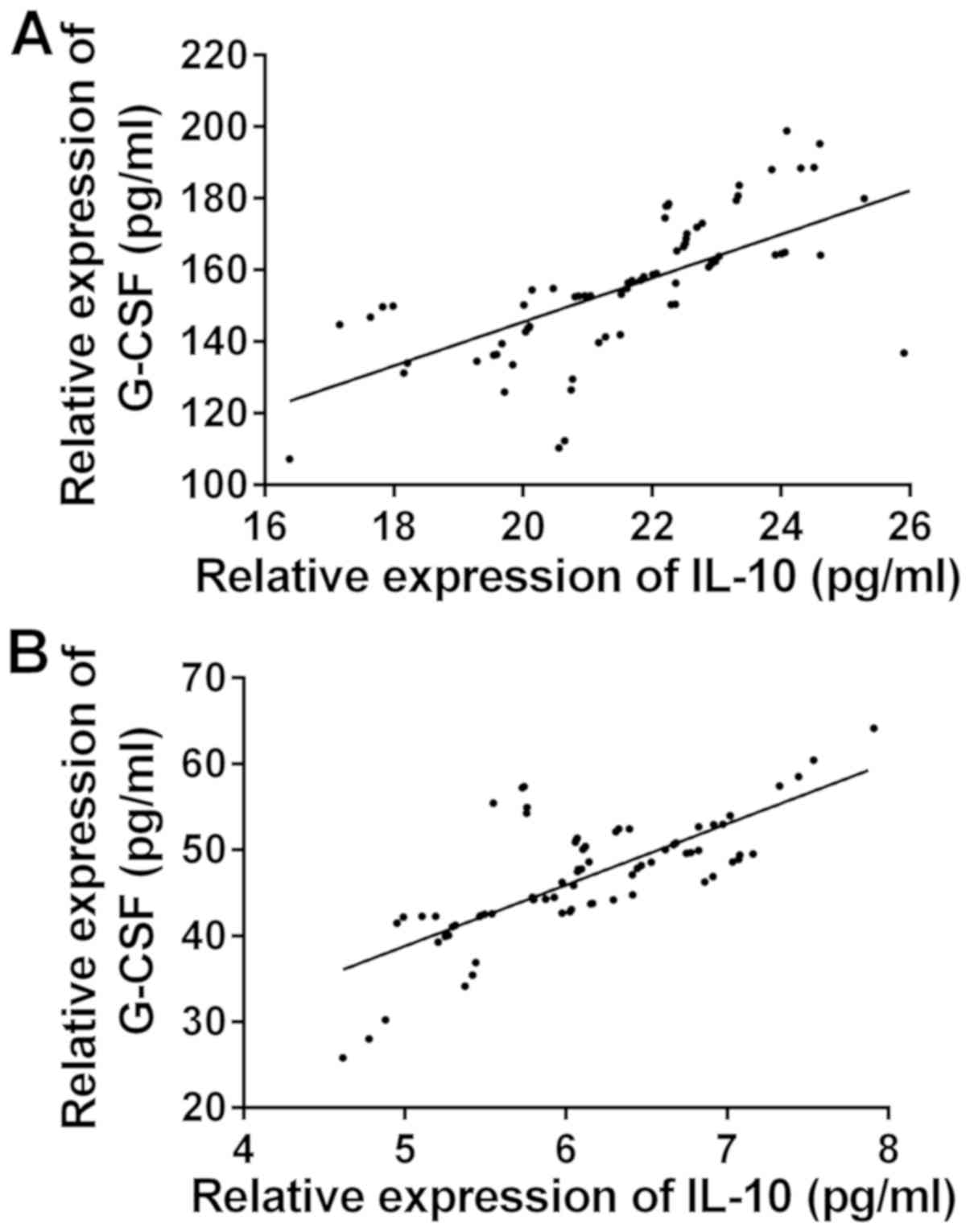
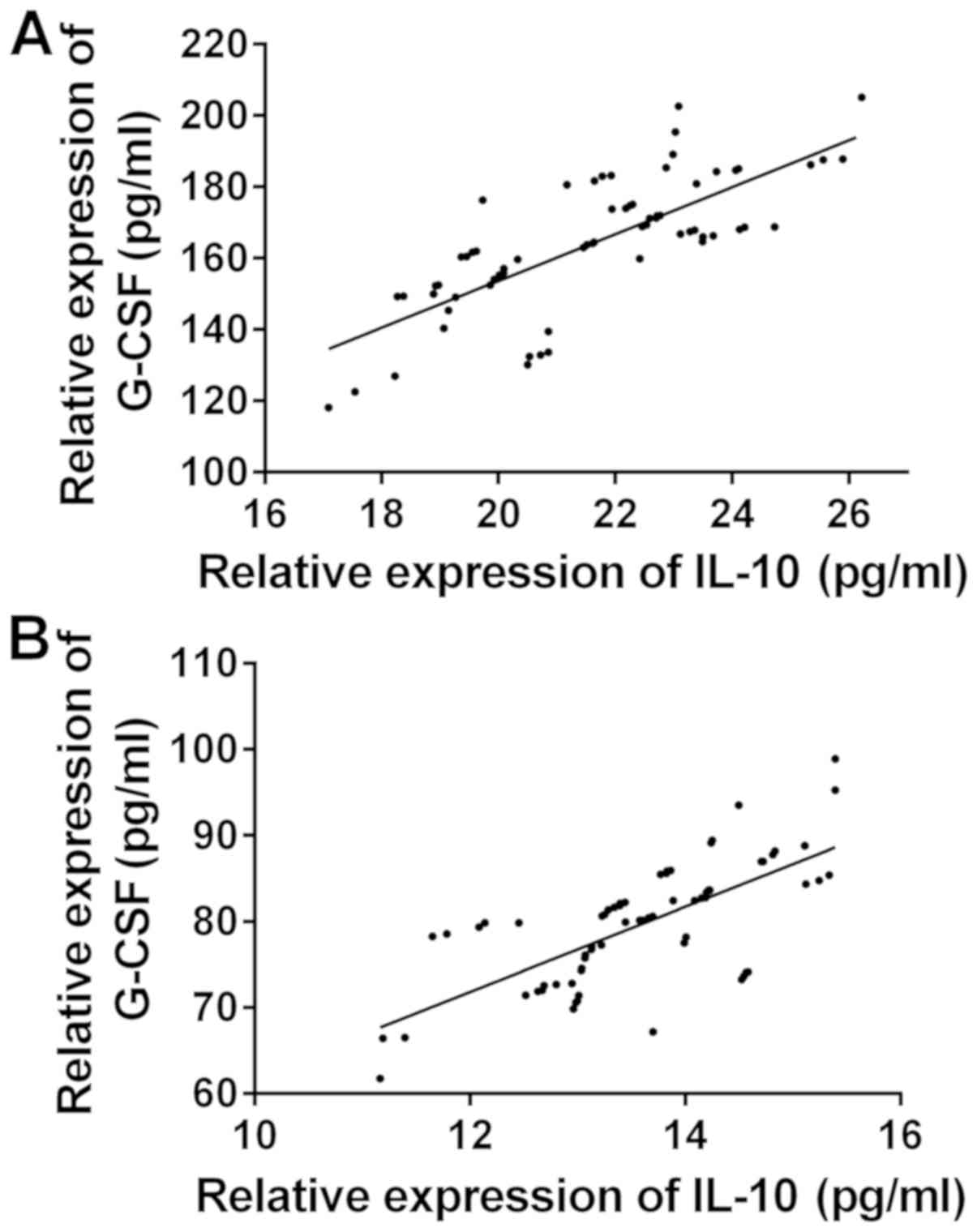
|
1
|
Gong L, Zhang C-L and Zhen Q: Analysis of
clinical value of CT in the diagnosis of pediatric pneumonia and
mycoplasma pneumonia. Exp Ther Med. 11:1271–1274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Waites KB and Talkington DF: Mycoplasma
pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 17:697–728. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang L: Comparison of the effect of
erythromycin combined with azithromycin sequential therapy and
azithromycin in treatment of mycoplasma pneumonia in children.
China Med Her. 13:173–176. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Bajantri B, Toolsie O, Venkatram S and
Diaz-Fuentes G: Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia: Walking
pneumonia can cripple the susceptible. J Clin Med Res. 10:891–897.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bajantri B, Venkatram S and Diaz-Fuentes
G: Mycoplasma pneumoniae: A potentially severe infection. J
Clin Med Res. 10:535–544. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim JH, Kwon JH, Lee JY, Lee JS, Ryu JM,
Kim SH, Lim KS and Kim WY: Clinical features of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae coinfection and need for its testing in influenza
pneumonia patients. J Thorac Dis. 10:6118–6127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jin X, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Chen J, Rong L and
Zhao X: Assessment of levels of D-dimer and interferon-γ in
pediatric patients with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia and
its clinical implication. Exp Ther Med. 16:5025–5030.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mathur S, Fuchs A, Bielicki J, Van Den
Anker J and Sharland M: Antibiotic use for community-acquired
pneumonia in neonates and children: WHO evidence review. Paediatr
Int Child Health. 38 (Suppl 1):S66–S75. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saraiva M and O'Garra A: The regulation of
IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:170–181.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Medjo B, Atanaskovic-Markovic M, Nikolic
D, Radic S, Lazarevic I, Cirkovic I and Djukic S: Increased serum
interleukin-10 but not interleukin-4 level in children with
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. J Trop Pediatr. 63:294–300.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Akashi Y, Hayashi D, Suzuki H, Shiigai M,
Kanemoto K, Notake S, Ishiodori T, Ishikawa H and Imai H: Clinical
features and seasonal variations in the prevalence of
macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Gen Fam Med.
19:191–197. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mehta HM, Malandra M and Corey SJ: G-CSF
and GM-CSF in neutropenia. J Immunol. 195:1341–1349. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liongue C and Ward AC: Granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor receptor mutations in myeloid malignancy.
Front Oncol. 4:932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dutow P, Lingner S, Laudeley R, Glage S,
Hoymann HG, Dittrich AM, Fehlhaber B, Müller M, Braun A and Klos A:
Severity of allergic airway disease due to house dust mite allergen
is not increased after clinical recovery of lung infection with
Chlamydia pneumoniae in mice. Infect Immun. 81:3366–3374. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hall MW, Geyer SM, Guo CY,
Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Jouvet P, Ferdinands J, Shay DK, Nateri J,
Greathouse K, Sullivan R, et al Pediatric Acute Lung Injury, Sepsis
Investigators (PALISI) Network PICFlu Study Investigators, : Innate
immune function and mortality in critically ill children with
influenza: A multicenter study. Crit Care Med. 41:224–236. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Trikha P and Carson WE III: Signaling
pathways involved in MDSC regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1846:55–65. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liang H, Liu Y and Mo L: Clinical study of
using additives qianjin weijing decoction in treating children with
phlegm and blood stasis mutual junction type mycoplasma pneumonia.
J Sichuan Trad Med. 7:81–83. 2017.
|
|
18
|
Fleming-Dutra KE, Demirjian A, Bartoces M,
Roberts RM, Taylor TH Jr and Hicks LA: Variations in antibiotic and
azithromycin prescribing for children by geography and
specialty-United States, 2013. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 37:52–58.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He HX and Zhang XQ: Clinical observation
on self-made yiqi xiaozhi decoction and azithromycin in the
sequential treatment of mycoplasma pneumonia in children. J Sichuan
Trad Med. 7:43–46. 2018.
|
|
20
|
Li W, Zhang X, Chen Y, Xie Y, Liu J, Feng
Q, Wang Y, Yuan W and Ma J: G-CSF is a key modulator of MDSC and
could be a potential therapeutic target in colitis-associated
colorectal cancers. Protein Cell. 7:130–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Salvatore CM, Techasaensiri C, Tagliabue
C, Katz K, Leos N, Gomez AM, McCracken GH and Hardy RD: Tigecycline
therapy significantly reduces the concentrations of inflammatory
pulmonary cytokines and chemokines in a murine model of
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 53:1546–1551. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Taher TE, Bystrom J, Ong VH, Isenberg DA,
Renaudineau Y, Abraham DJ and Mageed RA: Intracellular B lymphocyte
signalling and the regulation of humoral immunity and autoimmunity.
Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 53:237–264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mavropoulos A, Varna A, Zafiriou E,
Liaskos C, Alexiou I, Roussaki-Schulze A, Vlychou M, Katsiari C,
Bogdanos DP and Sakkas LI: IL-10 producing Bregs are impaired in
psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis and inversely correlate with
IL-17- and IFNγ-producing T cells. Clin Immunol. 184:33–41. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morris KT, Castillo EF, Ray AL, Weston LL,
Nofchissey RA, Hanson JA, Samedi VG, Pinchuk IV, Hudson LG and
Beswick EJ: Anti-G-CSF treatment induces protective tumor immunity
in mouse colon cancer by promoting protective NK cell, macrophage
and T cell responses. Oncotarget. 6:22338–22347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Z, You X, Peng Z, Zhang H, Gao S, Zeng
Y, Yu M and Zhu C: Mycoplasma pneumoniae capsular
polysaccharides bind to DC-SIGN and promote the secretion of IL-10.
Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 29:10–13. 2013.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang X, Ma X, An H, Xu C, Cao W, Yuan W
and Ma J: Upregulation of microRNA-125b by G-CSF promotes
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 8:50642–50654.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guilbert TW and Denlinger LC: Role of
infection in the development and exacerbation of asthma. Expert Rev
Respir Med. 4:71–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morris KT, Khan H, Ahmad A, Weston LL,
Nofchissey RA, Pinchuk IV and Beswick EJ: G-CSF and G-CSFR are
highly expressed in human gastric and colon cancers and promote
carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Br J Cancer.
110:1211–1220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takahashi H, Kimura T, Yuki N and Yoshioka
A: An adult case of recurrent Guillain-Barré syndrome with
anti-galactocerebroside antibodies. Intern Med. 57:409–412. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chakraborty A, White SM and Guha S:
Granulocyte colony-stimulating receptor promotes
beta1-integrin-mediated adhesion and invasion of bladder cancer
cells. Urology. 68:208–213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He J, Liu M, Ye Z, Tan T, Liu X, You X,
Zeng Y and Wu Y: Insights into the pathogenesis of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae (Review). Mol Med Rep. 14:4030–4036. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao JL, Wang X and Wang YS: Relationships
between Th1/Th2 cytokine profiles and chest radiographic
manifestations in childhood Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.
Ther Clin Risk Manag. 12:1683–1692. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Waites KB, Xiao L, Liu Y, Balish MF and
Atkinson TP: Mycoplasma pneumoniae from the respiratory
tract and beyond. Clin Microbiol Rev. 30:747–809. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jeong YC, Yeo MS, Kim JH, Lee HB and Oh
JW: Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection affects the serum levels
of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-5 in atopic
children. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 4:92–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun J, Xiao Y, Zhang M, Ao T, Lang S and
Wang J: Serum inflammatory markers in patients with adenovirus
respiratory infection. Med Sci Monit. 24:3848–3855. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lei WT, Lin HH, Tsai MC, Hung HH, Cheng
YJ, Liu SJ, Lin CY and Yeh TL: The effects of macrolides in
children with reactive airway disease: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Drug Des Devel Ther.
12:3825–3845. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hakansson AP, Orihuela CJ and Bogaert D:
Bacterial-host interactions: Physiology and pathophysiology of
respiratory infection. Physiol Rev. 98:781–811. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|